Biology Study Material: Block 4 - Detailed Exploration of Chapters 25, 26, & 27
1/120
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
121 Terms
Place a single word in each sentence to make it correct. Not all terms will be used.
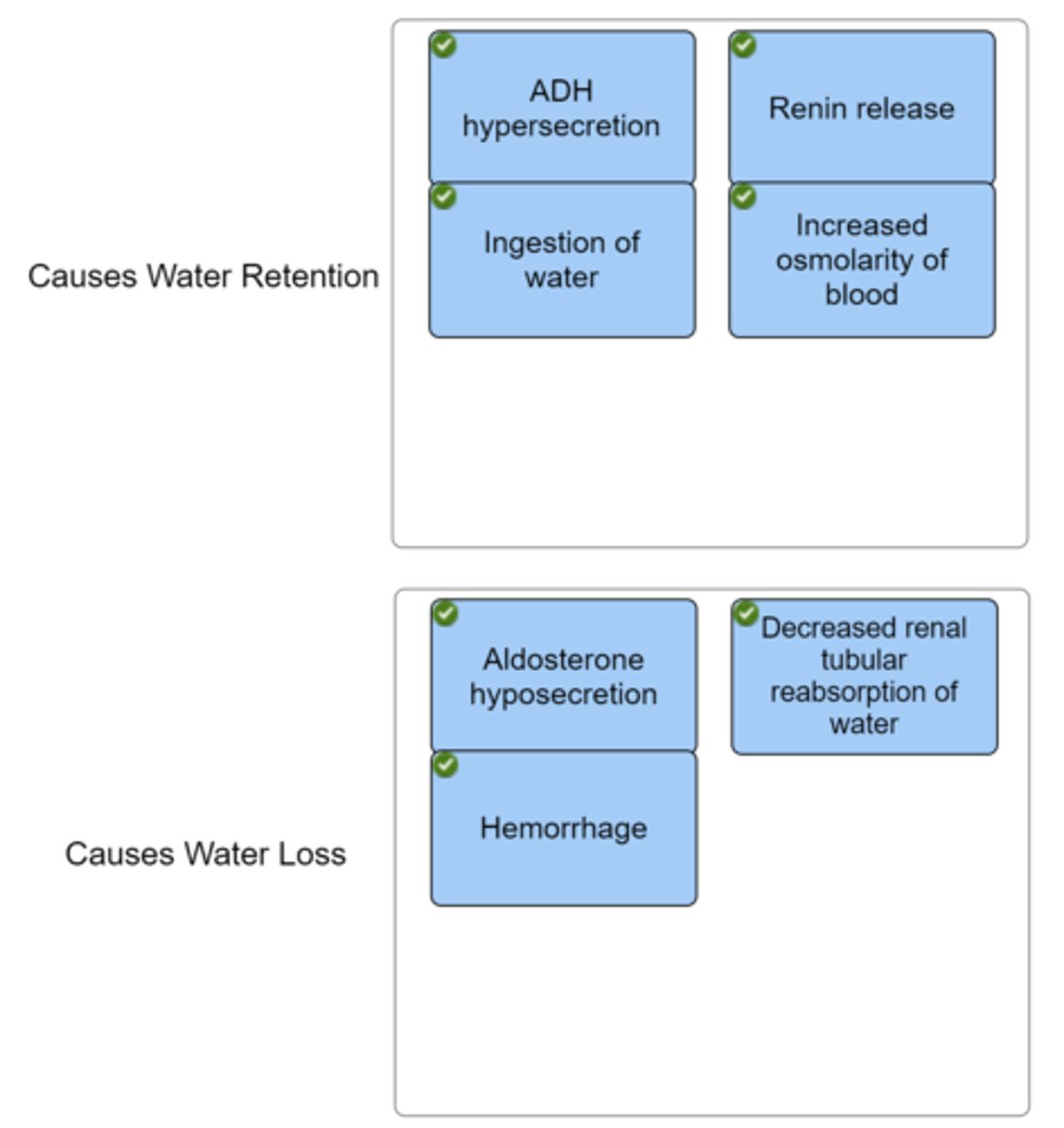
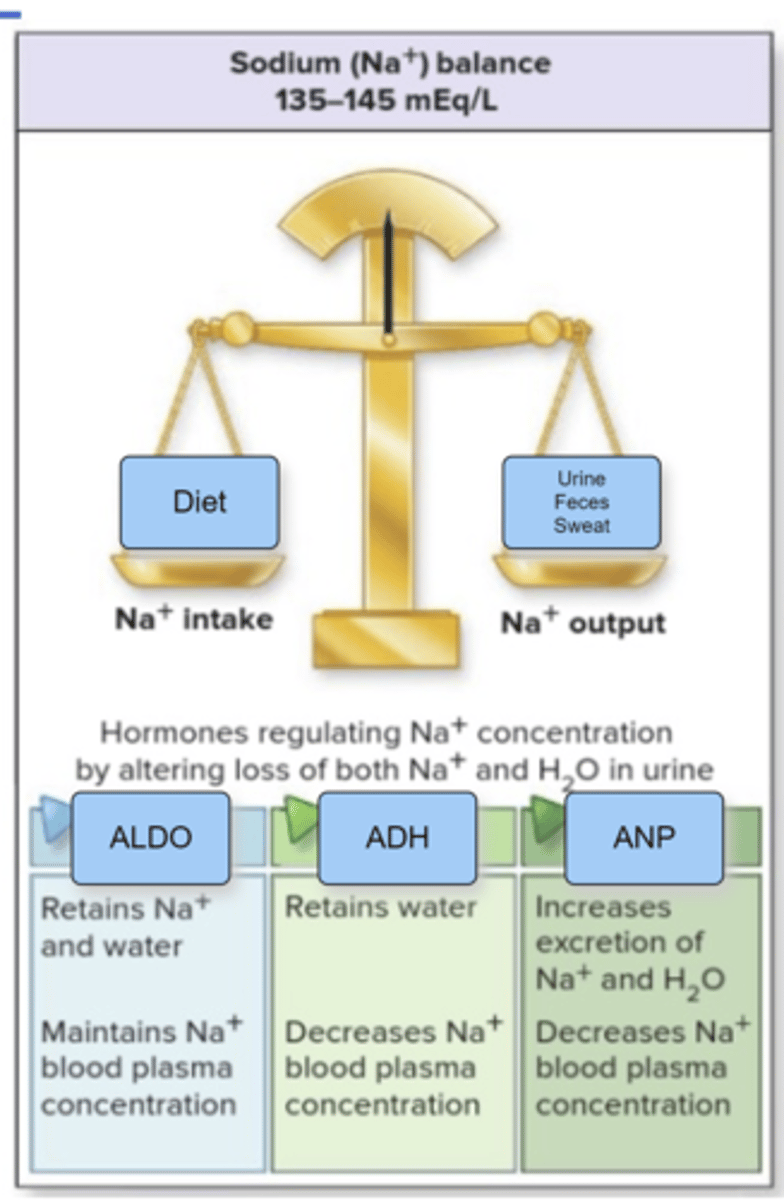
Antidiuretic hormone provides a means of controlling water output.
During dehydration blood volume declines and sodium concentration rises.
The increased osmolarity of the blood stimulates the hypothalamus to stimulate the posterior pituitary to release ADH.
ADH will work on the kidneys to reabsorb water into the bloodstream.
A negative feedback system is used until the blood volume and osmolarity return to normal levels.
