A+ Jason Dion (220-1101) Complete Course Exam with complete accurate questions and answers ( 2025-2026 latest release )
1/80
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
81 Terms
IoT (Internet of Things)
a large network of physical objects including sensors and equipment
driver
A small program that instructs the operating system on how to operate specific hardware.
Frimware
Specialized type of software on a chip
Troubleshoot Steps
Identify the problem
Theory
Set up Plan
Verify full system function
Document finding
what is
B=
b=
B= Byet
b= bit
DB9
connectors used for a mouse

DVI
Digital Visual Interface - used to connect a video source, such as a video display controller, to a display device, such as a computer monitor.
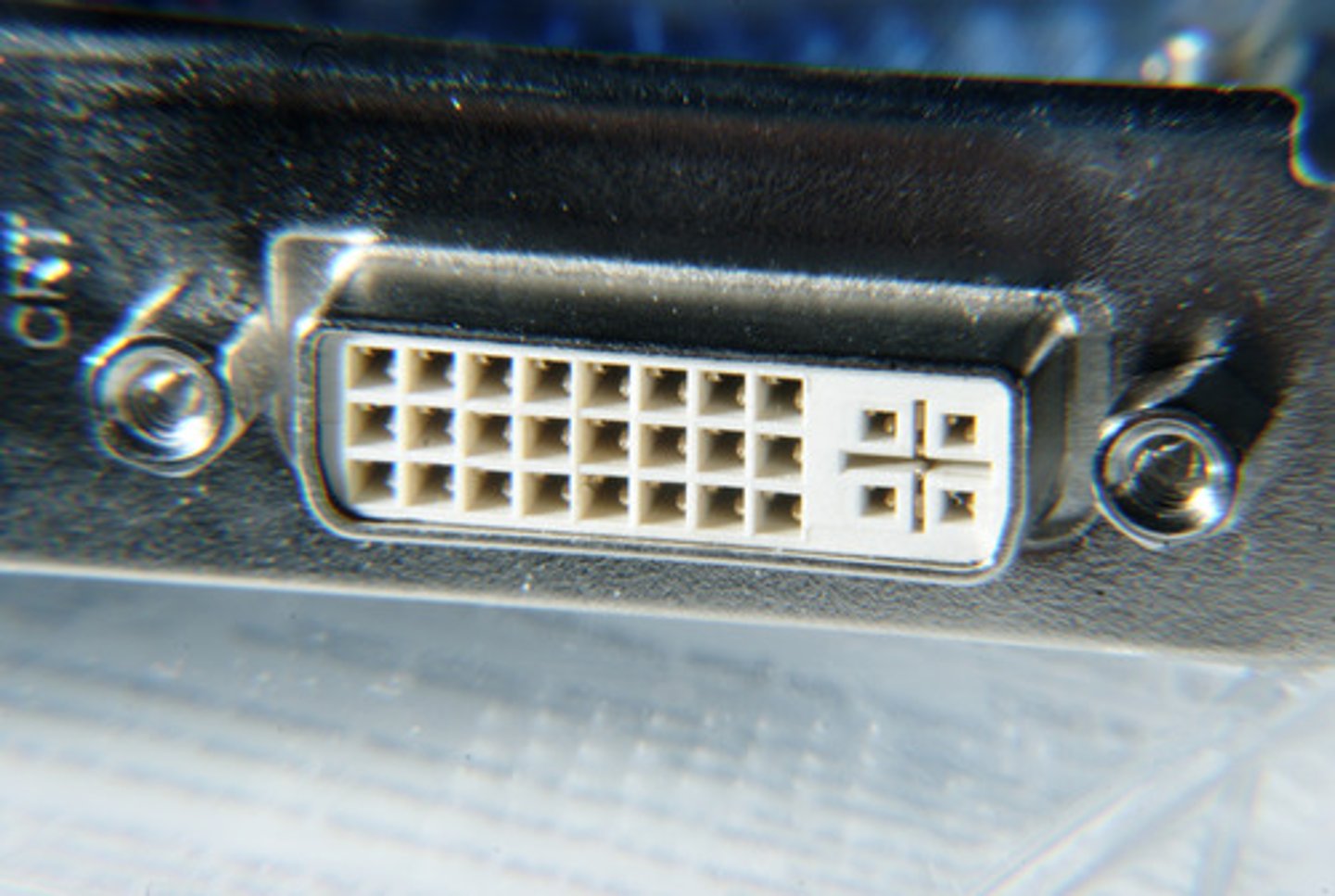

