A2.2 Cells
1/31
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
Cell
The basic unit of structure and function in living things
Cell theory
The theory that cells form the fundamental structural and functional units of all living organisms.
structures common to all cells
plasma membrane, cytoplasm, ribosomes, DNA
differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells
70S ribosomes (prokaryotic) vs 80S ribosomes.
DNA isn't enclosed by nucleus in prokaryotic cells.
Eukaryotic cells are much bigger than prokaryotic cells.
Eukaryotic cells have membrane bound organelles.
Some prokaryotic cells have flagellum and plasmids.
only unicellular vs multicellular (and unicellular sometimes)
Eukaryotic cells
Larger and more complex.
Contain a membrane-enclosed nucleus, and membrane-bound organelles.
Can be multicellular.
prokaryotic cell
earliest and most primitive type of cell.
unicellular
Does not contain membrane-bound organelles.
DNA
contains genetic information which are the instructions the cell needs to survive, mature, and replicate.
organelles
structures in the cell that are adapted to perform a specific function.
tend to be membrane bound (separate subunit of cells)
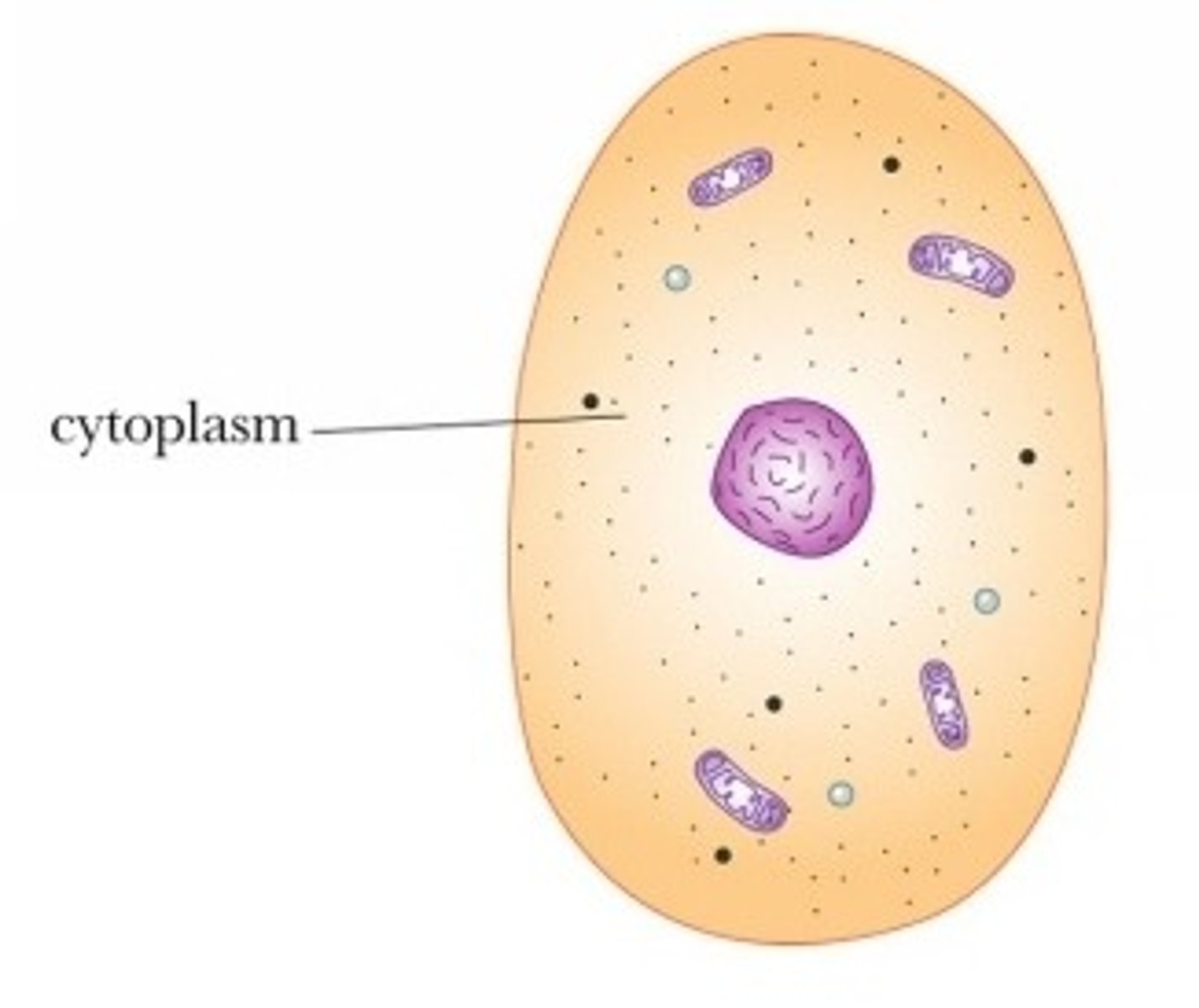
Cytoplasm
A jellylike fluid (made mostly of water) inside the cell in which chemical reactions occur
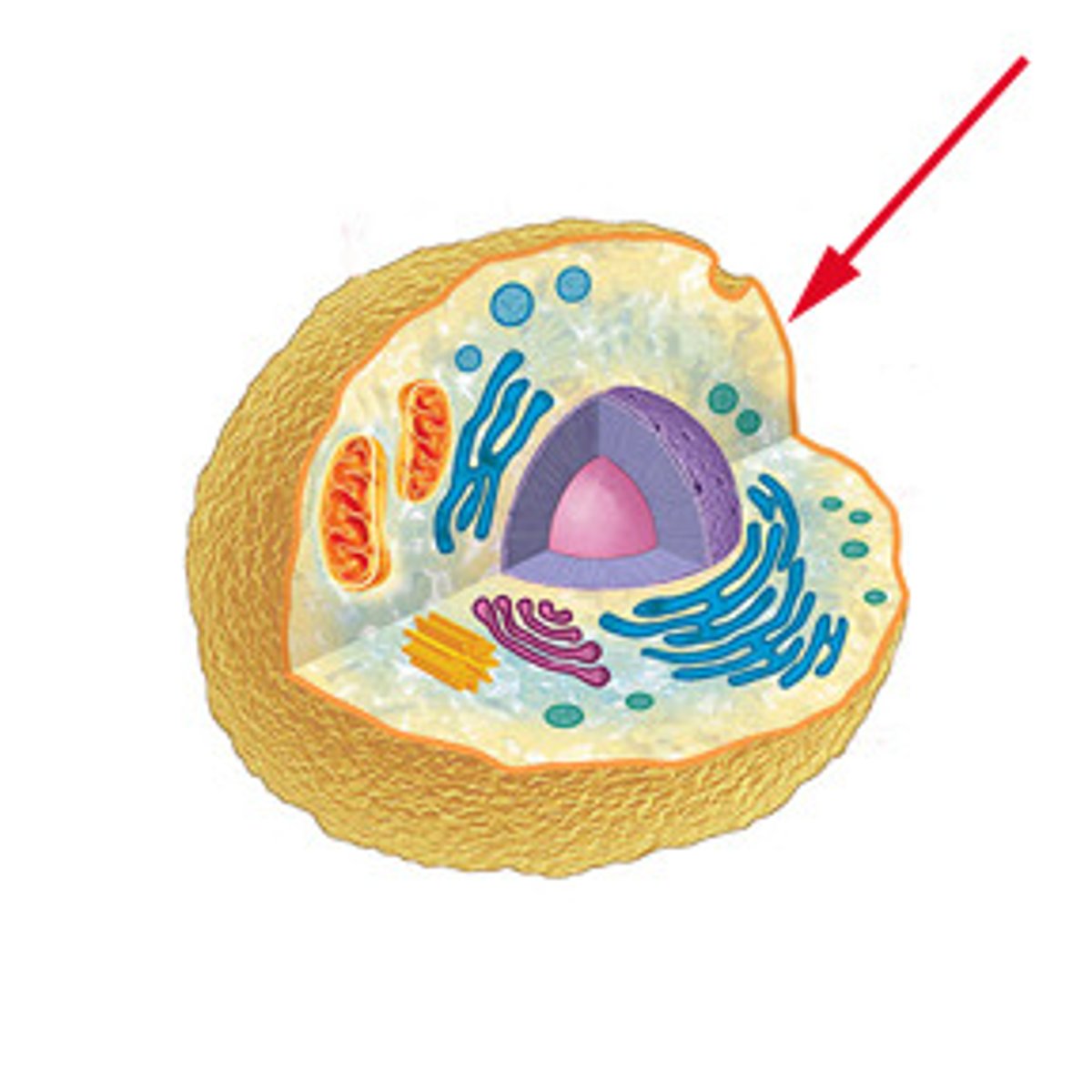
plasma membrane in cells
A semi-permeable phospholipid bilayer forming the boundary of the cells. Controls what can enter and exit the cell.
