AP Modern World History Unit 1, 1200-1450
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
65 Terms
Patriarchy
a system of society in which men hold the power

Social Stratifcation
a system by which a society ranks categories of people in a hierarchy

Monotheism
belief in one god
Polytheism
belief in more than one god
Shamanism
The practice of identifying special individuals (shamans) who will interact with spirits for the benefit of the community.
Animism
The belief that bodies of water, animals, trees, and other natural objects have souls
Judaism
A religion with a belief in one god. It originated with Abraham and the Hebrew people. Developed written scriptures and an ethical code (Torah, 10 Commandments) over time.
Vedas
Ancient Sanskrit writings that are the earliest sacred texts of Hinduism.
Hinduism
A religion and philosophy developed in ancient India, characterized by a belief in reincarnation and a supreme being who takes many forms
Monasticism
A way of life in which men and women withdraw from the rest of the world in order to devote themselves to their faith (as monks and nuns)
legtimacy
the popular acceptance of an authority, like a King or ruler
Diasporic communities
immigrants who have relocated from their ancestral homelands and retain their distinct cultural identities as ethnic minority groups in their new locations
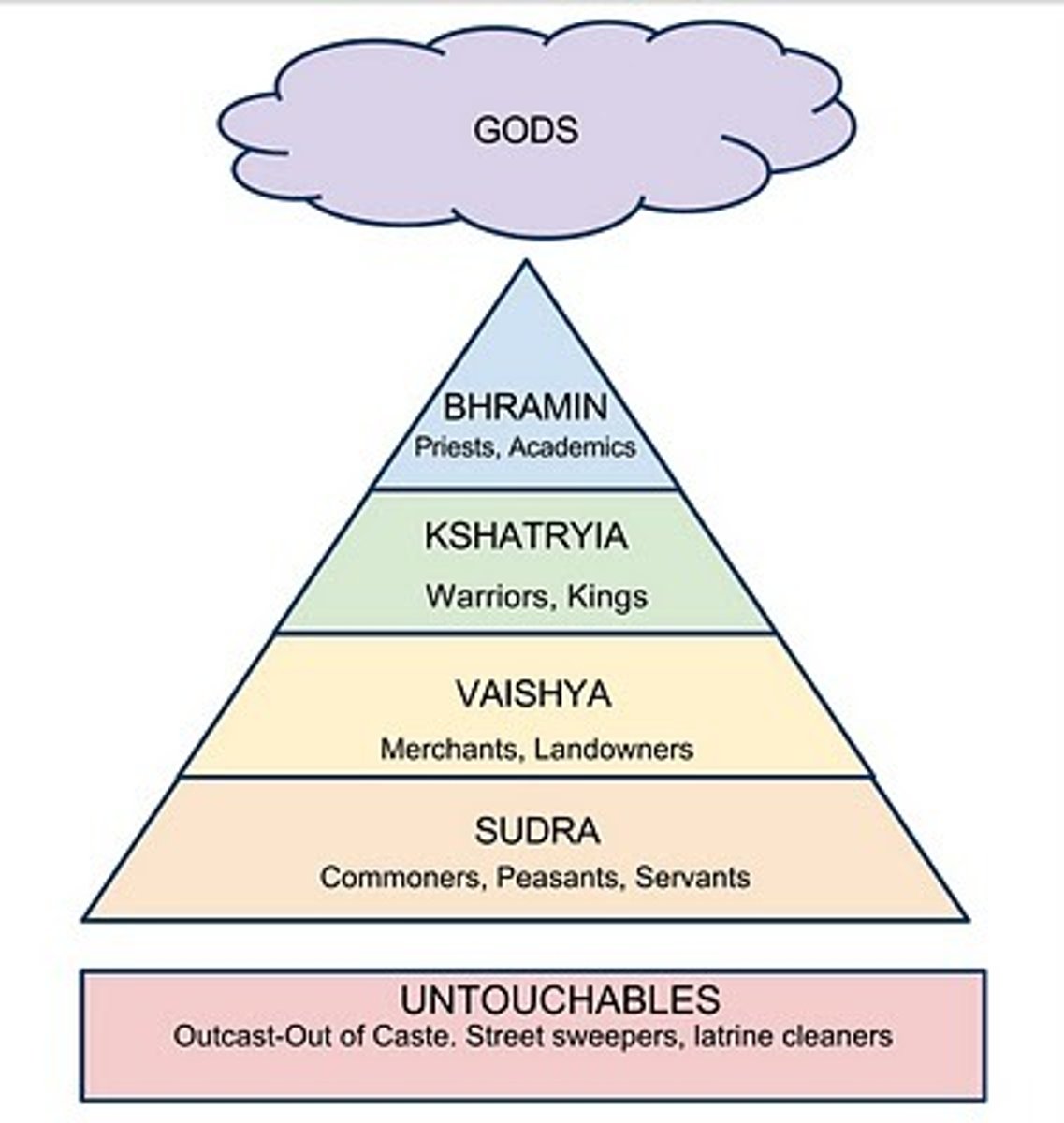
Caste System
a set of rigid social categories that determined not only a person's occupation, but also his or her position in society in Hinduism
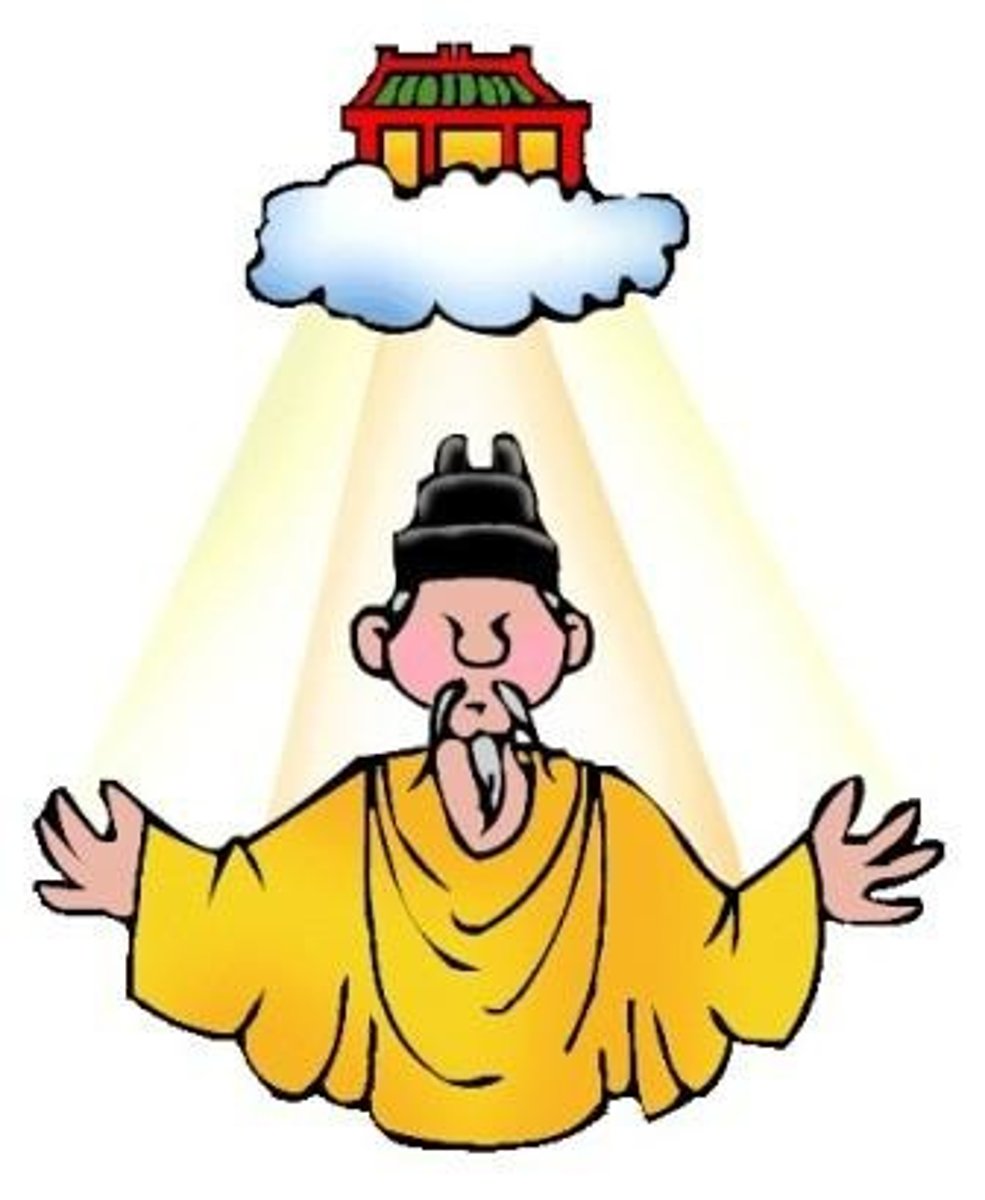
Mandate of Heaven
an ancient Chinese belief and philosophical idea that tiān (heaven) granted emperors the right to rule based on their ability to govern well and fairly.

Reincarnation
the rebirth of a soul in a new body.
Eightfold Path
In Buddhism, the path to nirvana. Comprises eight aspects in which an aspirant must become practiced: right views, intention, speech, action, livelihood, effort, mindfulness, and concentration.
Confucianism
A philosophy that adheres to the teachings of the Chinese philosopher Confucius. It shows the way to ensure a stable government and an orderly society and stresses a moral code of conduct.

Buddhism
the teaching of Buddha that emphasizes that life is filled with suffering caused by desire and that suffering ceases when desire ceases. Through right conduct, wisdom and meditation one can end the cycle of rebirth and reach Enlightenment.

Christianity
A monotheistic system of beliefs and practices based on the Old Testament and the teachings of Jesus as embodied in the New Testament, emphasizing the role of Jesus as savior.
State
a nation or territory considered as an organized political community under one government.
Siddhartha Gautama (The Buddha)
Means "Enlightened One." He is said to have renounced his worldly possessions and taught of a way to overcome suffering.
filial piety
In Confucian thought, one of the virtues to be cultivated, a love and respect for one's parents and ancestors.
ancestor veneration
Veneration of the dead or ancestors is based on the beliefs that the dead have a continued existence, and may possess the ability to influence the fortune of the living
Conscript labor
unpaid forced labor usually by lower classes, forced upon them by the government like a tax (China and Inca used this)
tribute system
payment made by one nation to another in acknowledgment of submission, notably used by Aztec and Chinese dynasties
Bureaucracy
A system of managing government through departments run by appointed officials
Missionaries
people who work to spread their religious beliefs
Song dynasty
During this Chinese dynasty (960 - 1279 CE) China saw many important inventions. There was a magnetic compass; paper money; gun powder; moveable type printing. Mass produced goods for trade on the Indian Ocean, experienced great urbanization, population increase, and embraced Neo-Confucianism.
