2 ~ fluid flow + sediment transport
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
what is hydrodynamics?
study of flow + behaviour of sediment particles
what is fluid flow?
entrainment of sediment particles by fluids (water, air, water/sediment mix)
gravity of pressure driven flows
what is a fluid?
substance that continually flows under applied shear stress
what is fluid viscosity?
measure of ability of fluid flow
low visc - flow readily
high visc - flow sluggishly
temp dependent - flow faster with inc T
flow by internal shear
what is newtons law of viscosity?
relationship between shear stress and fluid flow
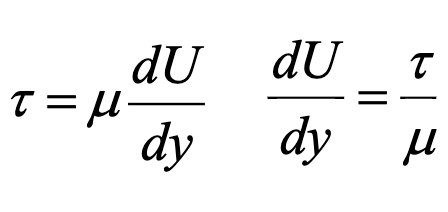
what is the shear box experiment?
viscous fluid sheared btwn 2 plates
lower plate immobile, upper plate moves to the right
laminar shear transmitted through fluid
velocity increases upward
SKIPPED A BUNCH OF EQ
SKIPPED A BUNCH OF EQ
what is reynolds experiment?
inject dye streak int fluid moving and constant velocity through tube
varied fluid density, tube diameter and velocity of flow
what were the results of reynolds experiment?
low discharge - dye follows straight path
med discharge - dye follows wavy path
high discharge - dye rapidly mixed with fluid
what are the 3 types of flow behaviours?
laminar (low) - fluid molecule follows straight path parallel to boundaries of the tube
transitional (med) - fluid molecules follow wavy parallel path
turbulent (high) - fluid molecules follow very complex path that mixes
what is reynolds number?
predicts transition from laminar to turbulent flow

what is the turbulent flow structure?
velocity increases upward
outer layer - fully turbulent, not affected by bed friction
transition layer - intermediate between laminar and turbulent
viscous sub layer - thin layer, laminar flow
what is hydraulic roughness?
smooth bed - particles withing VSL, low flow rate, behaves laminar
rough bed - particles above VSL, VSL thins, particles subject to eddies
what are the 3 forces on the particle?
lift force (upwards)
drag force (parallel to bed)
gravity force (downwards)
how does the lift force act on a grain?
flow lines converge over grain
inc in velocity + dec in pressure at top
how does gravity act on the grain?
opposes lift force
acts to keep grain on bed
what is fluid force?
result of lift force and drag force
is diagonal
what is a bed load?
sediment that resides on bed but goes into transport during high flow events
what are the types of bed loads?
contant - sliding/rolling
saltation - jump/hop along
suspensive saltation - longer trajectory of hopping
intermittent suspension
what is a suspended load?
sediment suspended in upper region of turbulent flow
continuous - eddies keep particles aloft
intermittent - grains periodically drop back to bed
what is a wash load?
silt and clay size material remains in suspension even during low flow events
what is stokes law?
falling particles reach terminal fall velocity where drag and buoyancy forces are balanced by gravity
what are the complications of stokes law?
natural grains are not perfect spheres
grains are in contact as they settle - clump and collide
grains larger than fine sand fall fast enough to cause turbulent eddies
what did hjulstrom determine?
determined critical velocity for entrainment/transport experimentally
what is cohesion?
clay + fine silts are cohesive sediments
held together by electrostatic forces
must break bonds to erode clay
what is shields diagram?
determine critical boundary shear stress required to initiate entrainment of spherical grains of varying diameters n density
what is middletons diagram?
particles will remain in suspension when the shear velocity exceeds settling velocity