Part 4 PRC Lua - Hema Terminologies
1/106
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
107 Terms
Chromosome 16
There are two copies of the hemoglobin alpha gene, HBA1 and HBA2, both located on _____________, and each encodes an α-globin chain.
HMP Shunt
This shunt involves the enzyme (G6PD). A deficiency in this pathway impairs the production of NADPH, leading to oxidative damage and denaturation of hemoglobin, which manifests as Heinz bodies in RBCs.
HSCs
This cells possess the capacity for self-renewal through asymmetric cell division
≥20%
The WHO classifies AML when ____of bone marrow cells are
blasts;
≥30%
the FAB requires ___
Diagnostic Flow Cytometry
The gold standard for diagnosing PNH
Common pathway
Both the intrinsic and extrinsic pathways converge into the __________, culminating in the conversion of prothrombin to
thrombin.
37°C
Prothrombin Time (PT) is performed at
Hemolysis
The sucrose hemolysis test (also called the sugar water test) is a screening test for (PNH); a positive result is indicated by
Karyotyping
The process of arranging and analyzing an individual's chromosomes, providing a genome-wide overview for detecting chromosomal abnormalities
Sphingomyelin
Niemann-Pick disease primarily affects mononuclear and phagocytic cells, due to the accumulation of
Ham test (acidified serum lysis test)
A definitive diagnostic test for PNH, where red blood cells lyse in acidified serum but remain intact in heat-inactivated serum
56°C for 20 minutes
complement is inactivated at
11.5% - 14.5%
Normal value of RDW in adults
vitamin B12 or folate deficiency, macrocytic anemia, or chronic liver disease.
A high RDW with high MCV is suggestive of:
iron deficiency anemia or other forms of microcytic anemia
A high RDW with low MCV typically indicates
Phloxine
A stain used to identify white blood cells (WBCs)
New methylene blue (NMB) and Brilliant cresyl blue (BCB)
used to stain reticulocytes
Acute leukemia
characterized by a short clinical course and a high number of
immature leukocyte forms in the peripheral blood
Sigmoidal oxygen dissociation curve
Hemoglobin exhibits cooperative binding, showing low affinity for oxygen at low oxygen tension and high affinity at high tension, resulting in a _________
Protein S
_________ may exert anticoagulant effects independent of activated protein C by directly inhibiting factor VIIIa in the tenase complex and factors Va and Xa in the prothrombinase complex.
Deletion
A chromosome breaks and genetic material is lost.
Duplication
A segment of a chromosome is abnormally copied.
Translocation
A broken chromosome segment attaches to a different
chromosome.
EDTA-induced pseudothrombocytopenia
Platelets clump and adhere to WBCs, falsely lowering platelet
count.
Schistocyte (Schizocyte)
Fragmented RBCs caused by rupture in the peripheral circulation.
Acute Promyelocytic Leukemia (APL, M3 subtype)
•Subtype of AML characterized by malignant promyelocytes
•Responds to all-trans retinoic acid (ATRA)
t(15;17)(q22;q11)
Acute Promyelocytic Leukemia (APL, M3 subtype) is associated with _________translocation
EMP
Produces ATP through glycolysis.
Rapoport-Leubering Pathway
Produces 2,3-DPG to regulate oxygen delivery to tissues.
HMP
Produces NADPH to reduce glutathione and protect against oxidative damage
Methemoglobin Reductase Pathway
Reduces methemoglobin back to hemoglobin, preventing iron oxidation.
Immunophenotyping
Most common flow cytometry application; used to identify cell surface markers.
Alkaline Hemoglobin Electrophoresis
Separates hemoglobin variants (e.g., HbA, HbS, HbC) based on charge at alkaline pH.

Myoglobin
Shows a hyperbolic oxygen dissociation curve, releasing oxygen only at very low pO₂.
