Unit 4: Fixing the economy part 2- Monetary policy
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
Medium of exchange
Money is valuable bc it’s accepted in the buying and selling of goods and services. Money makes trading easier than it would be with barter
Store of Value
Money is a way of storing wealth (keep purchasing power). If you work today, you can get paid in money and wait to spend it in the future
Unit of account/standard of value
Money can be used to state how much things are worth. The value of goods and services can be expressed in money prices to allow for each comparisons
Liquidity
Ease with which an asset can be converted to cash without losing much value. Cash is the most liquid asset, while tangible items like a house are less liquid
Commodity money
Something that performs the function of money and that has intrinsic value, derived from the material it is made of, such as gold or silver.
Fiat money
Currency that has no intrinsic value but is established as money by government regulation. Unlike commodity money, its value comes from the trust and confidence of the people who use it. Example paper money
Stocks
(equities) represent ownership of a corporation and the stockholder is often entitled to a portion of the profit paid out as dividends
Bonds
(securities) are loans, or IOUs, that represent debt that the government, business, or individuals must repay to the lender
bond price and interest rates are ___ rated
inversely
Money supply
all the money in society, defined in several ways (ex M1, M2, etc)
M1
coins, currency held by the public, traveler’s checks, checking account balances, and other cash accounts
M2
Includes M1, plus savings and small short-term time deposits (CDs), overnight “repos” at commercial banks, and non-institutional money market accounts. The common economic indicator used to forecast inflation.
M3
Includes M2, plus large time deposits, repos of maturity greater than one day at commercial banks, and institutional money market accounts
Monetary base=
Currency in circulation+ bank reserves
interest rate
percentage extra that must be paid back on a loan
nominal interest rate
total percentage (what you see on the loan)
real interest rate
adjusted for inflation
real interest rate formula
Real Interest Rate = Nominal Interest Rate - Inflation Rate.
Financial market
where households place their current saving and accumulated savings (wealth)
financial assets
are a paper claim to future income (loans, stocks, bonds, bank deposits)
Physical assets
It is a claim on a tangible object (house, lump of gold, car)
Asset
are anything of value (cash, houses, cars, the shirt on your back)
Financial system or financial markets provide 3 key functions
1) Reducing transaction costs
2)Reducing risk
3) providing liquidity
Financial intermediaries
institutions that amasses funds from one group and makes them available to another such as banks, credit unions, and insurance companies. They play a crucial role in facilitating the flow of funds in the economy.
2 traditional ways of borrowing
1) borrow from a bank: the interest rate is set in the contract
2) sell bonds: interest rate is set when bond is auctioned
Bond
promise to pay back a certain amount at a certain time
Maturity date for a bond
when a bond ends and is paid off
face value for a bond
the amount paid to the bondholder at maturity
when bond prices fall, interest rates ___
rise
when bond prices rise, interest rates ___
fall
Nominal interest rates=
real interest rate + inflation
Liabilities
obligations to other parties (debt)
net worth=
assets-liabilities
deposit multiplier (used in t-accounts)
=1/required reserve ratio
if asking abt change in demand deposits the ____ amount of initial deposit gets multiplied through the multiplier (1/RR)
WHOLE
If asking abt change in money supply as a result of a deposit you have to
take out the required reserve amount before multiplying by the multiplier
if asked abt the change based on a fed or central bank purchase multiply the ___ amount to see the overall change in the money supply
full
money market demand graph
A graphical representation of the relationship between the quantity of money demanded and the nominal interest rate, showing how changes in the money supply can affect interest rates and overall economic activity.
