Amines and Amides: Structure, Properties, and Reactions
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
Amines
Derivatives of ammonia with hydrogen replaced by R groups.
Primary amine
One hydrocarbon group attached to nitrogen.
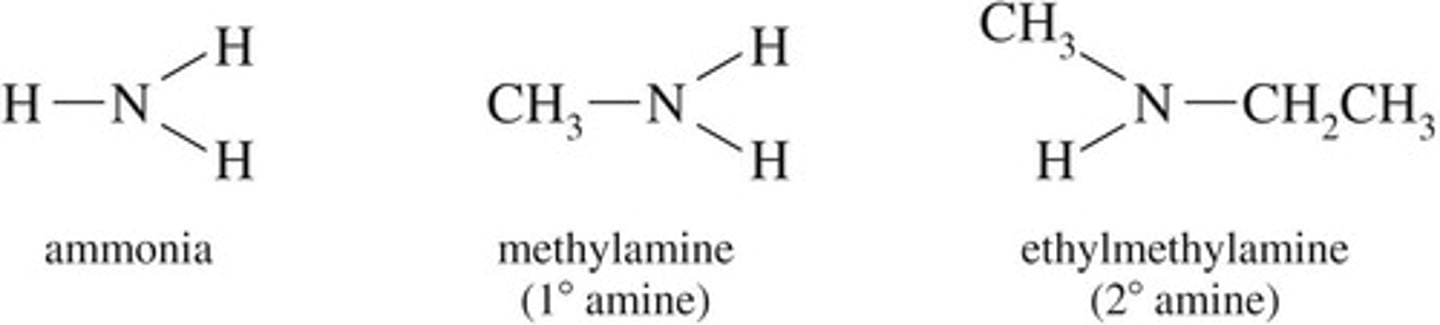
Secondary amine
Two hydrocarbon groups attached to nitrogen.
Tertiary amine
Three hydrocarbon groups attached to nitrogen.
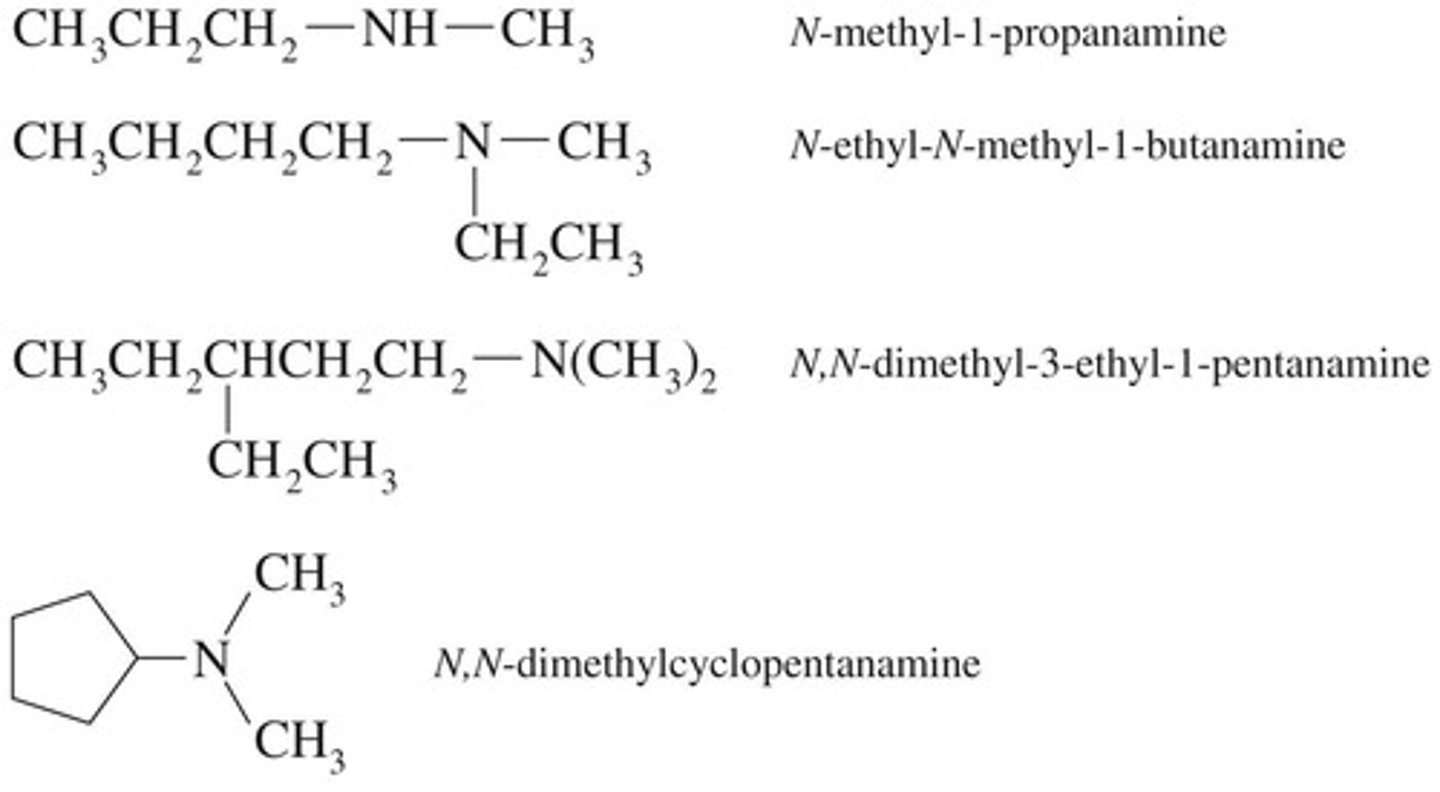
IUPAC naming for amines
Use longest carbon chain, suffix -amine.
