DNA and RNA Structure
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid, a stable double-stranded polymer of nucleotides
What does DNA do?
stores genetic information, and codes for RNA during transcription
RNA
Ribonucleic acid, a versatile single-stranded polymer of nucleotides
Bases in DNA
Adenine, Guanine, Thymine, Cytosine
Bases in RNA
Adenine, Guanine, Uracil, Cytosine
What sugar is found in DNA?
Deoxyribose
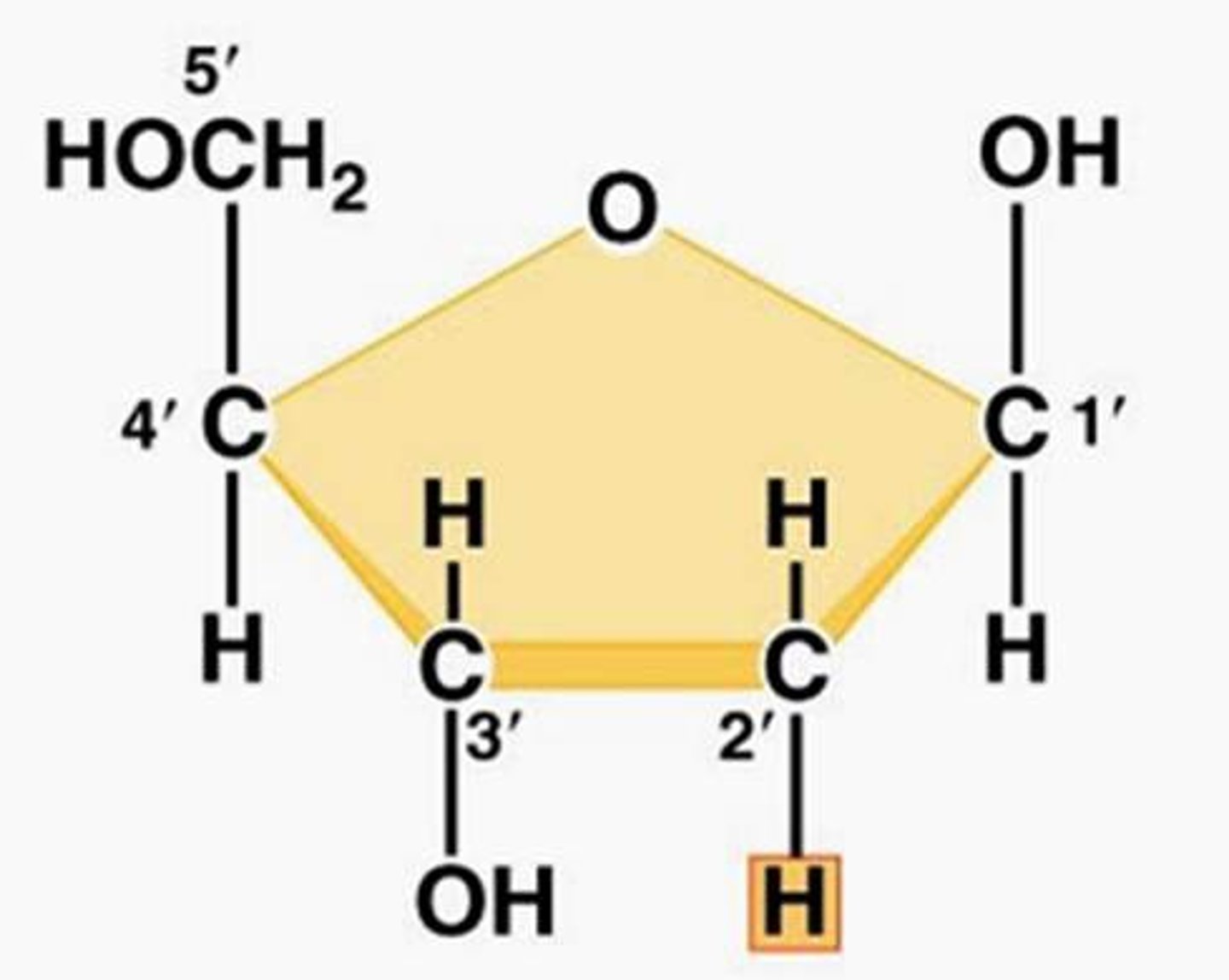
What sugar is in RNA?
Ribose
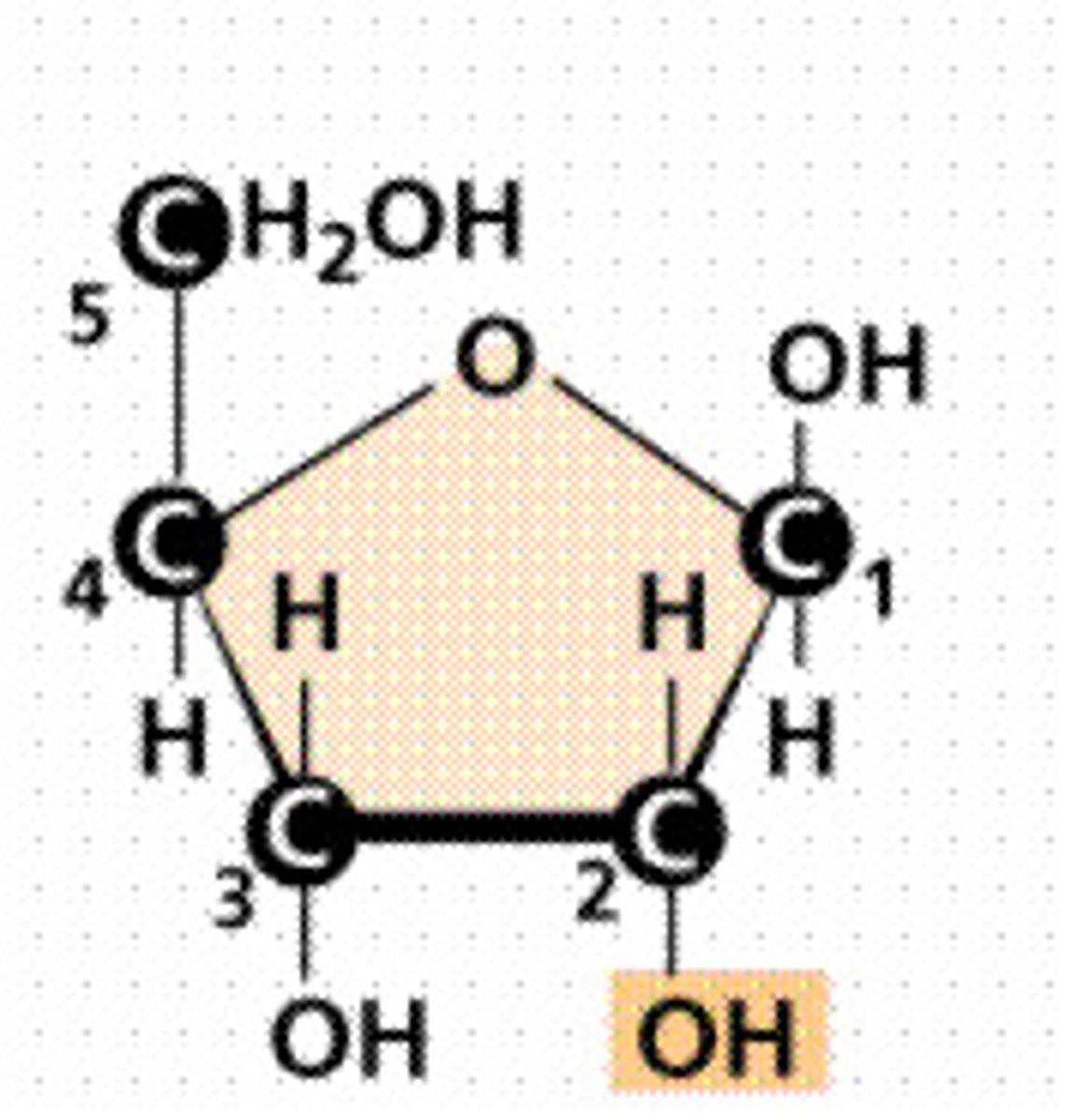
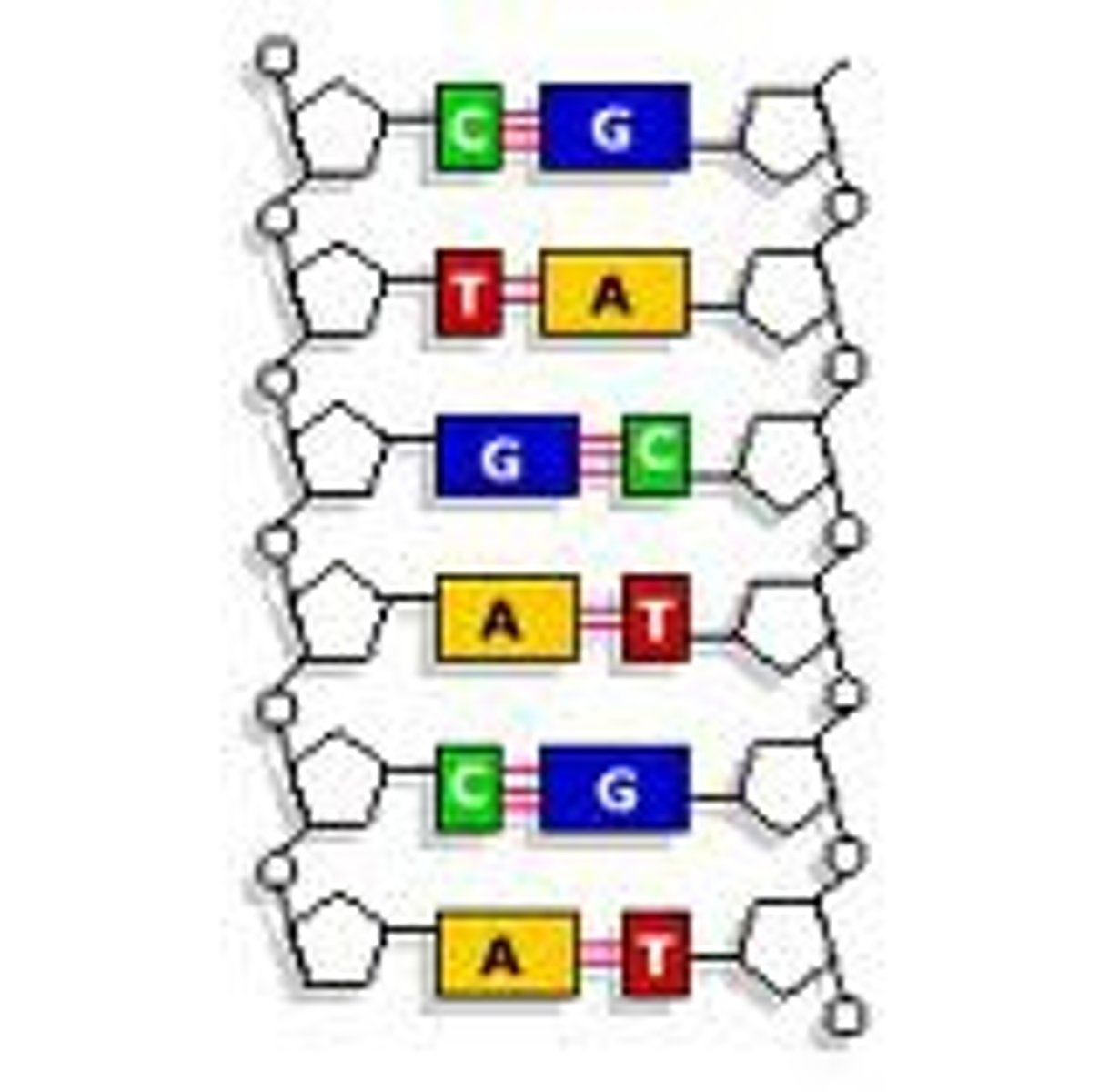
What is the structure of DNA?
Double helix, two antiparallel strands of nucleotides
What is the structure of RNA?