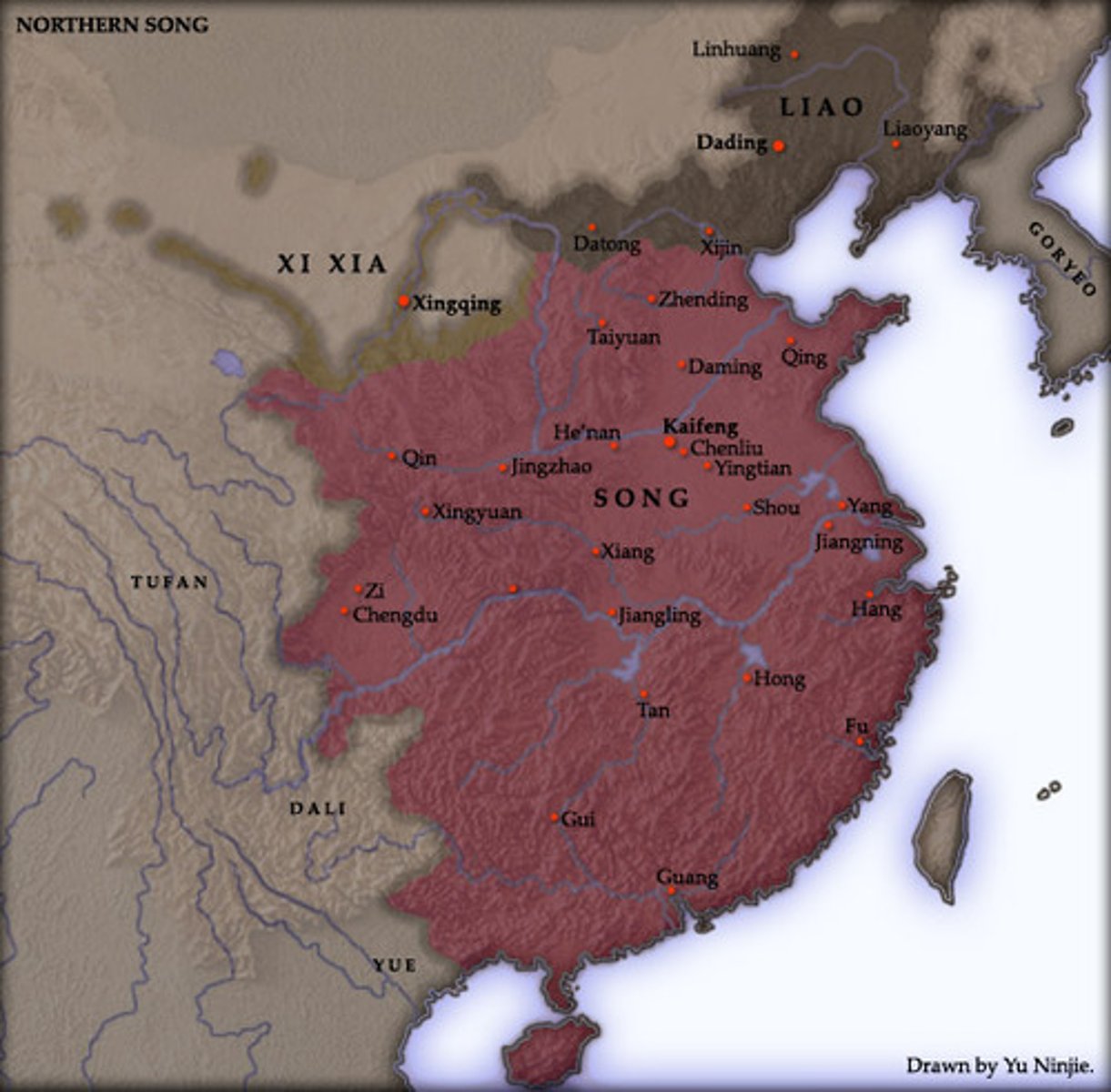
Hangzhou
Capital of later Song dynasty; located near East China Sea; permitted overseas trading; population exceeded 1 million.