DM shifters of the money market demand graph
PL (direct)
rGDP (direct)
technology (inverse)
Monetary policy
The Federal reserve’s ability to stabilize the economy by changing the SM in order to change interest rates
Monetary policy tools for recessionary and inflationary
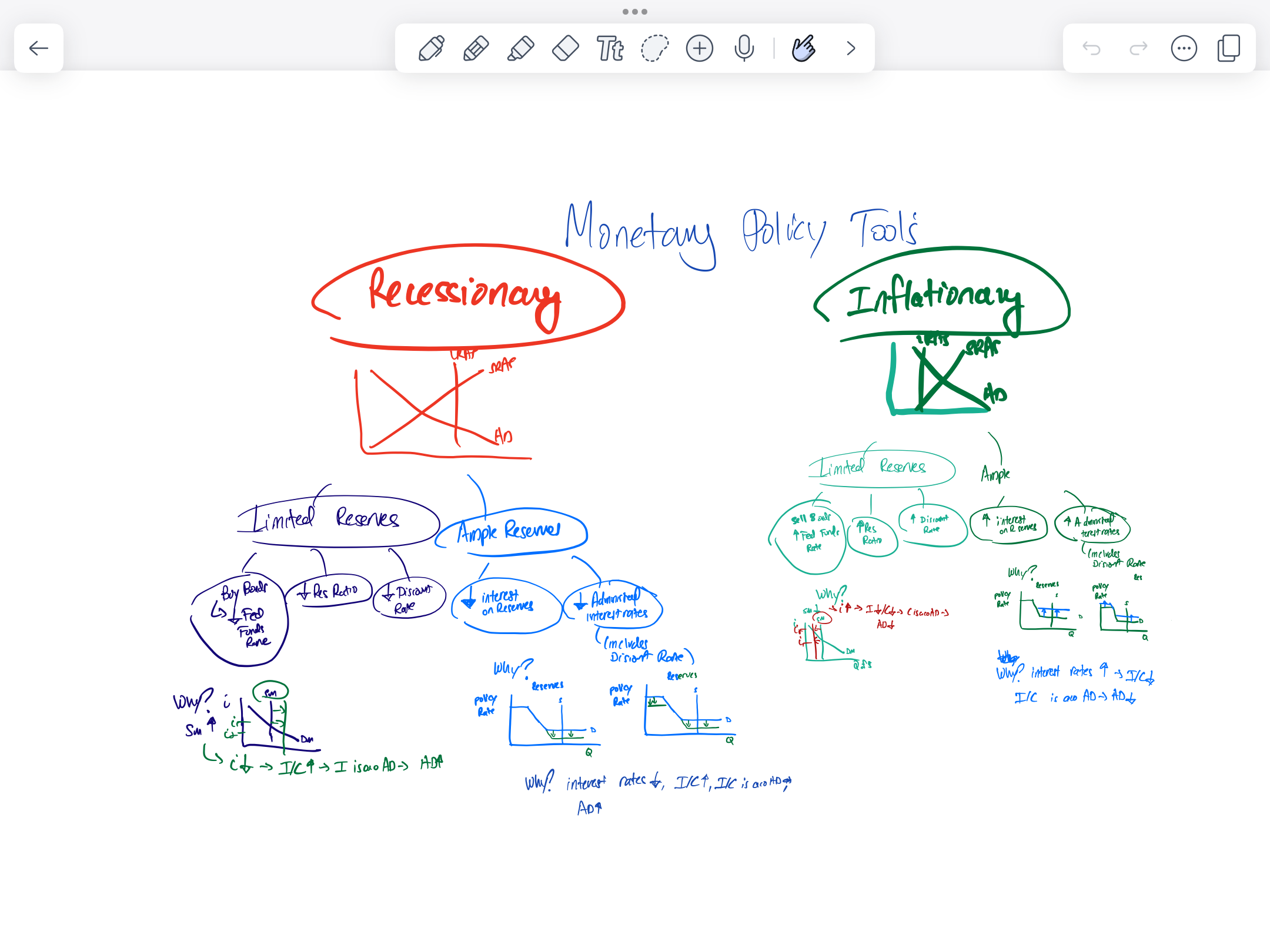
Interest on reserves (IOR)