Diamines
Compounds with two nitrogen atoms present.
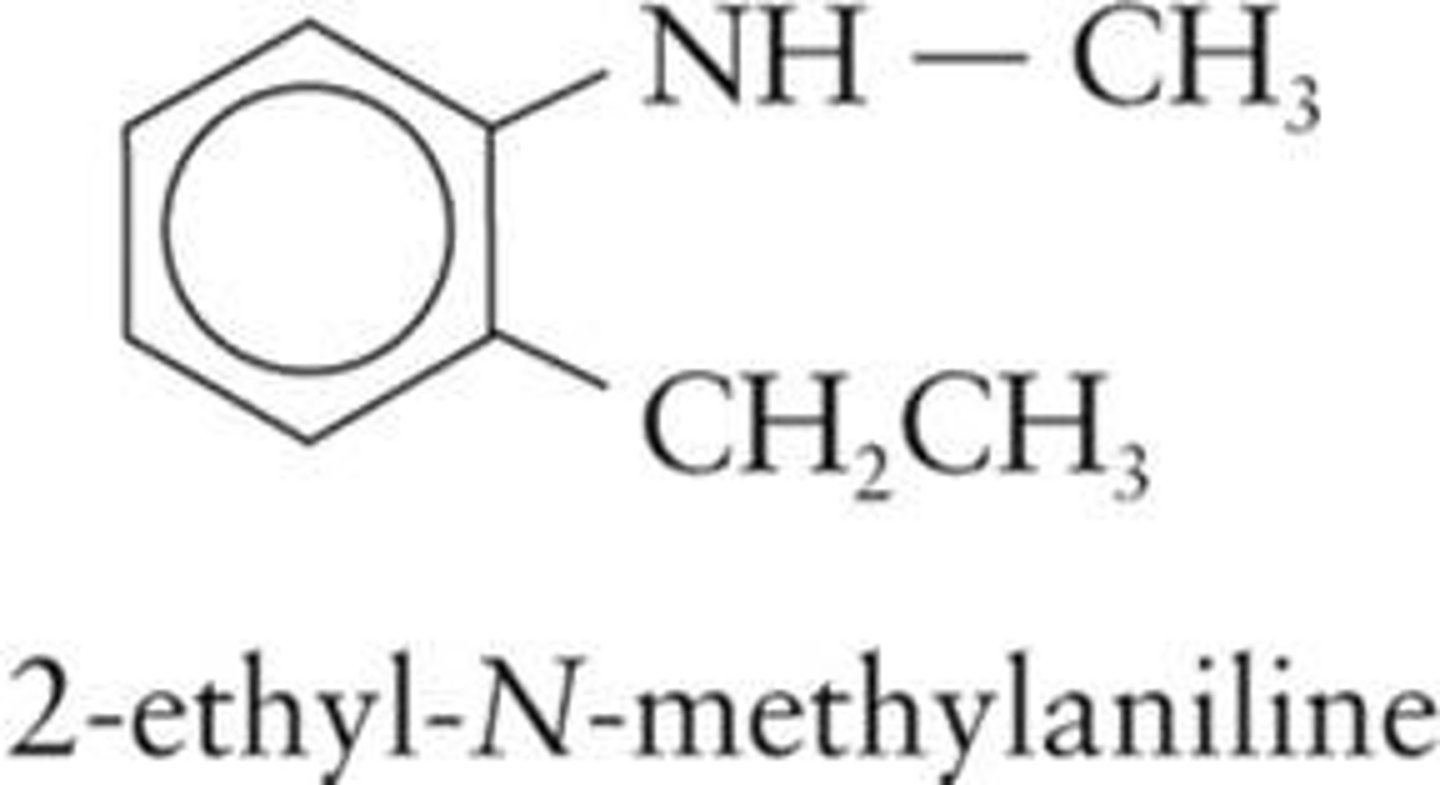
Aniline
Most important aromatic amine, C6H5NH2.