DVI-D
A DVI (Digital Visual Interface) video port that works only with digital monitors.
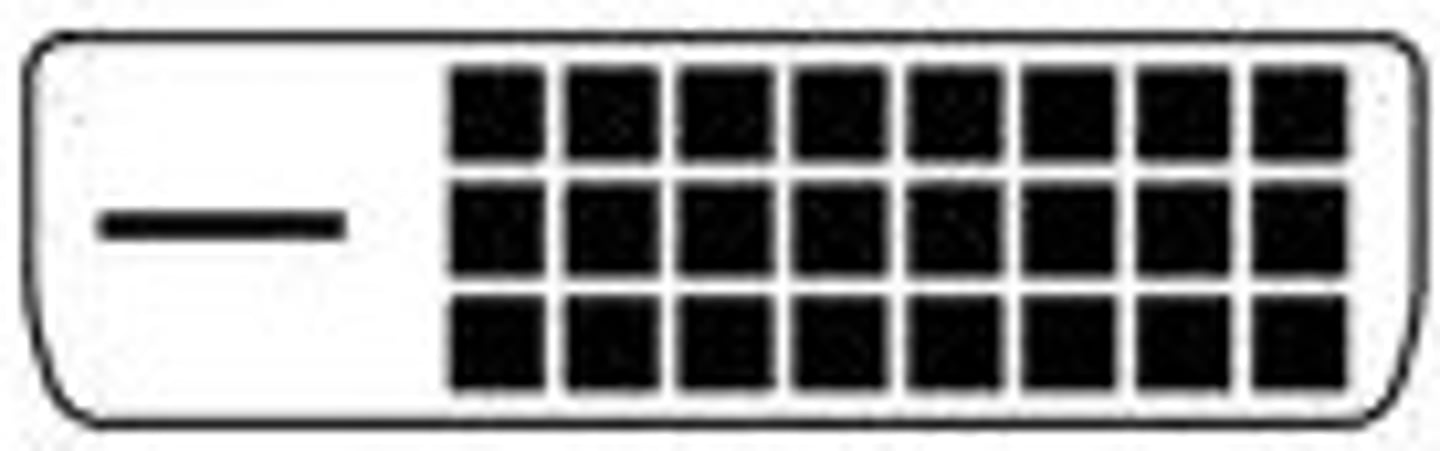
DVI-A (Analog)
Provides an analog video signal. Used by older HDTVs. Cables typically have a DVI-A connector on one end and a VGA connector on the other. Maximum supported resolution of 1920 × 1200 @ 60 Hz
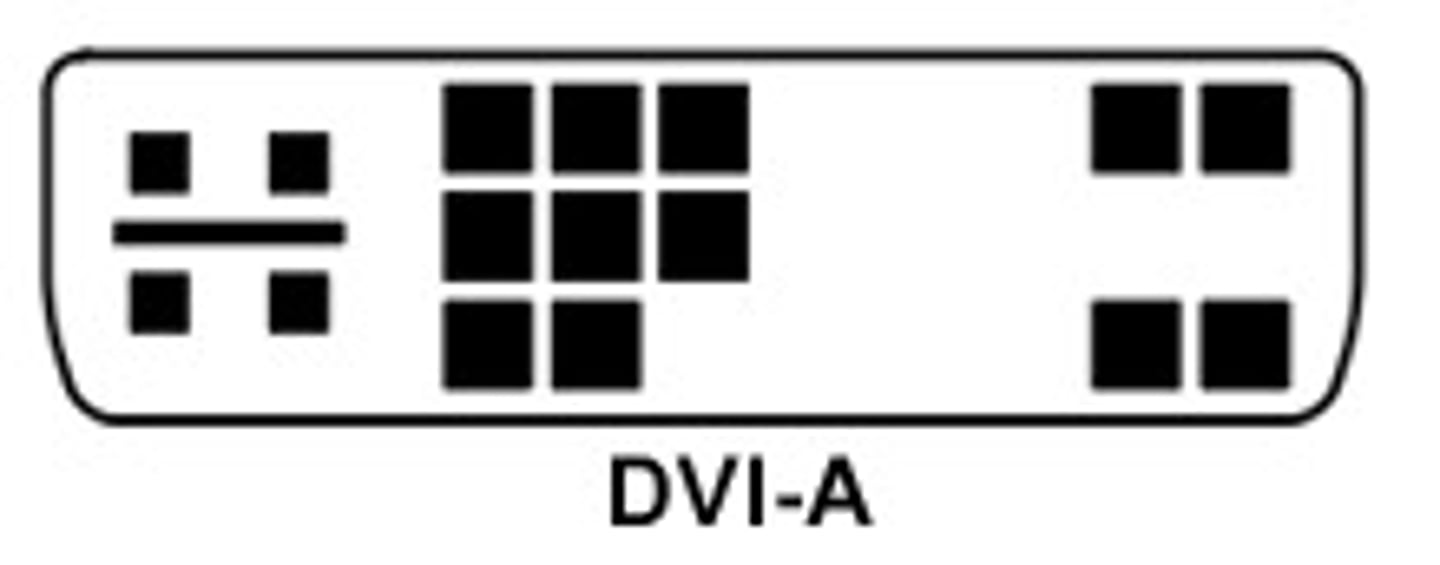
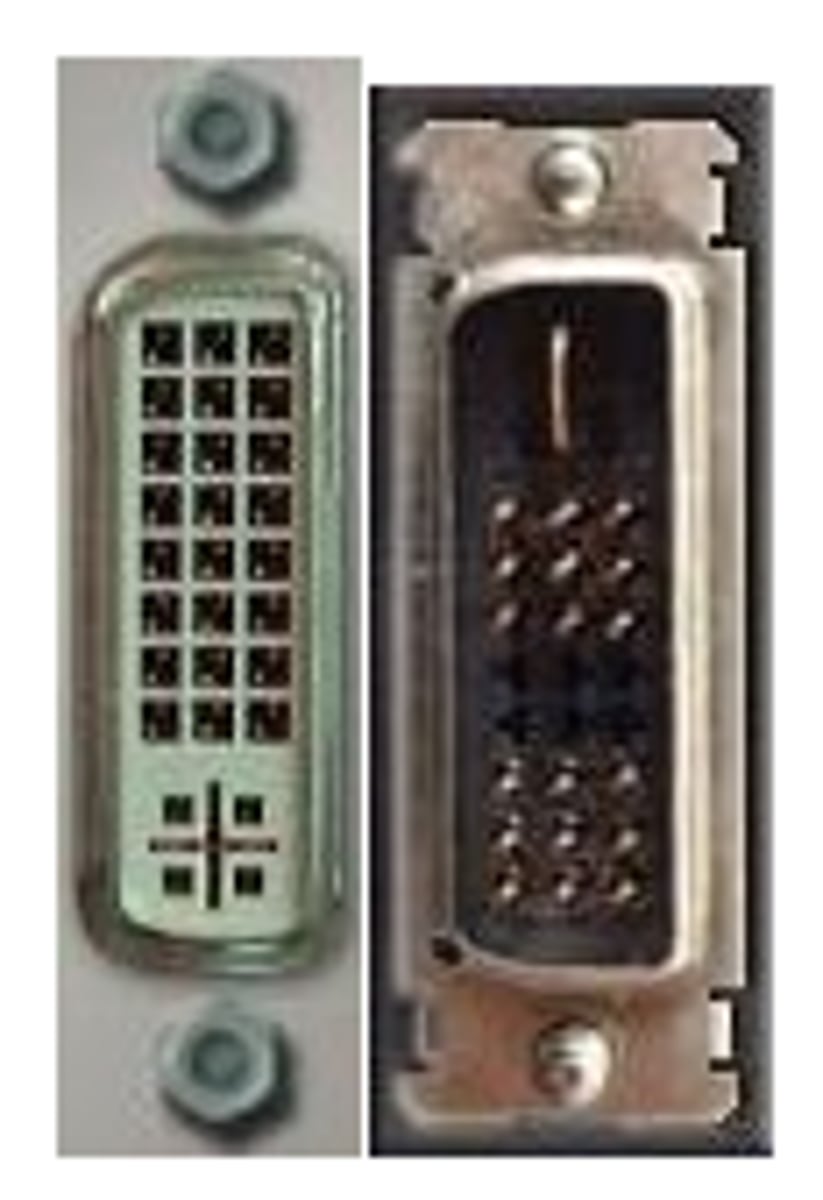
DVI-I
A DVI (Digital Visual Interface) video port that supports both analog and digital monitors.

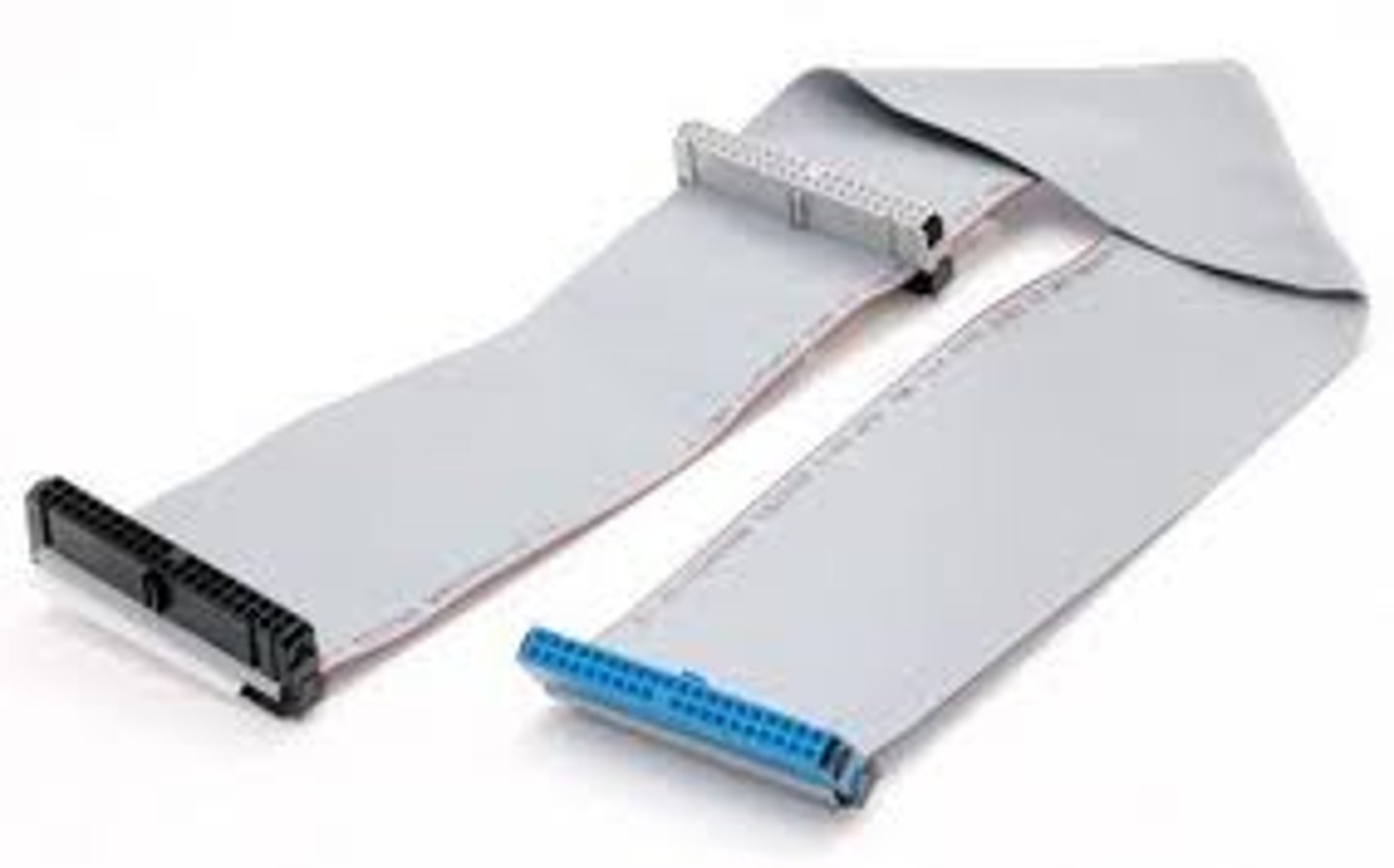
PATA
flat parallel connectors

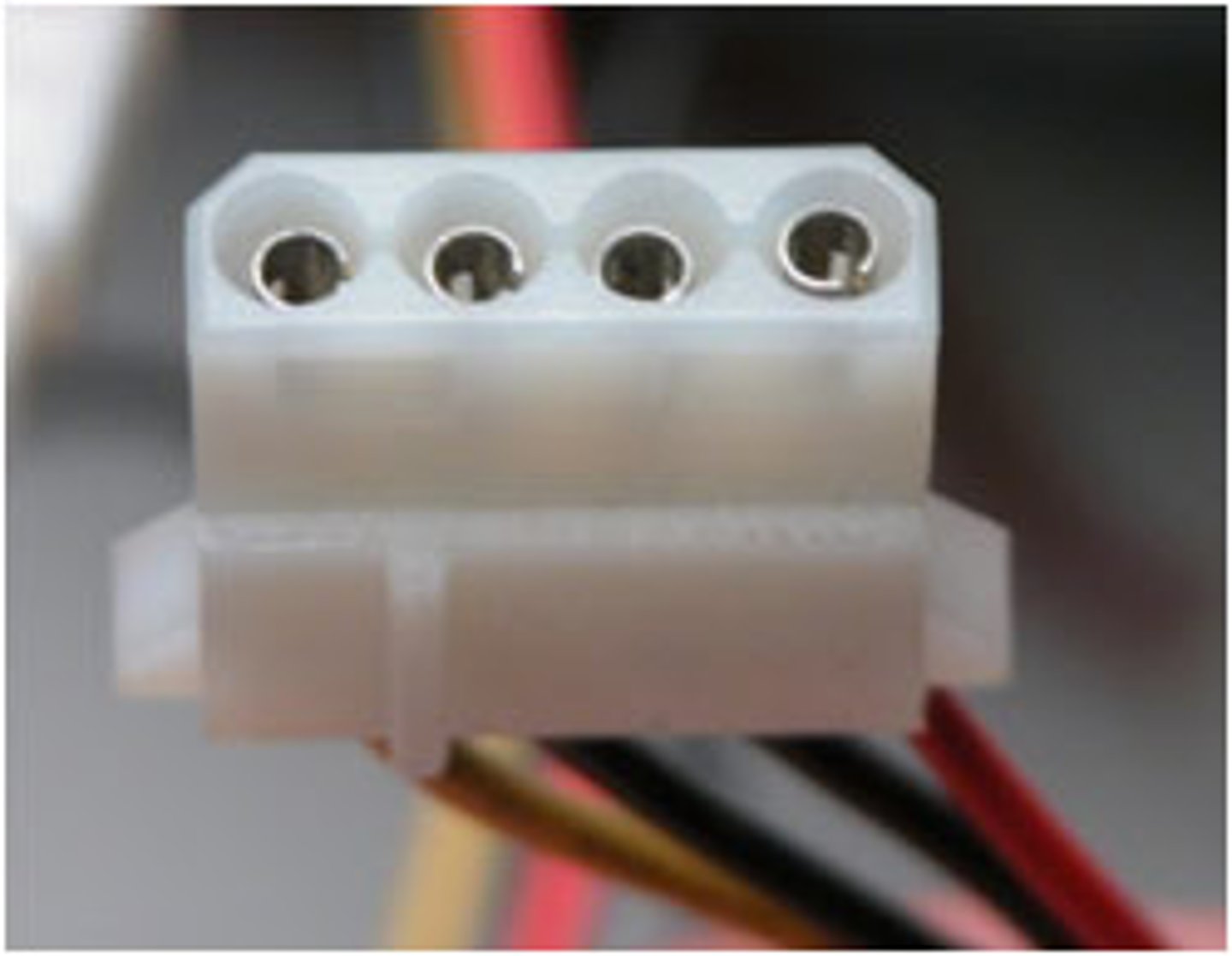
Molex power connector
A 4-pin power connector used to provide power to a PATA hard drive or optical drive.