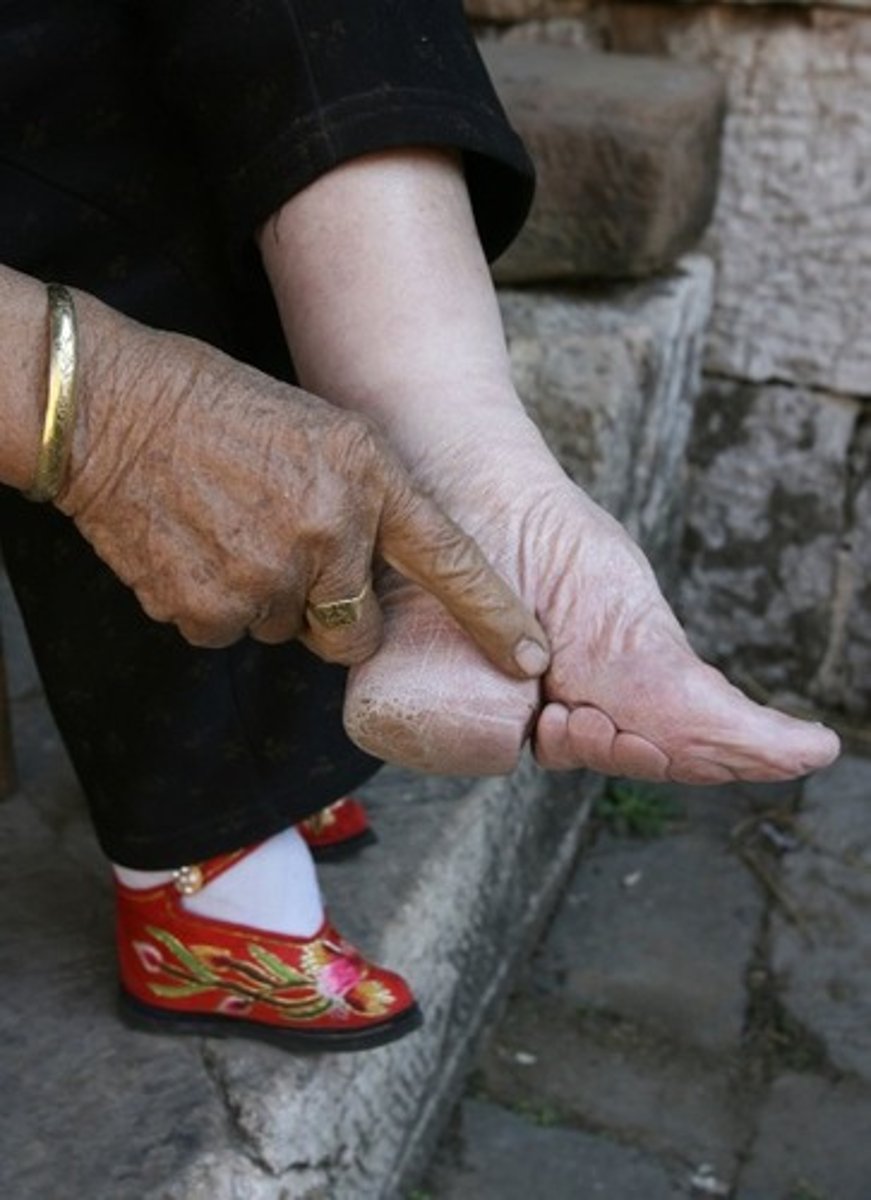
foot binding
Becoming prominent during the Song dynasty, practice in Chinese society to mutilate women's feet in order to make them smaller; produced pain and restricted women's movement; made it easier to confine women to the household.
Chinese influence on Japan
Centralized government; Confucian ideals; architecture (pagodas); Buddhism spread
Quran
The holy book of Islam
umma
The community of all Muslims. A major change where in Arabia traditionally kinship rather than faith had determined membership in a community.

Pillars of Islam
The five core practices required of Muslims: a profession of faith, regular prayer, charitable giving, fasting during Ramadan, and a pilgrimage to Mecca (if physically and financially possible).
sharia
Body of Islamic law that includes interpretation of the Quran and applies Islamic principles to everyday life
jizya
the extra tax paid by Christians and Jews who lived in Muslim communities
Caliphates
(661-1258CE) The Islamic caliphate that established a capital at Damascus, then later Baghdad. Conquered North Africa, the Iberian Pennisula, and the Middle East. Had an extensive bureaucracy and encouraged long-distance trade.