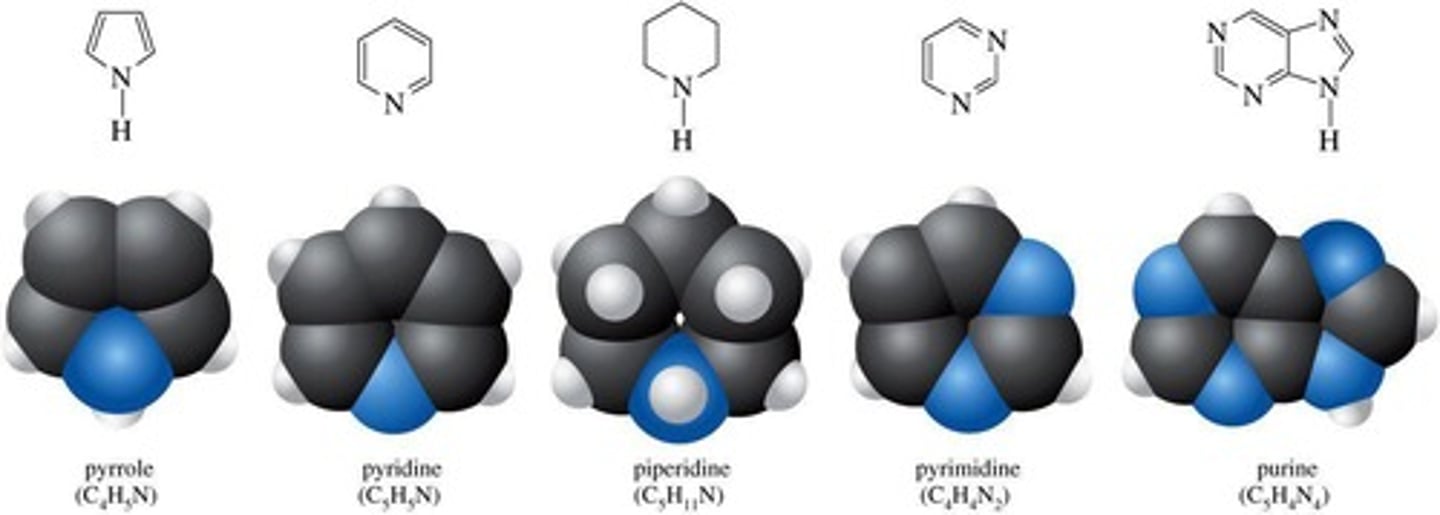
Heterocyclic amines
Amines in ring compounds with different atoms.
Hydrogen bonding in amines
Primary and secondary amines can form hydrogen bonds.

Boiling points of amines
Lower than alcohols of similar molecular weight.
Tertiary amines and hydrogen bonds
Cannot form hydrogen bonds due to no H attached.
Solubility of amines
Amines with <6 carbons are water soluble.
Odor of low molecular weight amines
Sharp, penetrating odor similar to ammonia.
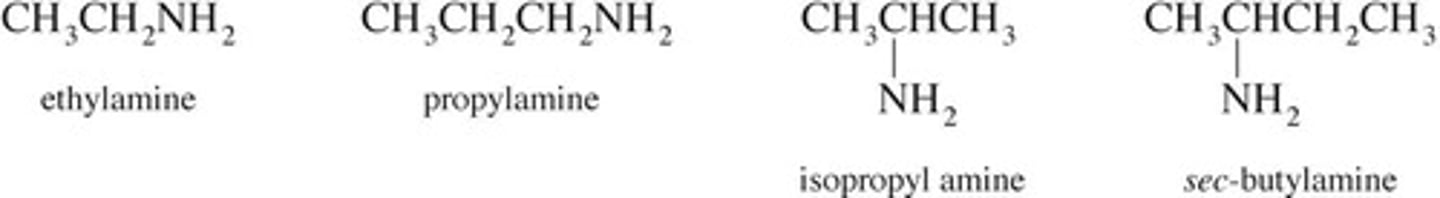
Hydrogen bonding influence
Affects physical properties like boiling points.
