Understanding the Process of Photosynthesis
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
69 Terms
Photosynthesis
Process converting sunlight into glucose and oxygen.
Glucose
Simple sugar produced during photosynthesis.
Pyruvate
Intermediate product in cellular respiration from glucose.
ATP
Energy currency of the cell, produced during respiration.
Chlorophyll
Green pigment essential for photosynthesis in plants.
Accessory pigments
Molecules aiding chlorophyll in light absorption.
Chlorophyll a
Primary pigment absorbing violet-blue and red light.
Chlorophyll b
Accessory pigment that complements chlorophyll a.
Xanthophylls
Yellow pigments that assist in photosynthesis.
Carotenoids
Pigments like beta-carotene aiding light absorption.
Stomata
Small openings on leaves for gas exchange.
Guard cells
Cells regulating the opening and closing of stomata.
Xylem vessels
Specialized cells transporting water to leaves.
Cuticle
Waxy layer protecting leaves from water loss.
Thylakoid
Flattened sac where photosynthesis occurs in chloroplasts.
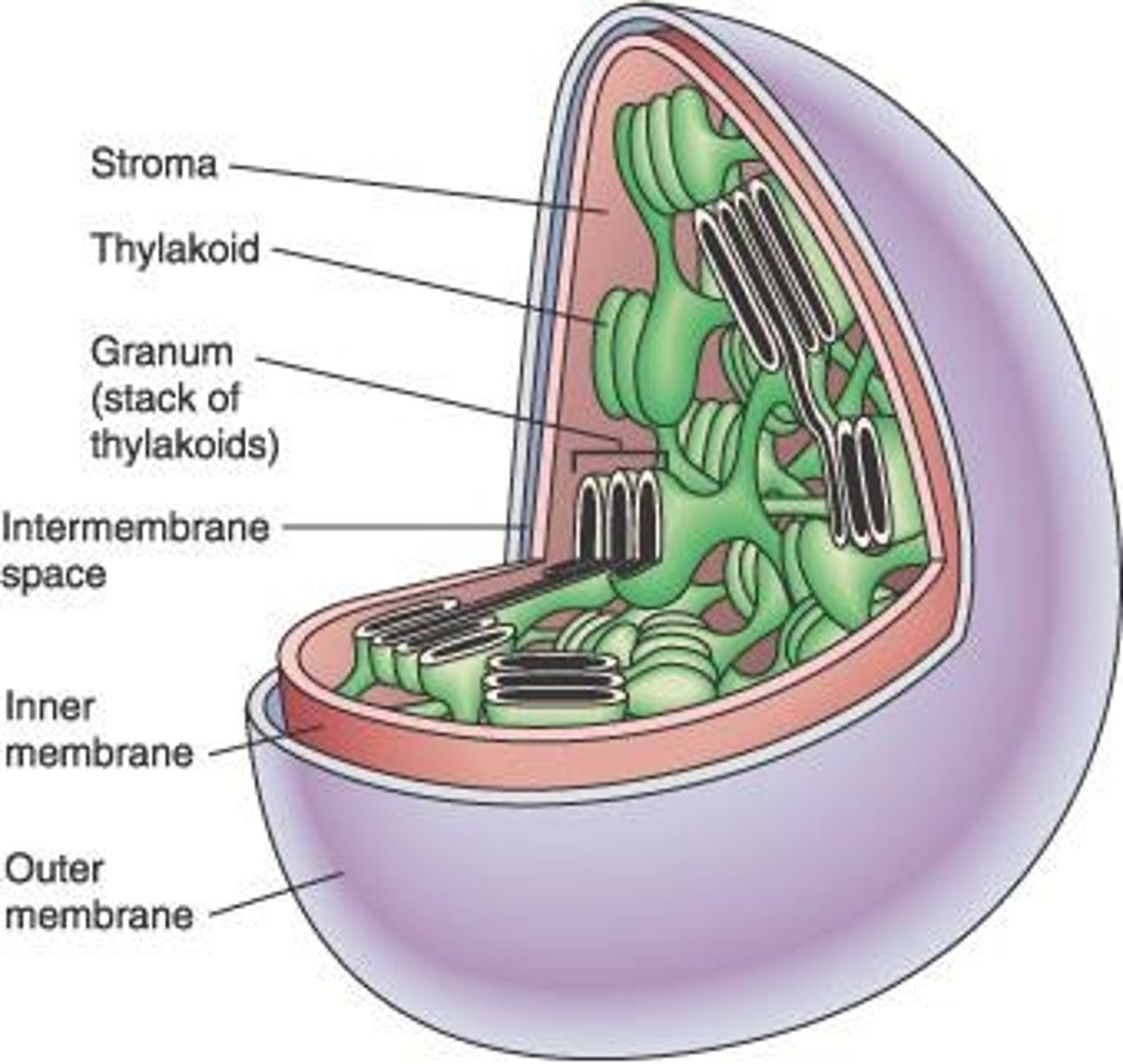
Grana
Stacks of thylakoids in chloroplasts.
