chapter 8: genetic analysis + mapping in bacteria and bacteriophages
1/96
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
97 Terms
importance to study bacteria and viruses
-disease causing agents, so important study subjects
-useful genetic models
special features in Prokaryotes
-haploid DNA (no homologous chromosome)
-no mitosis or meiosis
-chromosome DNA is circular
-plasmids
-extrachromosomal DNA (circular)
-genetic exchanges still occurs in prokaryotes
genetic exchange in prokaryotes involves
-a DNA molecule from an external source
-replacement of chromosomal information
how closely linked two genes are influences
-likelihood one molecule that includes both genes will be transferred to host simultaneously
-likelihood one recombination event will include both genes
genetic information can be
transferred from one bacterium to another, resulting in an altered genotype
-vertical or horizontal gene transfer
Conjugation: transfer of DNA between cells
1. Conjugation:
2. Transformation
3. Transduction
conjugation
transfer of DNA between cells
transformation
introduction of DNA into cells
transduction
introduction of viral DNA into cells
growth of bacteria and isolation of mutants
-grow in liquid or solid media
-minimal medium
-complete medium
minimal medium
salts + NH4+ + glucose
complete medium
minimal medium + yeast extract / amino acids
bacterial growth phenotypes
-prototrophs
-auxotrophs
-resistance mutants
prototrophs
wild type, strains that will grow on minimal medium
auxotrophs
mutant strains that can only grow on minimal medium if it is supplemented with some biochemical
-trp+, trp-, gal-
trp+
strain can make tryptophan
trp-
strain requires addition of tryptophan to medium
gal-
strain cannot grow on galactose as sole carbon source
reisstance mutants
will grow on media containing an antibiotic
-strR, strS
strR
resistant to streptomycin
strS
sensitive (wild type)
bacterial mutants typically identified by
growth phenotypes
spontaneous mutations are source of
variation in bacterial mutants
bacterial mutants are
haploid so phenotypes are directly affected
conjugation is a
DNA transfer between cells
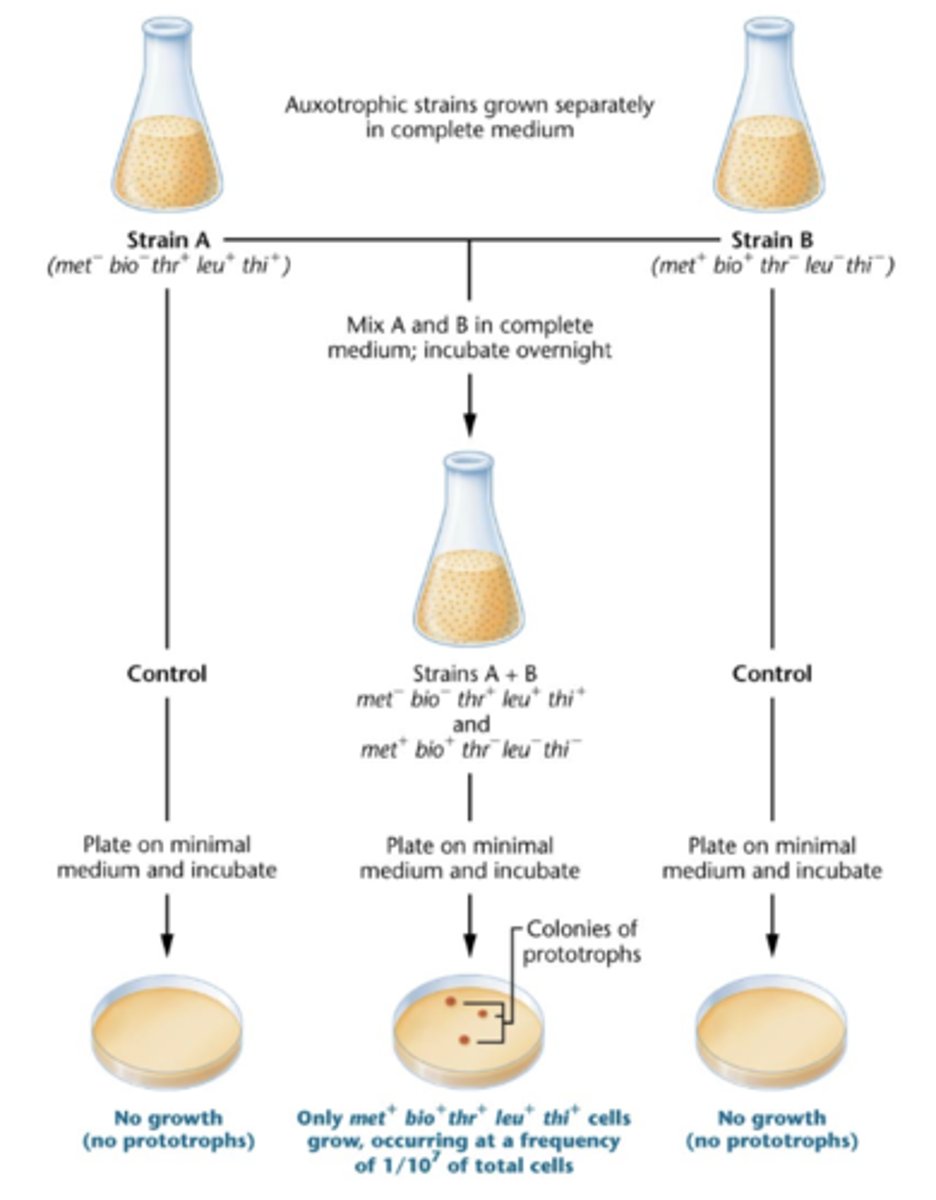
evidence of conjugation in bacteria
-only some strains can be donors, named F+
-cells that receive, F-
-Lederberg and Tatum, 1946
