Biomechanics of Braces
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
force / area =
pressure (⬆ Contact Area = ⬇ Pressure)
Force (F) x Distance (d) =
torque (moment)
the ground reaction force is equal and opposite to
the acceleration of COM
Distance between line of gravity and axis of rotation of a segment will cause
a rotational movement
In which case does COM ≠ Axis of Rotation?
??
With AFOs we focus on the Torques during gait at the
ankle
Poor control during IC example due to weakness, spasticity, paralysis ect can result in
knee buckling or hyperextension
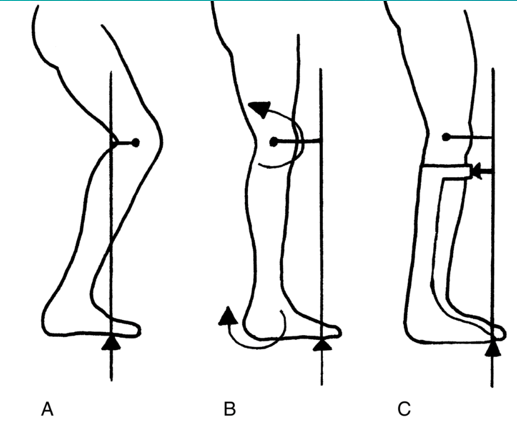
what kind of gait pattern is A?
crouched gait
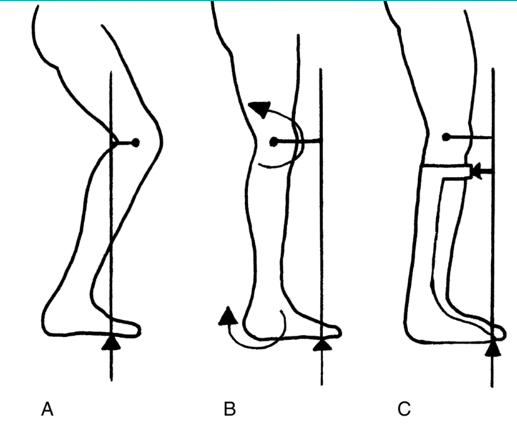
what kind of gait pattern is B?
normal gait
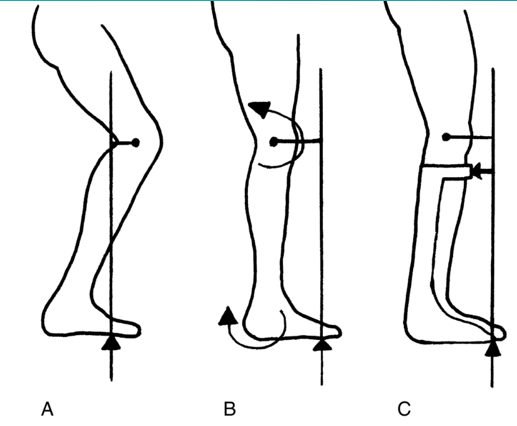
what kind of gait correction is C?
solid AFO
if someones knee is buckling the AFO shank angle should be?
reclined
if someones knee is hyperextending the AFO shank angle should be?
inclined
what is it called when 2 forces are = in magnitude, opposite in direction, parallel, & applied to the same object at different points?
force couple
Force couple acting at some distance from each other on the same object will always produce
a moment of force, or torque
what is the product of the magnitude (force) of 1 of the forces in force couple?
torque
what is the shortest perpendicular distance between the forces ?
moment arm
the sum of the forces equaling 0 (perfect equilibrium) will be a
stable system
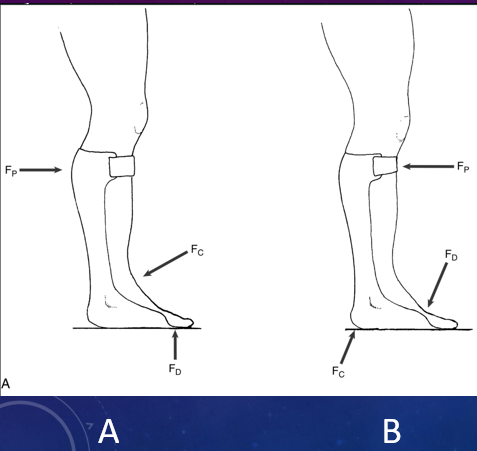
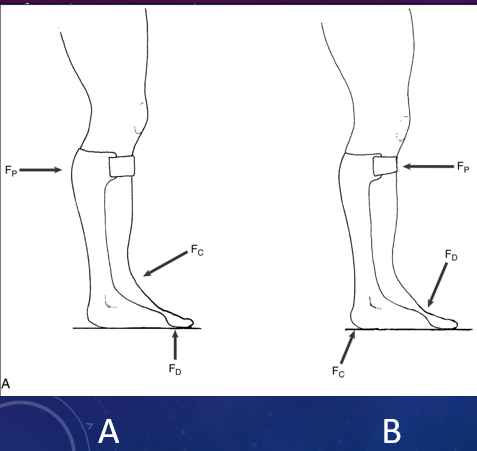
Which of these shows PF is controlled during swing phase by a proximal force (FP) at posterior calf band & a distal force at metatarsal heads (FD) that counter a centrally located stabilizing force (FC) applied at the ankle by shoe closure?