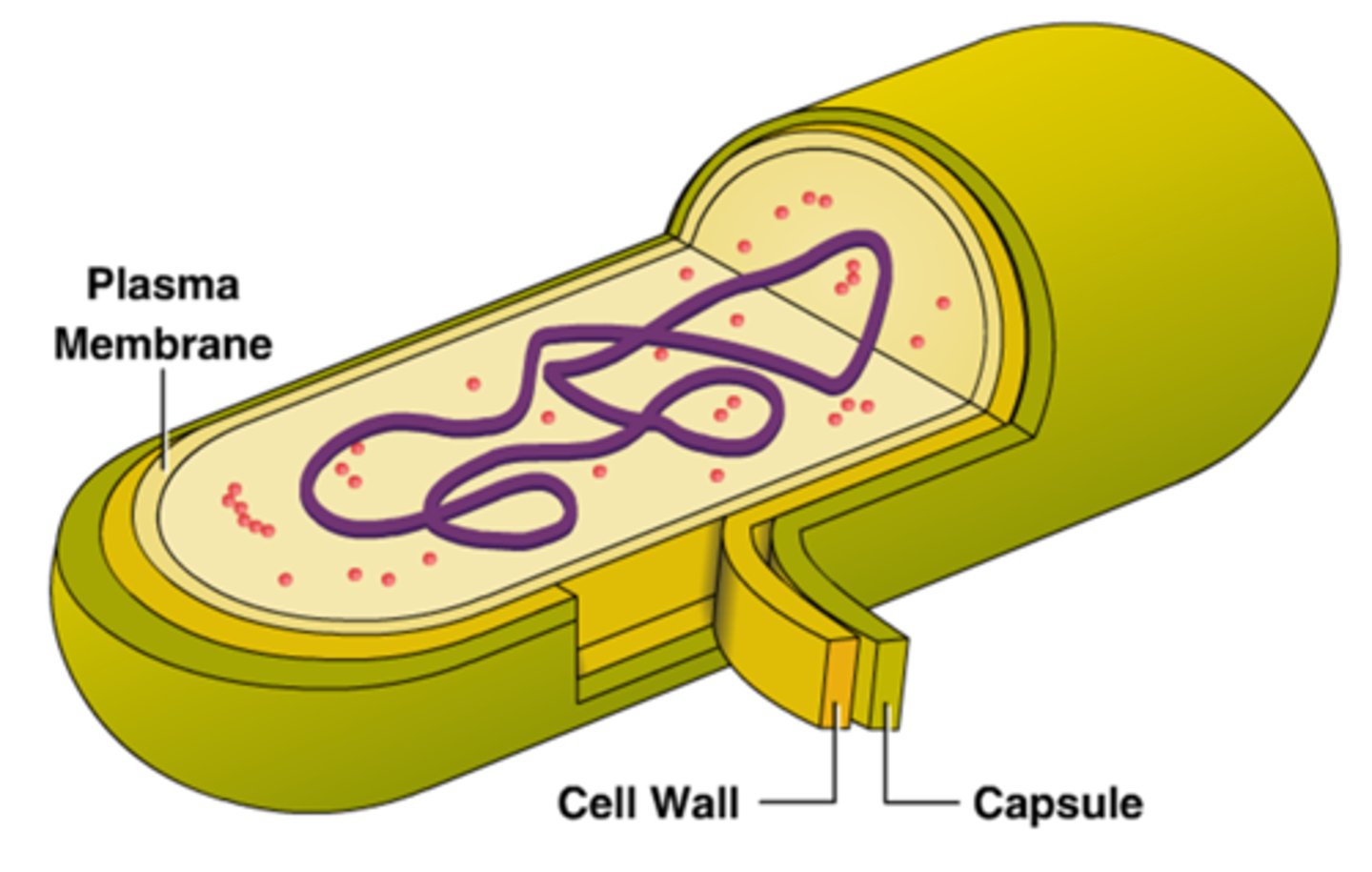
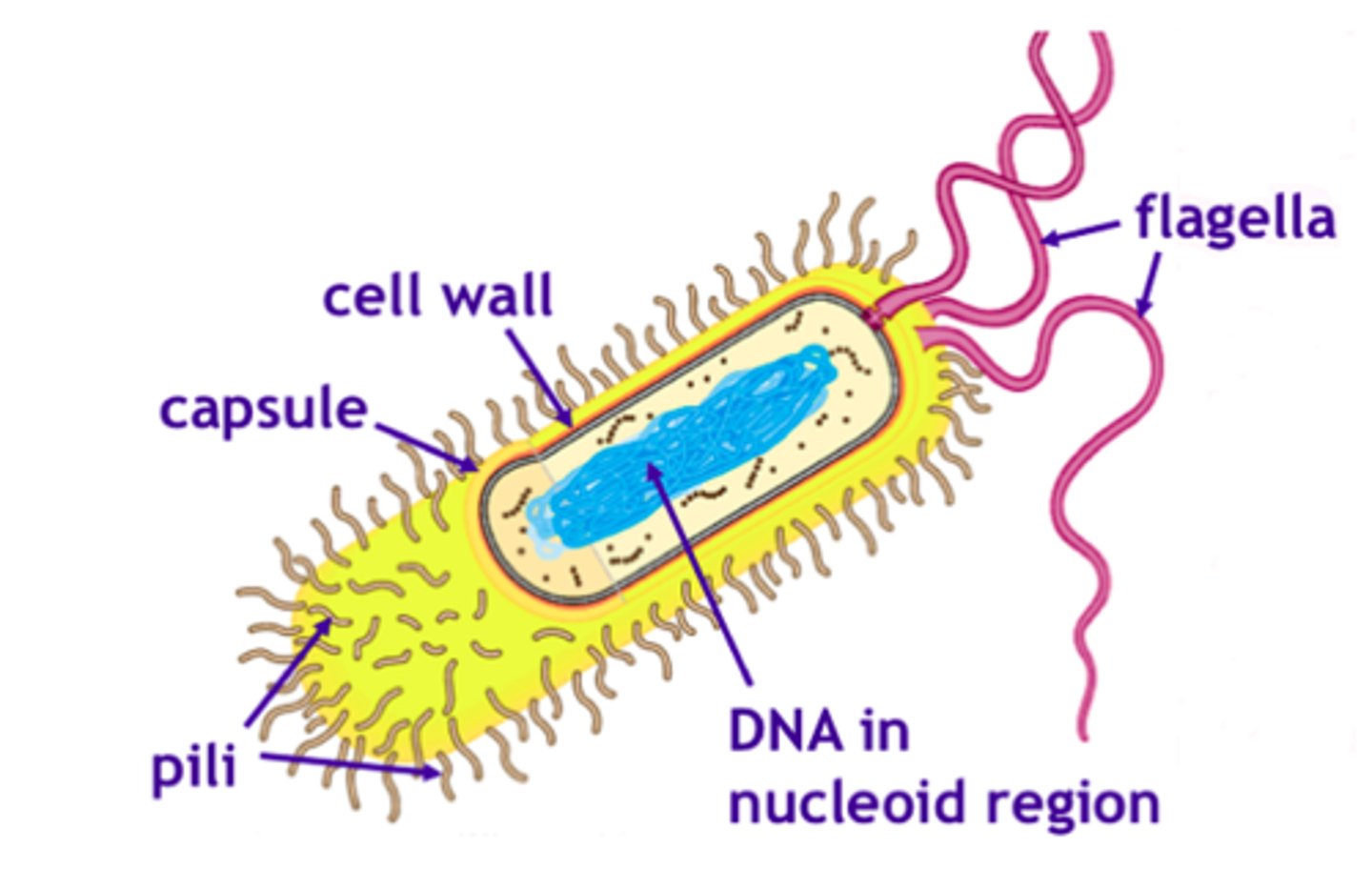
capsule (prokaryotes)
A polysaccharide outer layer that protecting the prokaryotic organisms and allow it to adhere to surfaces.
Flagellum (prokaryotes)
A long, hairlike structure that grows out of a cell and enables the cell to move.