Acidic hydrolysis of amides
Reaction producing carboxylic acids and amines.
Basic hydrolysis of amides
Reaction producing amines and carboxylate ions.
Uses of biological amines
Serve as neurotransmitters in biological systems.
N-alkyl group
Indicates an alkyl group attached to nitrogen.
Physical state of low molecular weight amines
Gases at room temperature, heavier are liquids/solids.
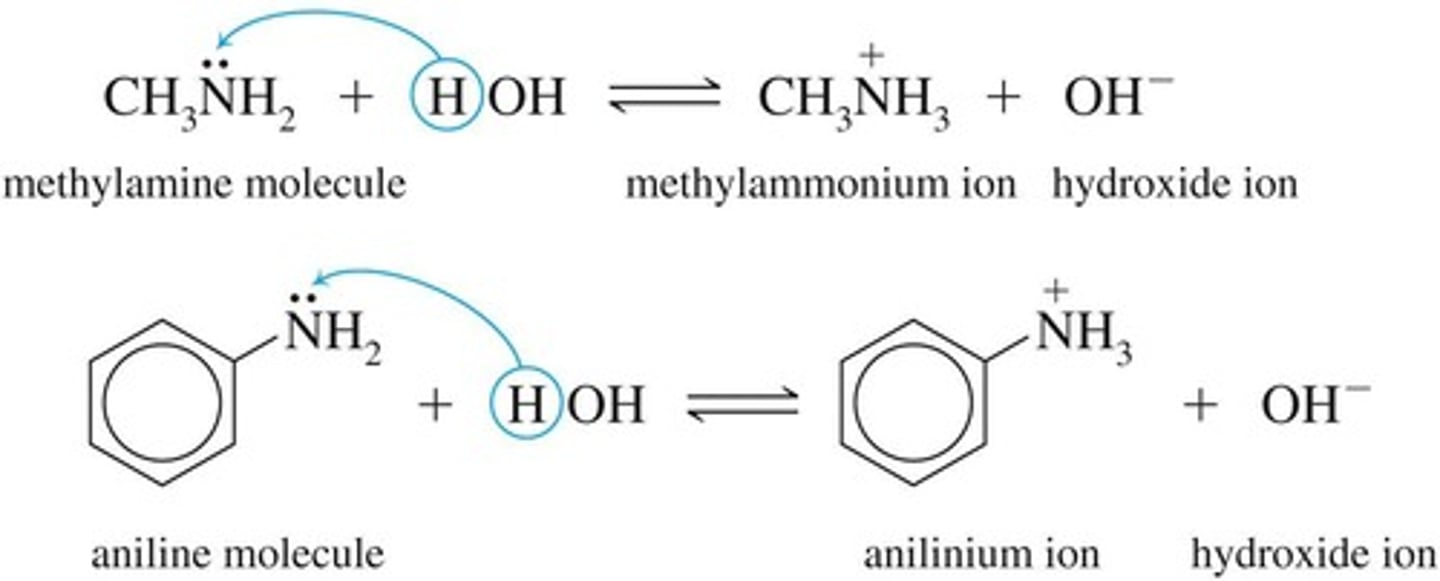
Weak Bases
Amines produce OH− ions in water solutions.
Ammonium Salts
Formed when amines react with strong acids.
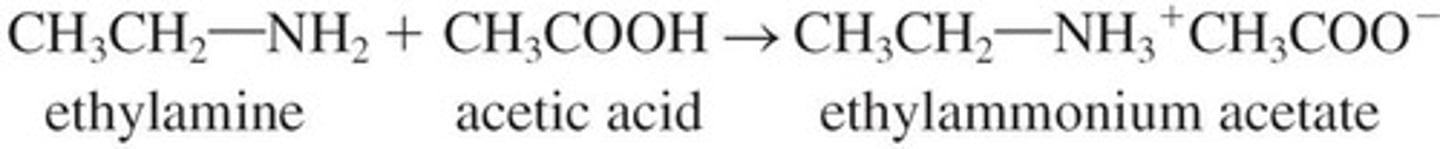
Amine Salts
Formed by amines reacting with acids, creating salts.
Solubility of Amine Salts
More soluble in water than parent amines.