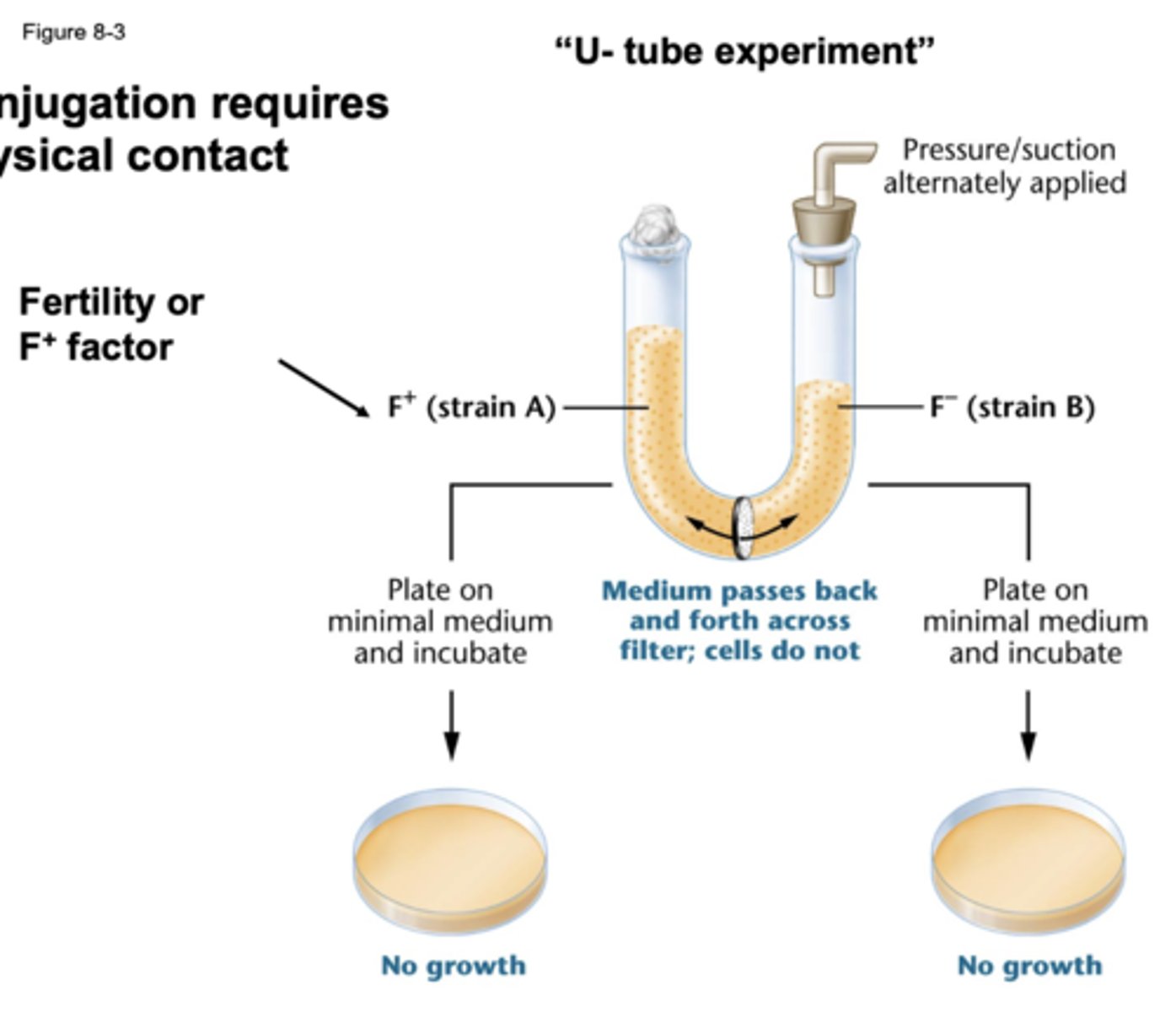
conjugation requires
physical contact
-U tube experiment
in U tube experiment the medium
passes back and forth across filter and cells do not
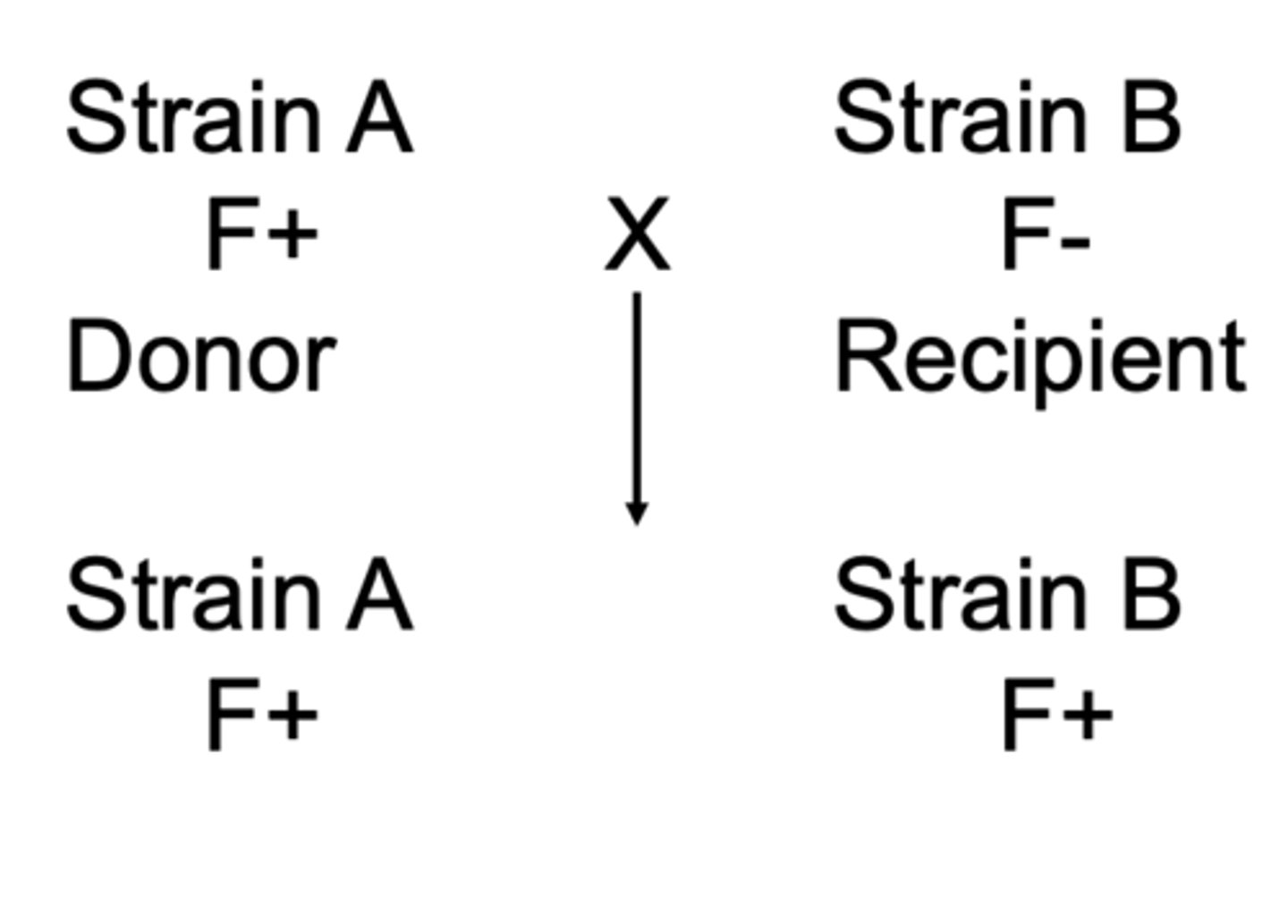
conjugation is
unidirectional
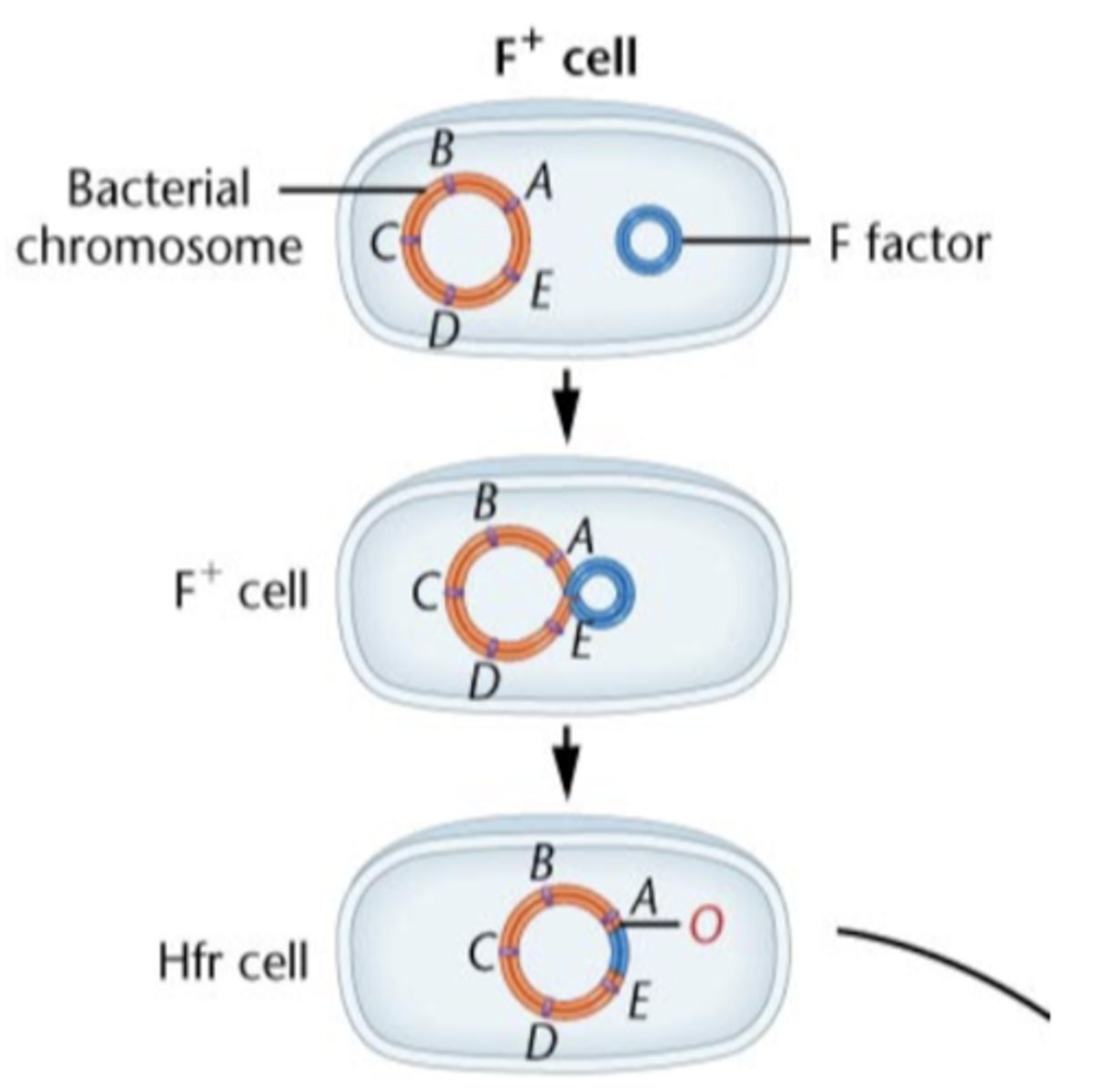
F factor is a
plasmid
plasmids are composed of a
double-stranded closed circle of DNA
plasmids exist in
multiple copies in the cytoplasm
plasmids may contain
one or more egenes
plasmids use the same
replication enzymes as host
plasmids are distributed to
daughter cells
plasmids replicated independently of the
bacterial chromosome
F factor plasmids confer
fertility
F factor plasmids contain genes for
sex pilus formation on which genetic recombination depends
conjugation of F plasmid
-F+ plasmid is copied into the F- cells
-F- cells become F+
-F= to F- conjugation occurs in 1x10^-7 cells
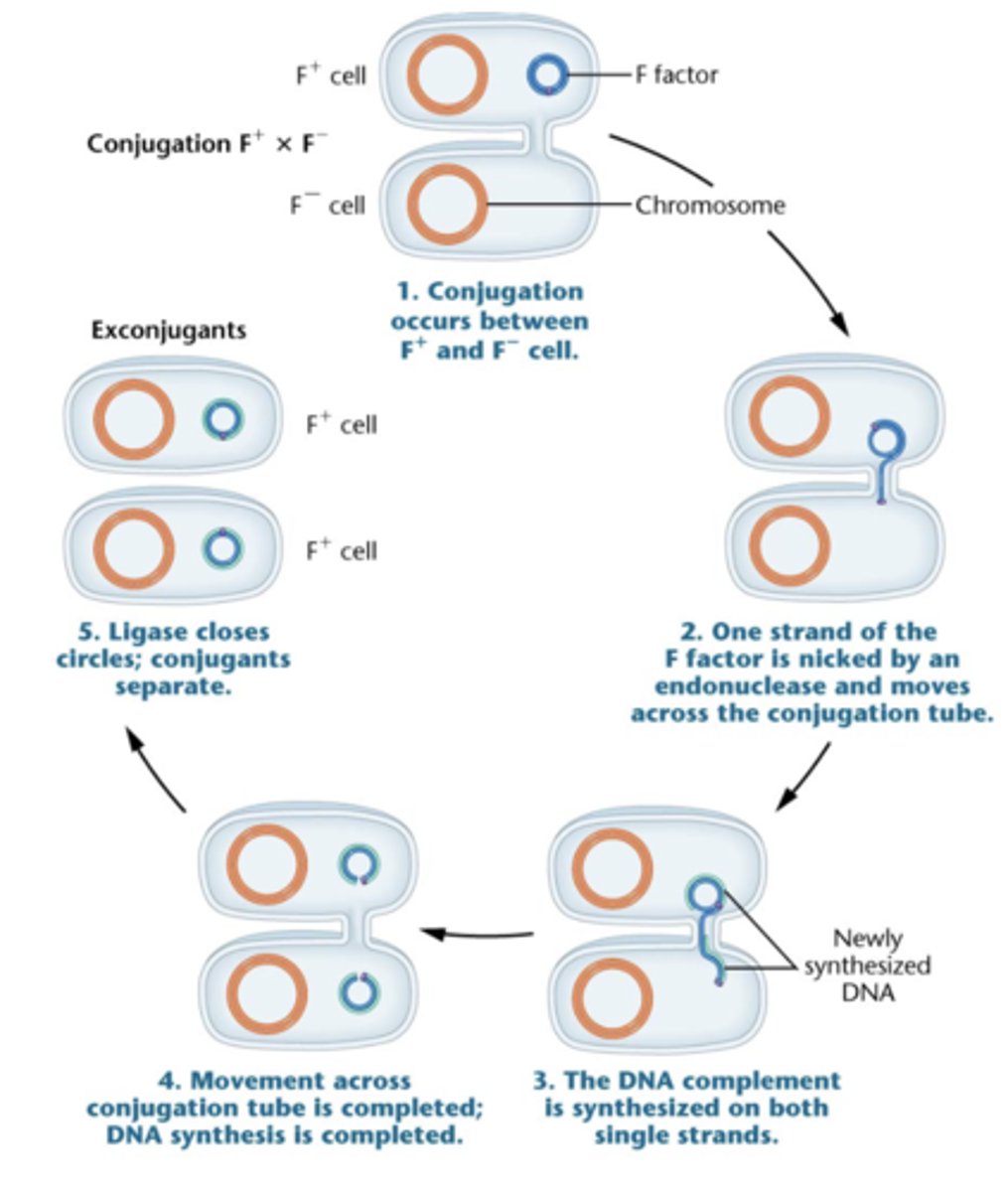
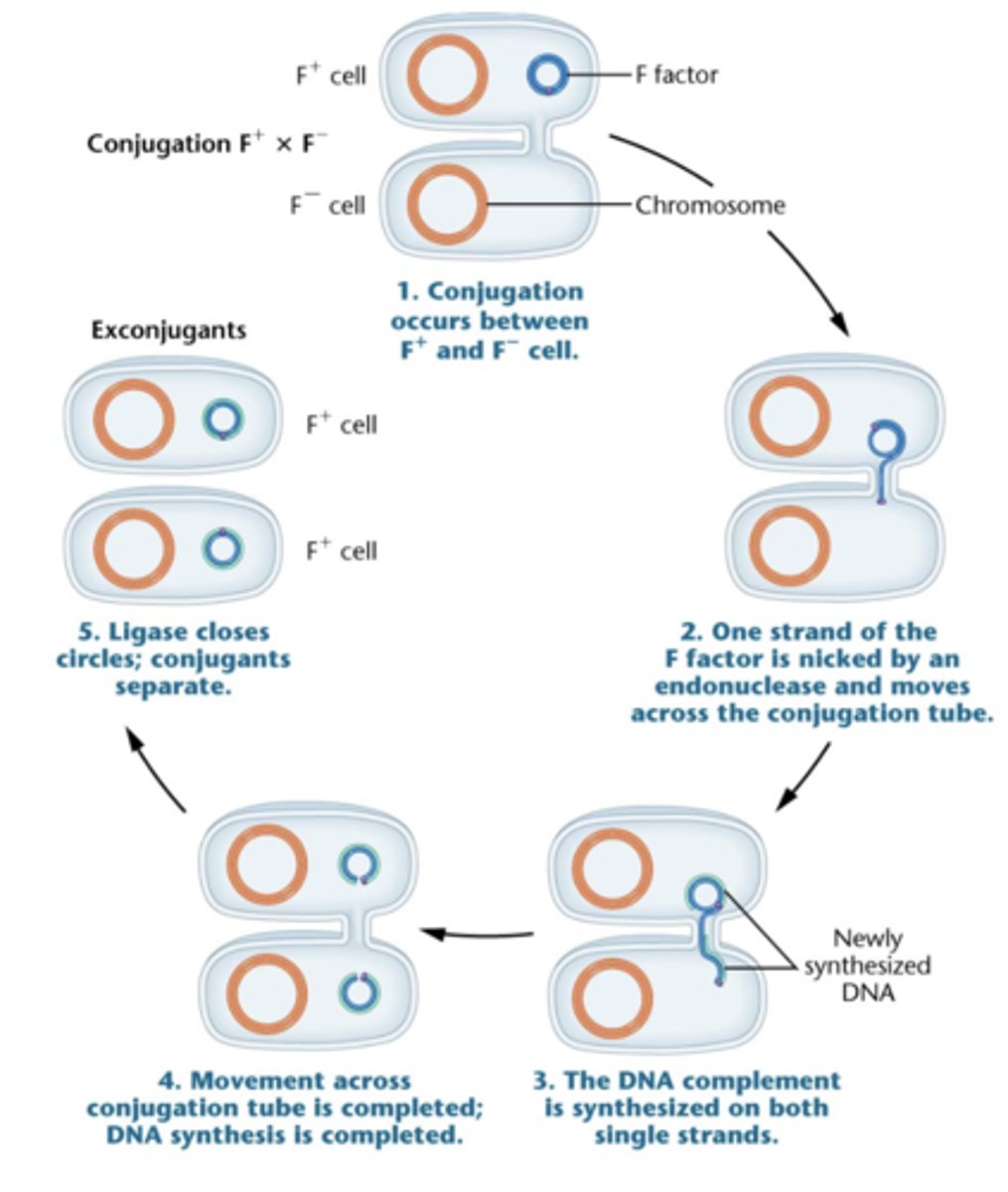
steps in F plasmid conjugation
1. conjugation occurs between F+ and F- cell
2. one strand of F factor is nicked by endonuclease and moves across conjugation tube
3. DNA complement is synthesized on both single strands