how long is USB 1.0
3 meters
how long is USB 1.1
how long is USB 2.0
temporary storage
RAM / Non persistent
how long is USB 3.0 and how long is USB 4
permanent storage
Permanent storage remains active when the computer is on and when it is off. Hard drives and solid state drives are permanent storage devices.

volatile storage
Temporary storage, such as in random access memory. When the power is off, the data in volatile storage is cleared out.
non-volatile storage
Storage which does not lose its contents when the power is removed.
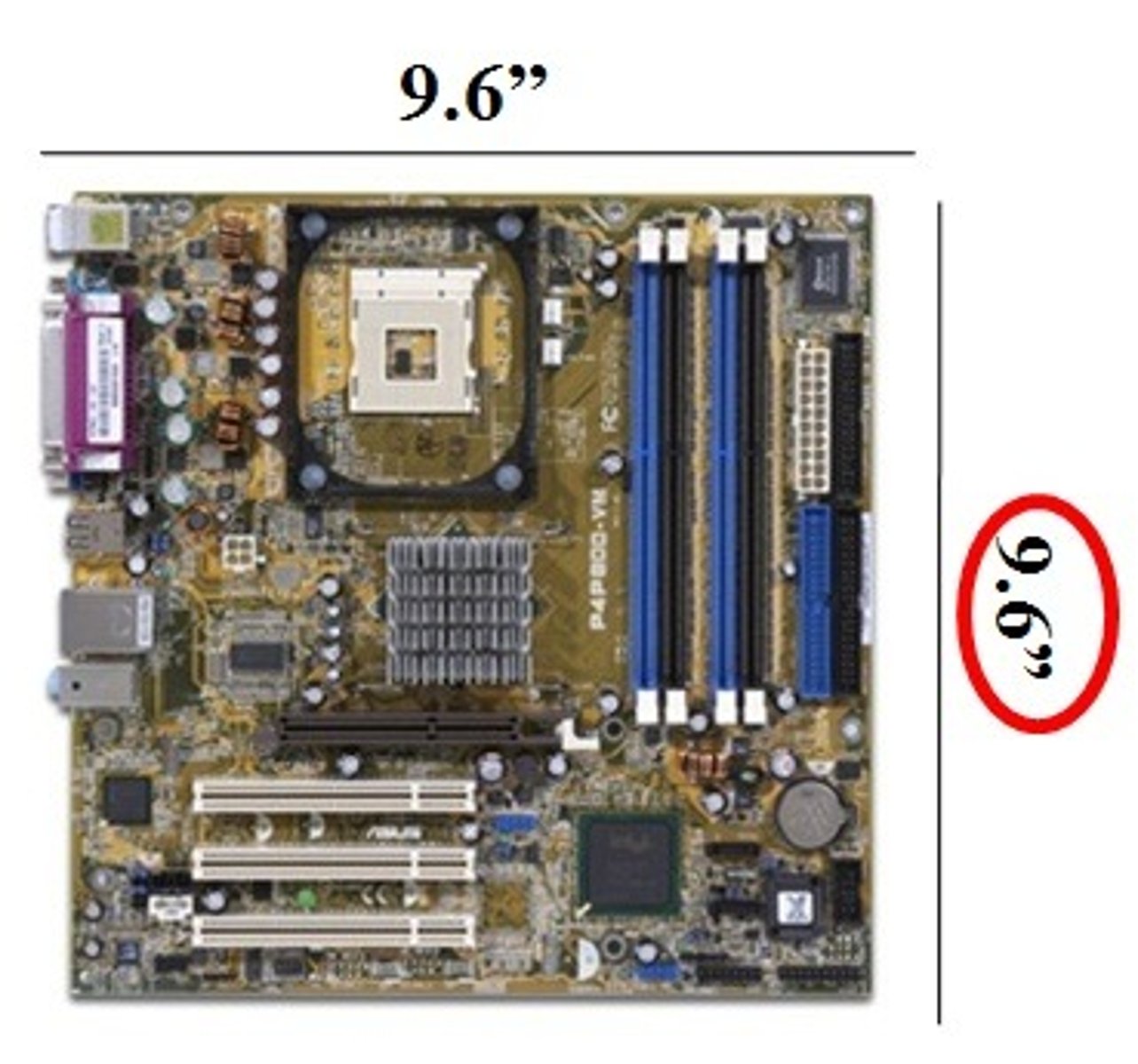
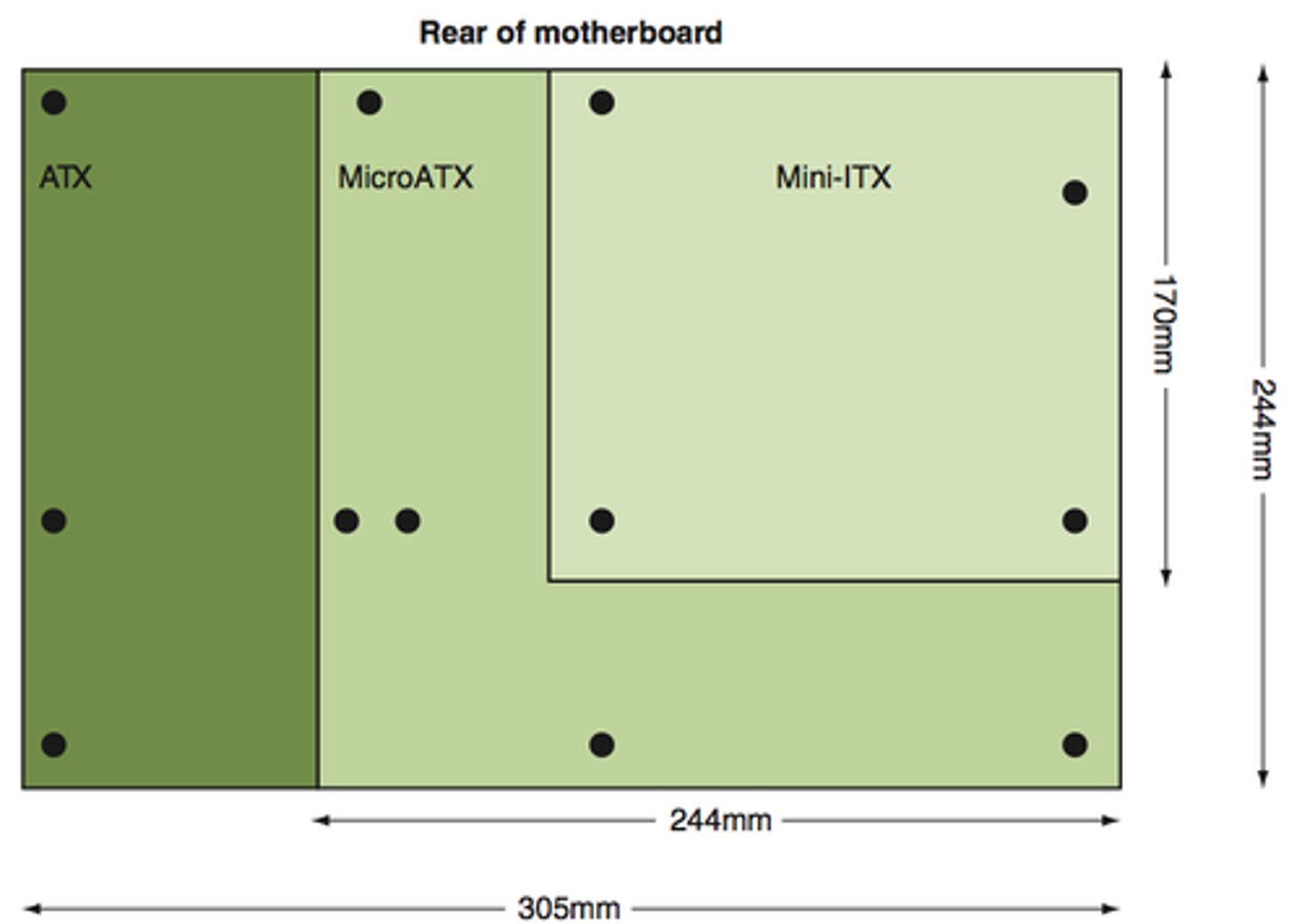
ATX Motherboard
Most popular motherboard type, 12 in X 9.6 in
Mini-ATX
A smaller variation of the ATX standard.
• Measures 11.2" x 8.2"