Single stranded, a structure of RNA
Where is there covalent bonding within DNA?
between phosphate, sugar, and base
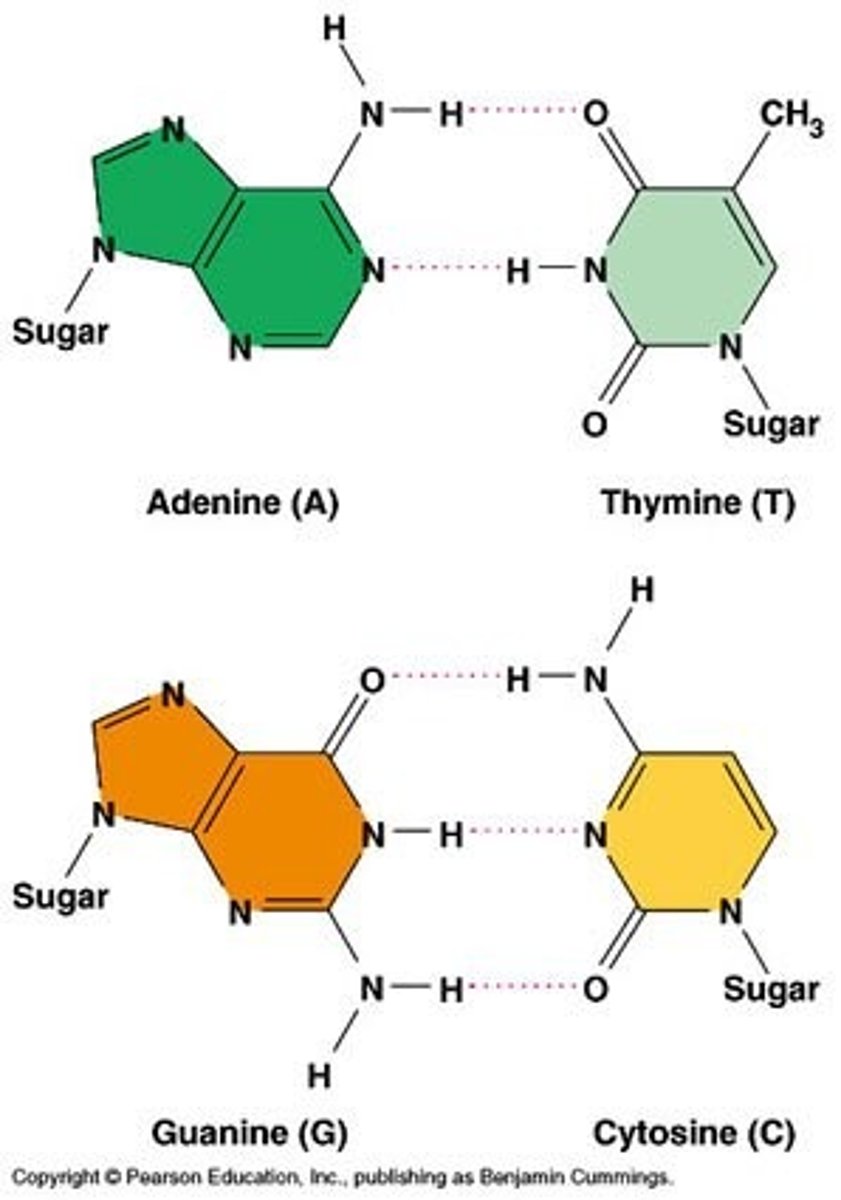
Where is there hydrogen bonding in DNA and RNA?
between bases in opposite strands to link the strands together
Nucleic Acids
Large biomolecules and polymers formed by condensation reactions between nucleotide monomers
Phosphodiester Bond
Bond formed between nucleotides in DNA strands after the condensation reaction
How many hydrogen bonds are between A and T?
2 hydrogen bonds
How many hydrogen bonds are between C and G?
3 hydrogen bonds
What does antiparallel mean?
Strands of DNA running in opposite directions
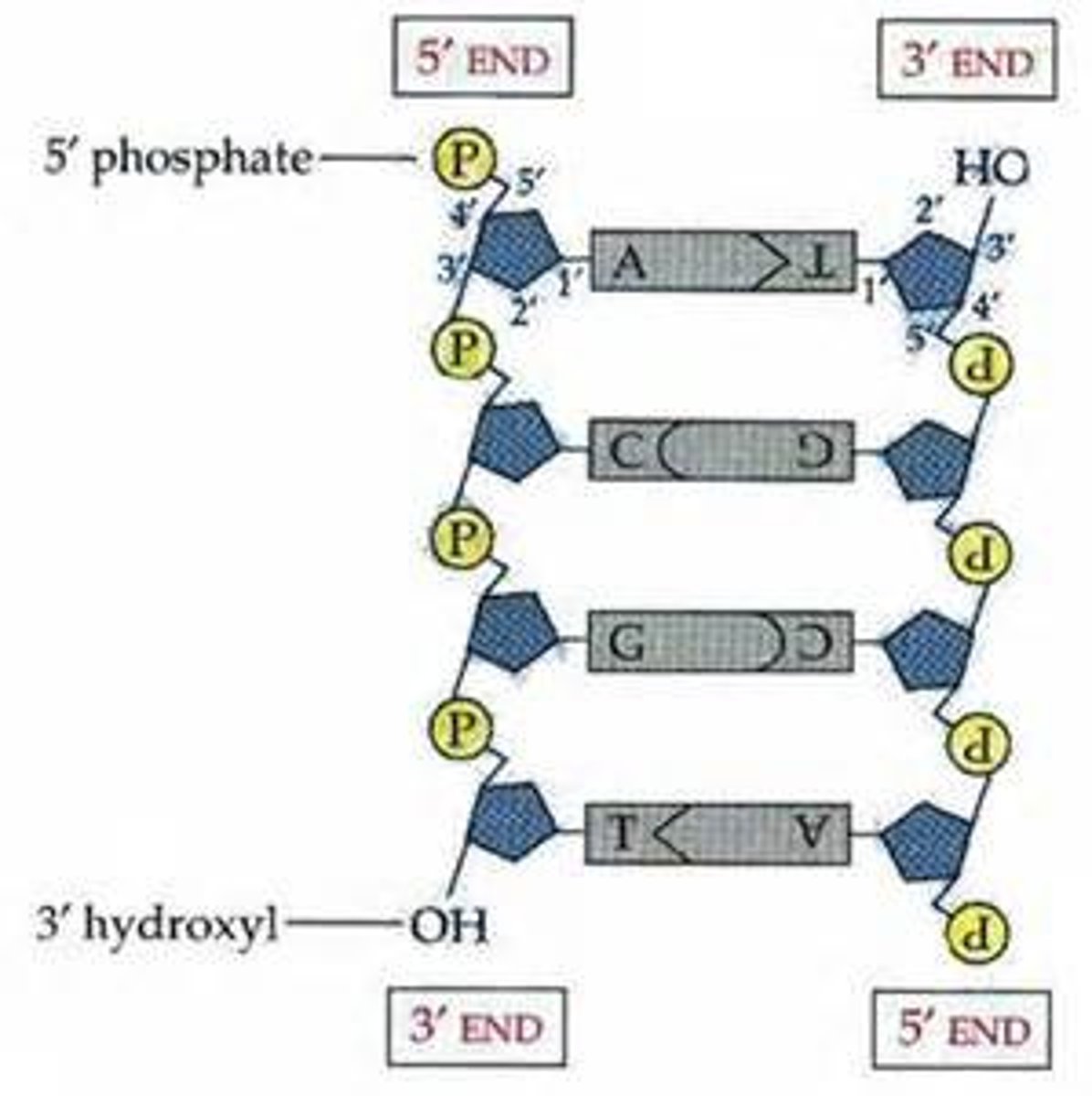
Why must DNA strands run antiparallel?
