Viral Diseases exam 4
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
Pathogen: Varicella
Varicella - Chickenpox
cause: Itchiness
Herpesvirus Varicella-Zoter
DNA virus
Transmitted via respiratory route
Caused Pus-filled Vesicles
Vesicles on skin (itchy)
Symptoms
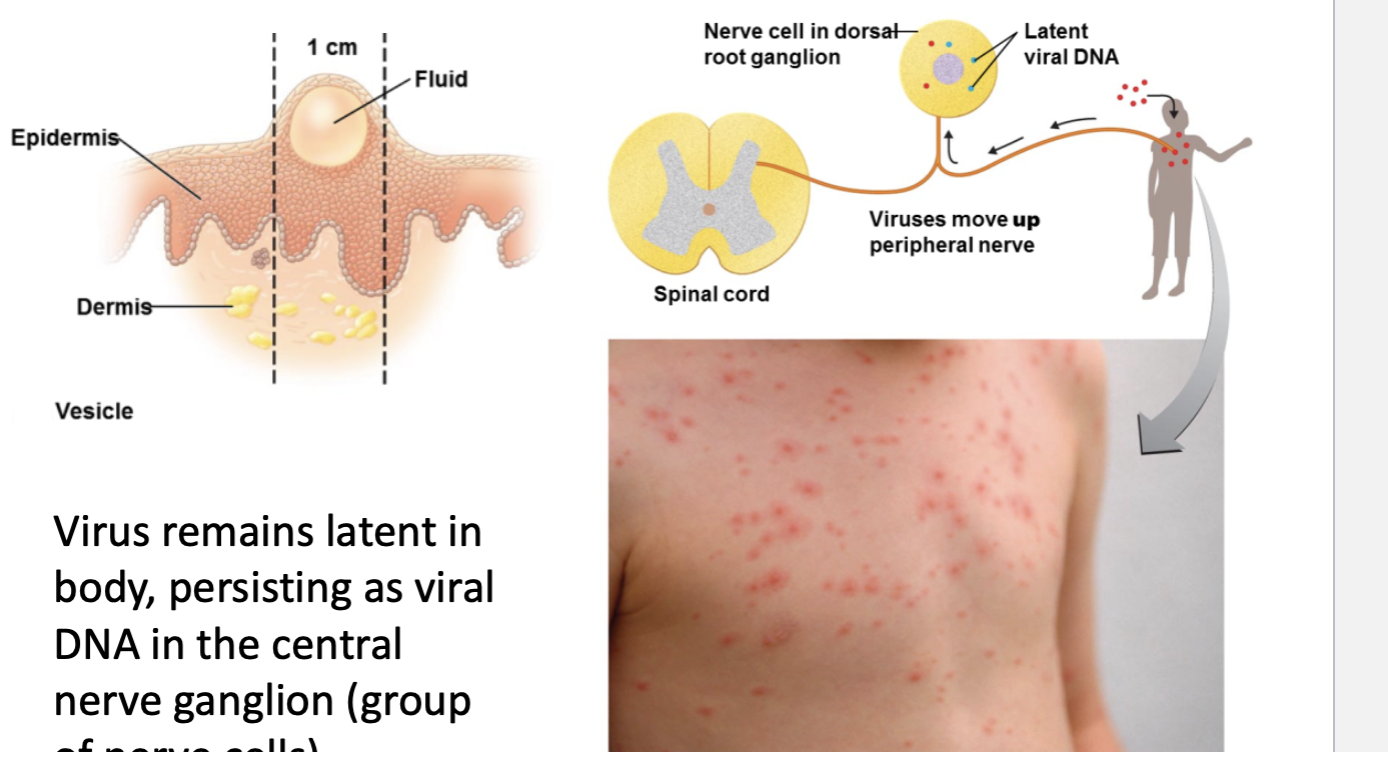
Latent in neurons of CNS
Reactivation leads to shingles
Varicella causes disease by:
Infecting respiratory mucosa.
Disseminating through blood to skin and internal organs.
Causing a systemic immune response and characteristic rash.