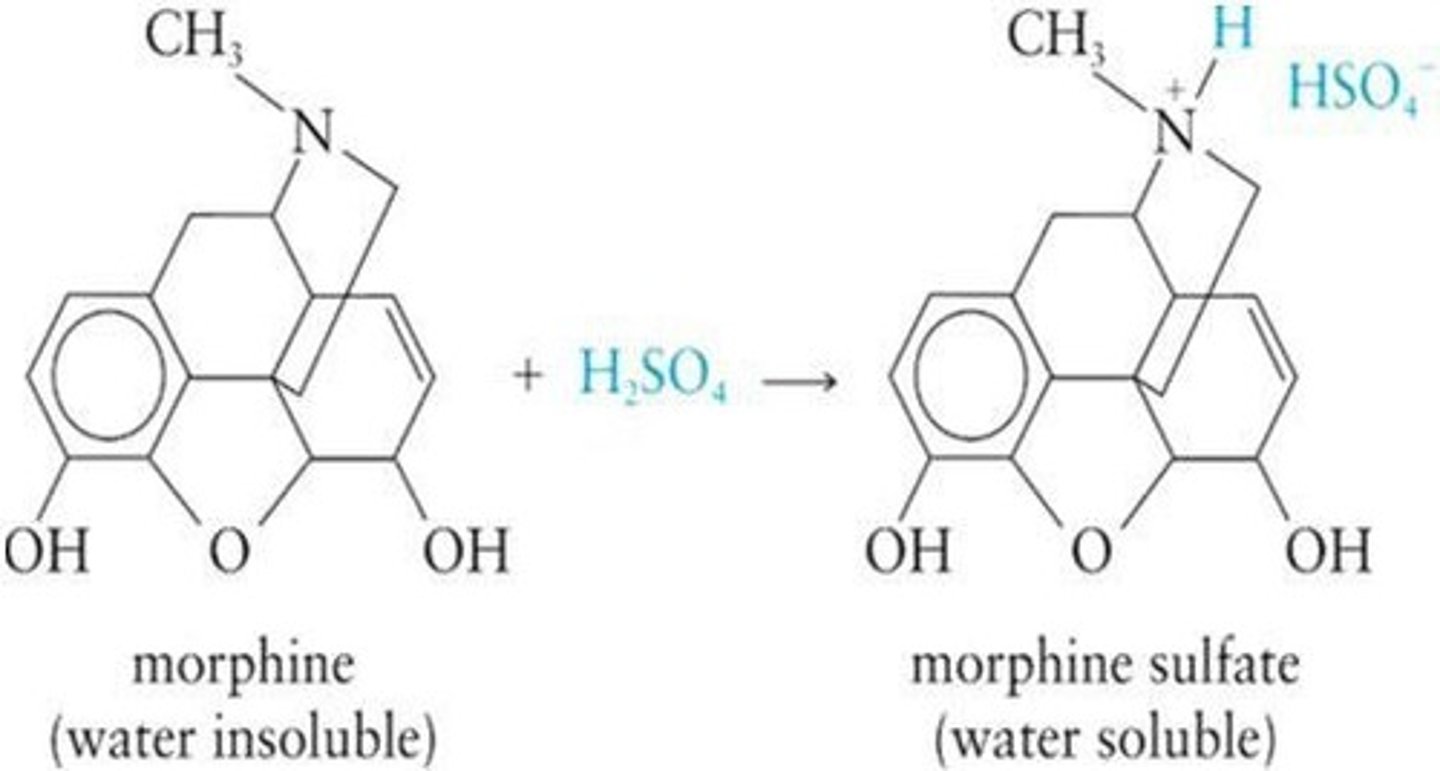
pH Dependence of Amines
Amines exist as salts in low pH solutions.