4. movement across conjugation tube is complete + DNA synthesis is complete
5. ligase closes circles + conjugates separate
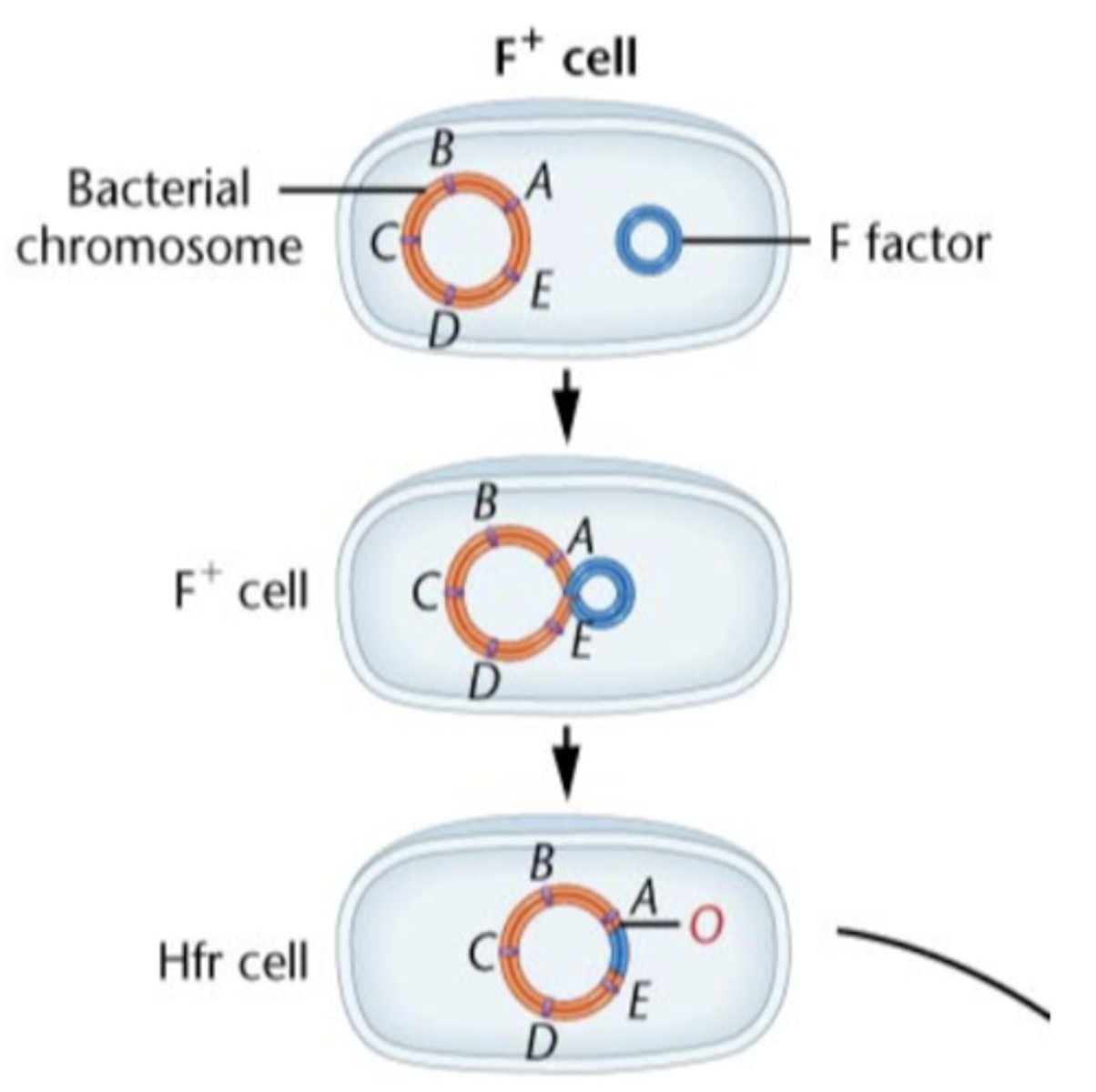
Hfr strains are
special types of DNA donors
Hfr
high frequency recombination (1 x 10-4)
in Hfr F+ plasmid is integrated into the
chromosome
in Hfr genes on the bacterial chromosome are
transferred to F- cells
in Hfr F+ plasmid is
not transferred
in Hfr F- cells do not become
F+
conjugation between Hfr and F- strains leads to
transfer of genes on the chromosome
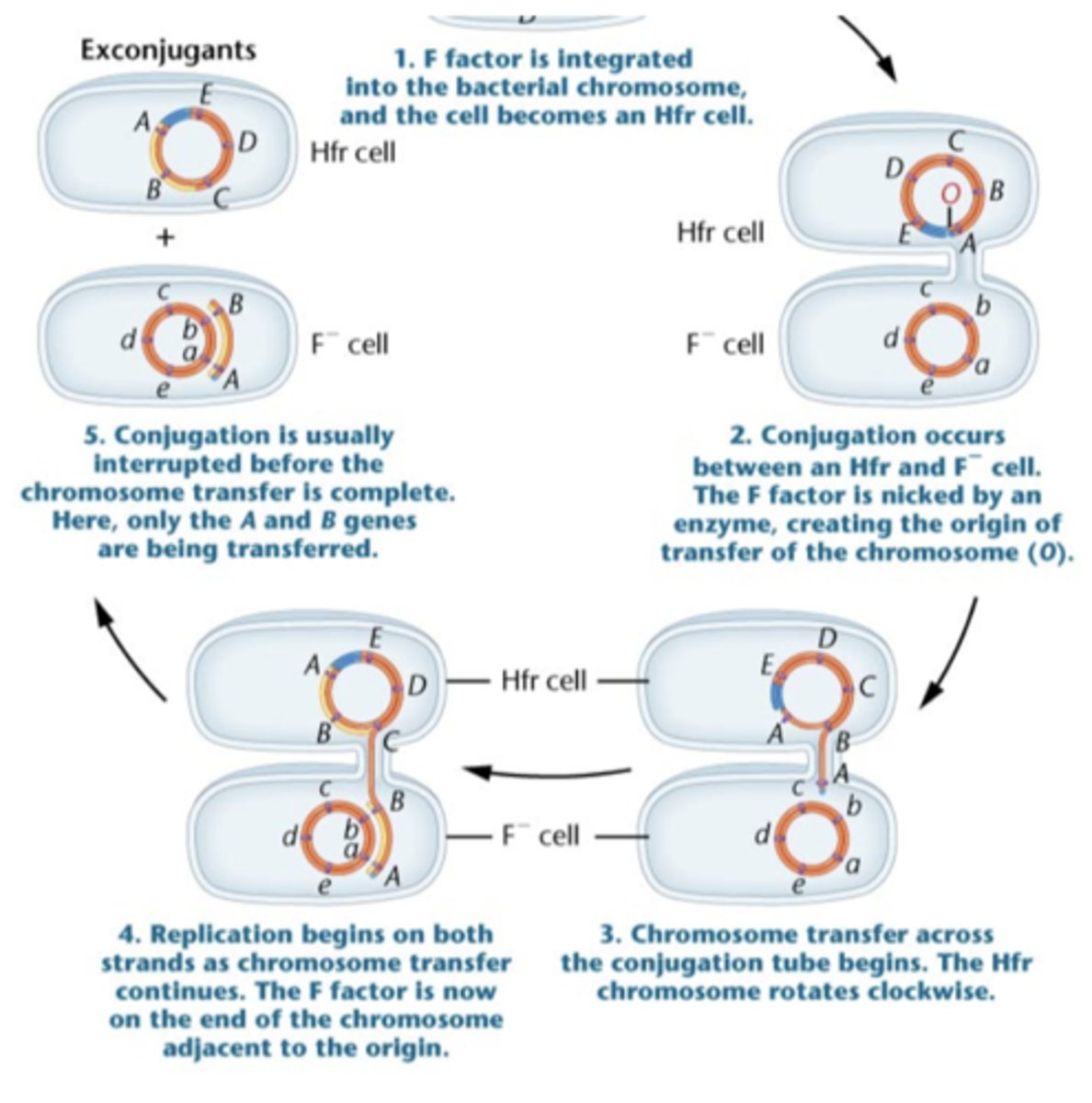
recombination between the incoming DNA and the chromosome can
place the new DNA into the chromosome
-basis for mapping in prokaryotes
once the molecule is present in the cell
crossing over can occur between these two molecules of DNA
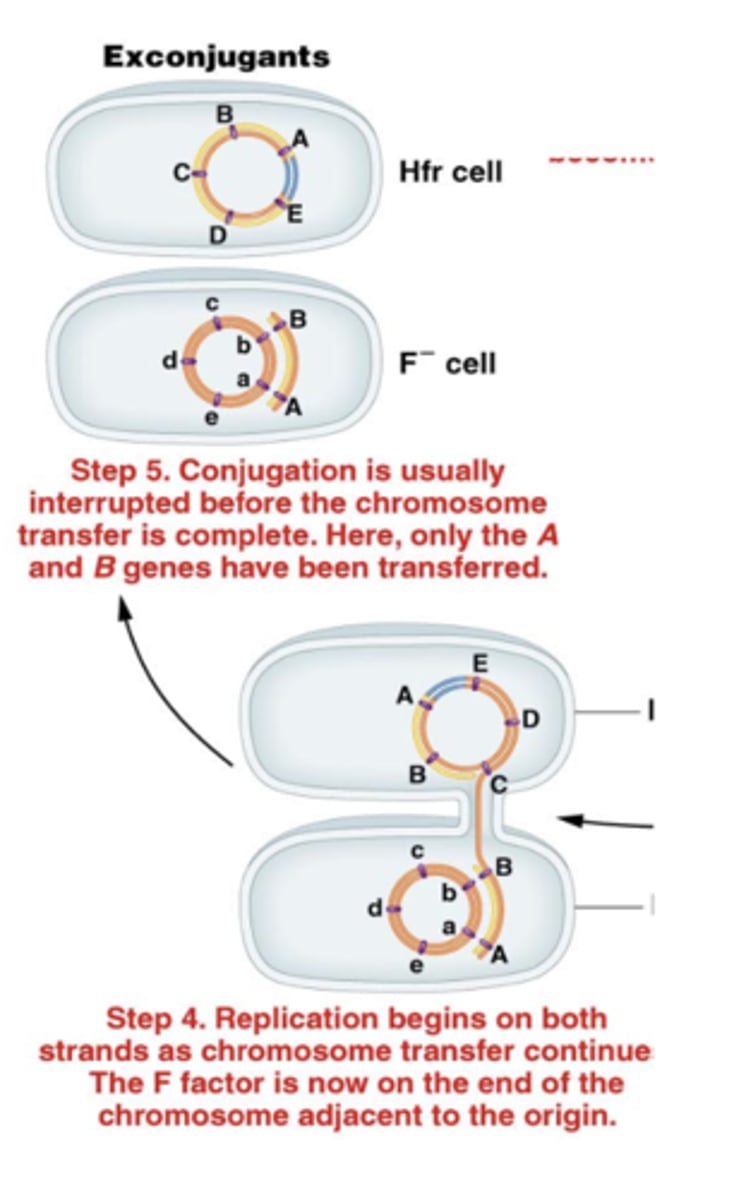
frequency at which two genes are included in the same recombination event is dependent on
their physical distance from one another on the molecule
interrupted mating technique is used to
map genes in E. coli
in interrupted mating technique
-conjugation is interrupted, resulting in recipients with various number of bacterial genes