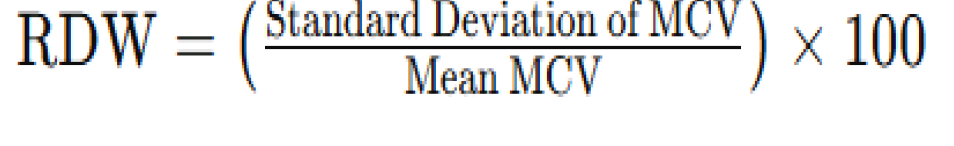
RDW (Red Cell Distribution Width) Formula
Right
Macrocytic red cells appear to the ____ of the normal peak in a histogram.
ANA Test
Screening test for Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE).
Alkali Denaturation Test
Differentiates fetal hemoglobin (HbF) from adult hemoglobin (HbA) in newborn stool/vomit or vaginal blood.
PT Test
Performed after suspected coumarin (rat poison) ingestion to evaluate coagulation function.
Photo-Optical Clot Detection
Measures changes in light transmission over time to assess coagulation stages or factor activity.
Icteric Samples
High bilirubin may cause interference/flagging in automated photo-optical coagulation assays.
stress platelets
Other term for reticulated platelets
VII
Coagulation factor that is known as preconvertin
No bleeding
A unique feature of factor XII deficiency
VWD
Most common inherited bleeding disorder
hemoglobinization
As RBCs mature diameter decreases, nucleoli disappear, chromatin becomes coarse, nucleus shrinks, N:C ratio reduces, and cytoplasm changes from blue to pink due to __________.
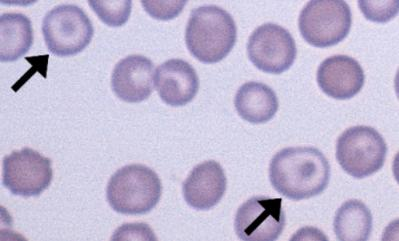
Bite cells (Degmacytes)
Seen in G6PD deficiency. Result from macrophage removal of Heinz bodies (denatured hemoglobin), visualized with supravital stains.
Hereditary Spherocytosis
Leads to reduced deformability, premature RBC destruction, and spherocyte formation.
membrane proteins (e.g., spectrin, ankyrin).
Hereditary Spherocytosis is caused by mutations in genes encoding __________
Stomatocytosis (Overhydrated type)
•Caused by increased membrane permeability to Na⁺ and K⁺. •Results in intracellular Na⁺ accumulation, water influx, cell swelling, and low cytoplasmic viscosity.
lowers
Excessive anticoagulant use (e.g., EDTA overfilling) falsely _____ hematocrit due to cell shrinkage.
Anisocytosis
Variation in size of RBCs.
Poikilocytosis
Variation in shape of RBCs.
Schistocytes and Microspherocytes
Seen in Microangiopathic hemolytic anemia, traumatic cardiac hemolysis, extensive burns.
Micropspherocytes
Hallmark of ABO incompatibility in HDN.

Acanthocytes
Associated with abetalipoproteinemia (Bassen-Kornzweig syndrome).
Abetalipoproteinemia
Bassen-Kornzweig Syndrome
Echinocyte
Seen in Pyruvate Kinase Deficiency (ATP depletion, ↑ 2,3-BPG).
WAS
Characterized by smallest platelets.
Clot Retraction Test
Reflects platelet quantity and function
Bleeding Time
Assesses platelet adhesion and aggregation at the site of vascular injury.
K3 EDTA
Not used for routine coagulation tests (affects calcium-dependent assays).
Within ±2 SD
Acceptable range for quality control values
Coulter Principle
Counts and sizes cells via electrical impedance as they pass through an aperture.
Mechanical Endpoint Detection (Coagulation)
Rotating ball is displaced when fibrin forms
Photo-optical Coagulation Detection
Uses light transmission change to detect clot formation.
EPO
Used to treat anemia in chronic kidney disease.
IL-12
Potent immunoregulatory cytokine, useful as adjuvant in infectious disease therapy.
Cyanmethemoglobin Method
Classic method for hemoglobin measurement.
Ferritin Aggregates
Form in cells if globin synthesis is insufficient, leading to iron accumulation.
Splenic Platelet Sequestration
~1/3 of platelets are transiently sequestered
Retic count
1:1 ratio, typically 2–3 drops each or 50 µL each of blood and stain.
Pyruvate Kinase Deficiency
Autosomal recessive; causes ATP depletion, ↑2,3-BPG, many echinocytes.