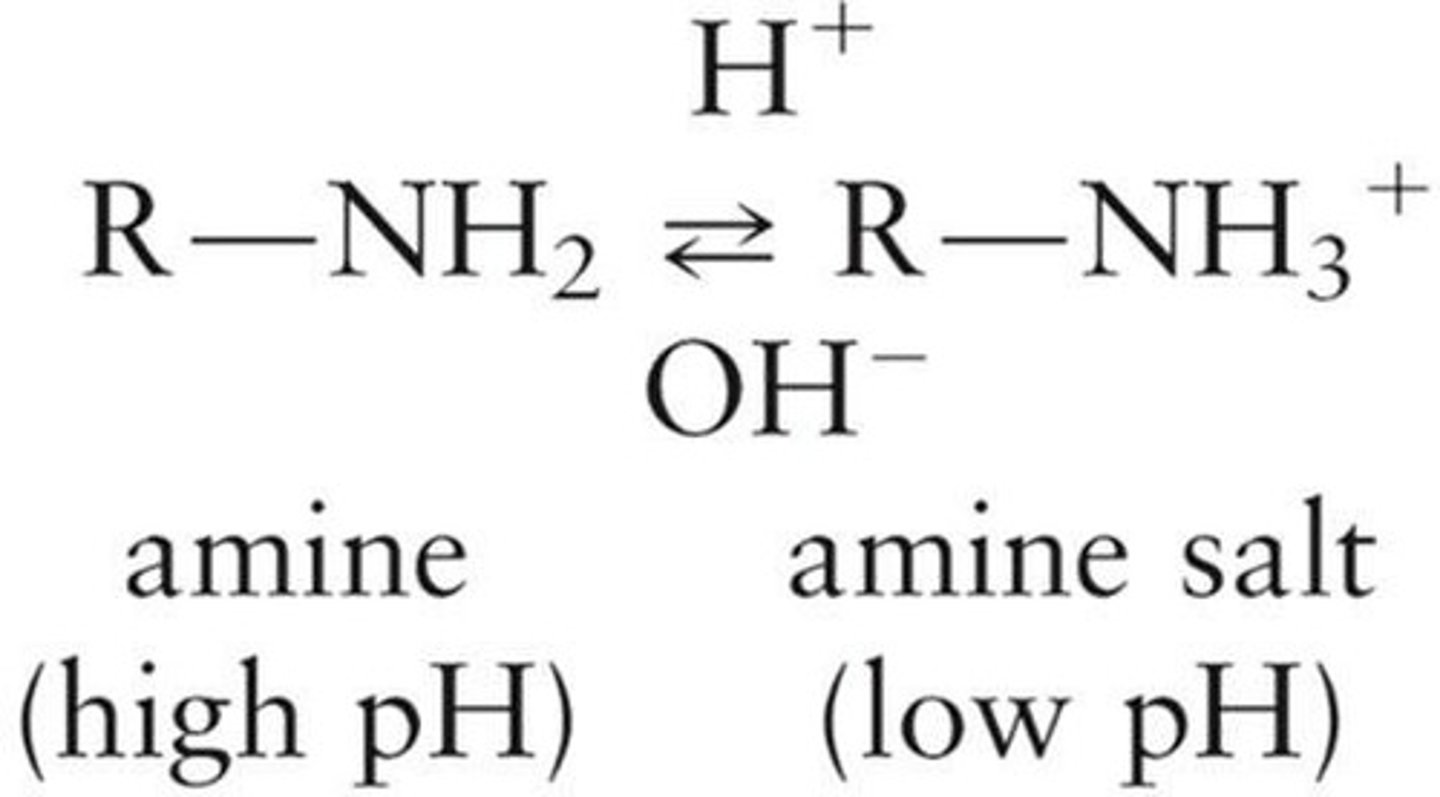
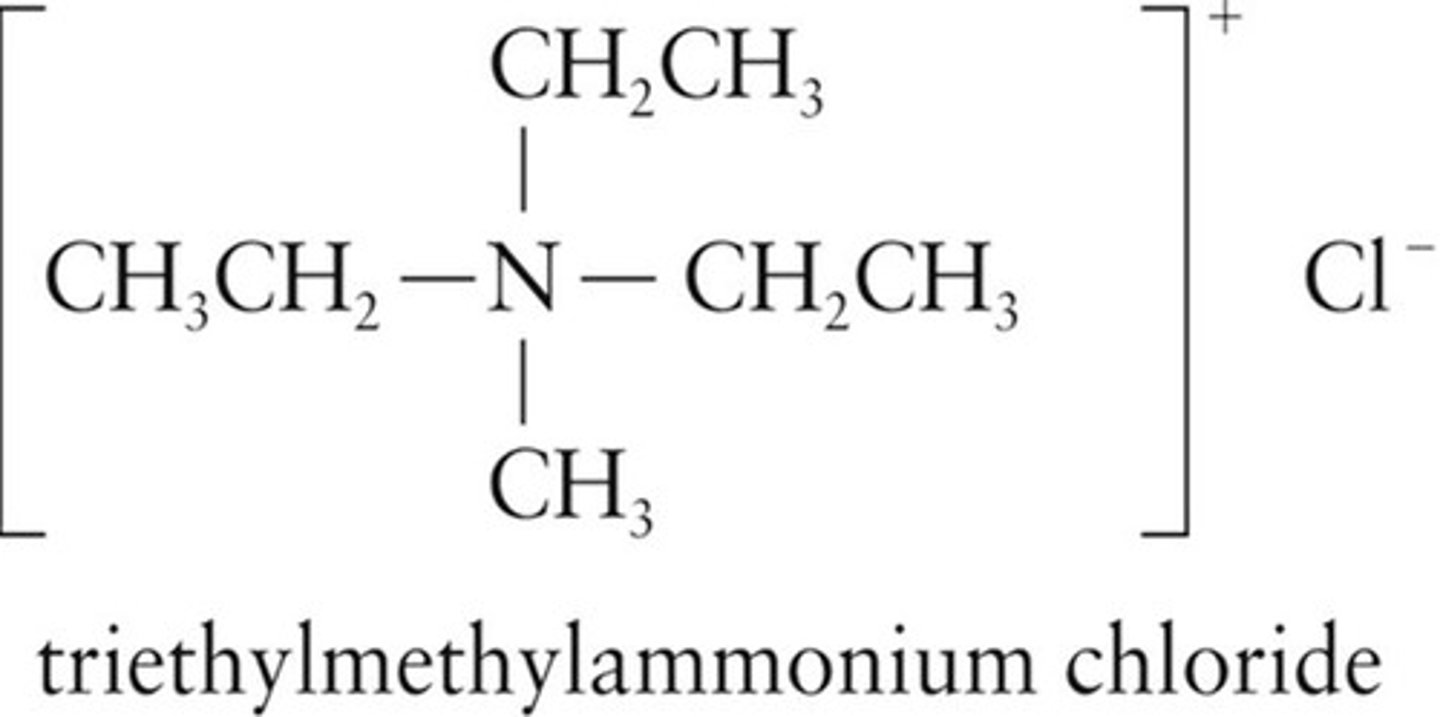
Quaternary Ammonium Salts
Positively charged ions with four groups attached to nitrogen.
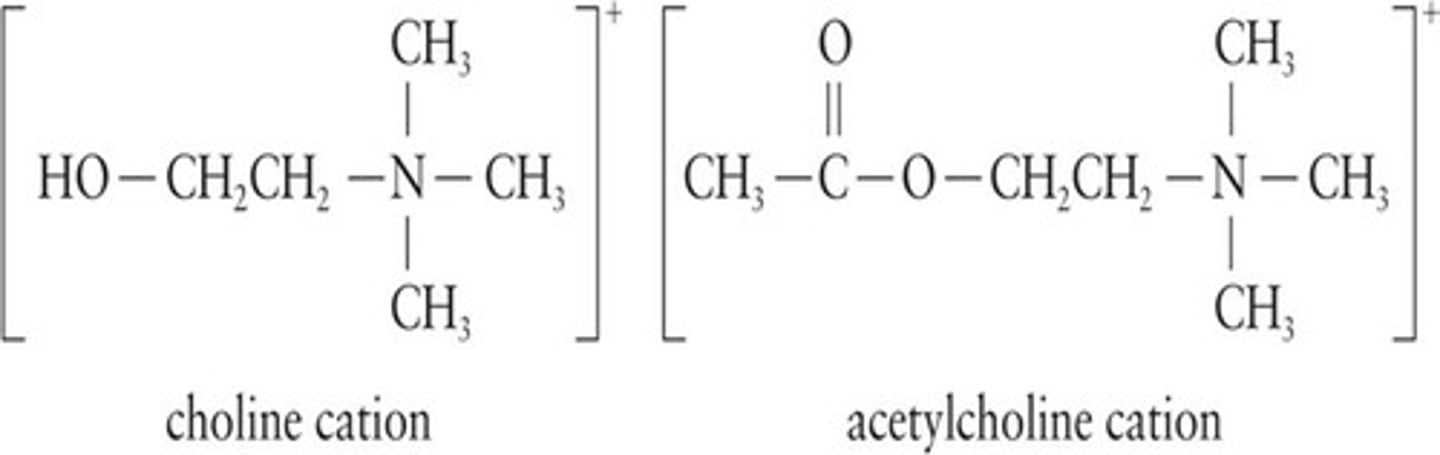
Choline
A component of certain lipids, important for health.
Acetylcholine
Neurotransmitter involved in nerve impulse transmission.
Amides
Compounds with a carbonyl group bonded to nitrogen.