• Lower number of bus and possibly memory slots on the motherboard.
• Mounting holes for both are located in the same place.
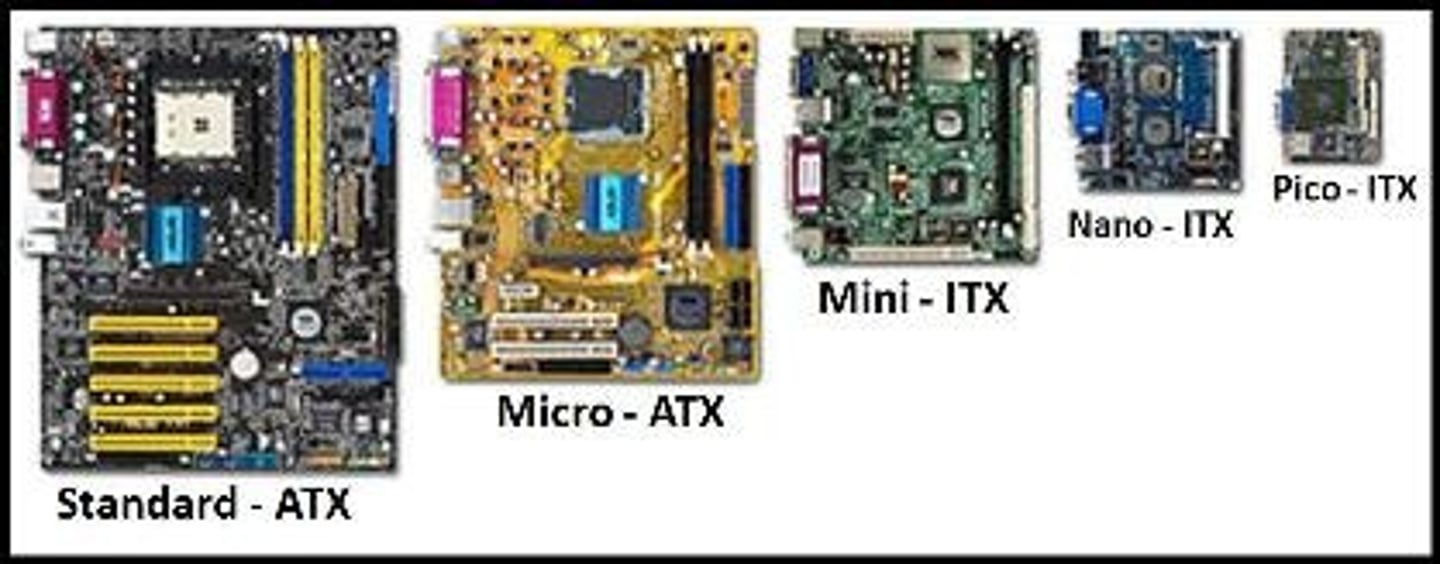
Micro-ATX
A smaller variation of the ATX standard.
• Maximum size of 9.6" x 9.6".
Designed to keep the same benefits of ATX but reduce overall cost. Less I/O slots and smaller motherboard. Still good for games.
• Mounting holes for both are located in the same place.
ITX (Information Technology Extended)
Smaller form factor than any ATX, this form factor was released to meet the needs of very small (SFF-Small Form Factor) PCs.
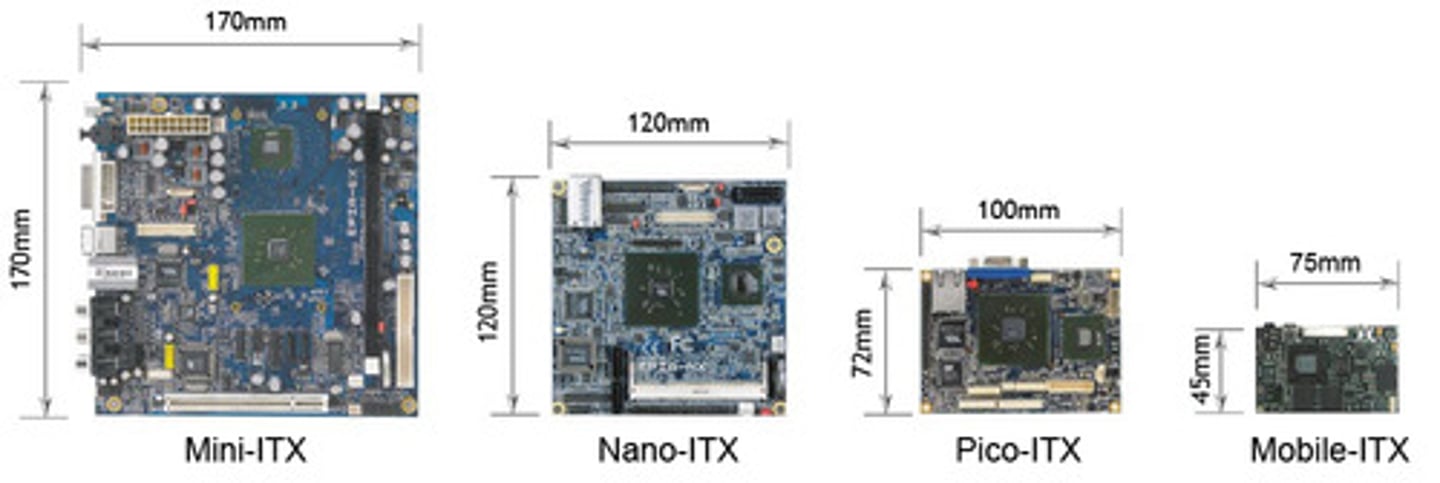
Nano/Pico/Mobile ITX
used for Smart phones/ smart devices
CPU (Central Processing Unit)
The internal operating unit or "brain" of a computer.