So that the bases can face each other and pair up
What are the twists like in DNA?
10-15 bases per twist
What forms the double helix shape of DNA?
The sugar-phosphate backbones run anti-parallel to each other and twist together.
Nucleotides
A single unit of nucleic acid that is composed of sugar, phosphate, and base
Nucleotide Components
Pentose sugar, phosphate group, nitrogenous base
In a nucleotide drawing, what shape would you use to represent a sugar?
A pentagon because it's a pentose sugar
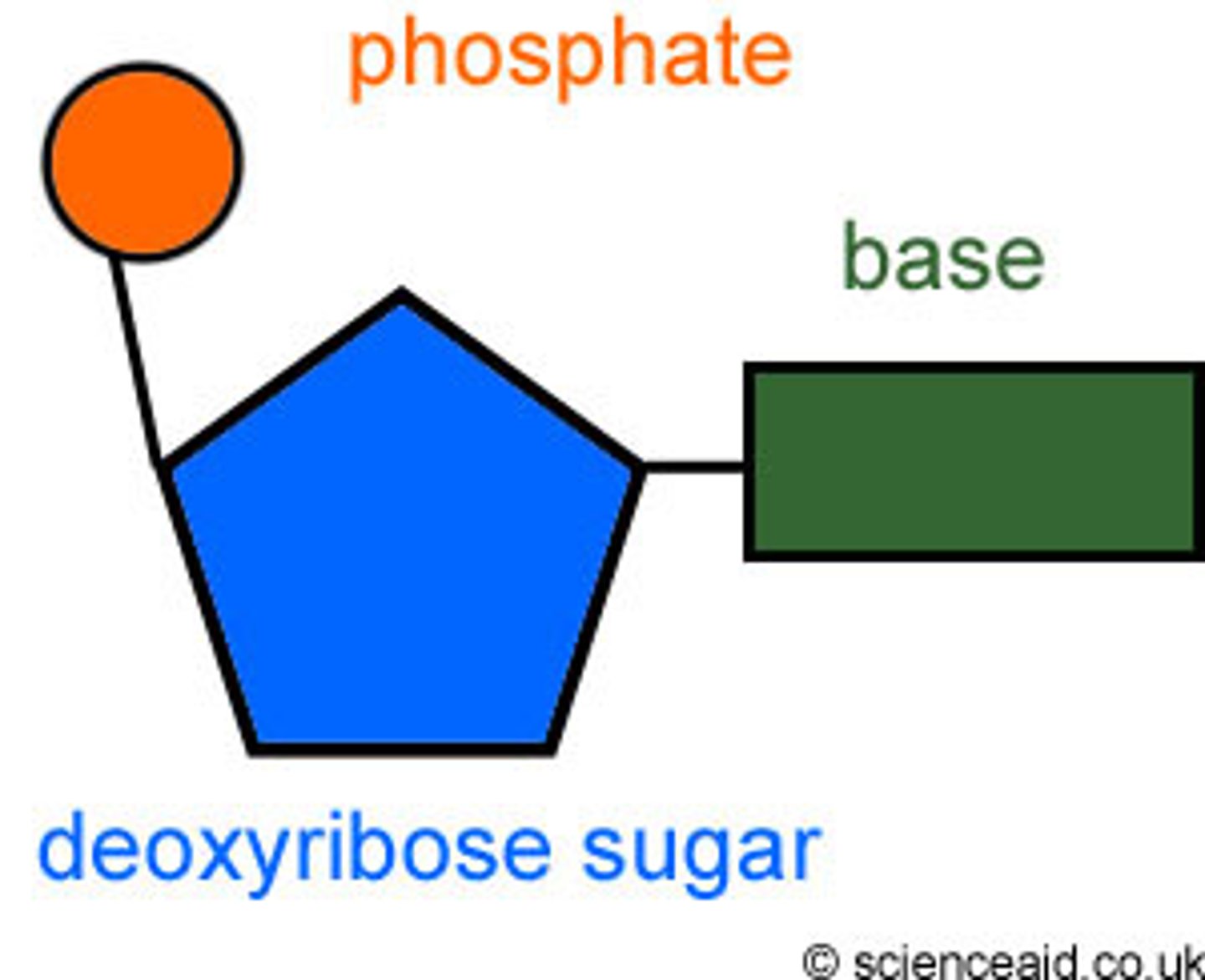
In a nucleotide drawing, what shape would you use to represent a phosphate group?