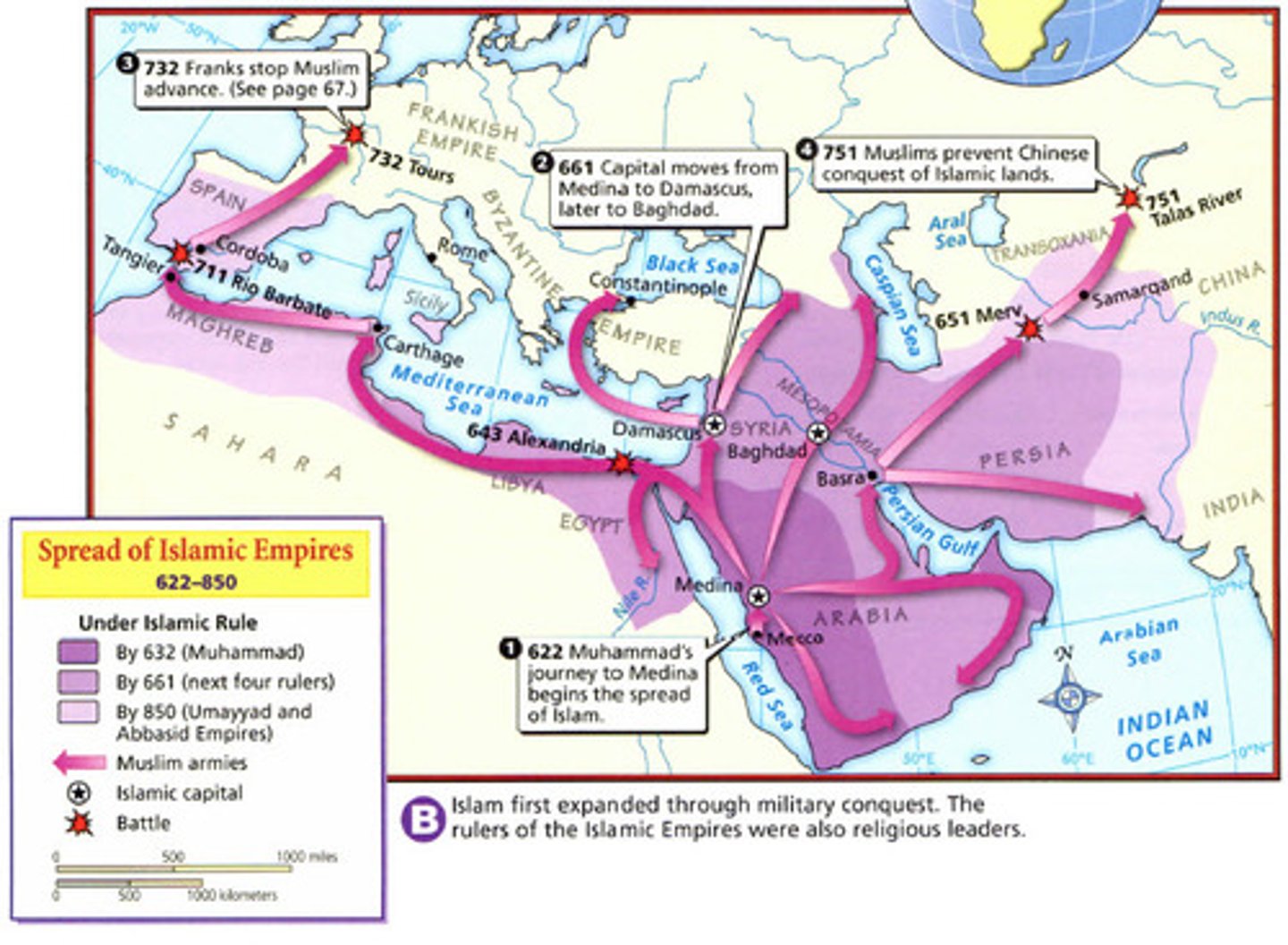
House of Wisdom
Combination library, academy, and translation center in Baghdad established in the 800s.