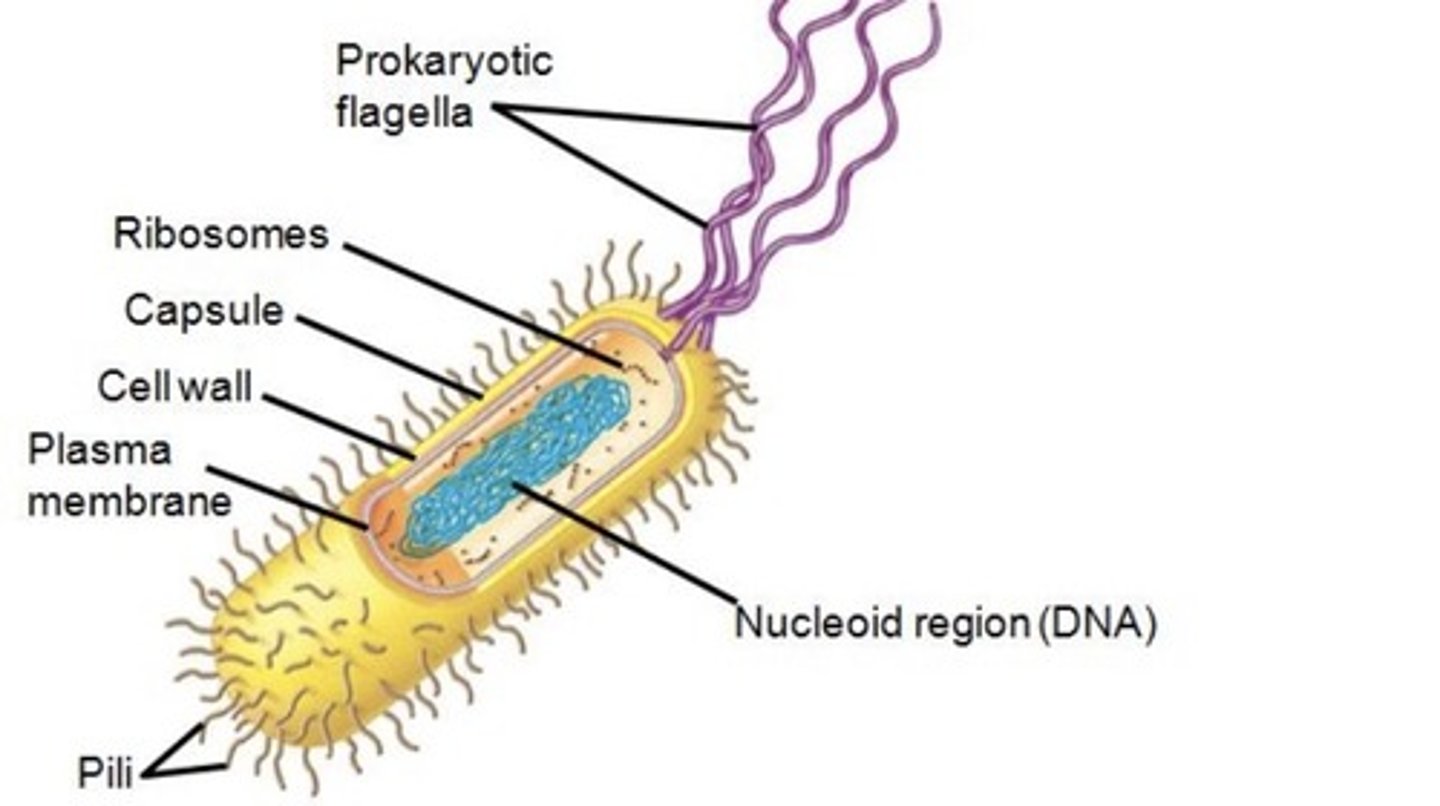
Pili (prokaryotes)
Protein filaments on the cell wall that help with cell adhesion and transferring of DNA between two cells.