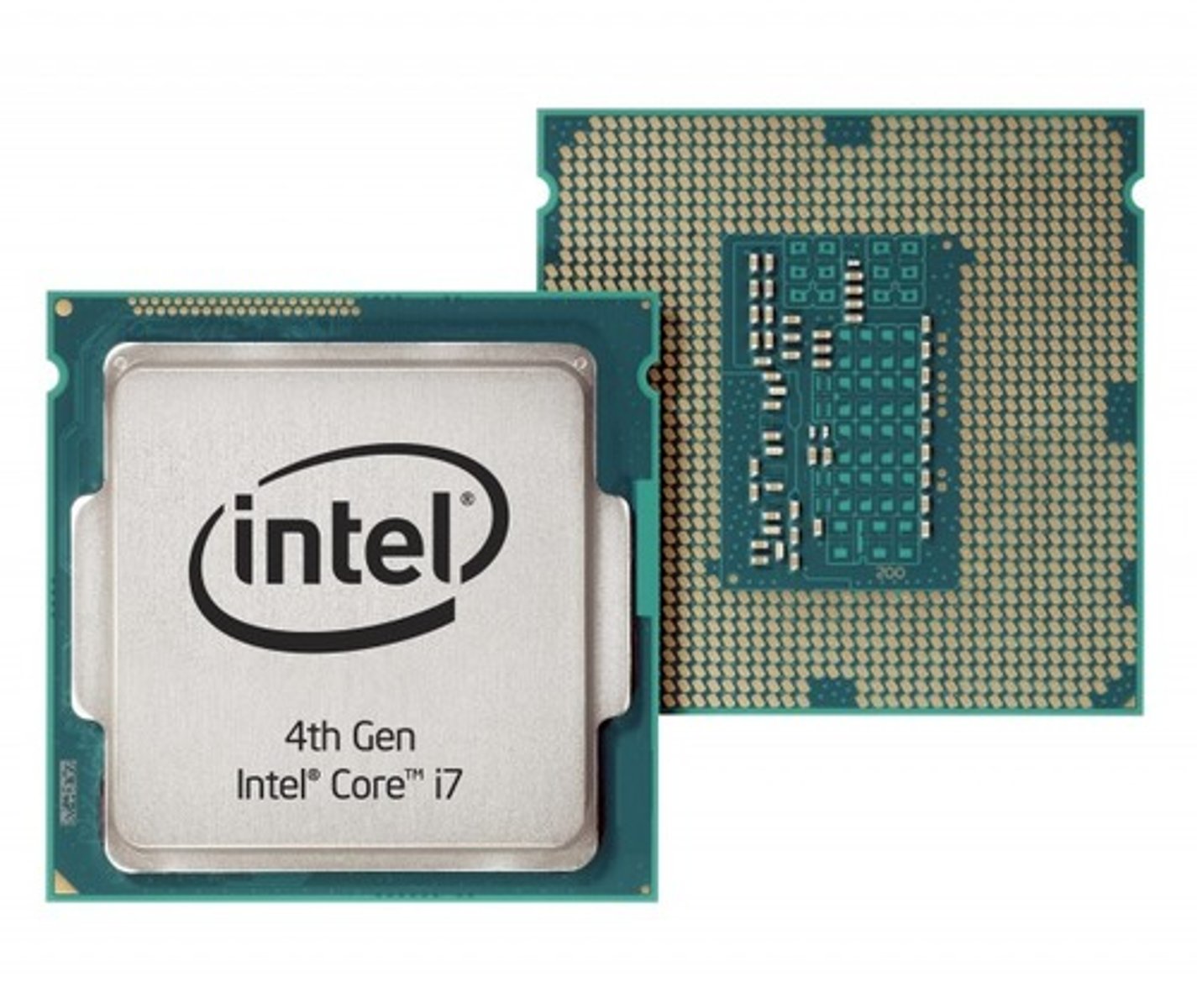

x86 processors
A family of processors manufactured by Intel and AMD that use a common instruction set (list of commands that the processor can execute).
uses a 8, 16, 32 bit processor

x64
Indicates a 64-bit processor supporting a 64-bit operating system. 64-bit versions of Windows can run on x64-based systems.
Advanced RISC Machines (ARM) Processors
ARM processors use a reduced instruction set, which means they can't do as many types of things as x86 processors. The tradeoff is that they are smaller, consume less power, and generate less heat.
CPU Socket
The connector on the motherboard that houses a CPU and forms the electrical interface and contact with the CPU.
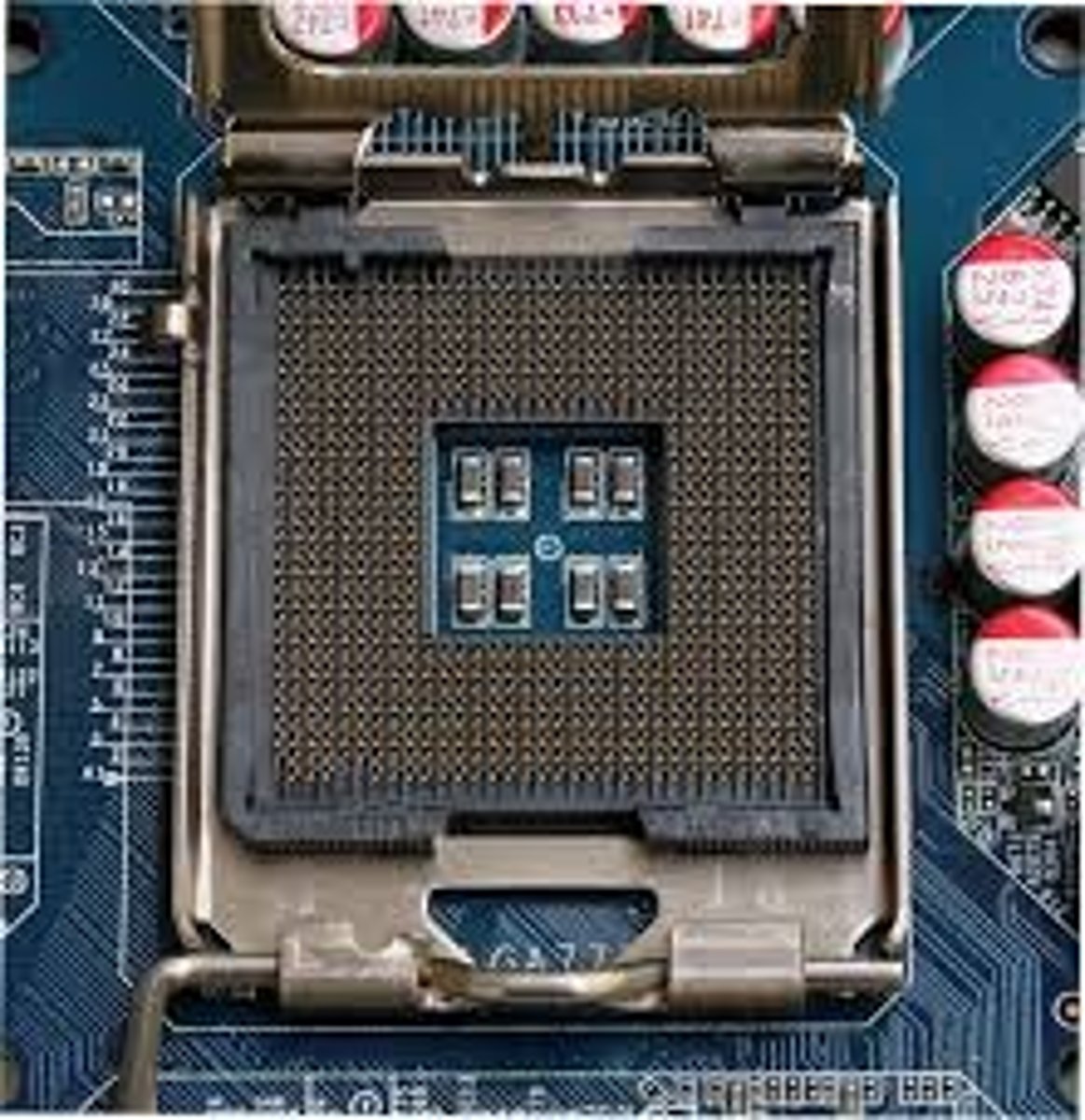

ZIF
Zero Insertion Force
Land Grid Array (LGA)