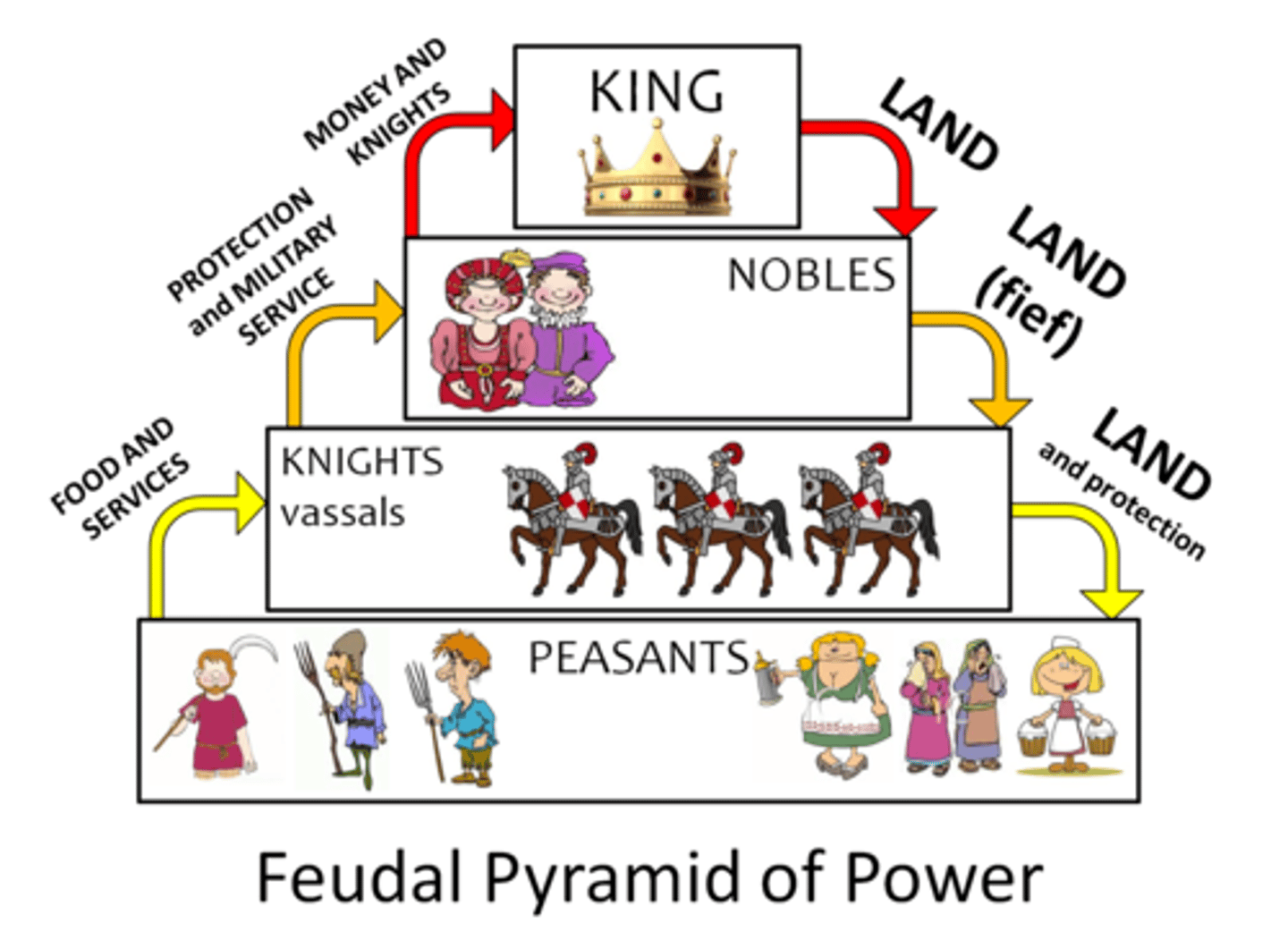
Serfdom
A type of labor used in in feudal Europe in which the laborers work the land in return for protection but they are bound to the land and are not allowed to leave or to pursue a new occupation.