A circle to the left of the sugar, connected to the carbon 4
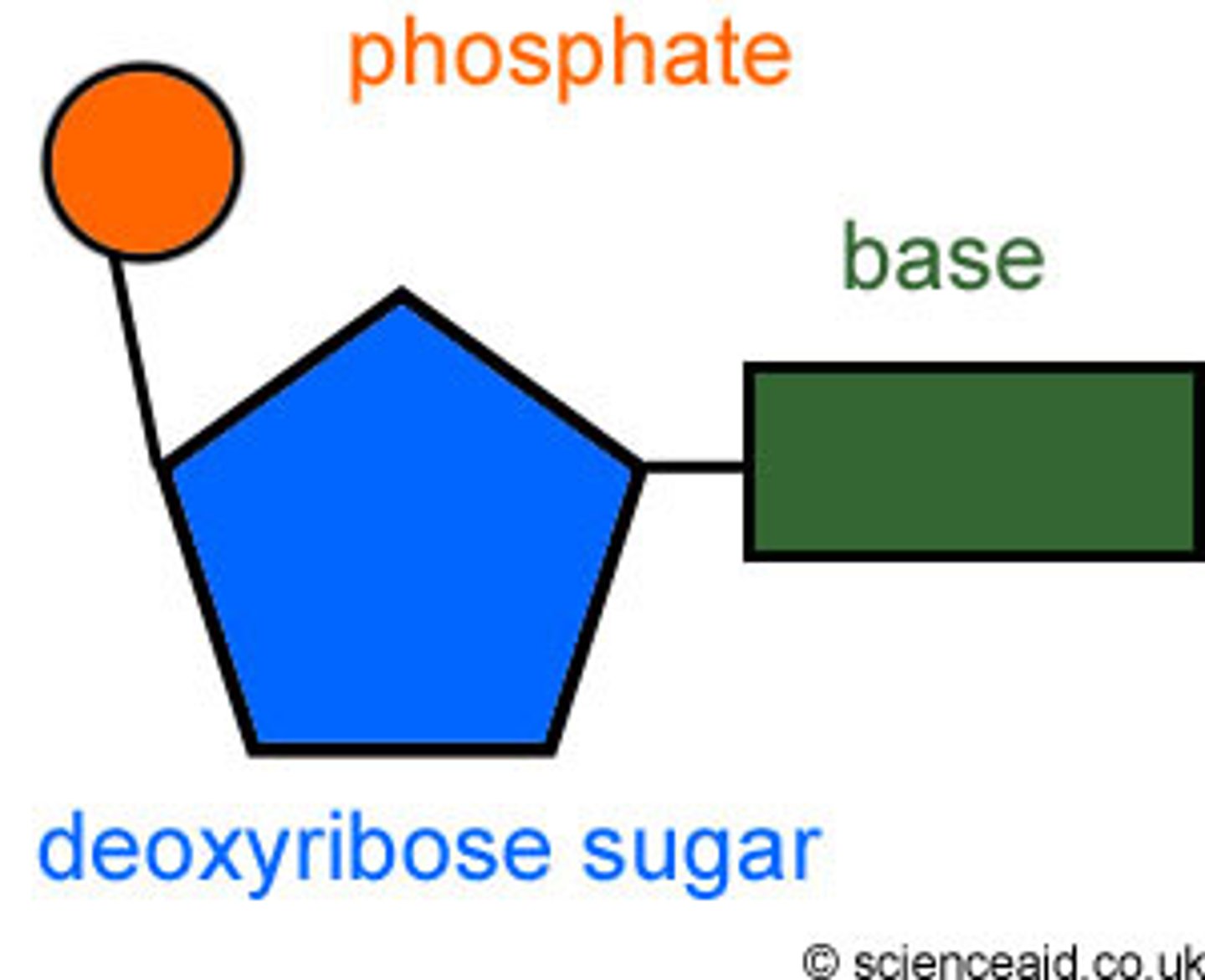
How is a nitrogenous base drawn in a nucleotide drawing?
As a rectangle on the right of the sugar connected to carbon 1
Base Pairing
Complementary base pairing in DNA: A = T, C = G
What are purines?
adenine and guanine because they have two rings in their structure
What are pyrimidines?
cytosine, thymine, uracil because they have 1 ring in their structure
Why are the outer edges of bases left exposed?
Allows access to replicative and transcriptional proteins
What do triplets of bases do?