Shingles
Result of latent chickenpox
reactivation leads to shingles - Postherpetic Neuralgia
Due to stress - low immunity
Herpes Zoster
“Varicella - Zoster” - pathogen
Symptoms: Rash wide spread right side
emotional stress
Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV)
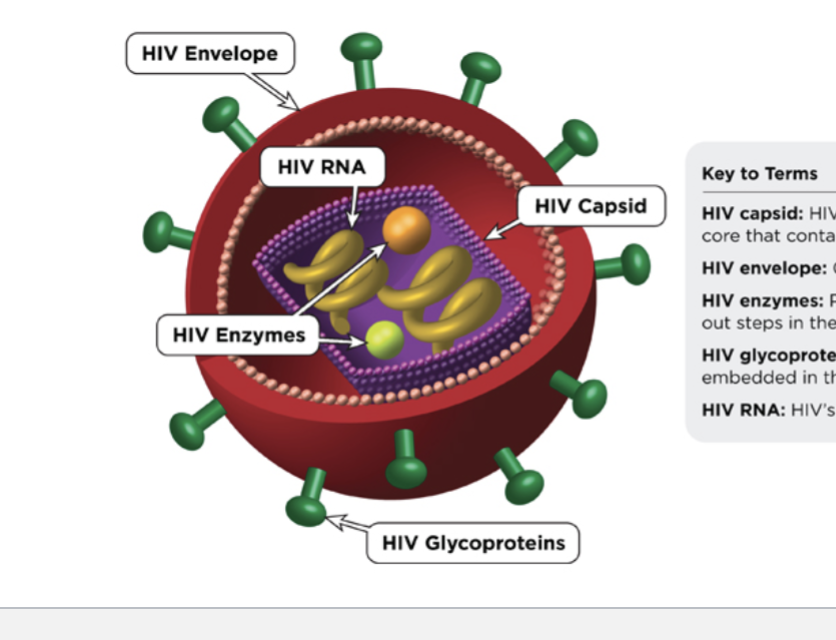
Retro Virus/ RNA
Enveloped
gp120 binds to CD4 receptors on Thelper cells, & macrophages & Dendritic
Symptoms:
Rare fungal infections
Rare cancers
low white blood cells and T cells count
weight loss fever
Hiv attach to host cell
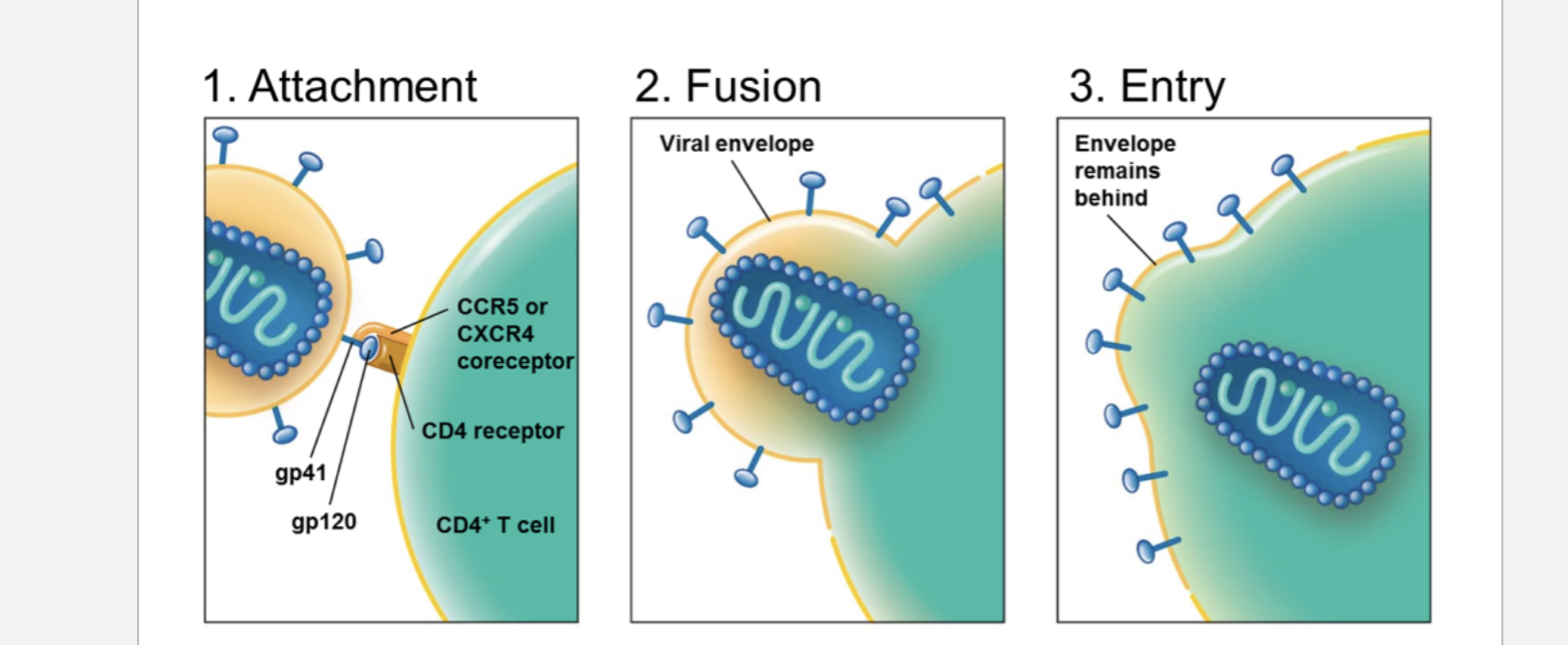
Spread by dendritic cells and carried
to the lymphoid organs; contacts
activated T cells
• gp120 spike combines with CD4+
receptor
– CD4 receptor molecules are
carried on T helper cells,
macrophages, and dendritic cells
• Virus fuses and enters into the cell
Pathogenicity of HIV
leading to immune damage*
HIV DNA will integrate into CD4 host cell Chromosome
Tend to target memory T Helper cells for integration
into a Provirus ( Integrate DNA)
into 2 Types of infections
Activation : new virus buds off from the host cell
Latent: DNA integrates into the host chromosomes as a provirus