-Does not contain any pins
-CPU is completely flat
-All pins are located on the motherboard CPU socket
-Possible damage to the CPU socket if objects are dropped onto it (pins can bend)
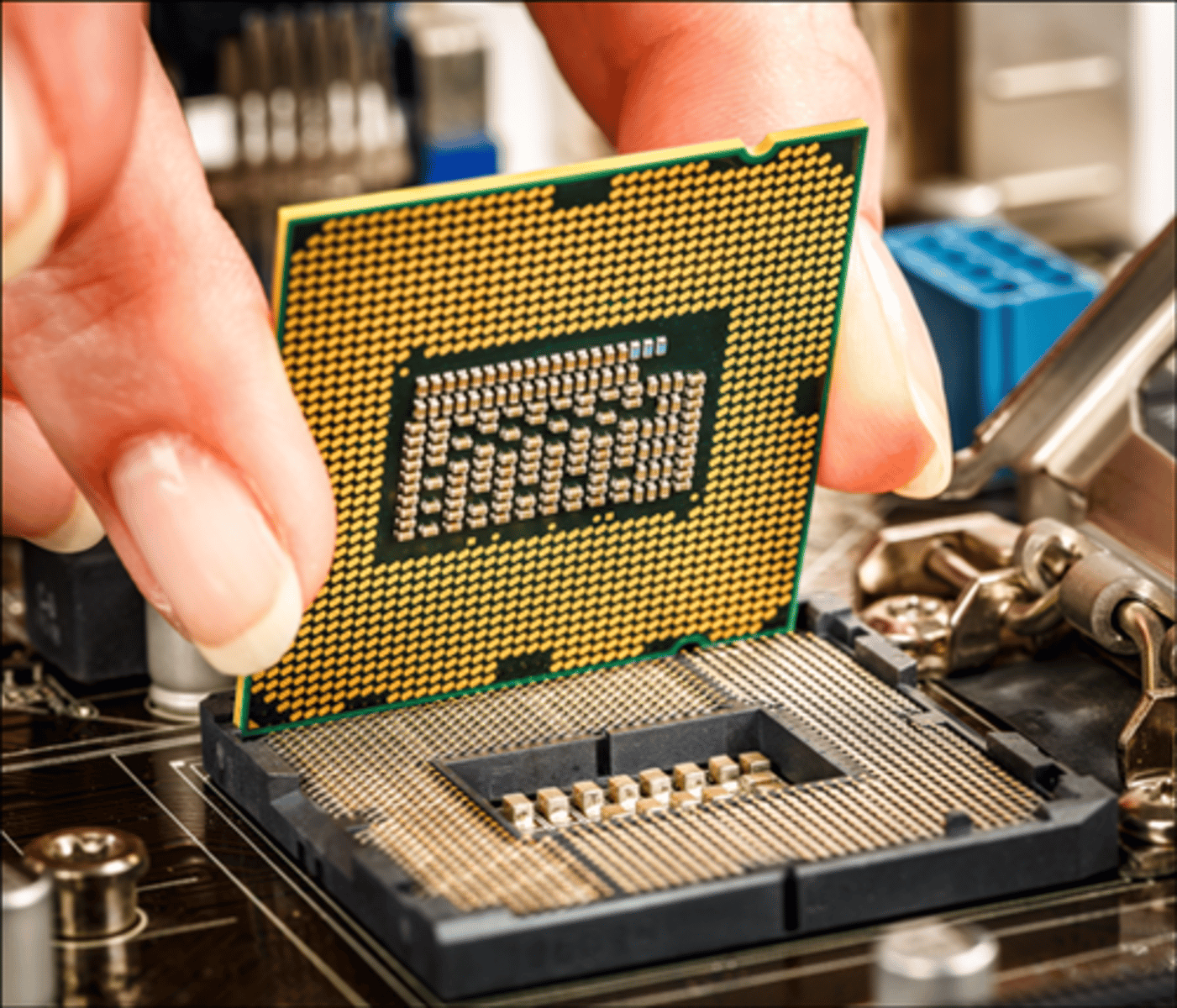
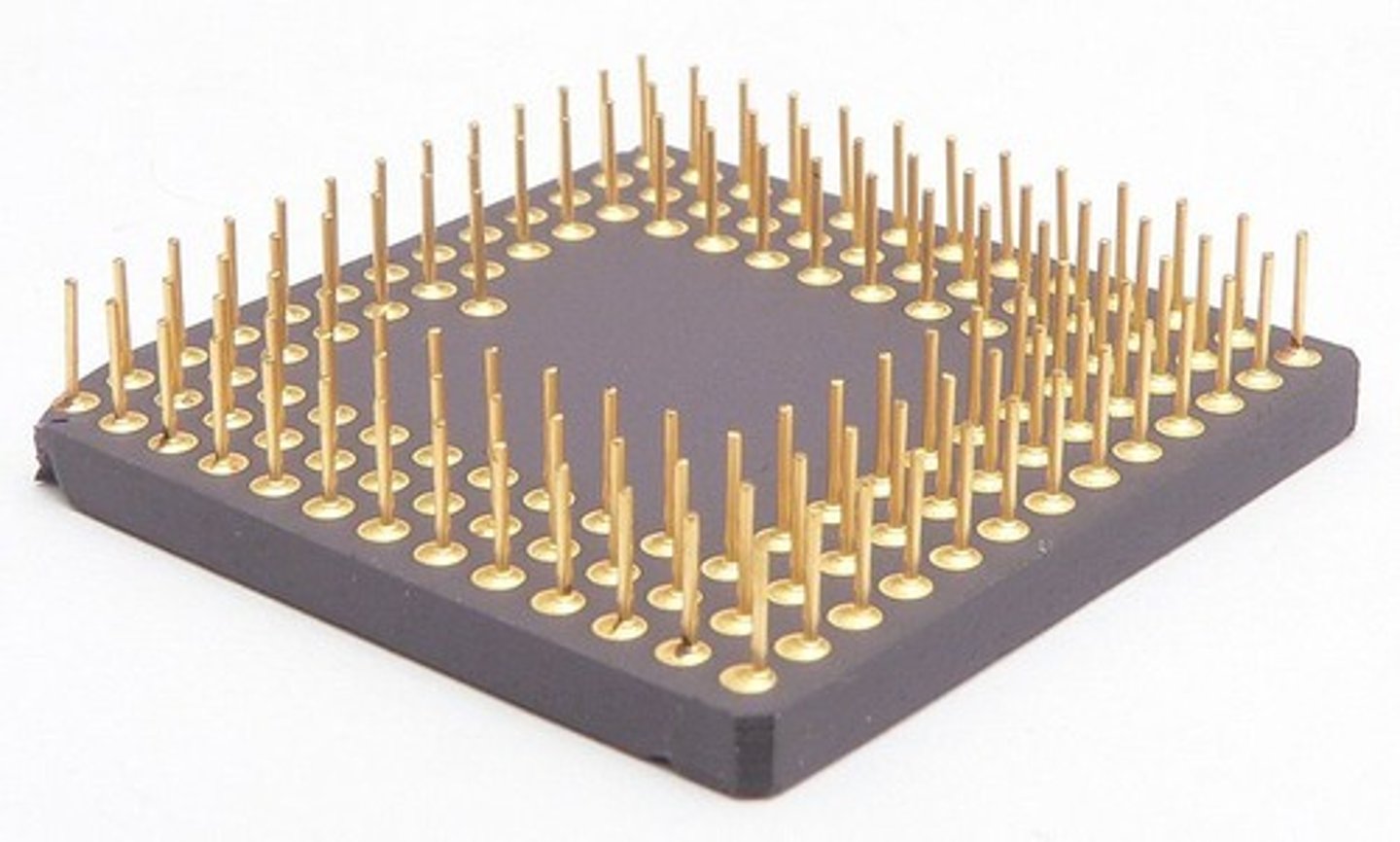
pin grid array (PGA)
-Many pins that are underneath the CPU
-CPU socket matches the pins on the CPU
-Plugs into a ZIF socket
-Possible damage to the CPU if not inserted correctly
multi socket plug
multiples CPus in a motherboard go in to a
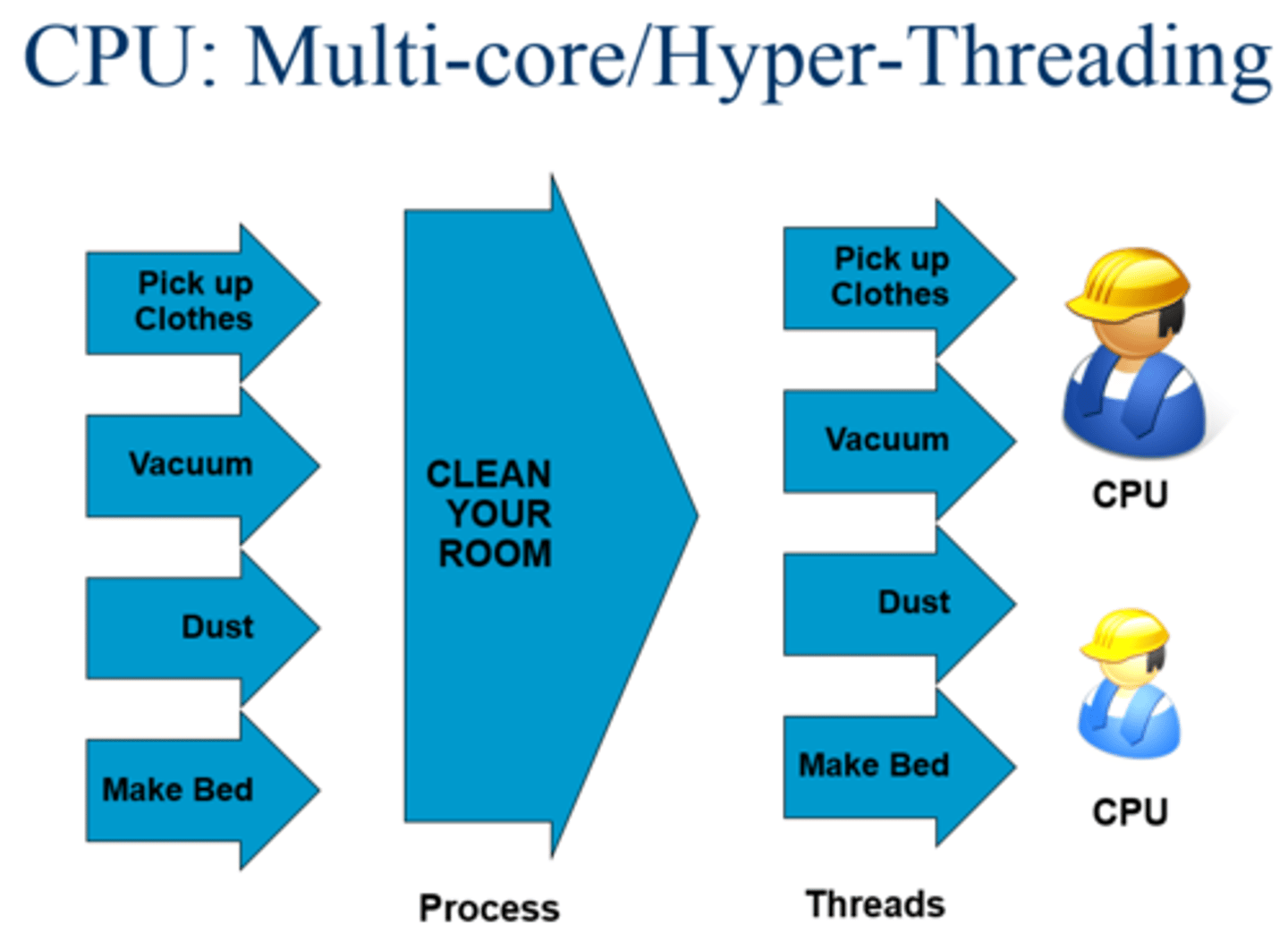
Hyper-Threading
A CPU technology that allows two threads to execute at the same time within a single execution core. This technology is considered to be partially parallel execution. Intel introduced it in the Pentium 4 Xeon CPU. Also known as simultaneous multithreading (SMT). (1)