-number of transferred genes increases with amount of time of conjugation
-genes close + the F+ factor is first transferred
-more time = more genes transferred
-transferred genes replace the genes in the chromosome by homologous recombination
gene order is determined by
transfer time
genes closer to the F+ are
transferred and recombined sooner than others
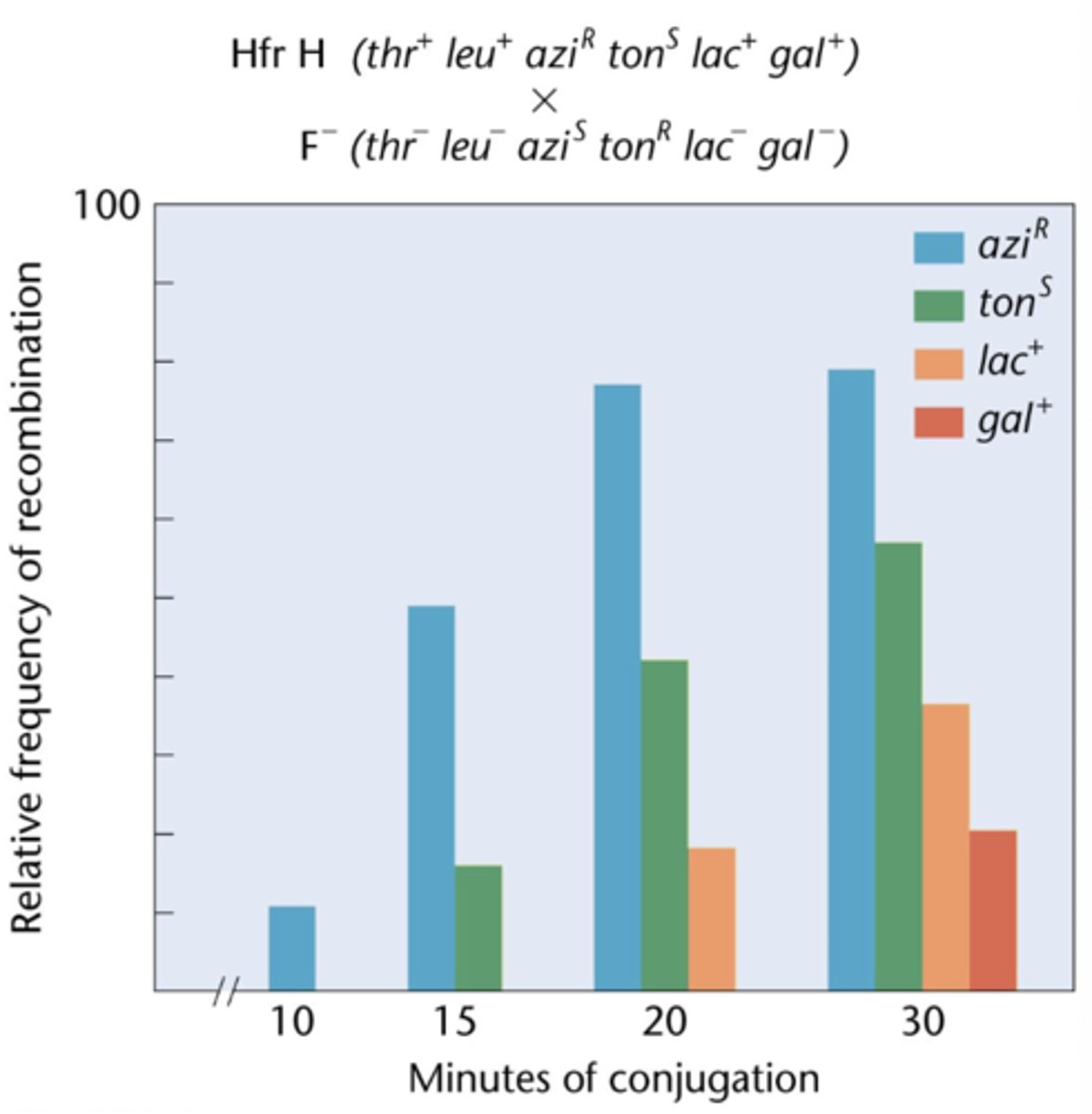
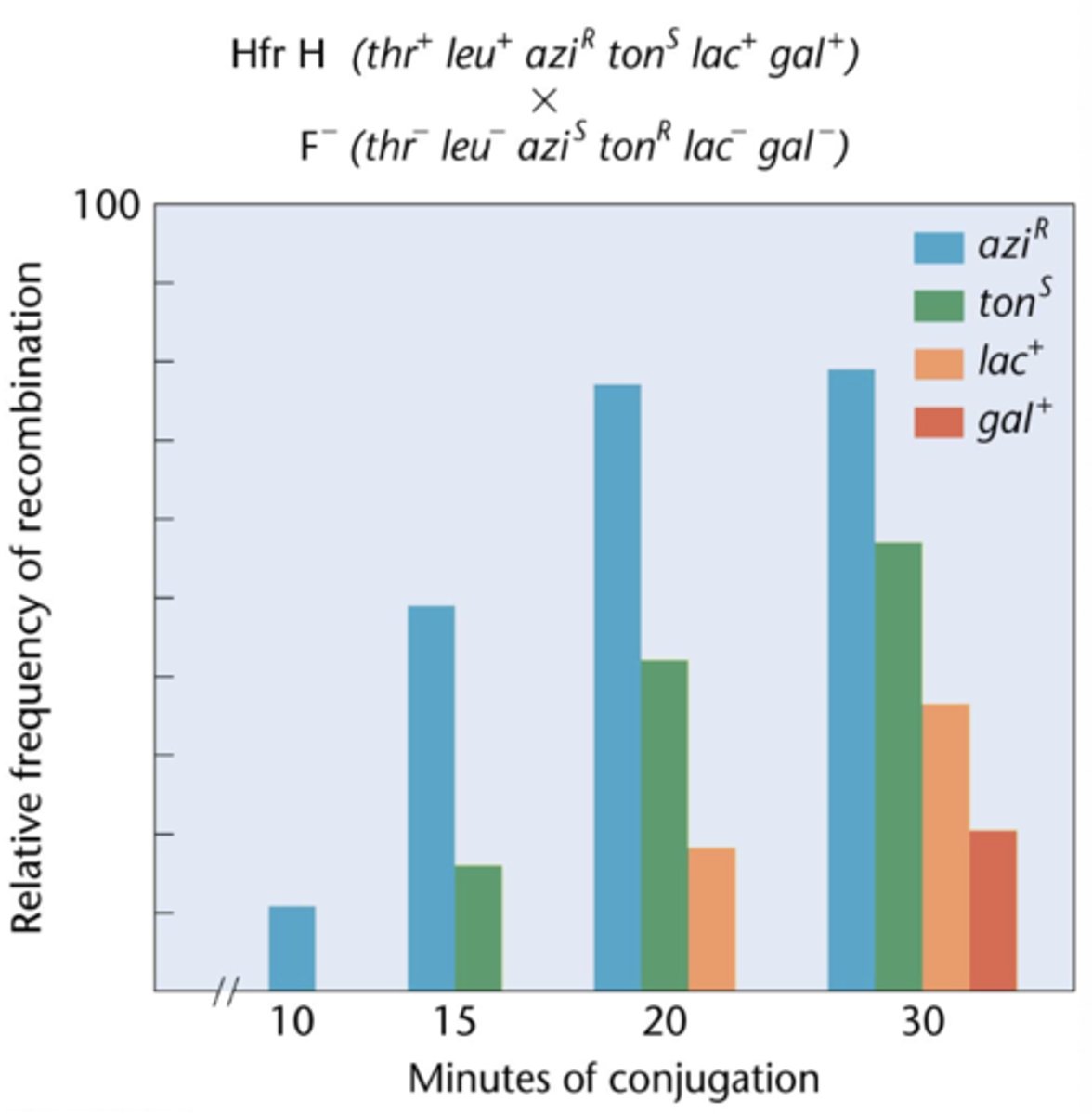
an ordered linear transfer of genes is correlated with the
length of time conjugation proceeded
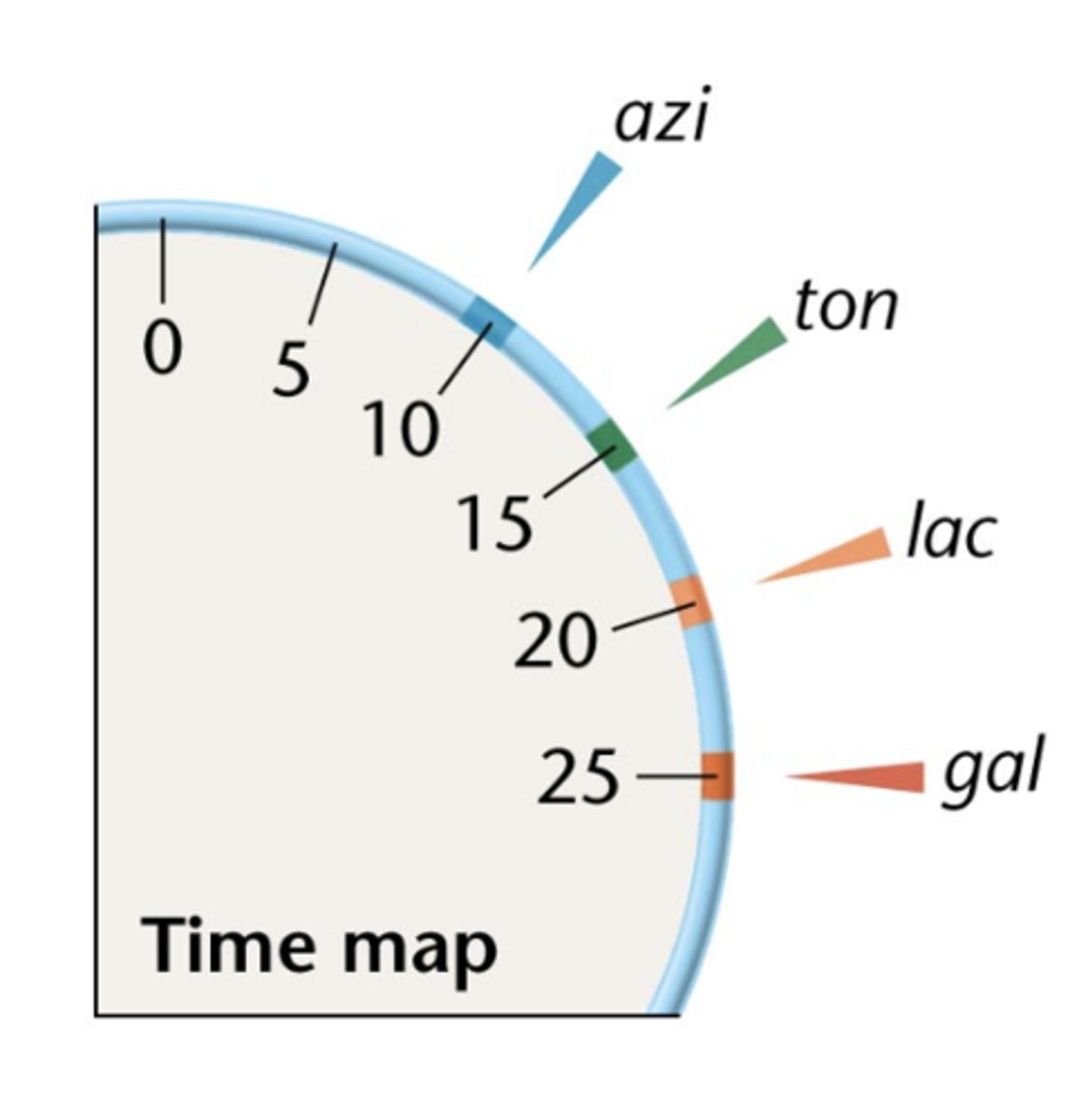
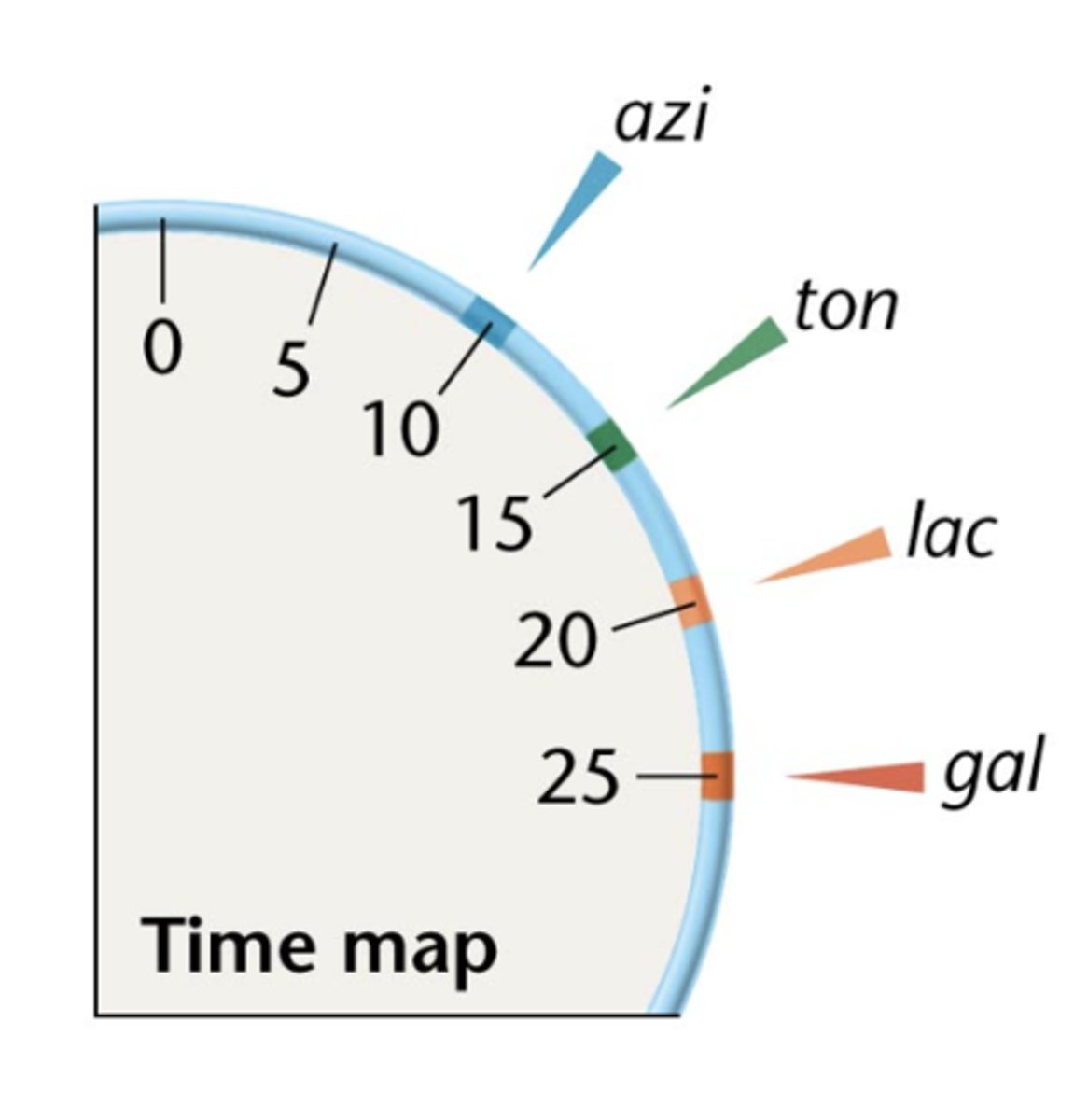
with a time map gene order and distance between genes could be
predicted
time maps are the basis for
first genetic map in bacteria
strains with F+ plasmid inserted at different locations of time map can be used for
mapping
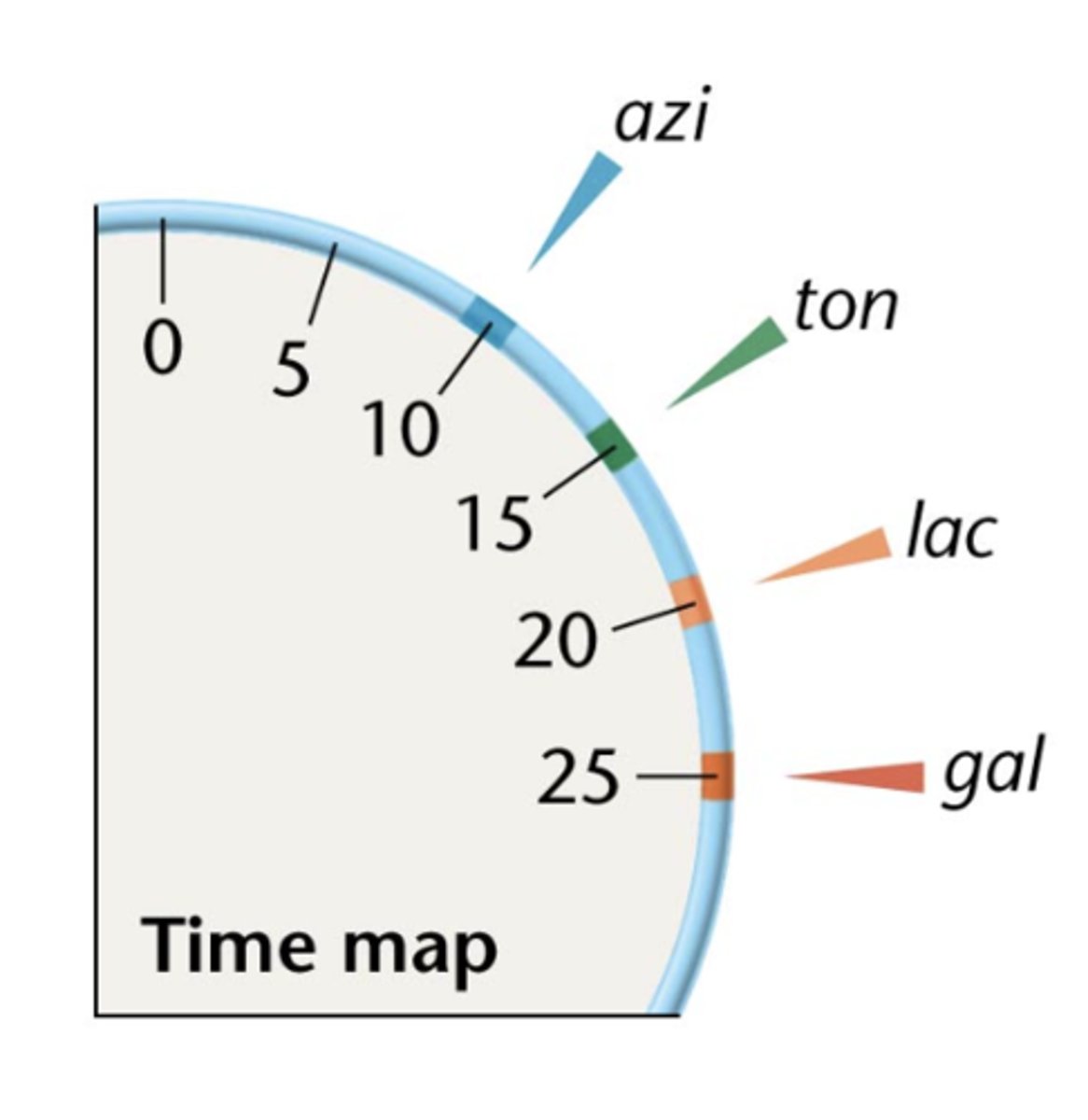
conjugation rarely goes on for long enough for
F factor itself to be transferred
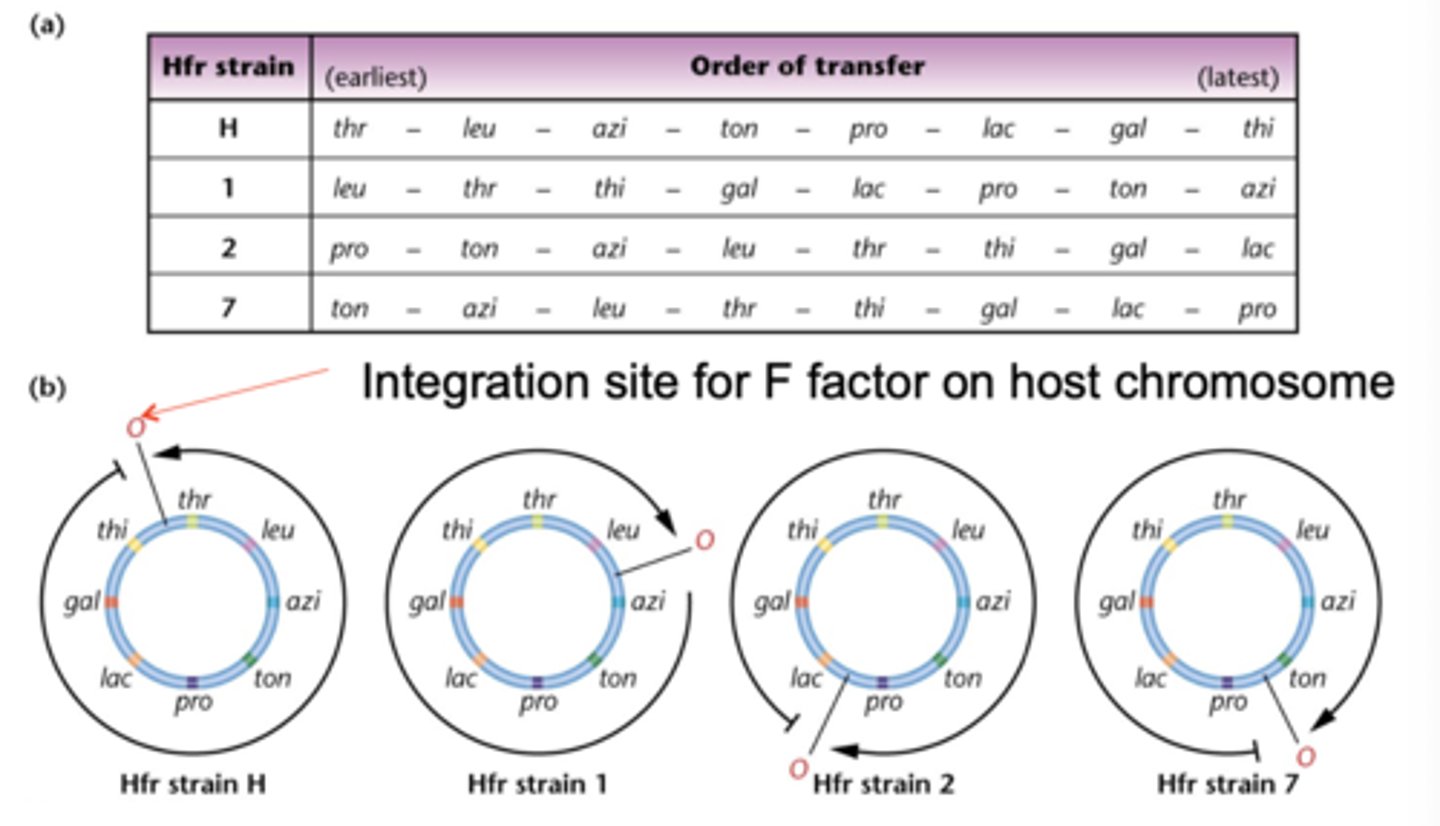
order of gene transfer in different Hfr strains shows
the E. coli chromosome is circular
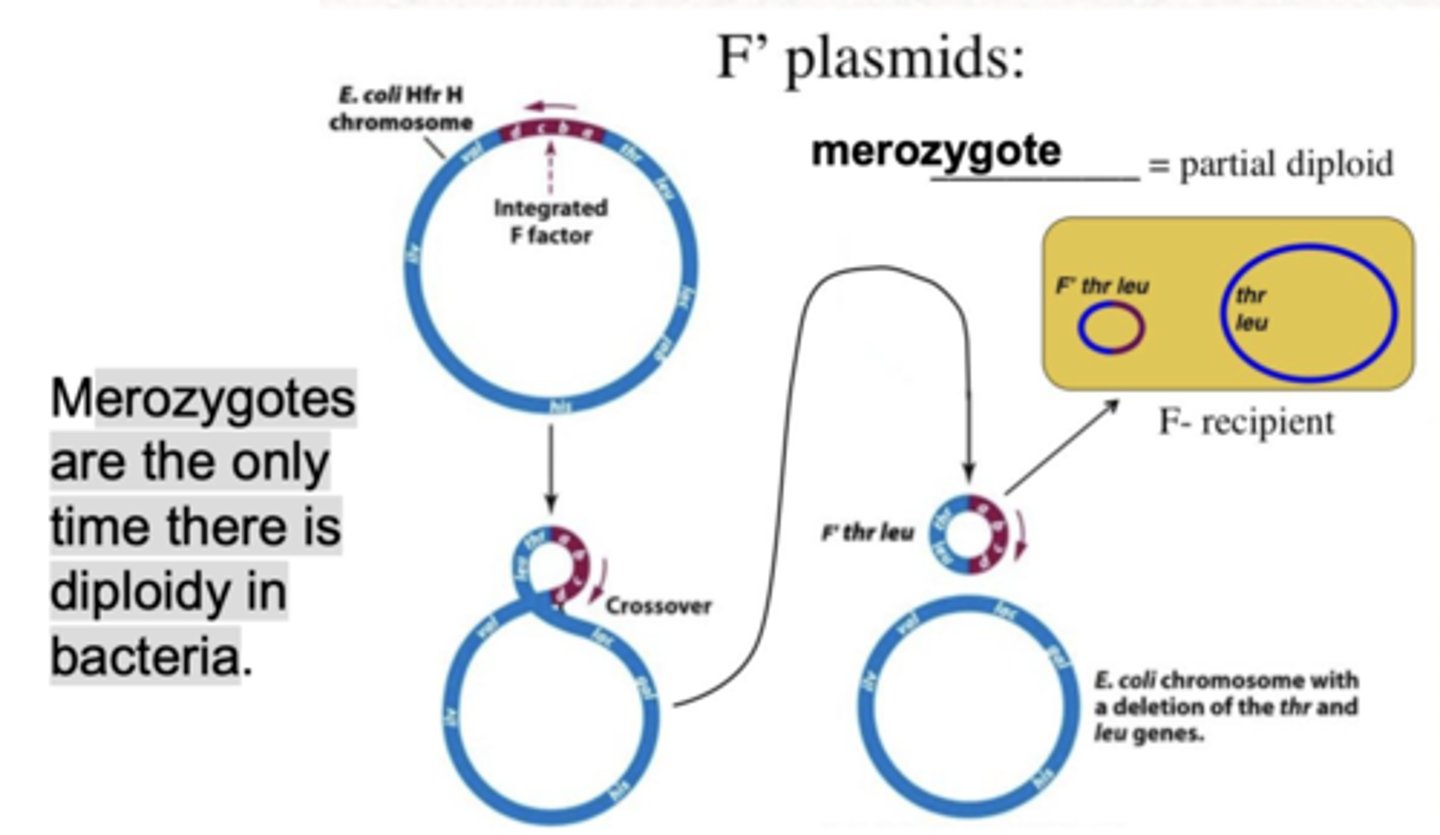