Stroma
Fluid surrounding thylakoids in chloroplasts.
Photoactivation
Process of chlorophyll absorbing light energy.
Primary electron acceptor
Molecule receiving excited electrons from chlorophyll.
NADP
Molecule that carries electrons in photosynthesis.
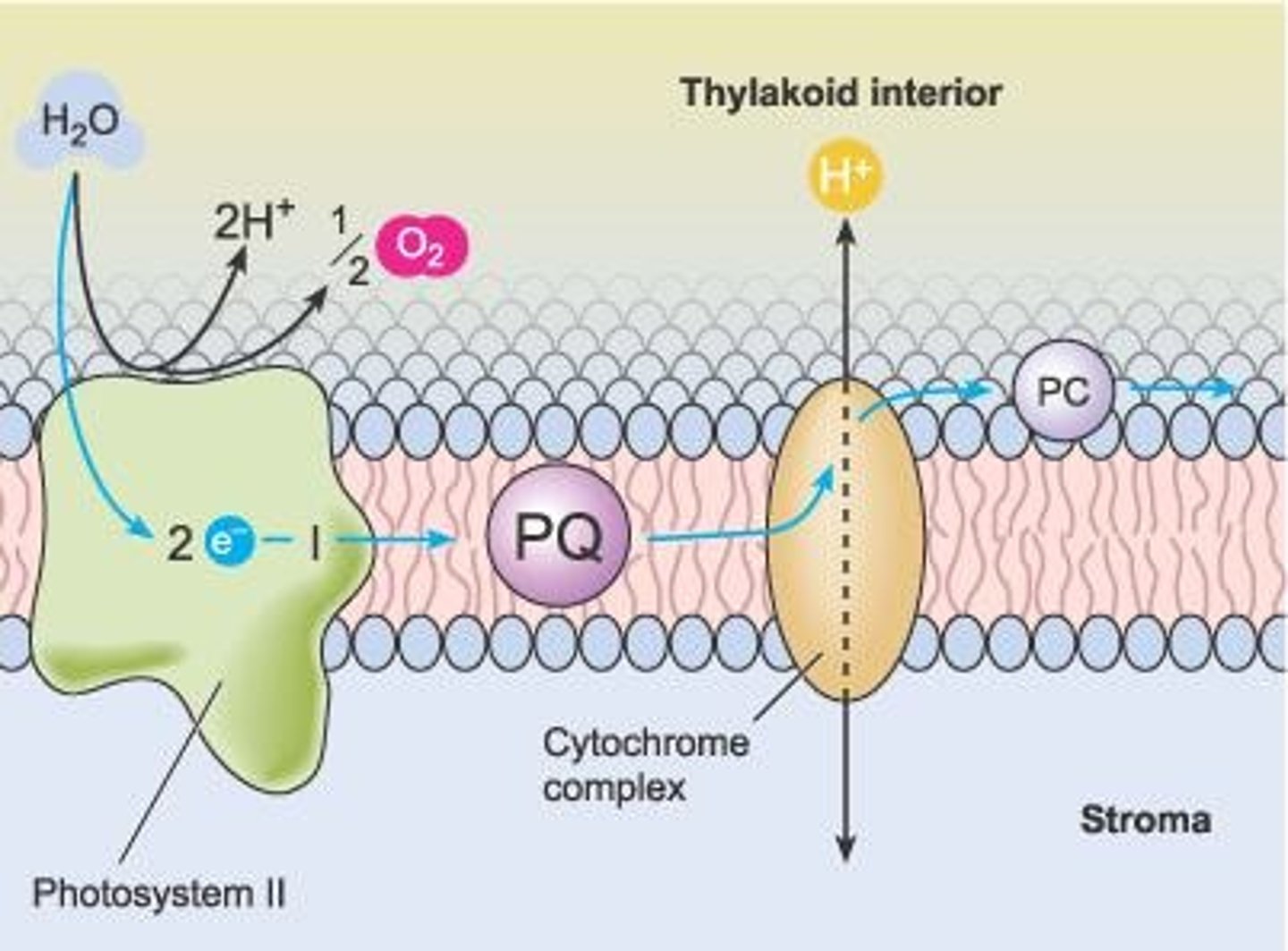
Water splitting
Process producing oxygen during photosynthesis.
Carbon dioxide
Gas absorbed by plants for photosynthesis.
Oxygen
Byproduct released during photosynthesis.
Condensation Reactions
Reactions that release water molecules during bonding.
Phosphorylation
Addition of a phosphate group to an organic compound.