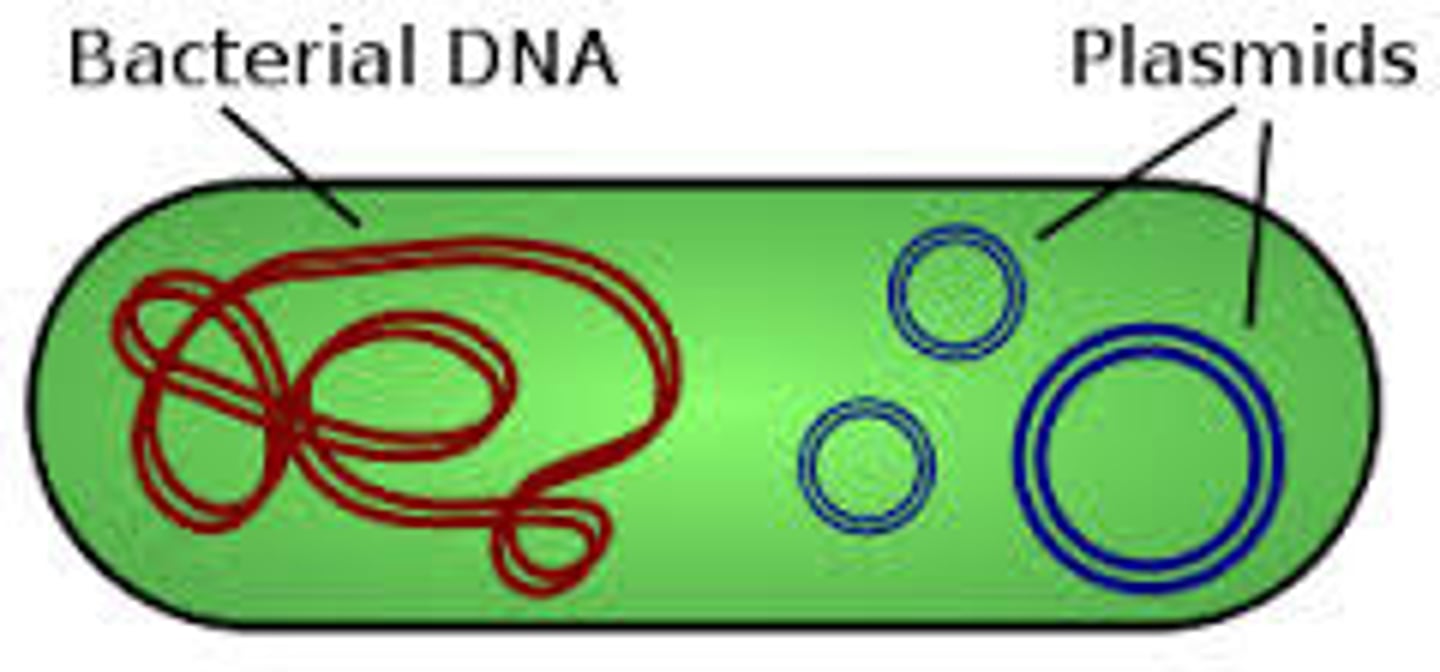
plasmids (prokaryotes)
small circular DNA molecules that can be transfered from one prokaryotic cell to another, through a process known as horizontal gene transfer.
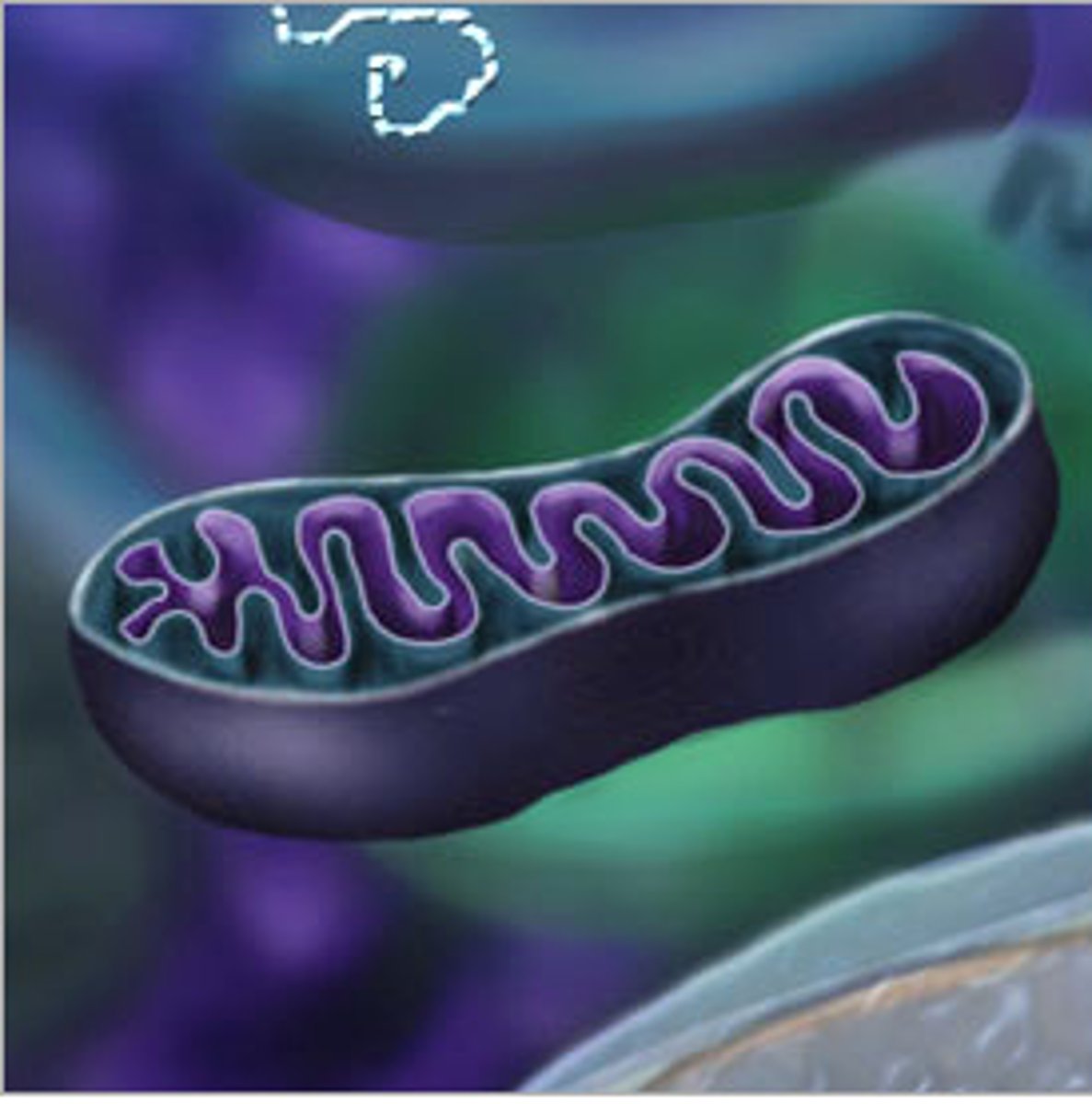
Mitochondria
membrane-bound organelle that converts glucose into ATP in the process of respiration
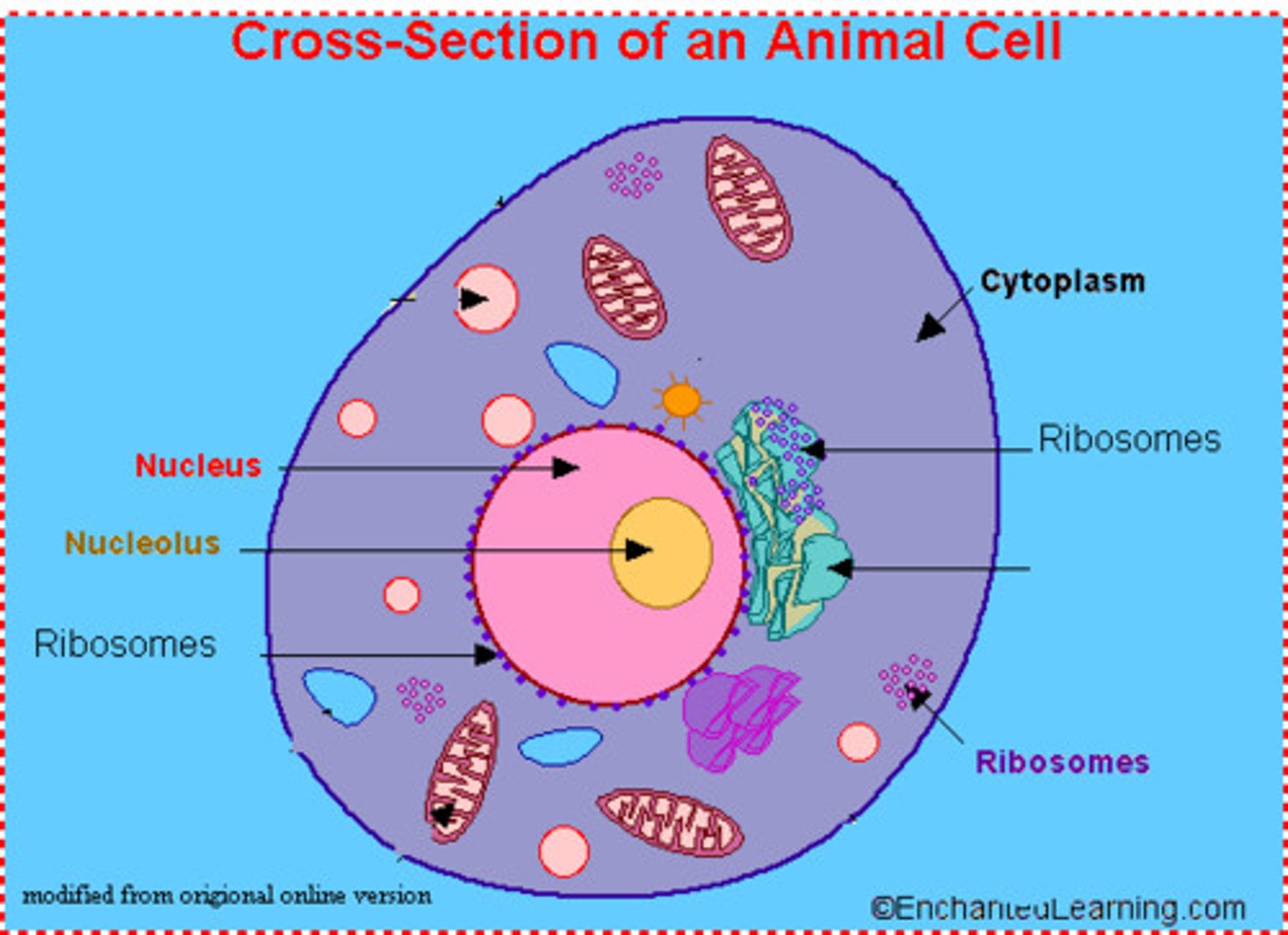
ribosomes
site of protein synthesis
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (SER)
has few or no ribosomes on its surface and synthesizes lipids, including steroids hormones. it also detoxifies chemicals
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (RER)
the region of the endoplasmic reticulum that is studded with ribosomes which engage in protein synthesis.
vesicle
Small, membrane-bound sacs within the cell that transport and store various molecules.
Golgi apparatus
A system of membranes that modifies, processes, and packages proteins for export by the cell
Vacuole
Membrane-bound organelle that helps to maintain the osmotic balance of the cell. Can also store substances.
Lysosomes
Compartmentalised spaces within cells that are responsible for breaking down and recycling waste materials.
Cytoskeleton
Made up of microtubules and microfilaments. It provides shape and allows for the movement of molecules around the cell.