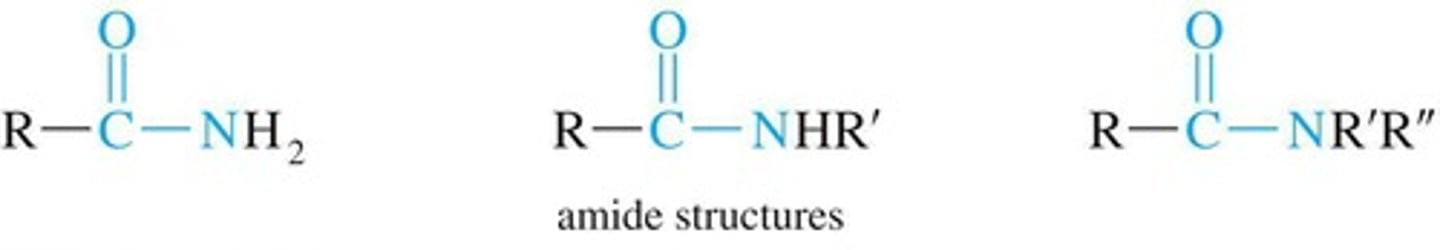
Amide Linkage
Carbonyl carbon-nitrogen single bond in amides.
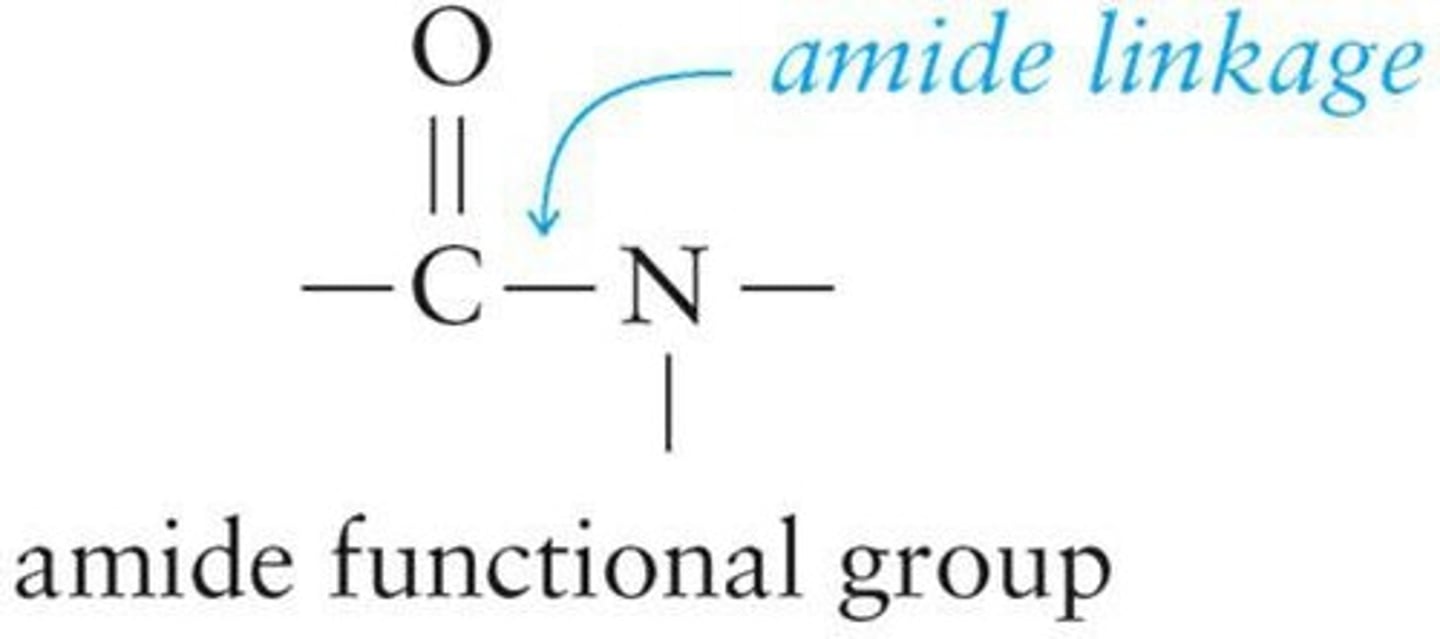
Amide Formation
Reaction of acid chlorides with amines to form amides.
Naming Amides
Change carboxylic acid name to -amide for amides.
Physical Properties of Amides
Most are colorless solids; formamide is a liquid.
Amide Hydrolysis
Cleavage of amides to produce carboxylic acid and amine.
Polyamides
Condensation polymers formed from diacid chlorides and diamines.
Uses of Polyamides
Used in textiles, fasteners, and medical applications.
Neurotransmitters
Chemical bridges for nerve impulse transmission.
Dopamine
Neurotransmitter synthesized from tyrosine, affects mood.
Norepinephrine
Influences mood, synthesized from dopamine, affects blood pressure.
Serotonin
Regulates mood, sleep, and sensory perception.
Epinephrine
Hormone increasing blood glucose, released in stress.