Virus undergoes rapid antigenic changes and a high rate of
mutation (due to not having
proofreading ability)
3 Stages of HIV infection
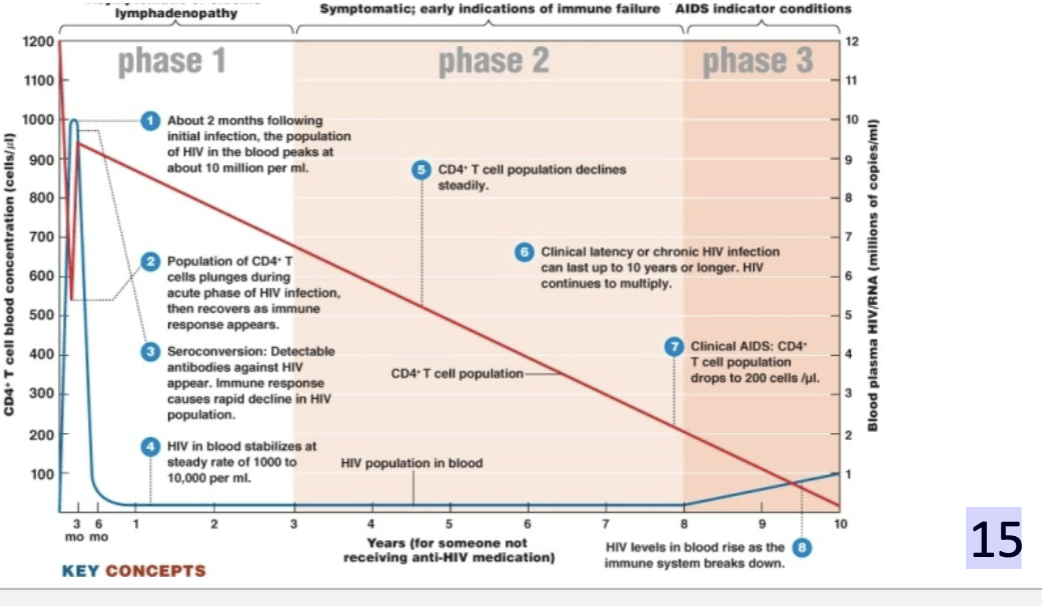
Stages of HIV infection
• Phase 1: asymptomatic ( No signs)
• Phase 2: CD4+ T cells decline steadily; only a few infected cells more persistent infection
release the virus; a few serious disease symptoms ( fever, and oral leukoplakia)
• Phase 3: AIDS develops; the CD4+ is count below 200 cells/μl;
risk for many opportunistic infections and rare cancers
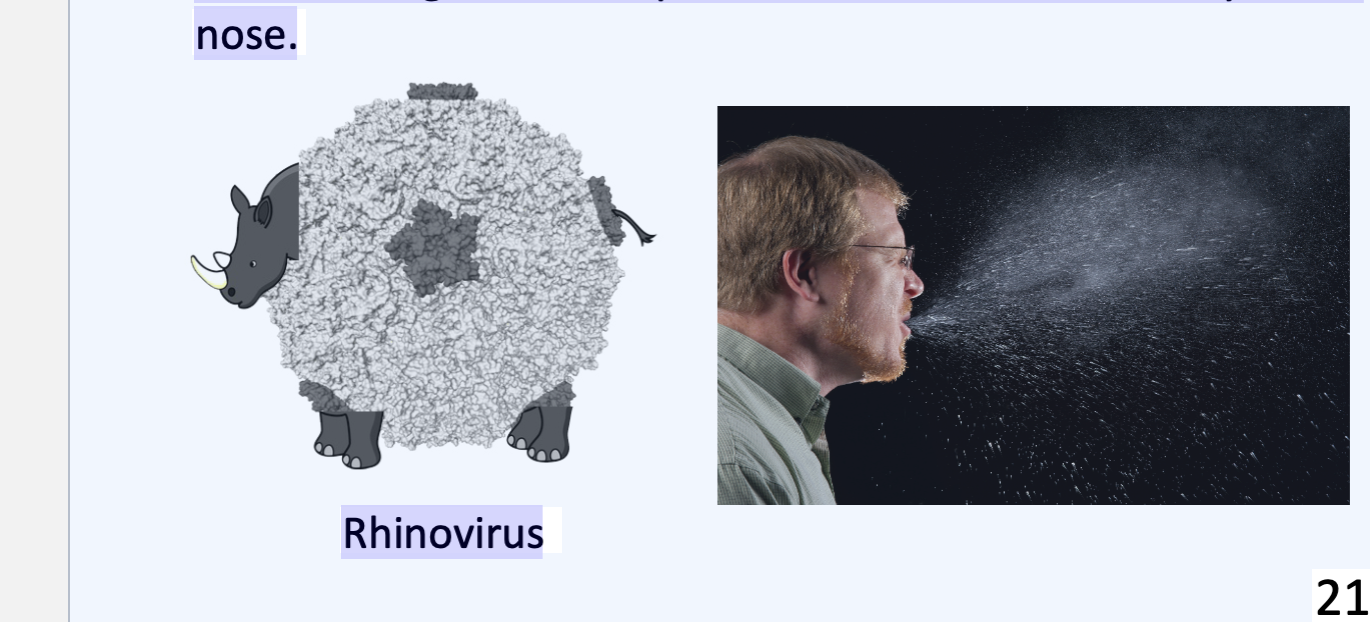
Common Cold
over 200 different viruses types
Most common : Coronaviruses & Rhinoviruses
Symptoms: Sneezing, nasal secretion, congestion
if infections spreads to lower
respiratory system.Transmitted: Viruses in mucus
• Virus can also spread through airborne droplets from coughing
and sneezing.Touching contaminated things
Influenzavirus
Causing agent for the Flu
3 Types A & B & C
A Type is most common and relevant
Influenza virus contains 8 RNA segments and an envelope
Virus has two spikes important for its virulence
- Hemagglutinin (HA)