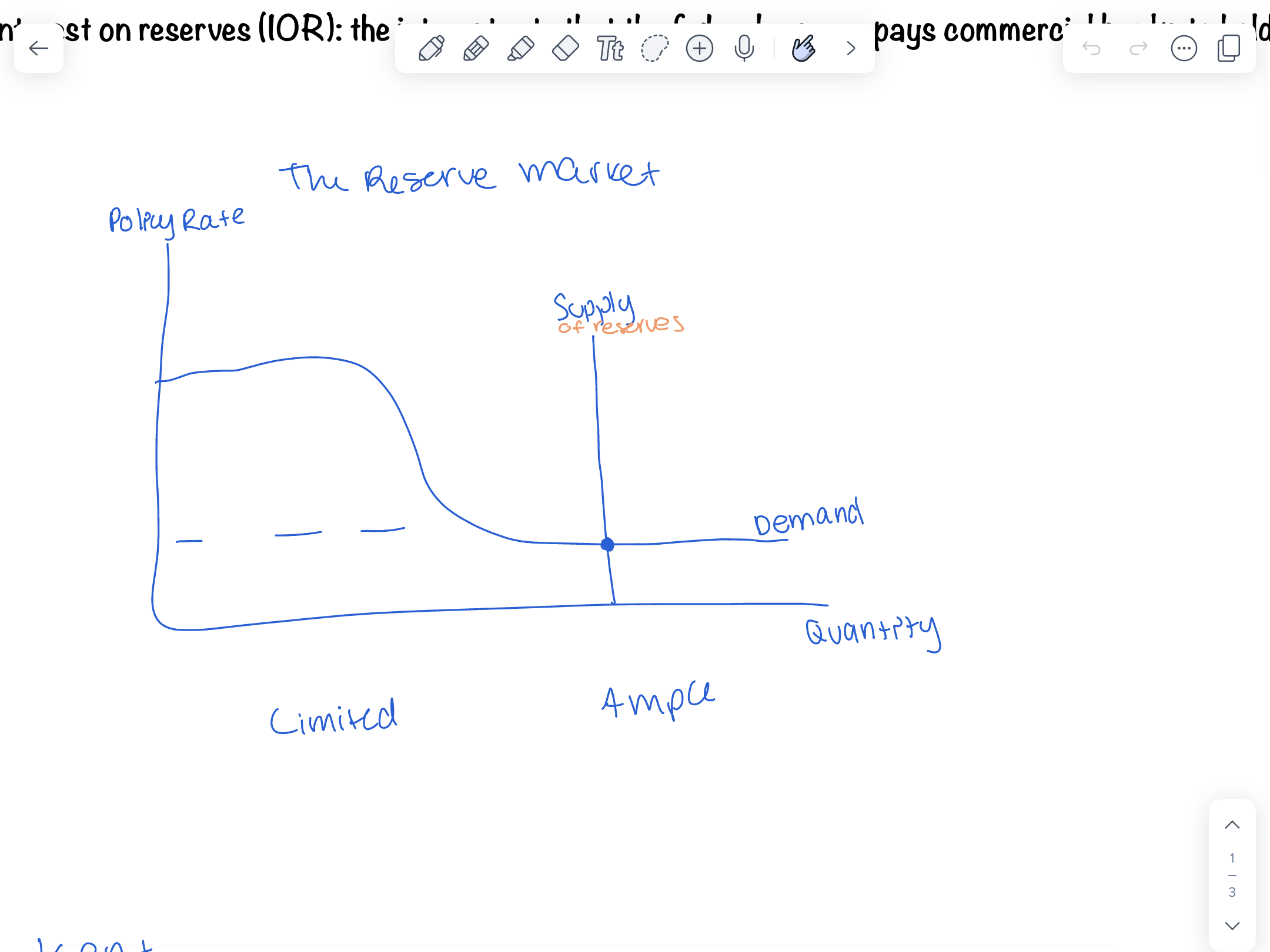
The interest rate that the federal reserve pays commercial banks to hold reserves
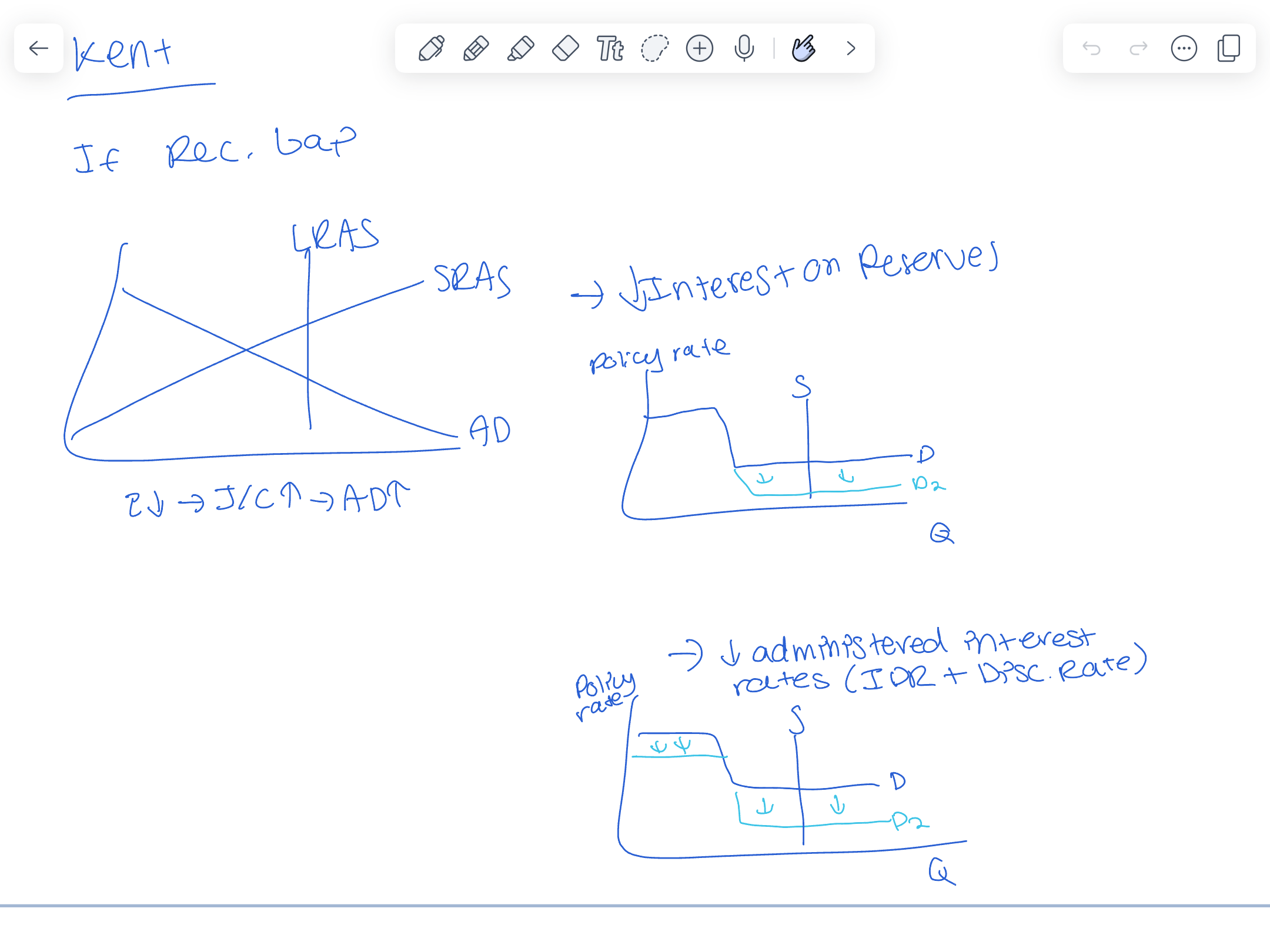