send instructions to the cell for proteins, enzymes and what genes should be switched on and off
What does the sequence of bases determine?
The amino acid sequence and therefore what protein is made
Why must purines pair with a pyrimidine?
To have an equal width between the two sugar-phosphate backbones, there should be 3 rings. Otherwise it's 2 or 4 rings
Which experiment determined whether the genetic code is protein or DNA?
The Hershey-Chase experiment
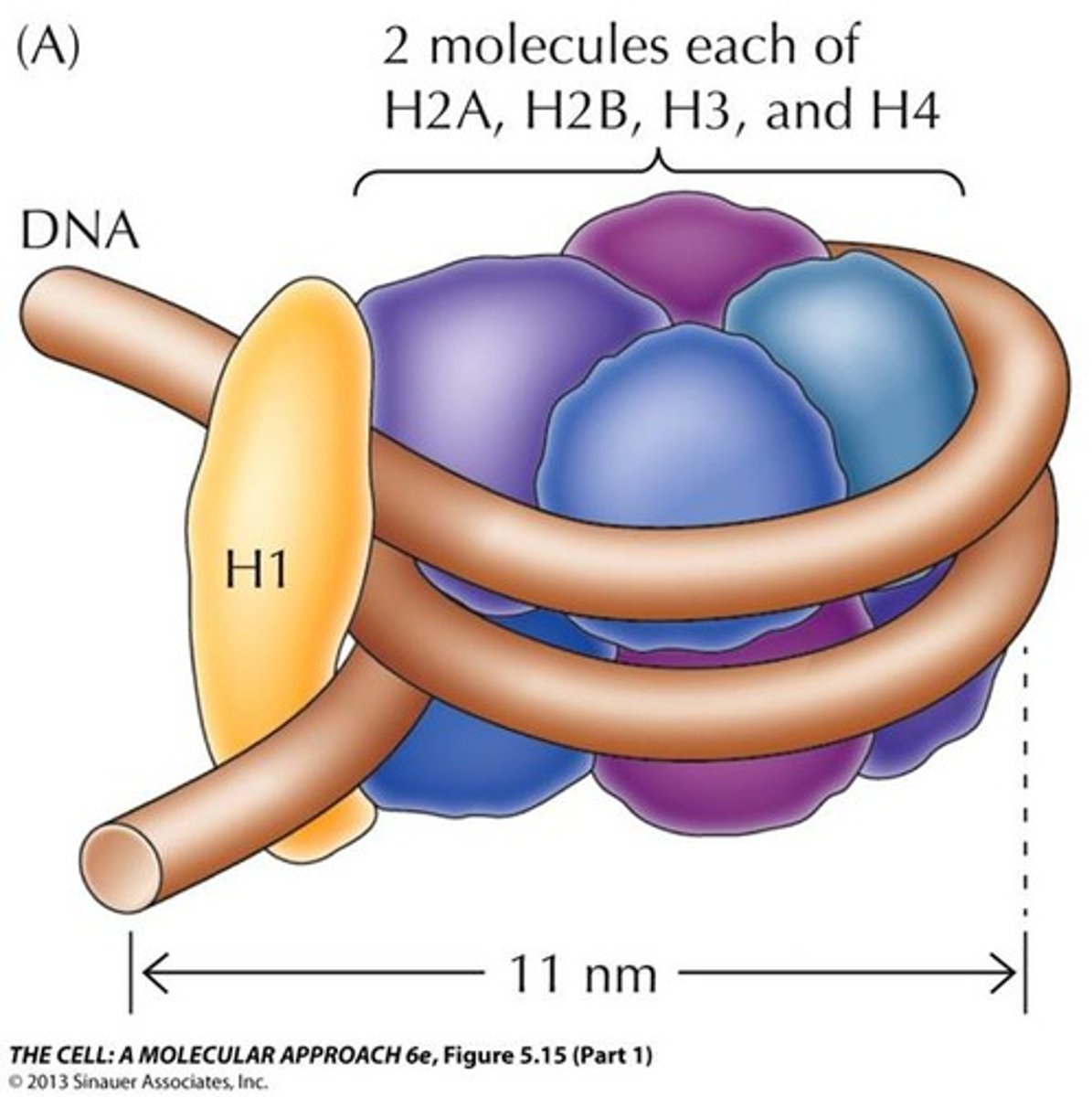
What is a nucleosome?
Section of DNA wrapped around 8 histone protein cores inside a chromosome
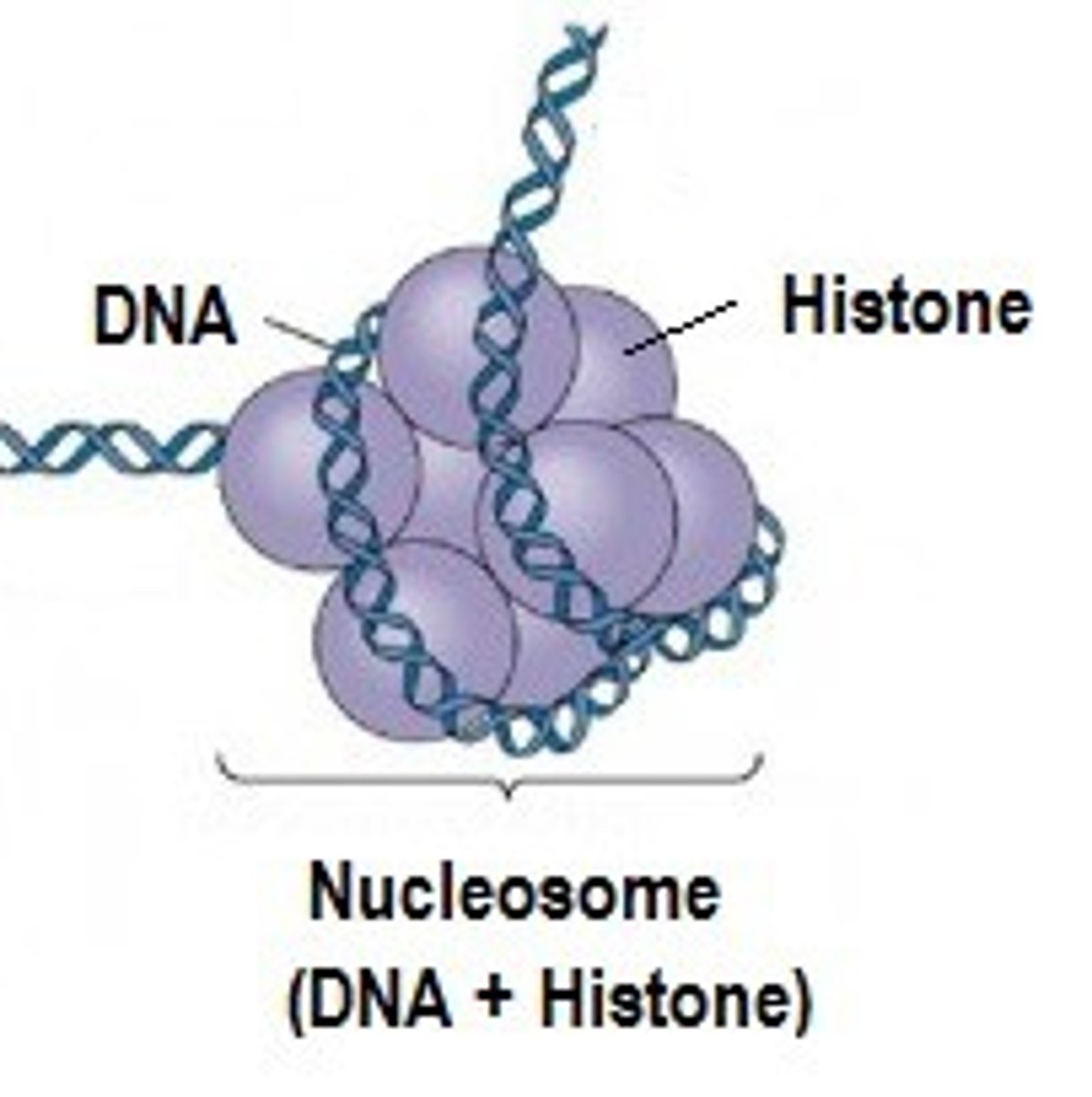
What can be found between adjacent nucleosomes?