through recombination the F DNA can
shuttle in and out of the bacterial chromosome
-when it comes out it may take a piece of the chromosome with it
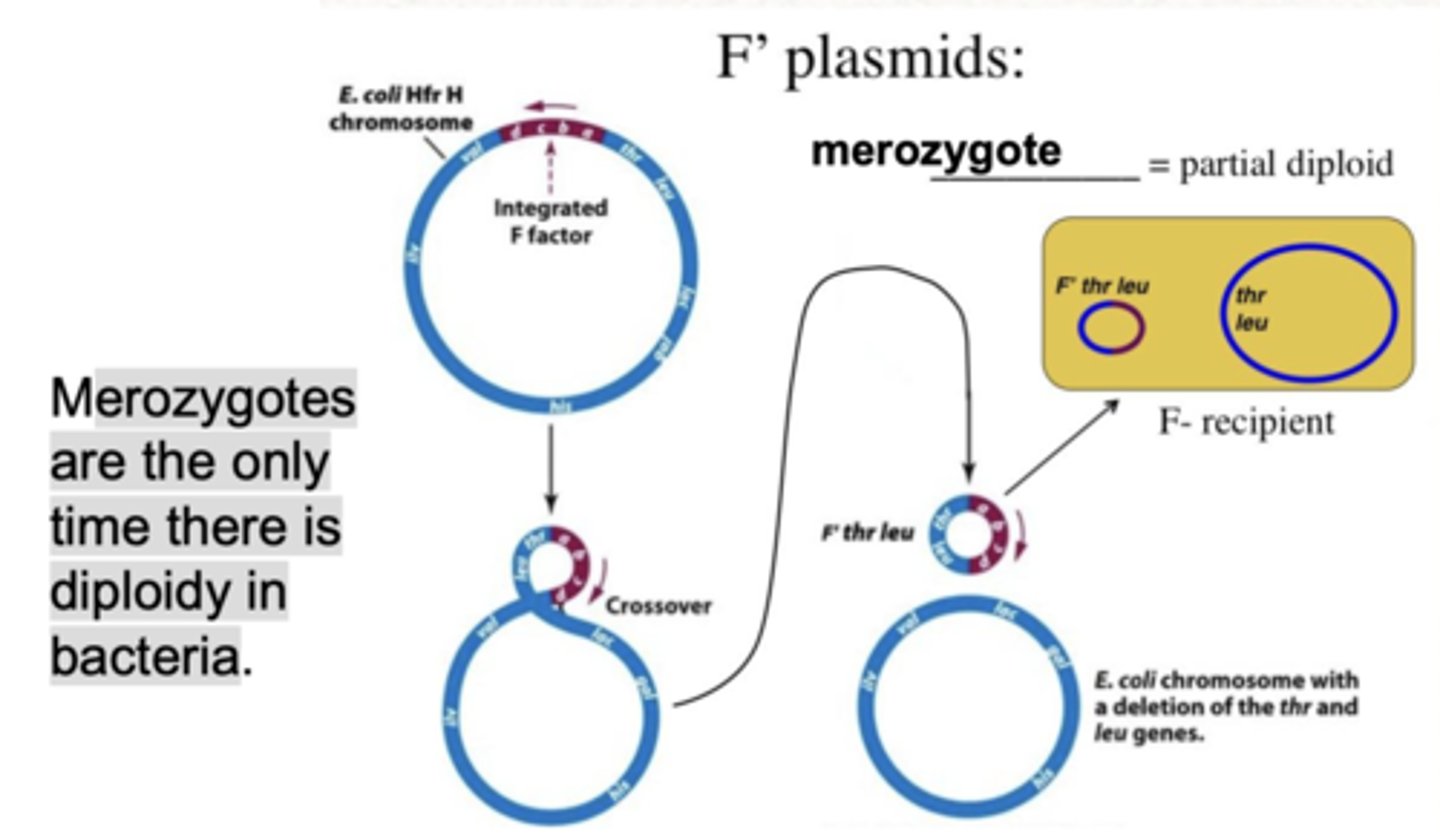
merozygotes are the only time there is
diploidy in bacteria
there are different types of plasmids which include
different genes
R plasmids consist of two components
1. resistance transfer factor (RTF)
2. one or more r- determinants
RTF encodes genetic information essential to
transferring the plasmid between bacteria
R-determinants confer resistance to
antibiotics
col plasmids encode
colicins that can kill neighboring bacteria
genetic recombination in bacteria is by
transformation
-uptake of "free DNA"
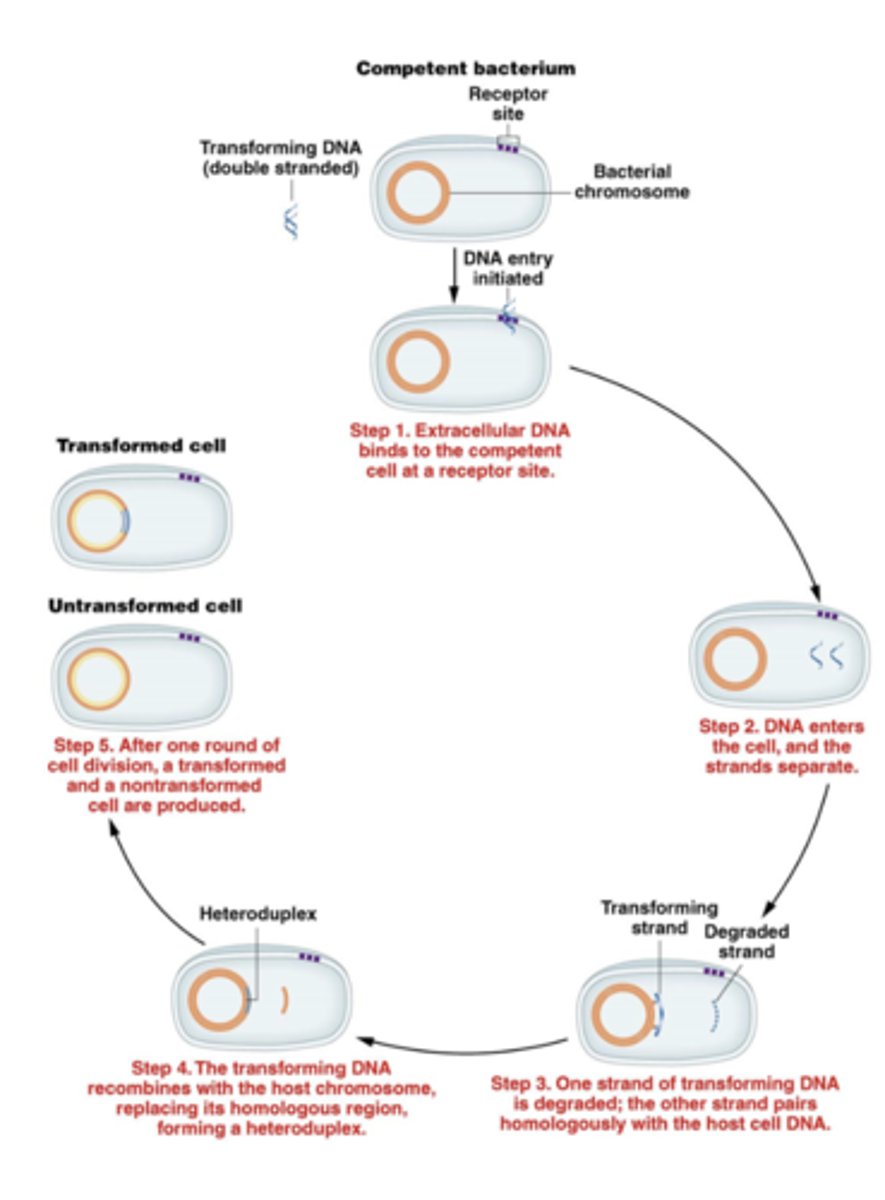
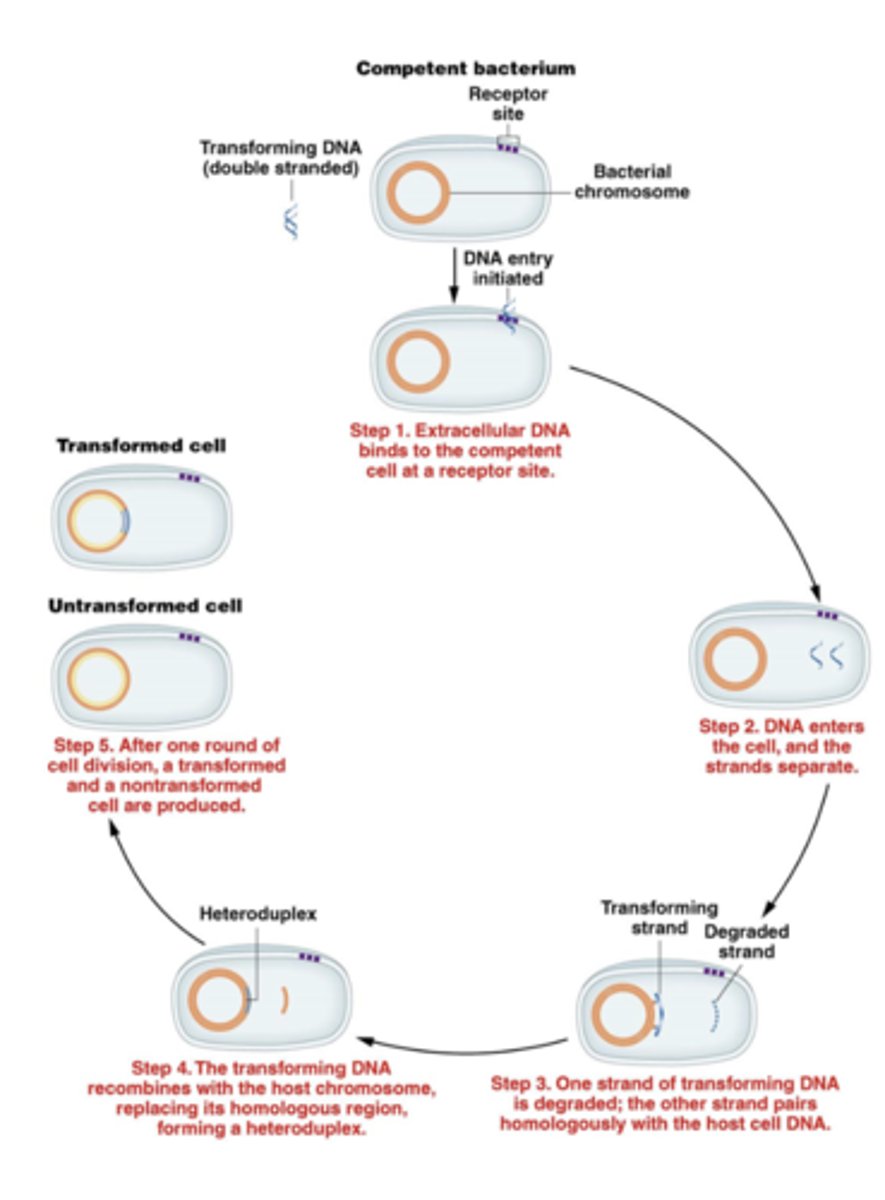
genes that are close enough to each other to be
cotransformed are linked
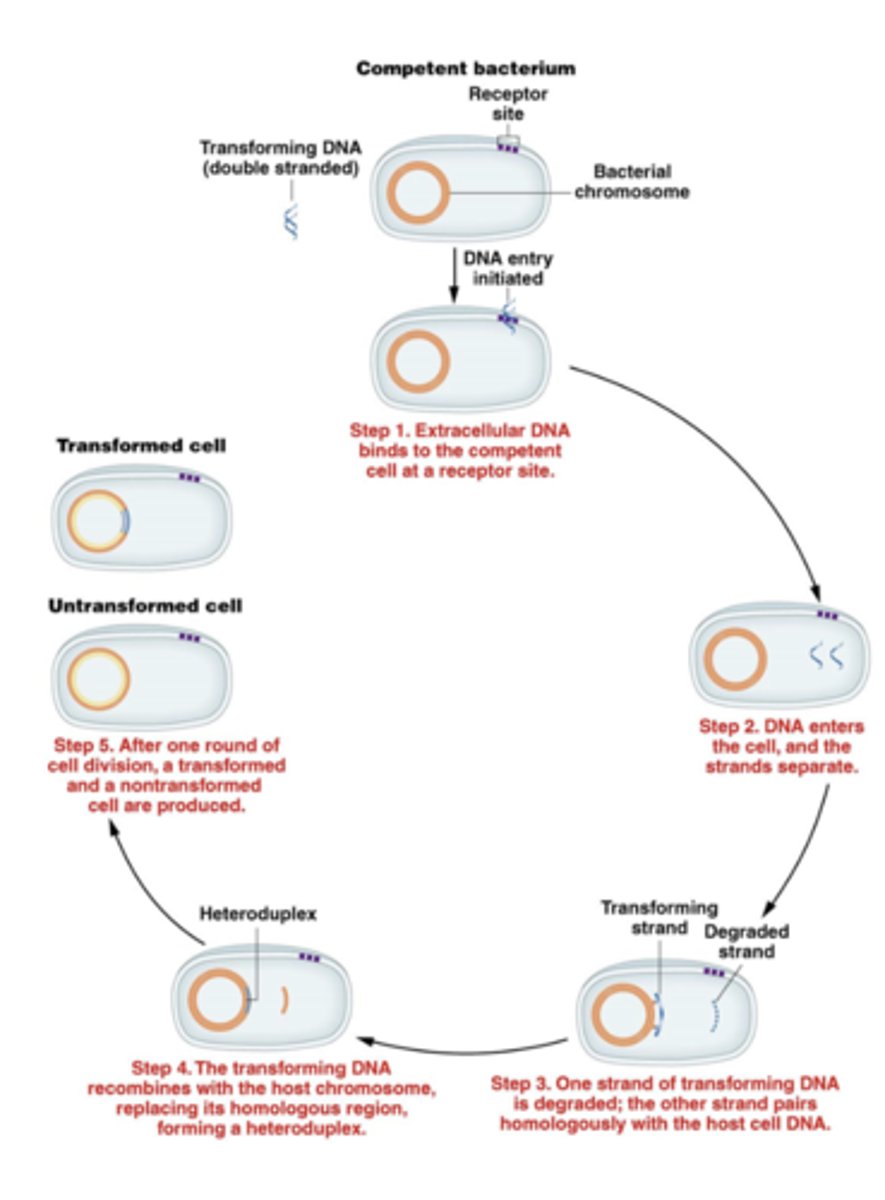
after transformation, DNA recombines with the
chromosome, creating a heteroduplex
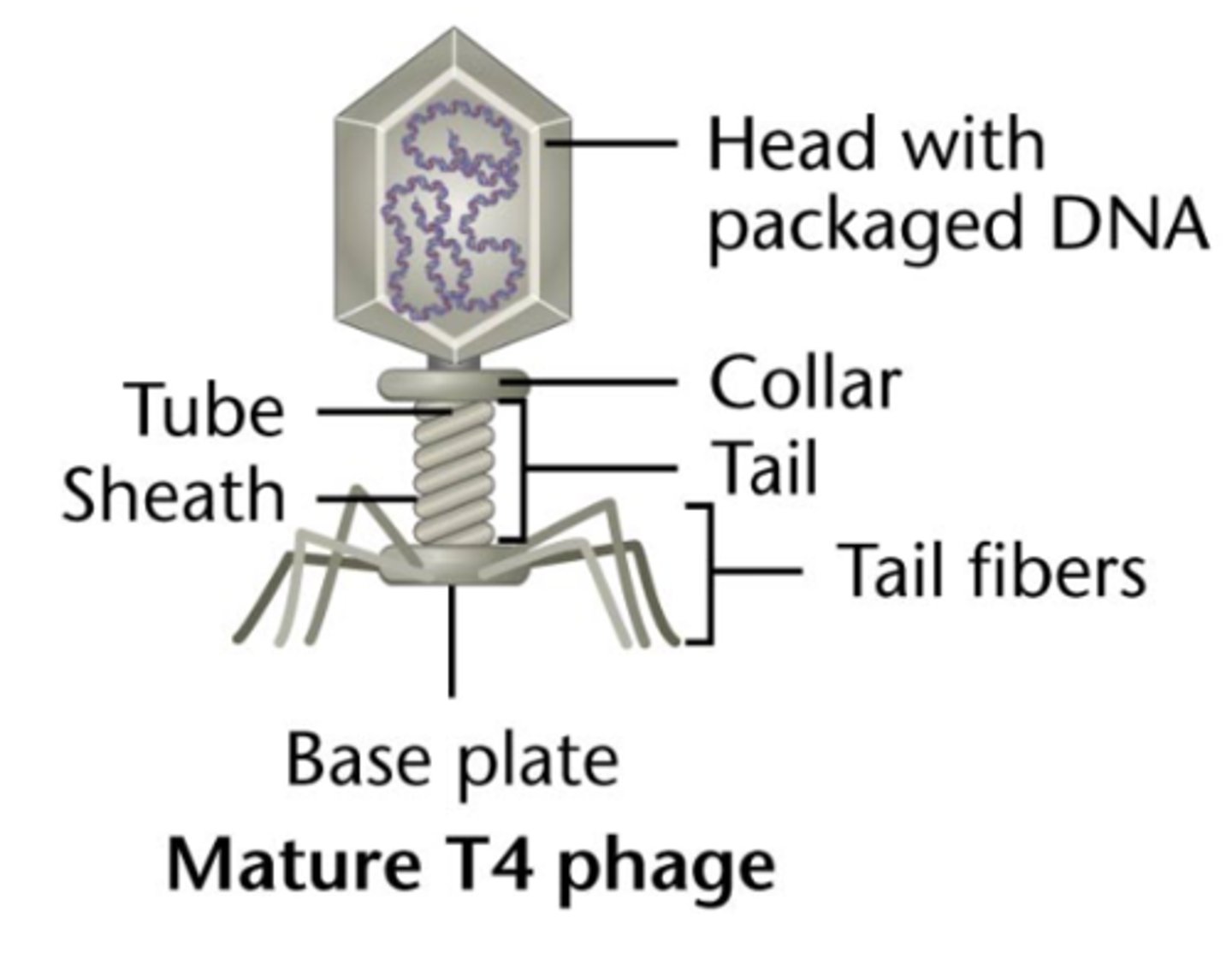
transduction in bacteria
-genetic recombination in bacteria via bacteriophages
-transfer DNA between bacteria by Viruses
phage
bacterial virus