Common Lymphoid Progenitor (CLP)
Gives rise to T lymphocytes, pre-T/pre-B cells, dendritic cells, NK cells.
Common Myeloid Progenitor (CMP)
Produces granulocyte-monocyte, basophil-eosinophil, megakaryocyte-erythrocyte, mast cells, all WBCs except lymphocytes, erythrocytes.
3-Part Differential Analyzer
Measures small (lymphocytes), medium (monocytes, eosinophils, basophils), large (neutrophils) WBC groups.
Aspirin
A common drug causing acquired platelet dysfunction
Megakaryocyte Differentiation
Undergoes endomitosis to produce platelets.
Sodium Metabisulfite
Traditional screening for sickle cell disease.
Apoptosis
Active, programmed, non-inflammatory. Cell death
Necrosis
Passive, accidental, inflammatory. Tissue death
Biconcave, 7–8 µm diameter, 2.5 µm thick.
Normal RBCs
Shows schistocytes, helmet cells, burr cells.
HUS Smear
Bernard-Soulier Syndrome
Giant platelets (largest seen), known as Giant Platelet Syndrome.
Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome (HUS)
Anemia, thrombocytopenia, schistocytes.
Hgb C/SC Disease
RBCs with folded membranes.
Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria (PNH)
GPI Anchor Deficiency (CD55/CD59); caused by PIGA mutation.
PNH
↑Retics, normal/increased MCV, ±nucleated RBCs, complement-mediated night hemolysis.
Hemoglobin
Major source of functional body iron.
Azurophilic Granules
Reddish-purple in Wright stain; formed in promyelocyte stage; last released.
Prorubricyte
12–17 µm diameter, N:C 4:1–6:1, basophilic cytoplasm, ±nucleoli
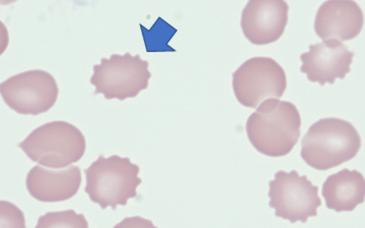
Acanthocyte (Spurr)
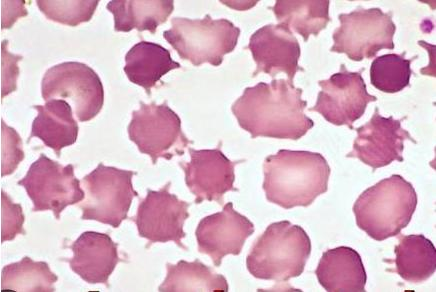
Spherocyte
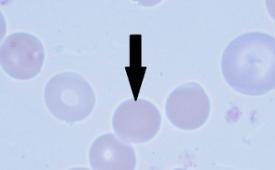
Sickle Cell (Drepanocyte)
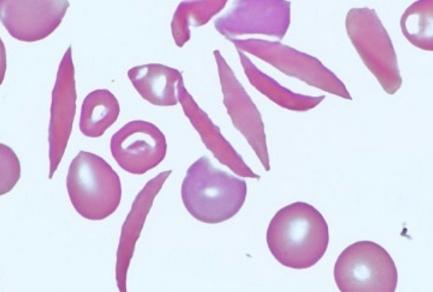
Elliptocyte
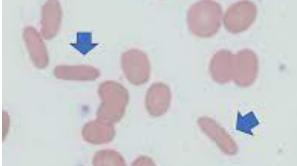
Bite cells (Degmacytes)
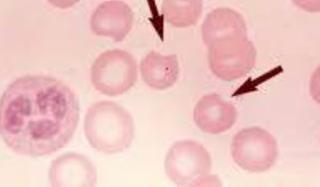
Stomatocyte (Mouth cell)
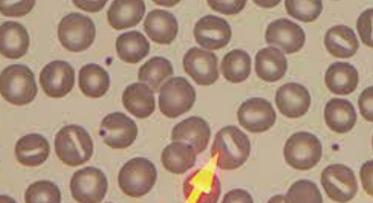
Target cell (Codocyte)
Echinocyte (Burr)