Redox Reactions
Reactions involving electron transfer between molecules.
Light-Dependent Reactions
Reactions requiring light energy to produce ATP.
Grana
Stacked thylakoid membranes in chloroplasts.
Photophosphorylation
Light energy used to generate ATP.
Photolysis
Splitting of water into oxygen and electrons.
NADP+
Oxidized form of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate.
NADPH
Reduced form of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate.
Light-Independent Reactions
Reactions using ATP and NADPH to synthesize carbohydrates.
Glyceraldehyde 3-Phosphate
A 3-carbon molecule formed during carbohydrate synthesis.
Photoexcitation
Absorption of light energy by chlorophyll electrons.
Photoionisation
Process of freeing an electron from chlorophyll.
Photosystem II (PSII)
First photosystem in the light-dependent reactions.
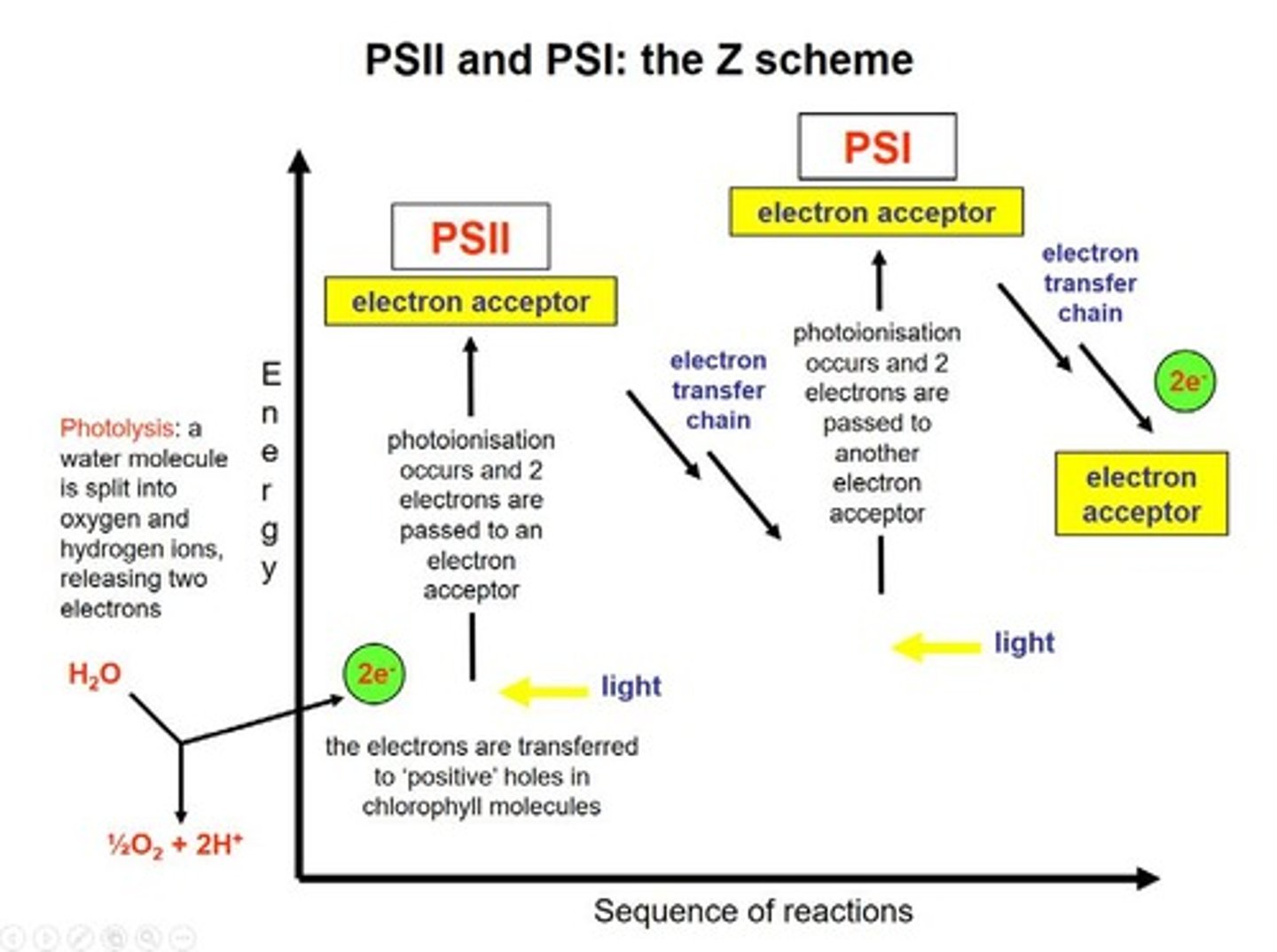
Photosystem I (PSI)
Second photosystem in the light-dependent reactions.
Z Scheme
Electron transfer process visualized as a Z shape.
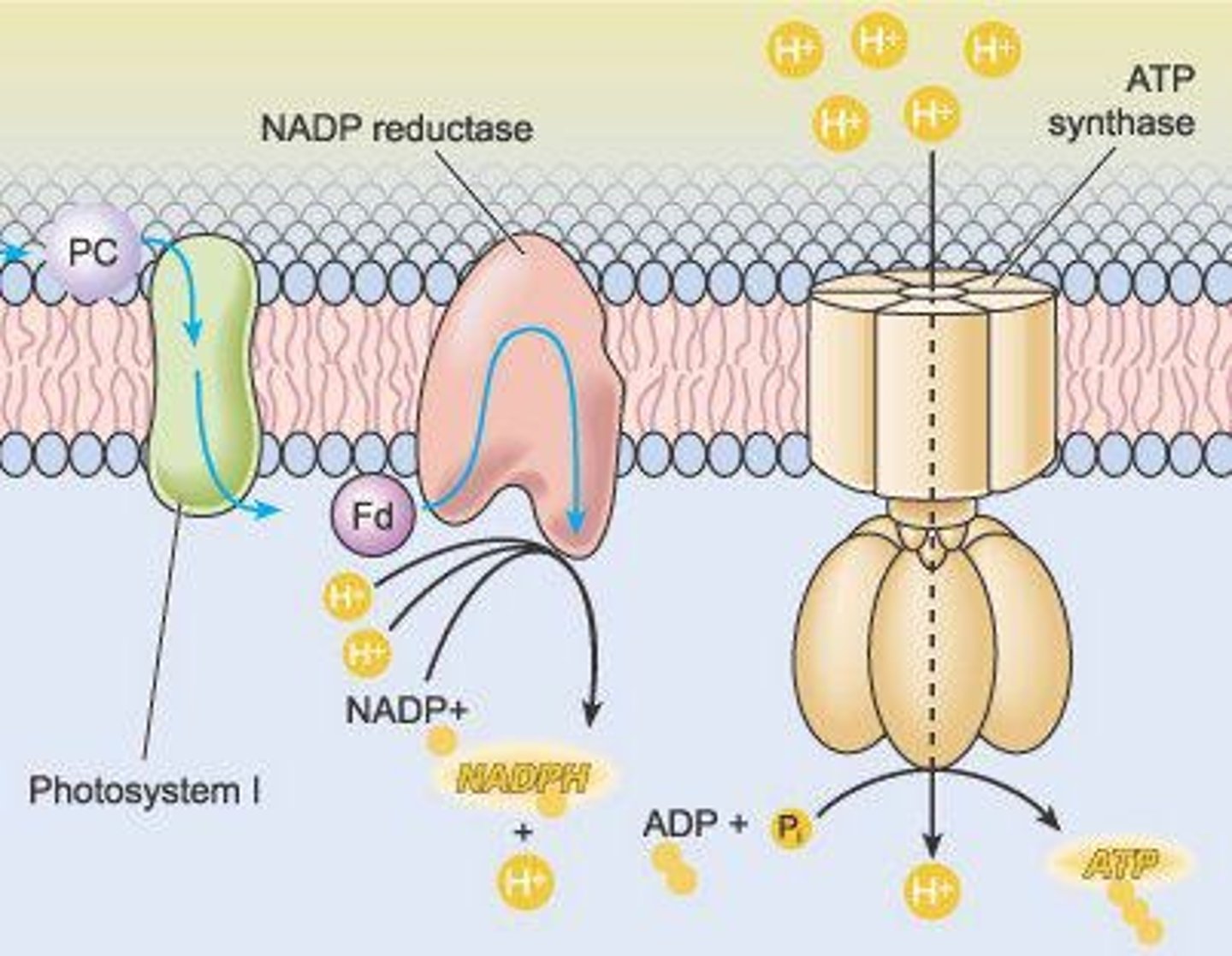
Electron Transport Chain
Series of reactions transferring electrons to produce energy.
Chemiosmosis
Process of ATP synthesis driven by ion gradients.