Linker DNA
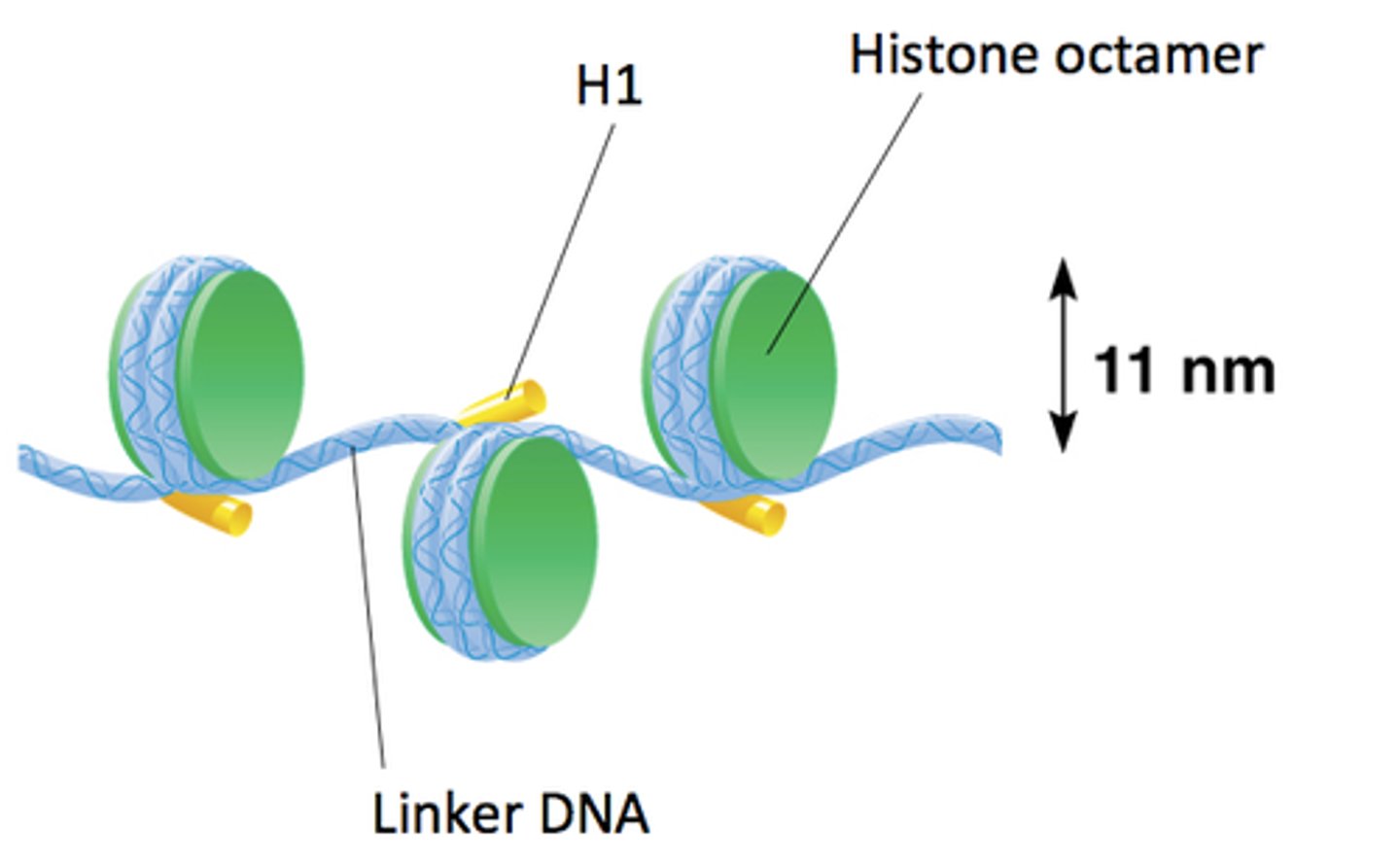
How many times are DNA molecules wrapped around histone protein?
twice
What does H1 histone protein do?
reinforce the binding and help package chromosomes when DNA is going to divide
What is supercoiling?
DNA strands being twisted around themselves so they're compact
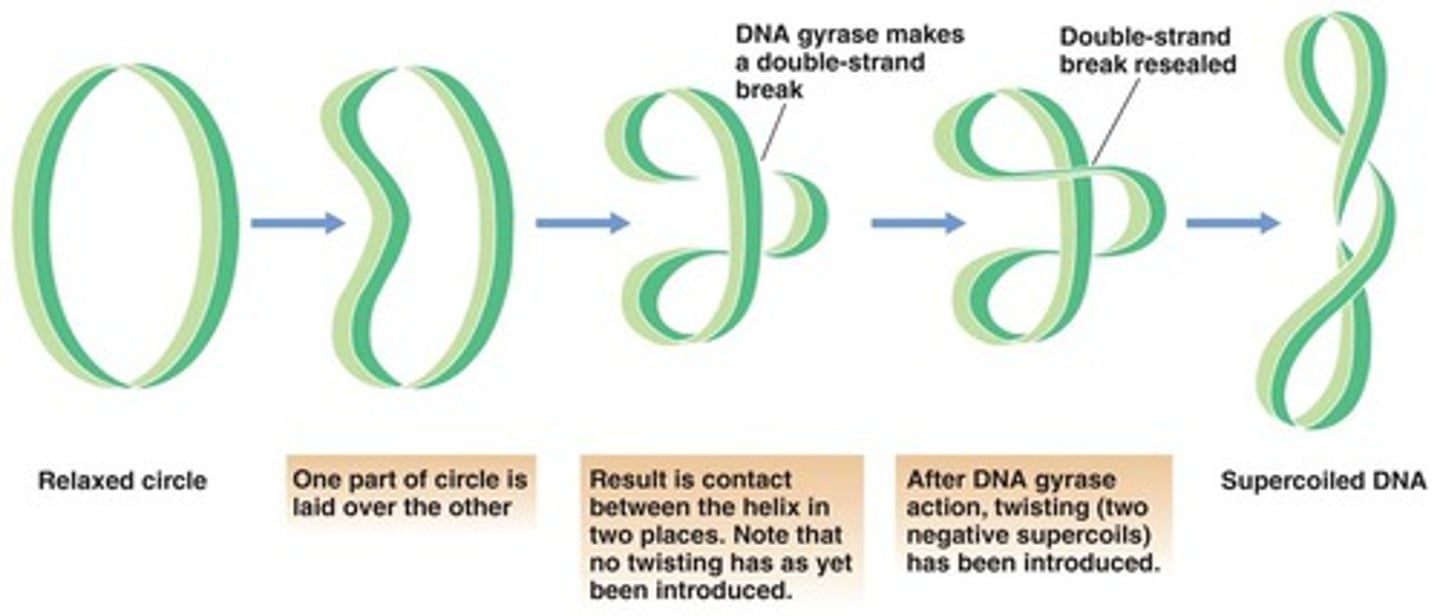
What are the benefits of DNA supercoiling?