A
Which of these shows for control of DF during stance phase (forward progression of tibia over foot), Fp is applied at the proximal tibia by the anterior closure, Fd at the ventral metatarsal heads by toe box of shoe, & counterforce Fc at heel, snugly fit in the orthosis?
B
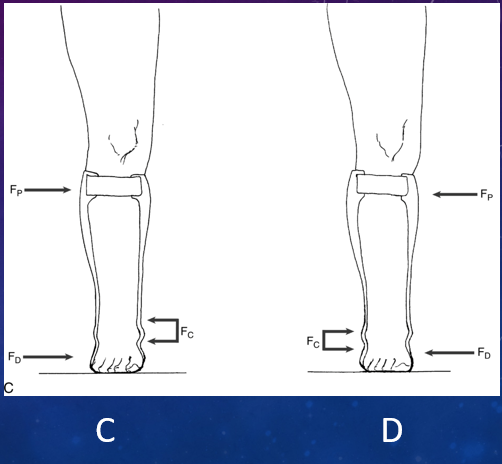
Which of these shows that the force system for eversion (valgus) locates Fd along 5th metatarsal, Fp at proximal lateral calf band, & Fc on either side of malleolus?
C
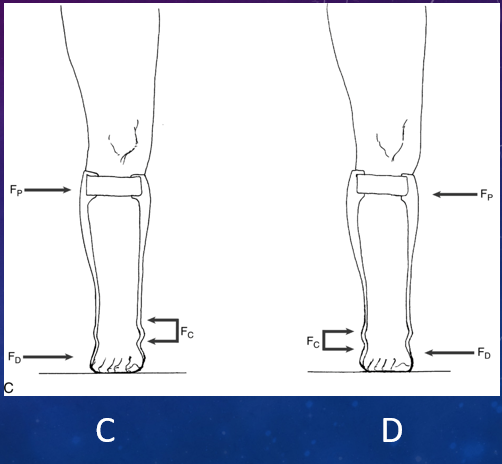
Which of these shows that to control inversion (varus) of foot & ankle, Fd is applied by distal medial wall of orthosis against 1st metatarsal, Fp at the proximal medial calf band, & Fc at distal lateral tibia & calcaneus/talus on either side of lateral malleolus?
D
goal for Foot Orthoses (FO)
Relieve Pain (weight transfer) = Enhance function
Improve COP transition during stance
how does a foot orthoses work?
Transferring WBing stress to pressure-tolerant sites
Protect painful areas from shoe contact
Correct non-fixed alignments
Accommodate fixed deformity
Accommodate leg length discrepancy or foot length issues
what are different types of FO?
Internal modification: Inside the shoe (insert)
External modification: Attached outside on sole or heel
for a FO, The closer to the foot (more direct contact) the….
more effective
how does a wearer of a higher heel compensate?
either by retaining slight knee & hip flexion or by extending knee & exaggerating lumbar lordosis
a high heel transmits more stress to the
metatarsals and knee
A heel raise is used for transferring load anteriorly if pt has
heel pain (spur)
The higher heel also reduces tension on the
Achilles tendon & other posterior structures
higher heel can accommodate a
rigid pes equinus
what type of orthotic can help with arch support?
scaphoid pad
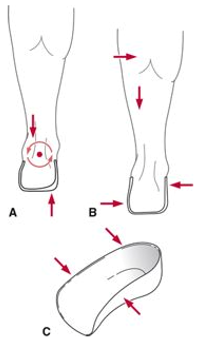
what is the action of the UCBL Foot Orthosis – Subtalar joint in A?
controls calcaneal eversion
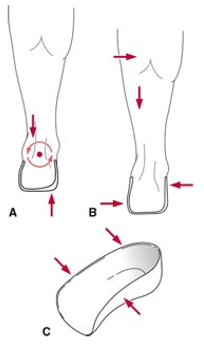
what type of UCBL Foot Orthosis – Subtalar joint is B?
second counterforce system
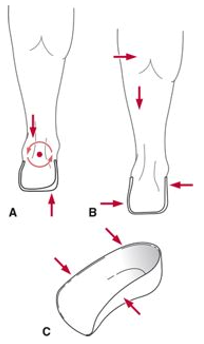
what does the UCBL Foot Orthosis – Subtalar joint do in C?
restrict foreftoot abduction
What is a convex component that may be incorporated in an insert or may be a resilient domed piece glued to the inner sole so that its apex is under the metatarsal shafts?
metatarsal relief pad
Metatarsal relief pad transfers stress from metatarsal heads to the metatarsal shafts & is effective in reducing
plantar pressure particularly in patients w/ diabetic neuropathy
a medial heel wedge, by applying laterally directed force, can aid in realigning
flexible pes valgus

a medial heel wedge can accommodate ____ by filling the void between sole & floor on the medial side
rigid pes valgus or can accommodate rigid pes varus
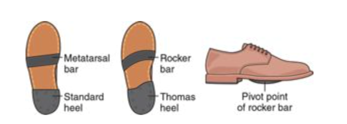
during which gait phase does a metatarsal bar transfer stress from the MTP joints to the metatarsal shafts?
At late stance
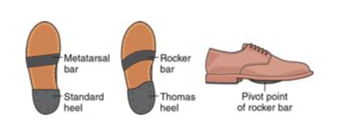
A rocker bar reduces distance wearer must travel during _____ by shifting load from MTP joints to metatarsal shafts?
stance phase and improves late stance