SMP
Symmetric Multiprocessing / used on workstations
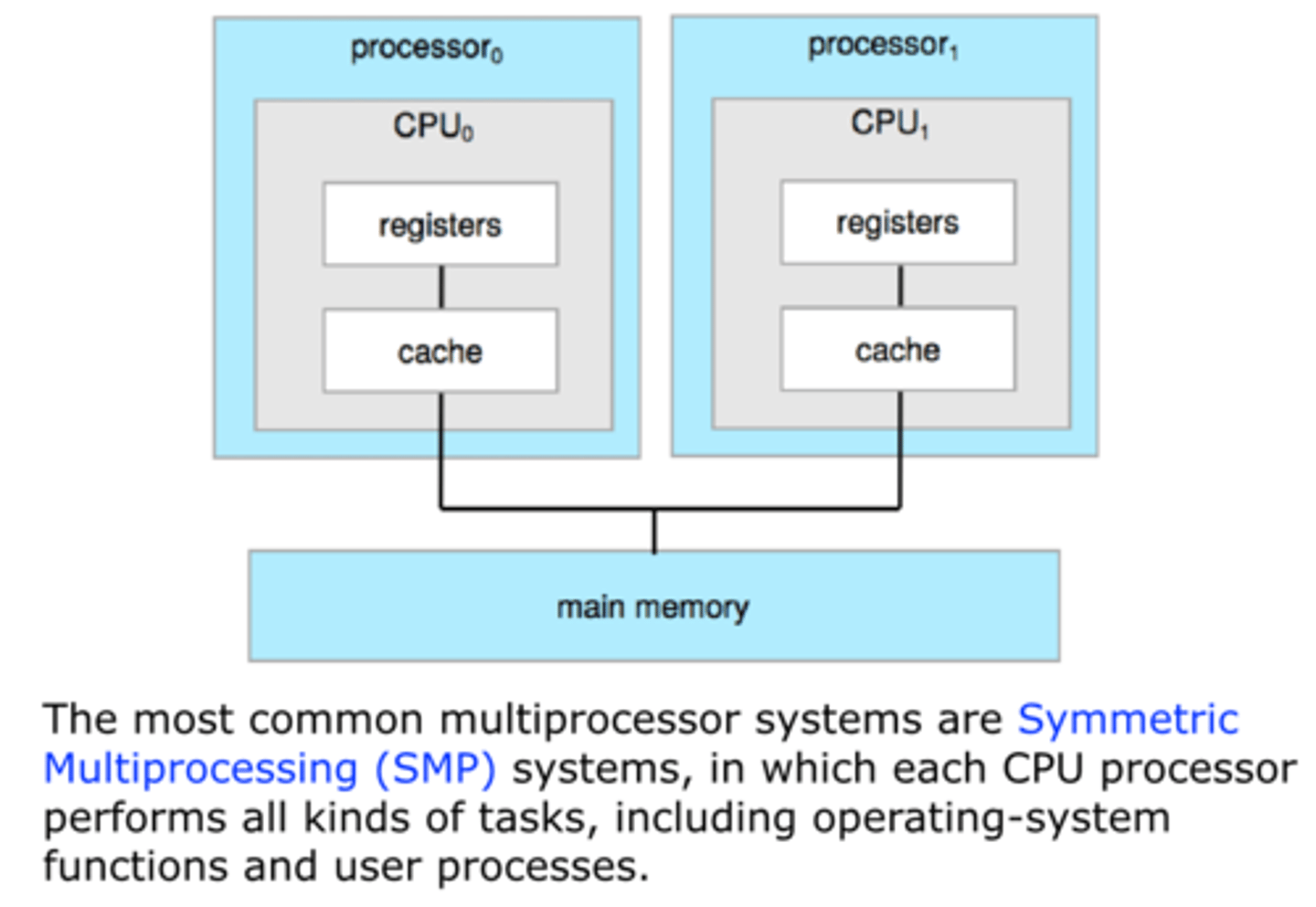
Multi-Processor
More than one processor sharing same memory, also know as parallel systems
dual-core processor
a single chip that contains two separate processors.
quad processor
computer with 4 CPUs
hexa-core
6 cores on single chip
Extended Page Table (EPT)
The term used for SLAT extensions by Intel.
slat
Nested Page Tables supported when Intel® Virtualization Technology
Rapid Virtualization Indexing (RVI)
The term used for SLAT extensions by AMD.
PCIe (PCI Express)
a faster version of PCI used to connect peripheral devices to a computer
common PCie used today
x-1 and x-16
what is PCie x1 used for ?
network cards, modems and input/ output systems
what is PCie x16 used for ?