Reserve market graph
Reserve market graph if recessionary gap
reserve market graph if inflationary gap
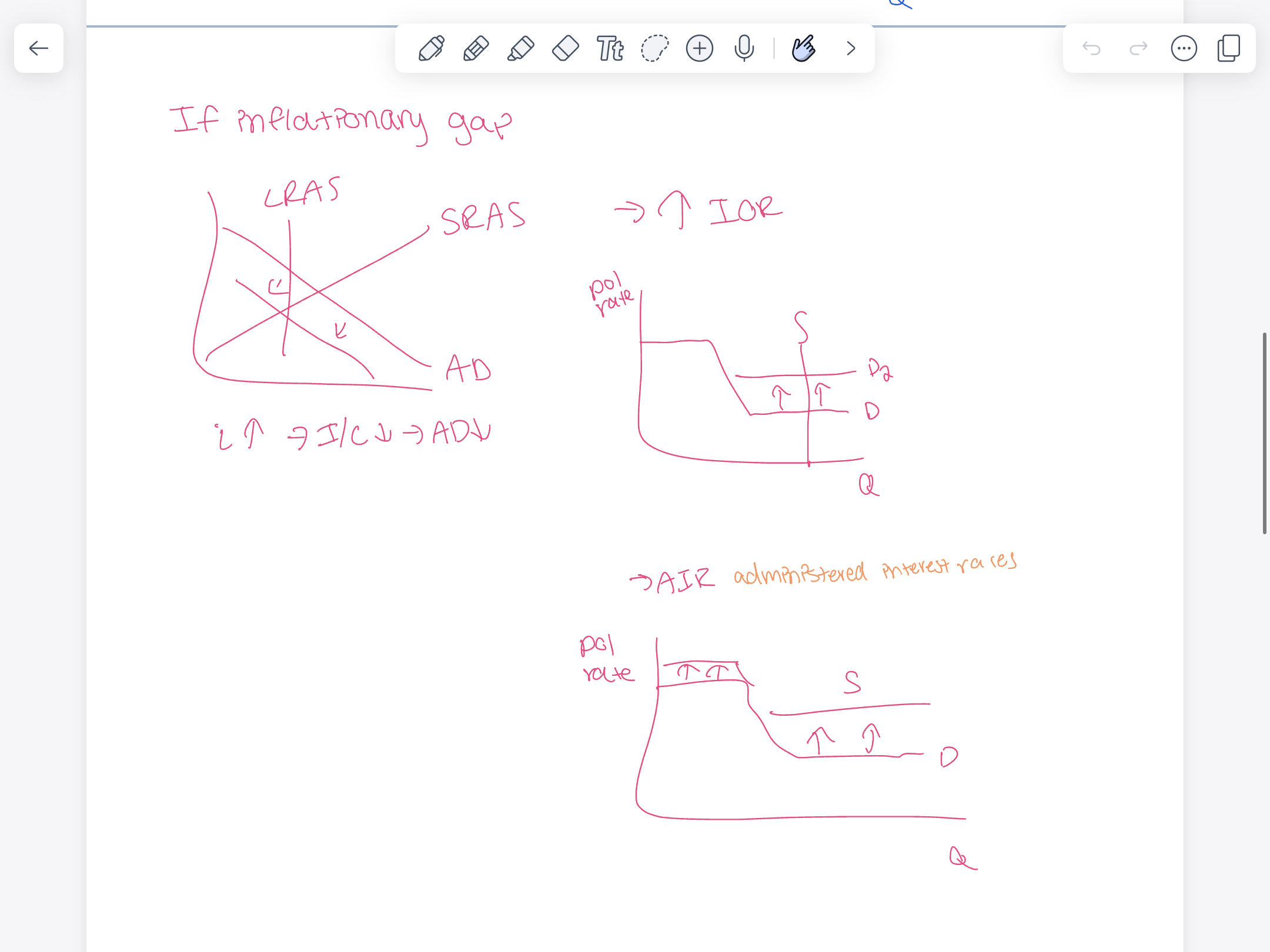