phage can
recombine with one another
phage can also recombine with
bacterial DNA (=transduction)
viral transduction does not require
cell to cell contact
when phage lyse host
they leave plaques
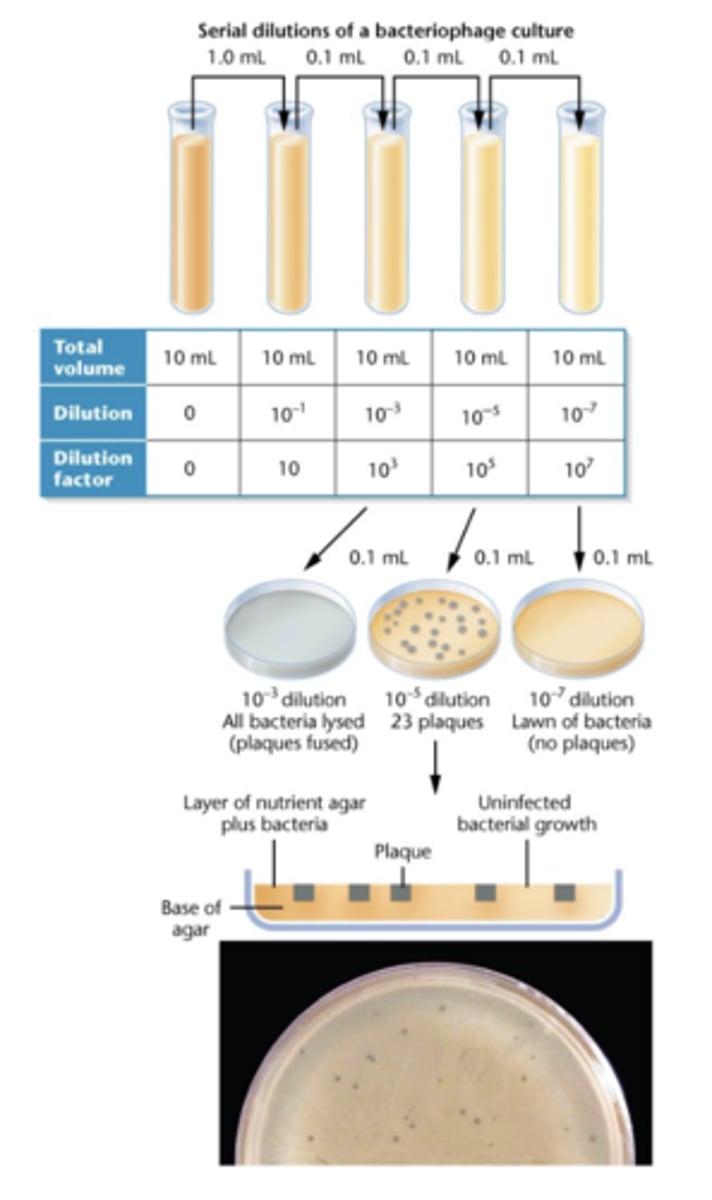
counting plaques is how we
assay phage phenotypes
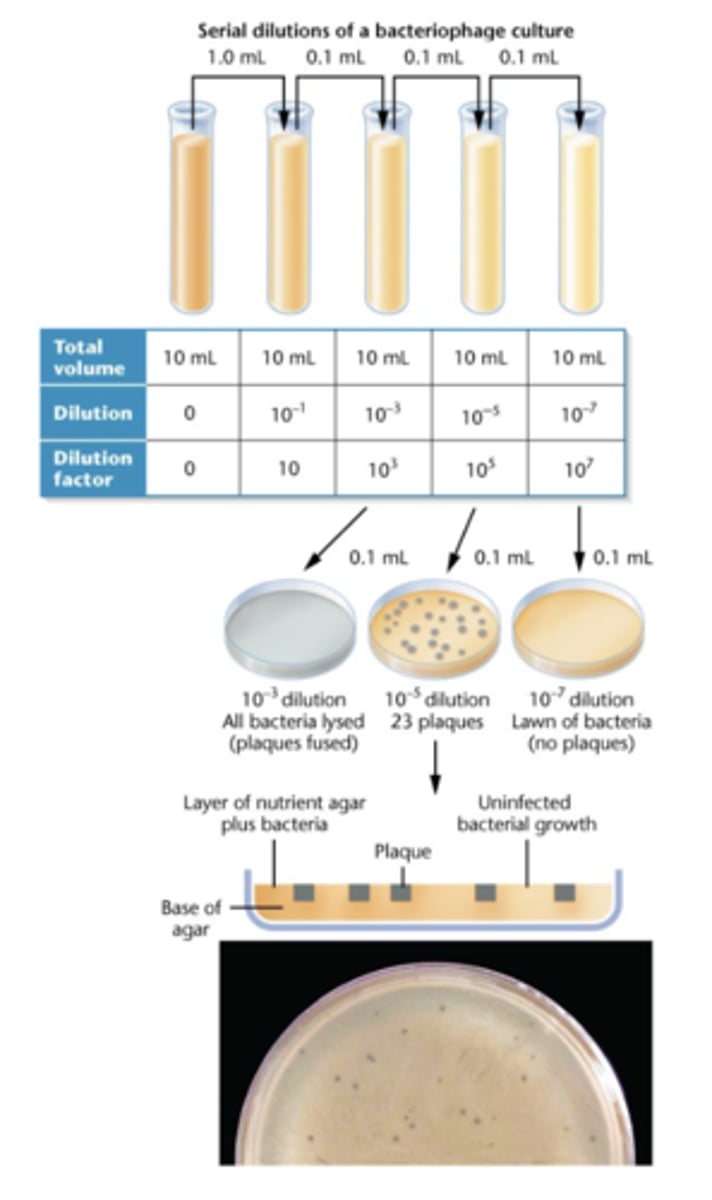
sometimes we have to dilute to
get an accurate count
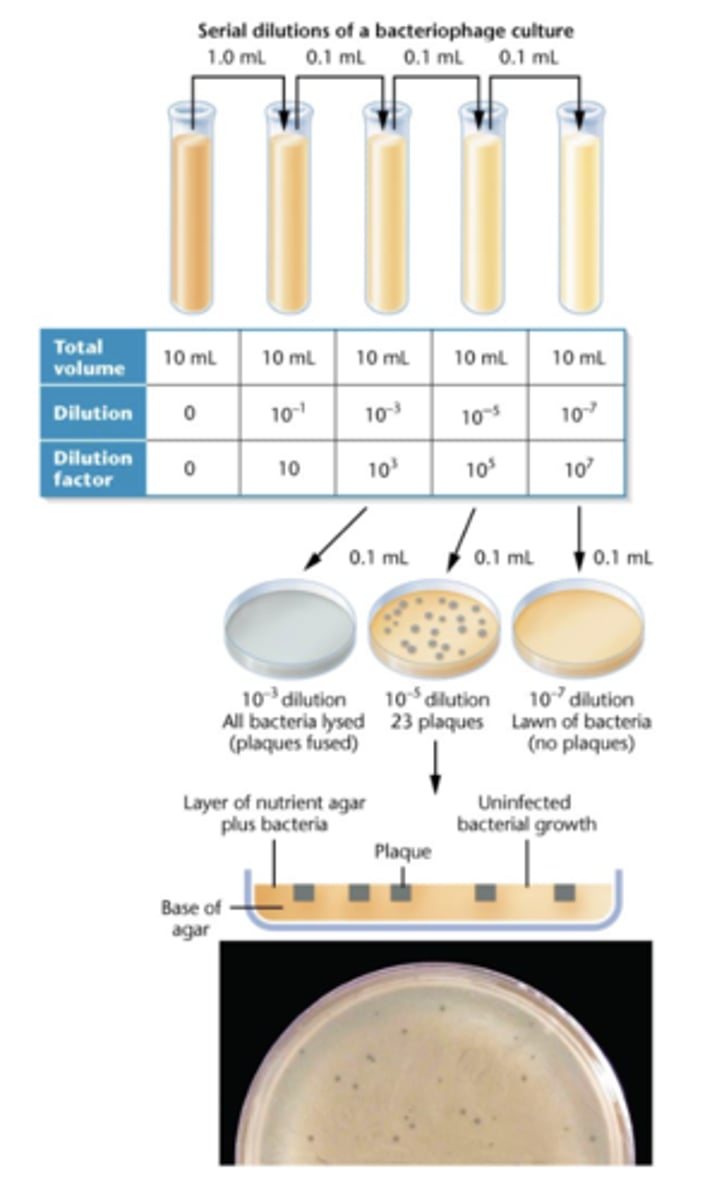
not all phage
lyse host cells
viruses that lyse cells are called
virulent
lysogeny occurs when
-the phage DNA integrates into the bacterial chromosome
-it is replicated along with the chromosome
-it is passed to daughter cells
some viruses (temperate viruses) can integrate their DNA into the bacterial chromosome and remain dormant
DNA into the bacterial chromosome and remain dormant
-lysogeny
lysogenic bacterium can be induced to
enter a lytic virus replication cycle by environmental conditions
life cycle of bacteriophages (lytic cycle) of T4 phage of e.coli
phage DNA enters bacterium
host DNA is degraded
-virus takes over host cell
machinery and replicates
-viral particles are assembled and release
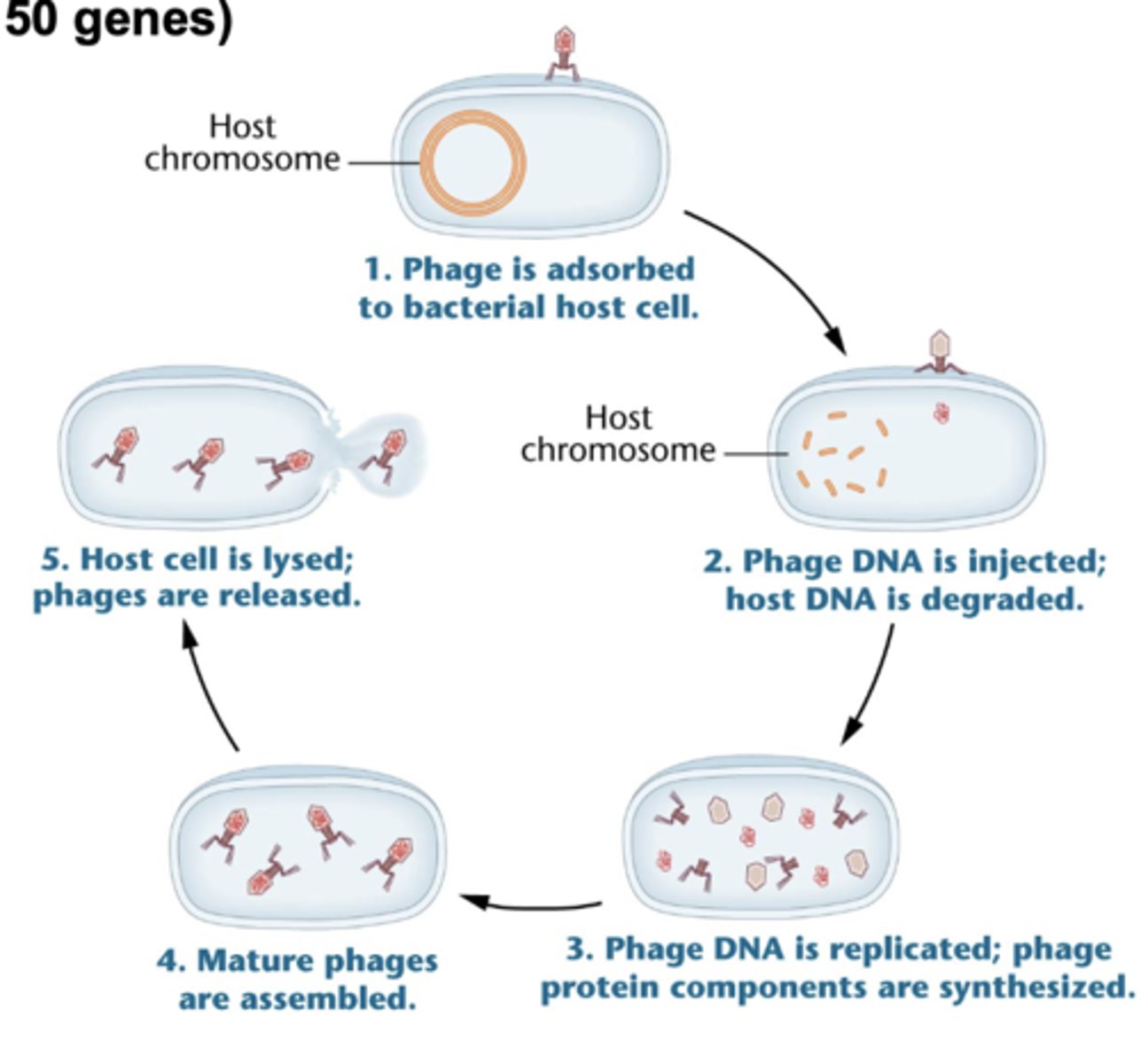