Graphic cards
how much watts does Pcie x1 provide
25 watts
how much watts does PCIE x16 provide
75 watts
un-plugging / PCIe
putting smaller card in larger port
down-plugging
putting larger cards in smaller slots
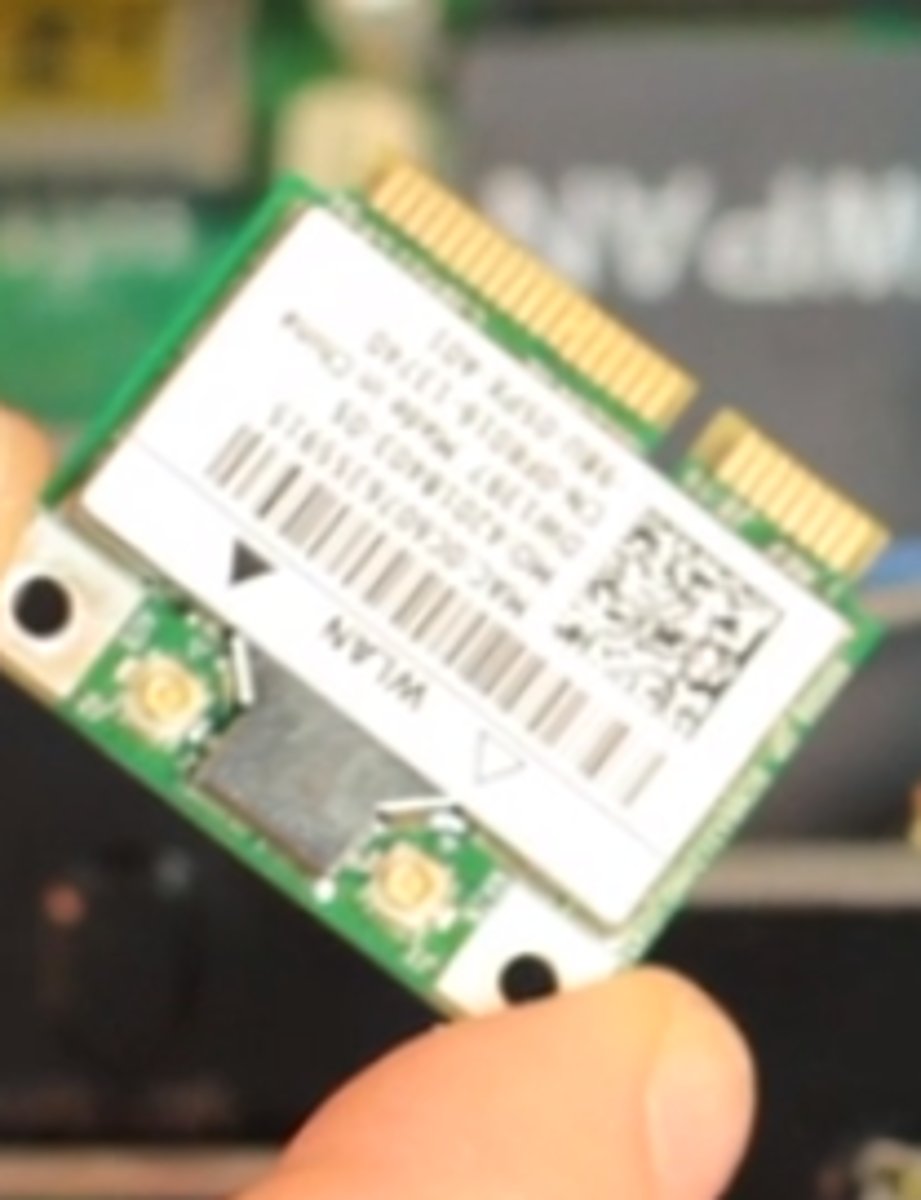
Mini PCI Express
A standard used for laptop internal expansion slots that follows the PCI Express standards applied to laptops.

video card (graphics card)
combines video processing and storage onto an expansion card, or integrates them onto the motherboard to manage video images for display
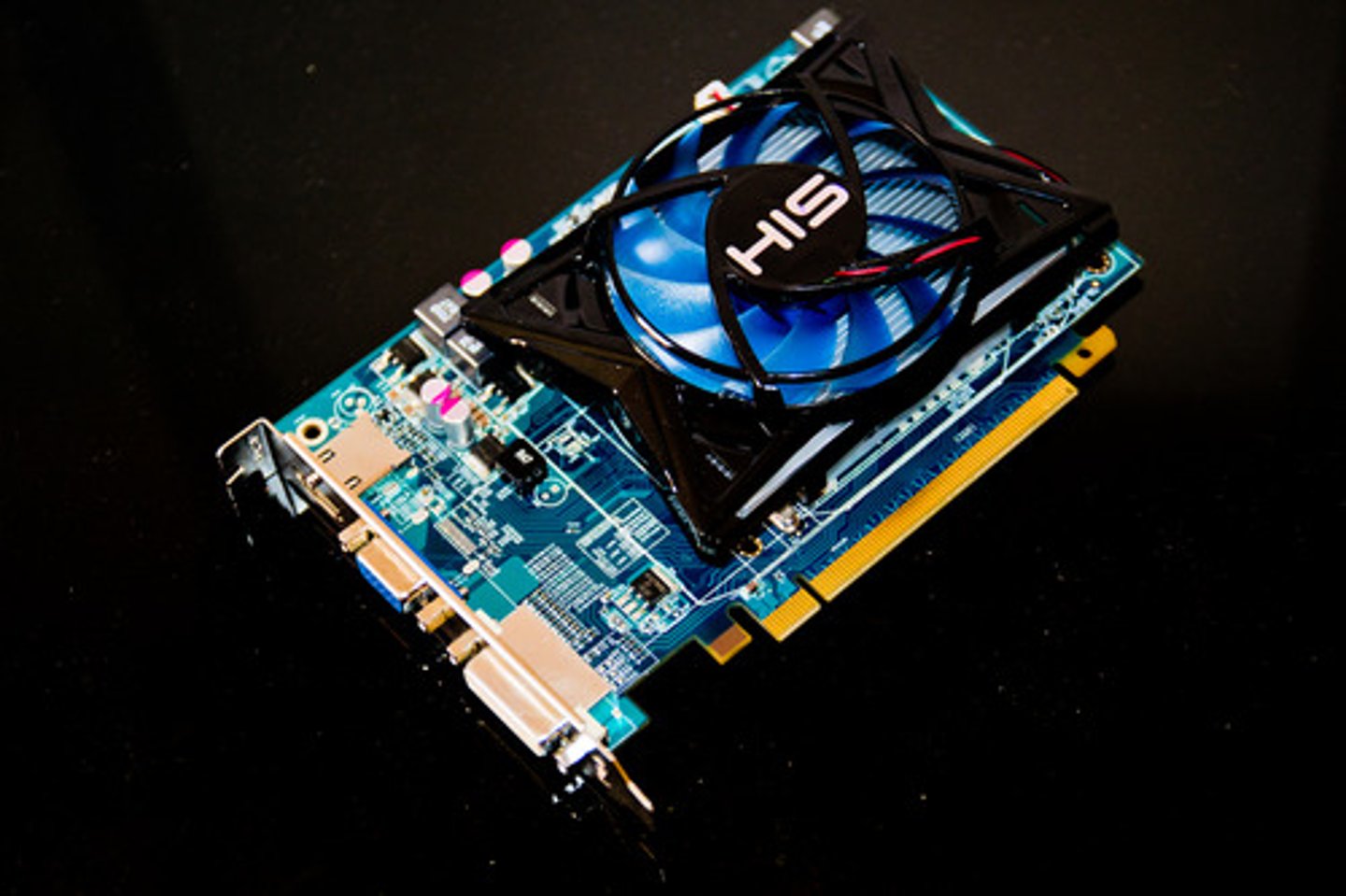

GPU (graphics processing unit)
A processor on a video card used to create graphics. It takes the load off the CPU.
high-speed memory
Dedicated video cards can store data on their own using ___________.
Graphic Port
installed outside of the card
tv capture card
Cables are plugged in to computer to get cable tv
Audio card (sound card)
Gives better Output Audio
Riser Card
A card that plugs into a motherboard and allows for expansion cards to be mounted parallel to the motherboard. Expansion cards are plugged into slots on the riser card.

A "thermal" load is a load that is created through ___
A set of items inside of a CPU heating up
Passive Cooling
A type of cooling process which does not use a fan or other type of forced-air cooling.
Active Cooling
A type of cooling process in which a fan is mounted directly onto a heatsink for forced-air cooling.
Liquid Cooling
A method of cooling a PC that works by running some liquid—
usually water—through a metal block that sits on top of the CPU, absorbing heat. The
liquid gets heated by the block, runs out of the block and into something that cools the
liquid, and is then pumped through the block again.
Closed Loop System
cooling of a sinlge component
Open Loop System
Liquid cooling based system of diffrent things
PSU
Power Supply Unit
AC
alternating current
ATX
A standard PC case, motherboard, and power supply specification. Mini-, Micro-, and Flex-ATX specify smaller board designs. with a 20 pin connector
ATX 12V
24 PIN mother board
Molex connector
Computer power connector used by optical drives, hard drives, and case fans. Keyed to prevent it from being inserted into a power port improperly.
Y connector
A connector that has three wires with a connector on the end of each. All the wires are tied together in the middle. The three ends of a Y-connector are used to split one signal into two signals, or to combine two signals into one.

USA voltage
120
Europe and Asia voltage
230
volt sensing
Detects the outlet and converts
12 VDC Rail
common rail used in PC
RAM
Random Access Memory
Addressing memory
Processor reaching the files inside RAM
cache
High speed Memory
mass storage devices
Devices such as file servers, RAID systems, tape libraries, optical jukeboxes, and more.
disk cache
Storage space on a computer hard disk used to temporarily store downloaded data.
Addressing Memory
Processor reaching the files inside RAM
single channel memory