- Neuraminidase (NA)
Hemagglutinin (HA)
HA → attaches to host cells
binds to host epithelial cells in the
respiratory tract
Neuraminidase (NA)
NA → During exit prevents curious from sticking together
helps with budding.
- Enzyme that breaks down respiratory mucus
Symptoms of the Flu
Chills, fever, headache, muscle
aches, and more
– Formation of new virulent
strains possible
Can infect avian, swine (animals) and human host
Swine - ( mixing vessels) to create new stains
Influenza Flu
Antigenic drift (swerving to a lane) - minor change
– Minor changes in HA and NA
( mutations)
– Allow the virus to elude some host immunity
• Antigenic shifts ( Big change)
– Changes great enough to evade most immunity
– Lead to pandemics
– Reassortment of segments from 2 different viruses
Antigenic drift (natural or vaccine-induced) fades over time.
Antigenic shift poses a global health risk because it can introduce a completely new virus strain, causing widespread illness and death.
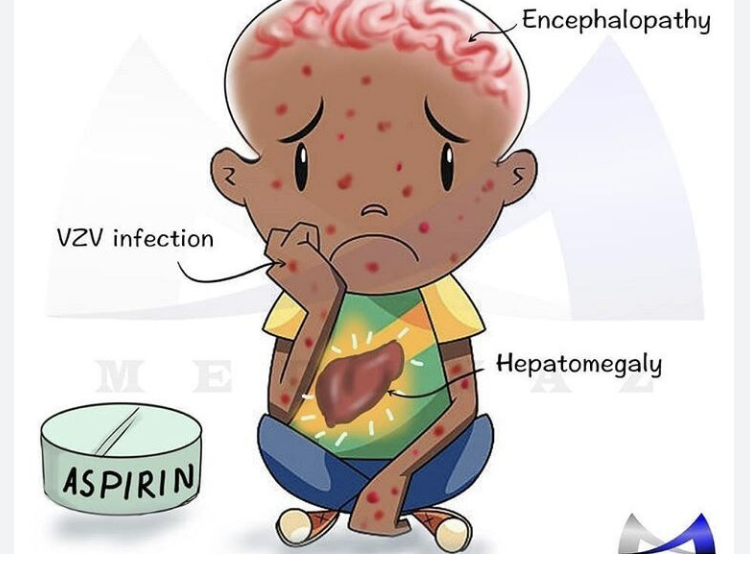
Reye Syndrome
Children develop when taking aspirin when infected with the flu
can lead to swelling of the liver, brain and damage organs