T4 phage of E. coli has _____ genes
150
bacterial DNA can be packed into
virus
like transformation, generalized transduction can be used in
linkage and chromosomal mapping of the bacterial chromosome
two closely aligned (linked) genes can be simultaneously
transduced (cotransduction)
the closer linked genes are to each other
the greater the frequency of transduction
the precise order of genes can be
determined in transduction
plaque morphology associated with mutations are
frequently used phenotypes for mapping genes on phage chromosome
two and three point mapping in phage
# of recombination events between two genes is proportional to the relative distance between the genes
results of a cross involving the h and r genes in phage T2 (hr+ x h+r)
mixed infection with two phage types
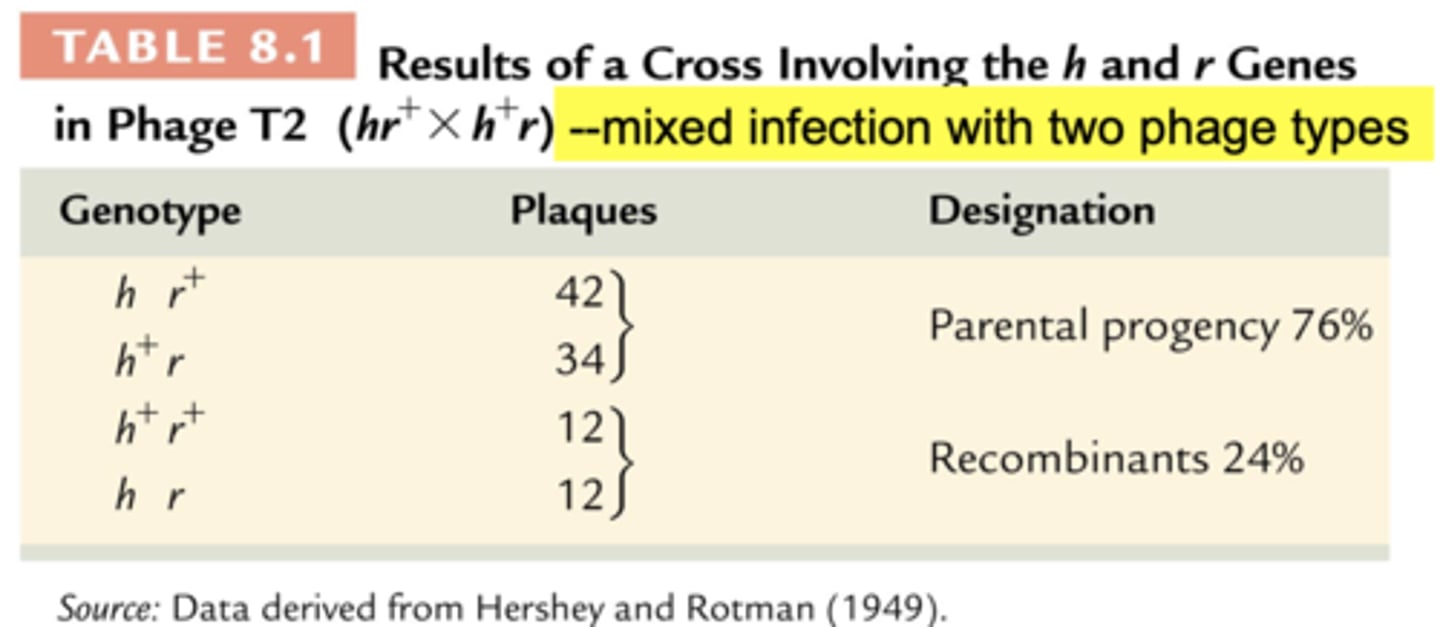
rec proteins are essential to
bacterial recombination
genetic recombination is a
regulated process in bacteria, like eukaryotes
bacterial recombination requires
functional gene products from RecA, and RecBCD
bacterial mutants deficient in any of these components (functional gene products) don't
undergo recombination