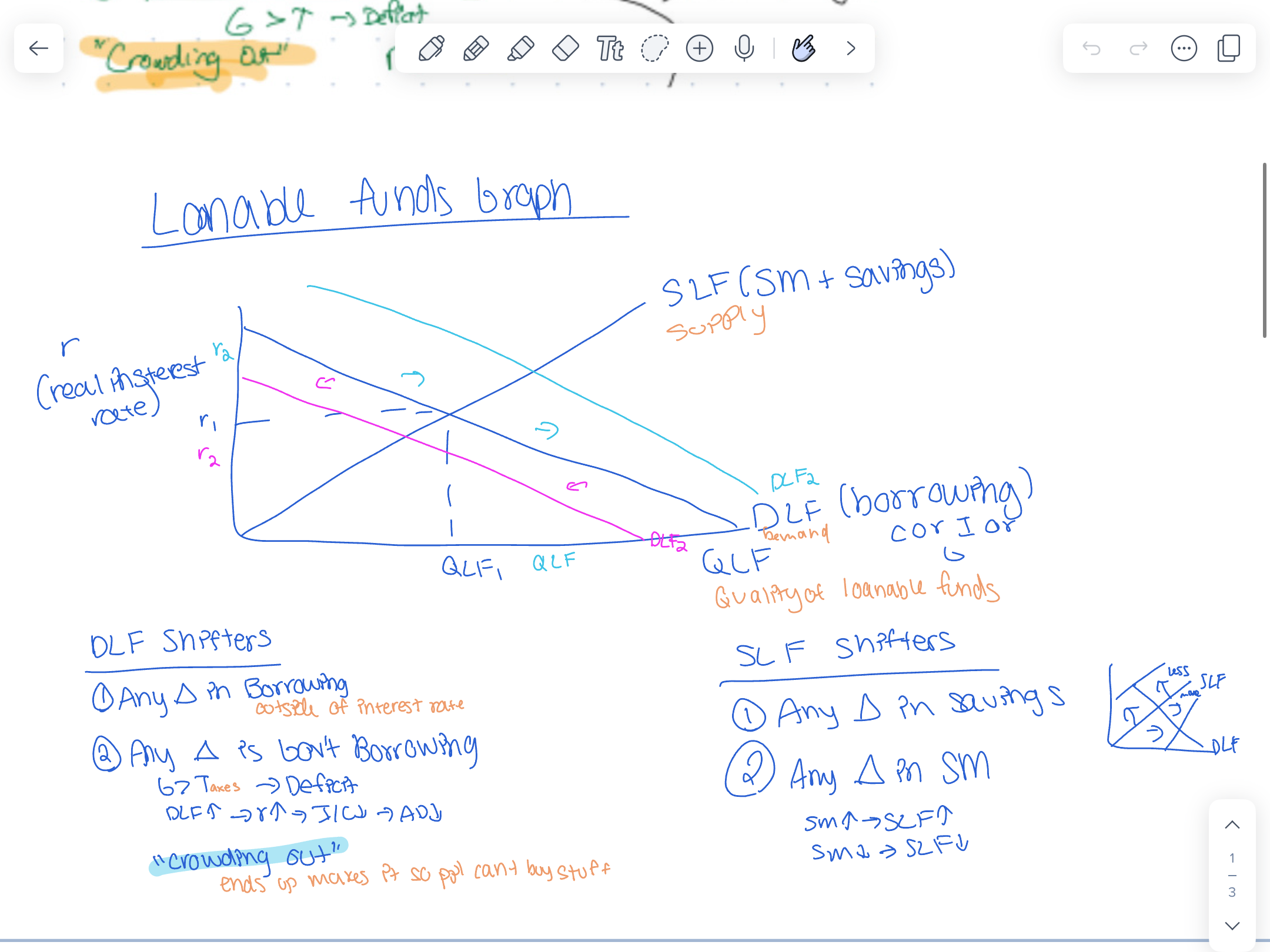
Loanable funds graph
equation of exchange
MV=PY
M= Money supply
V= Velocity of money
P= Price level PxY=nominal GDP
Y= Real output