Feudal Europe
Western Europe was far removed from the growing world trade routes, but coastlines and river systems facilitated internal exchange. Decentralized kingships were established over powerful lords, with manors dominating political and economic life.
Crusades
Armed pilgrimages to the Holy Land by Christians determined to recover Jerusalem from Muslim rule. The Crusades brought an end to western Europe's centuries of intellectual and cultural isolation.

Inca
Largest and most powerful Andean empire. Controlled the Pacific coast of South America from Ecuador to Chile from its capital of Cuzco. Built a strong network of roads, and relied on the mita system.

Syncretism
Religious syncretism exhibits blending of two or more religious belief systems into a new system

Mita System
Incan system for payment of taxes with labor
Grand Canal
The 1,100-mile waterway linking the Yellow and the Yangzi Rivers, facilitating trade and movement. It was expanded during the Song Empire.
Allyu
in Incan society, a small community or family group whose members worked together for the common good
Feudalism
System where kings give land to nobles in exchange for loyalty & service (as found in Western Europe)
Arabic
Language of the Islamic civilization; facilitated trade.
Quipu
An arrangement of knotted strings on a cord, used by the Inca to record numerical information.
Champa Rice
Quick-maturing rice that can allow two harvests in one growing season. It was later sent to China as a tribute gift by the Champa state (in Vietnam) and resulted in population increase under the Song.
moveable type
blocks of metal or wood, each bearing a single character, that can be arranged to make up a page for printing. Improved on by the Song Dynasty (from Korea) and disseminated agricultural and Confucian ideas.
Seljuk Turks
nomadic Turks from Asia who conquered Baghdad in 1055 and allowed the caliph to remain only as a religious leader, leading to the increasing fragmentation of the Caliphate (but the promotion of science, learning, and trade in the empire remained.)
Sufism
An Islamic mystical tradition that desired a personal union with God, active missionaries and greatly contributed to the spread of Islam
Centralized
power concentrated in the center, especially political power concentrated in the hands of one leader or government
Decentralized
governmental power is spread among more than one person or group (Ex: Feudal Europe or Maya City-States)
Maya
Mesoamerican civilization--never unified into a single empire, but rather collection of city-states. Major contributions were in mathematics, astronomy, and development of the calendar.
Aztecs
Also known as Mexica, they created a powerful empire in central Mexico (1325-1521 C.E.). They forced defeated peoples to provide goods and labor as tribute and POWs were used as slaves and sacrifices
llamas and alpacas
Animals used for food and labor by the Inca
Chinampas
floating farming islands made by the Aztec
Ethiopia
A Christian kingdom that developed in eastern Africa
Manorialism
An economic system based on the manor and lands including a village and surrounding acreage which were administered by a lord. It developed in Feudal Europe to increase agricultural production.
Dharma
the religious and moral duties of an individual (in Hindu and Buddhist beliefs)
Civil Service Exam
In Imperial China, it was an exam based on Confucian teachings that was used to select people for various government service jobs in the nationwide administrative bureaucracy.
Dar al-Islam
an Arabic term that means the "house of Islam" and that refers to lands under Islamic rule
Swahili Coast
region along east coast of Africa; part of Indian Ocean trade route; many converted to Islam; blending of East African and Muslim cultures