- Cells can control gene expression because DNA can't be transcribed in this form
- Cells can specialise by keeping some parts of DNA permanently wound up
- Helps the DNA fit into the nucleus
- Organises DNA for when division takes place
- Histones can promote or inhibit the transcription of chromatin
What is gel electrophoresis?
a technique used to separate molecules e.g DNA fragments according to their size and charge using an electrical field and a gel matrix
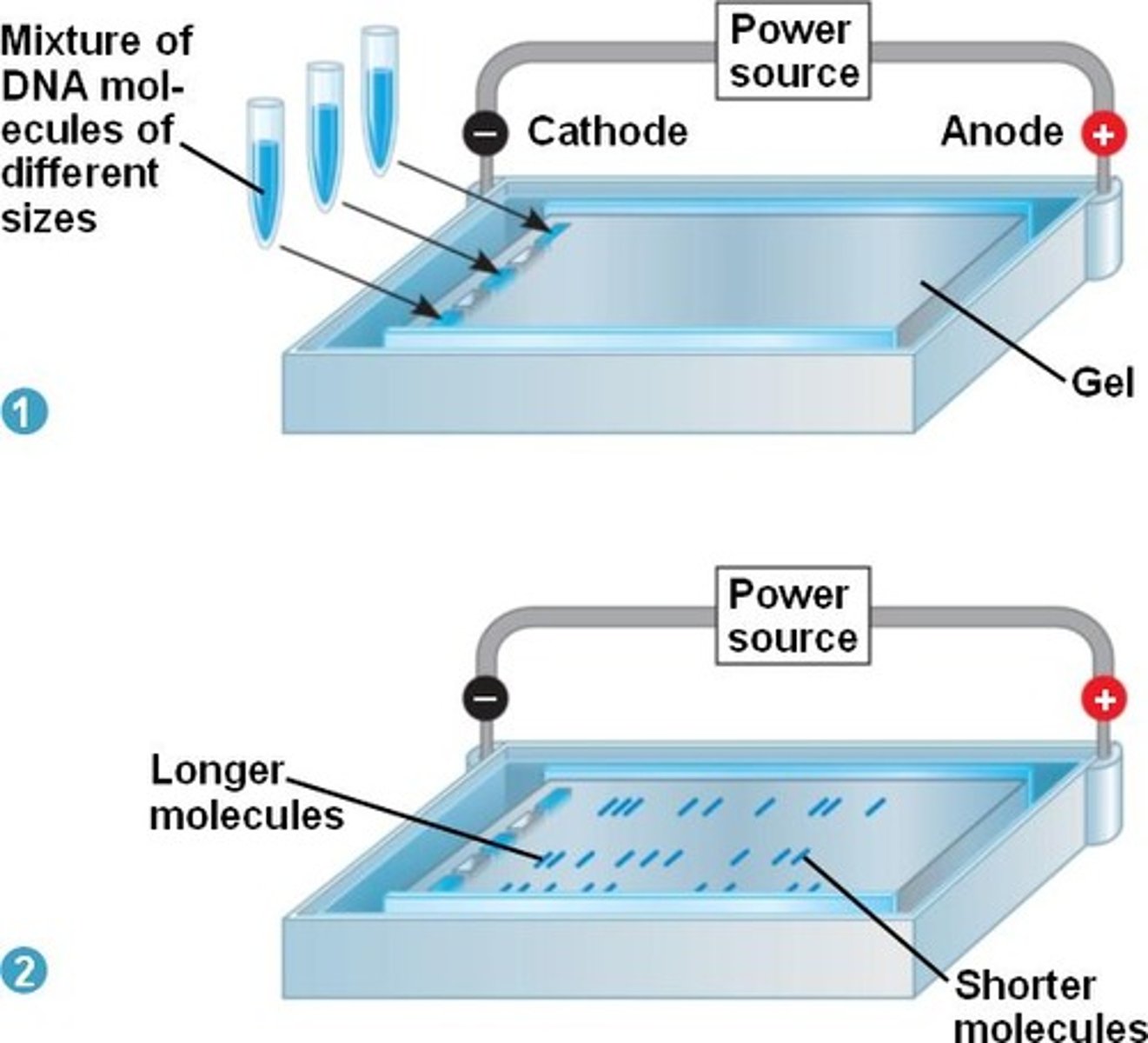
Explain the setup for gel electrophoresis?
Machine filled with gel and connected to a positive and negative electrode. There are wells to place your samples on the side of the negative electrode
Why gel?
So the DNA can travel through it
Why does DNA have a negative charge?
phosphate groups in backbone carry negativly charged oxygen
How are DNA samples prepared for gel electrophoresis?
Restriction enzymes cut up the DNA into tiny pieces at specific points in its sequence. Dye gets added so it can be seen under UV light
What happens is gel electrophoresis?
DNA moves towards the positive electrode. Shorter pieces move further and faster because they have lower molecular weight compared to the longer pieces. DNA bands can be seen under UV light once the gel is stained.
What is a DNA ladder used for?
Provides known bp lengths to compare your samples to
What are applications of gel electrophoresis?
Paternity/maternity testing, DNA fingerprinting, classifying organisms + species and testing for coronavirus
What is polymerase chain reaction (PCR0 for?
making more copies of a section of DNA (e.g from a crime scene to find the suspect)
What is the first step of PCR?
denaturation: heat is used to separate double-stranded DNA molecules.
What is the second step of PCR?
annealing - DNA primers bind to the DNA
What is the 3rd step of PCR?
DNA synthesis: taq polymerase replicates the DNA to build new strands using free nucleotides
How many times is PCR normally done?
30 times
Why is PCR done?
To create a large amount of sample DNA that can be analysed and identified