Thylakoid Membrane
Membrane where light-dependent reactions occur.
ADP
Adenosine diphosphate, precursor to ATP.
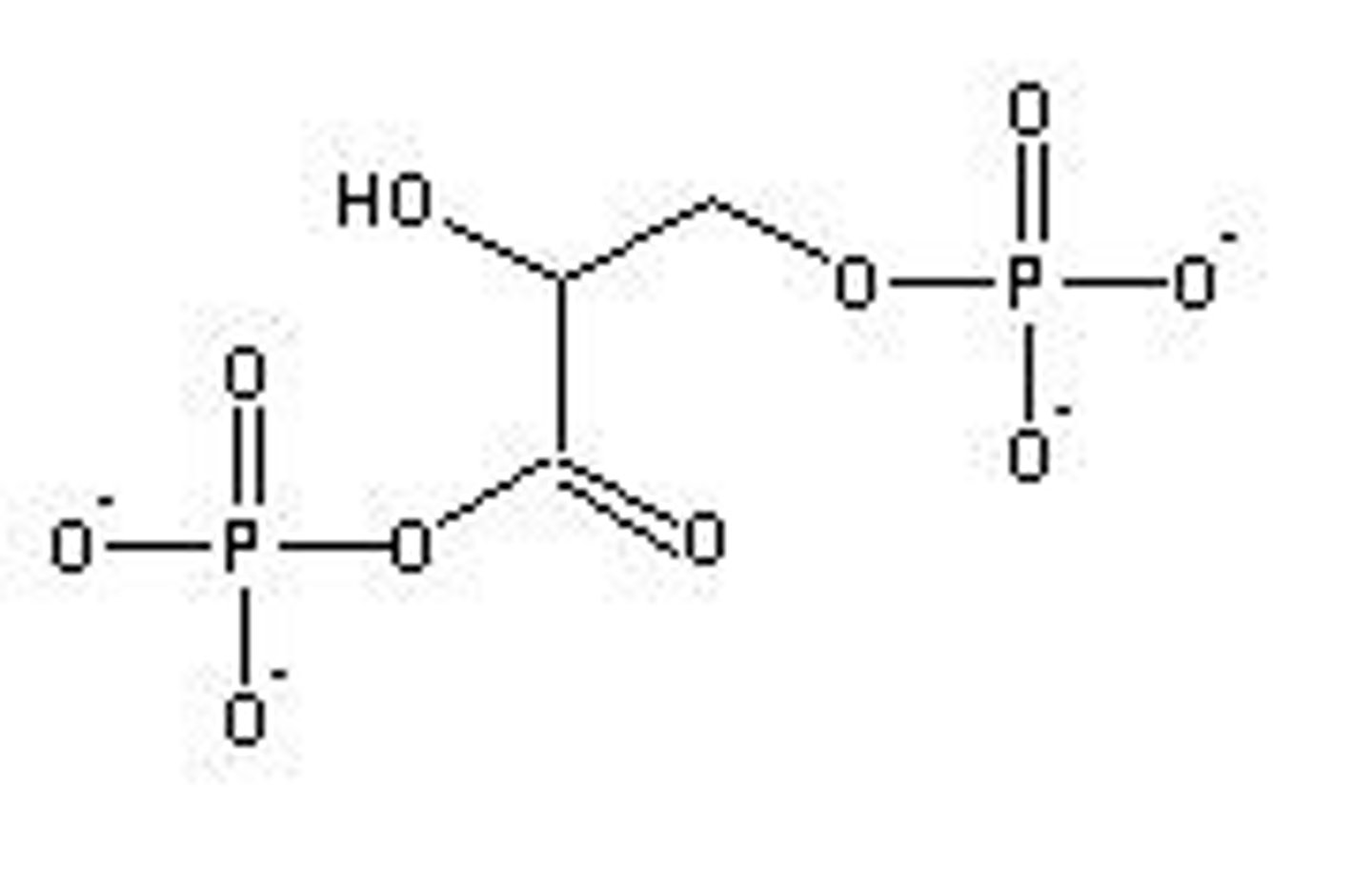
ATP
Adenosine triphosphate, energy carrier molecule.
Electron Acceptor
Molecule that receives electrons during electron transfer.
Electron Donor
Molecule that donates electrons during reactions.
Electrons
Charged particles providing energy in photosynthesis.
Transport chain
Series of proteins transferring electrons in chloroplasts.
H+ ions
Protons pumped across thylakoid membrane, creating gradient.
Electrochemical gradient
Difference in ion concentration across a membrane.
Chemiosmosis
Process using ion gradients to synthesize ATP.
Photophosphorylation
ATP production linked to light energy absorption.
Cyclic phosphorylation
ATP generation without NADPH formation in photosynthesis.
Photosystem I
Light-absorbing complex generating excited electrons.
NADP+
Electron carrier reduced to NADPH in photosynthesis.
Light-independent reactions
Carbon fixation process occurring without light.
Carbon fixation
Incorporation of CO2 into organic compounds.
Ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate (RuBP)
Five-carbon sugar combining with CO2 in Calvin cycle.
