Physics 2 Weaker concepts
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
10 Terms
What is the critical angle
Derive it:
Incidence angle that leads to angle of refraction = 90o. Plug 90o into Snell’s law.
Only occurs in slow to fast media.
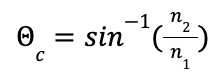
Minima and maxima for a double slit diffraction
d = distance between slits
theta = angle of diffraction
m = order of interference

Minima and maxima for a single slit diffraction
a = slit width

diffraction grating
maxima of a double slit grating

Sign Conventions for optics
s - distance from mirror

f focal length
focal point times 2 is radius of curvature
where all rays seem to converge/diverge from. When drawing the diagram, rays pass through here.
Concave v. convex
Concave - image is real, and focal point in front of mirror. Real rays converge at the focal point
Convex - image is virtual, and focal point behind the mirror. Real rays diverge from the focal point, but can be traced back to form virtual rays

Loop vs. Junction rule
Current in and out of junction is same
Voltage in and out of a loop is same
Photons
Basically light that can get absorbed and emitted from electrons. Photons are PARTICLES, light is both. Photons have light quality’s
Lens’s
Imagine as a mirror. If it would diverge (a converging lense)
what gets traced back is the path light takes.