centrioles
Cylindrical organelles that help to establish and organise the microtubules, playing an important role in cell division.
microtubles
long strands such as spindle fibers that move chromosomes
what is not considered a organelle? (the 3 C's)
cell wall: extracellular
cytoskeleton: not discrete enough
cytoplasm: not discrete enough
Processes of life in unicellular organisms (MR HM GREN)
Metabolism: chemical reactions in an organism that convert food to energy.
Response to stimuli: Reacting to changes in the external environment
Homeostasis: maintenance of constant internal optimal conditions, despite changes in external environment
Movement: living things have some control over their place and position
Growth: Can occur either through cells increasing in size, or an increase in the number of cells that make a multicellular organim.
Reproduction: the production of offspring. Reproduction can be sexual or asexual
Excretion: the removal of metabolic waste products
Nutrition: the intake or production of nutrients. Heterotrophic organisms obtain their nutrients from the external environment, whereas autotrophic organisms are able to produce nutrients from inorganic material
differences in eukaryotic cell structure between animals, fungi and plants
all:
contain nucleus, mitrochondria, can contain vacuoles, 80S ribosomes and plasma membrane.
similarities:
- both animal and fungal cells have centrioles.
-fungal and plants have cell walls.
differences:
- fungal has cell wall made of chitin. plants have cell wall made of cellulose. animals have no cell wall.
- only plants have chloroplasts.
- only animals have lysosomes and cilia.
- animal vacuoles are smaller than vacuoles found in plant cells.
multinucleate
many nuclei
anucleated
No nucleus
examples of atypical cell structures
red blood cells: anucleated- can't replicate, greater haemoglobin capacity and transport more oxygen.
skeletal muscle- multinucleated because of their wide length- speeds up processes.
hyphae of fungi- multinucleated because of their wide length- speeds up processes.
Sieve tube elements in the phloem of plants- anucleated to successfully transport sugar.
SA to volume ratio in cells
determines the efficiency of diffusion.
the lower surface area to volume ratio, the rate of diffusion decreases (less area available for substances to enter the cell but more volume these substances need to diffuse into).
because of this, cells are usually small and have specialised structures that can increase their surface area-to-volume ratio.