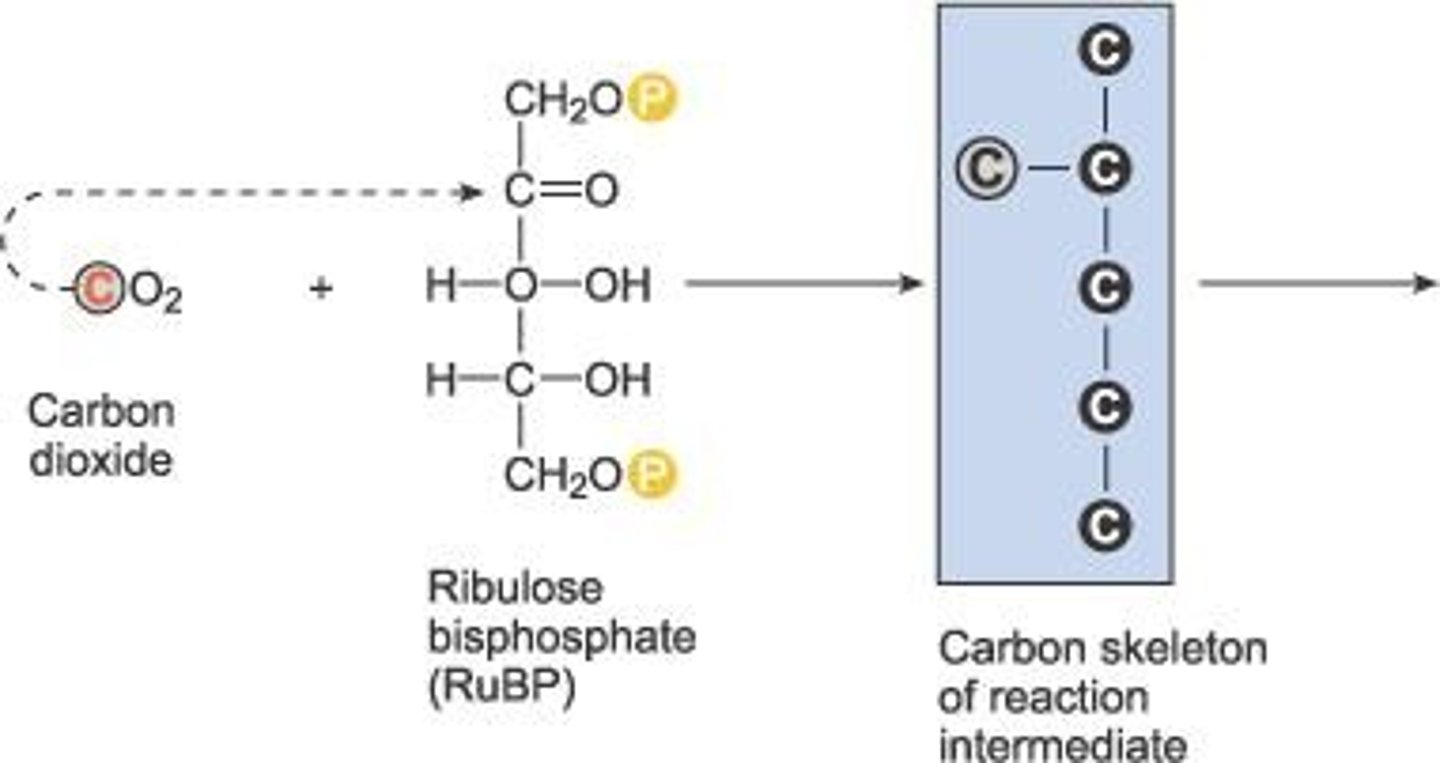
Glycerate 3-phosphate (GP)
Three-carbon compound formed from RuBP breakdown.
Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate (GALP)
Product of GP reduction, used in glucose synthesis.
Calvin cycle
Series of reactions converting CO2 to carbohydrates.
Phosphoglycerate (PGA)
First stable product of the Calvin cycle.
RuBP regeneration
Process reforming RuBP from GALP in Calvin cycle.
Limiting factors
Conditions affecting the rate of photosynthesis.
Light intensity
Amount of light affecting photosynthesis rate.
Optimal temperature
Temperature range maximizing enzyme activity in photosynthesis.
Chlorophyll a
Pigment used in both photosystems for light absorption.
Wavelength absorption
Specific light wavelengths absorbed by PSI and PSII.
Glycolysis
Metabolic pathway releasing energy from glucose.