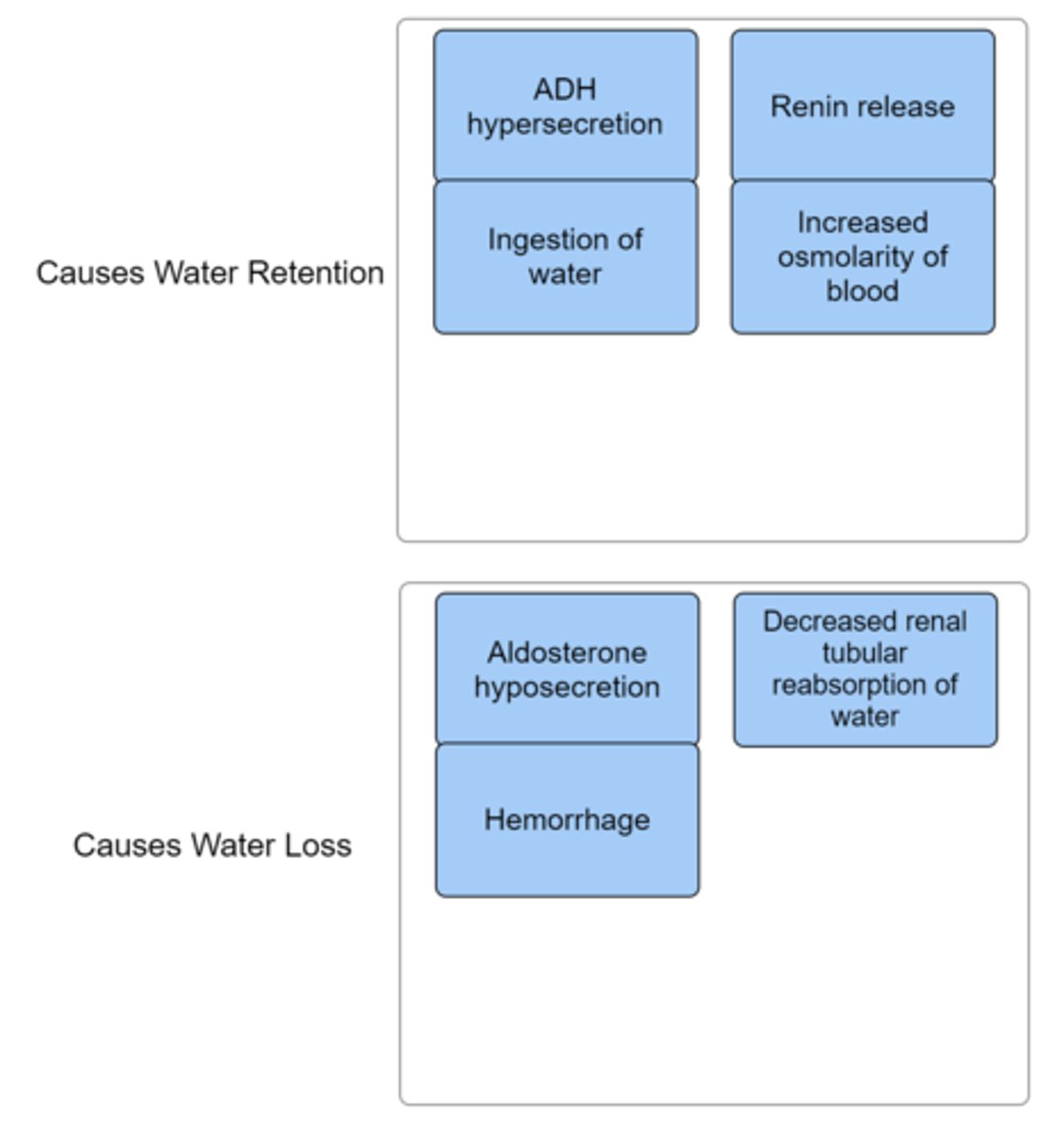
Indicate whether the given act would create water retention or water loss in the body.
Complete the sentences. Not all terms will be used.
Water and solutes are ingested.
Absorption of nutrients occurs in the digestive tract.
Fluid from the blood is filtered into the tissue fluid around cells.
The fluid around cells, interstitial, fluid can move into cells, or into lymphatics.
Fluid in the lymphatic system is brought back to the blood.
Fill in the blanks with the terms provided. Not all terms will be used.
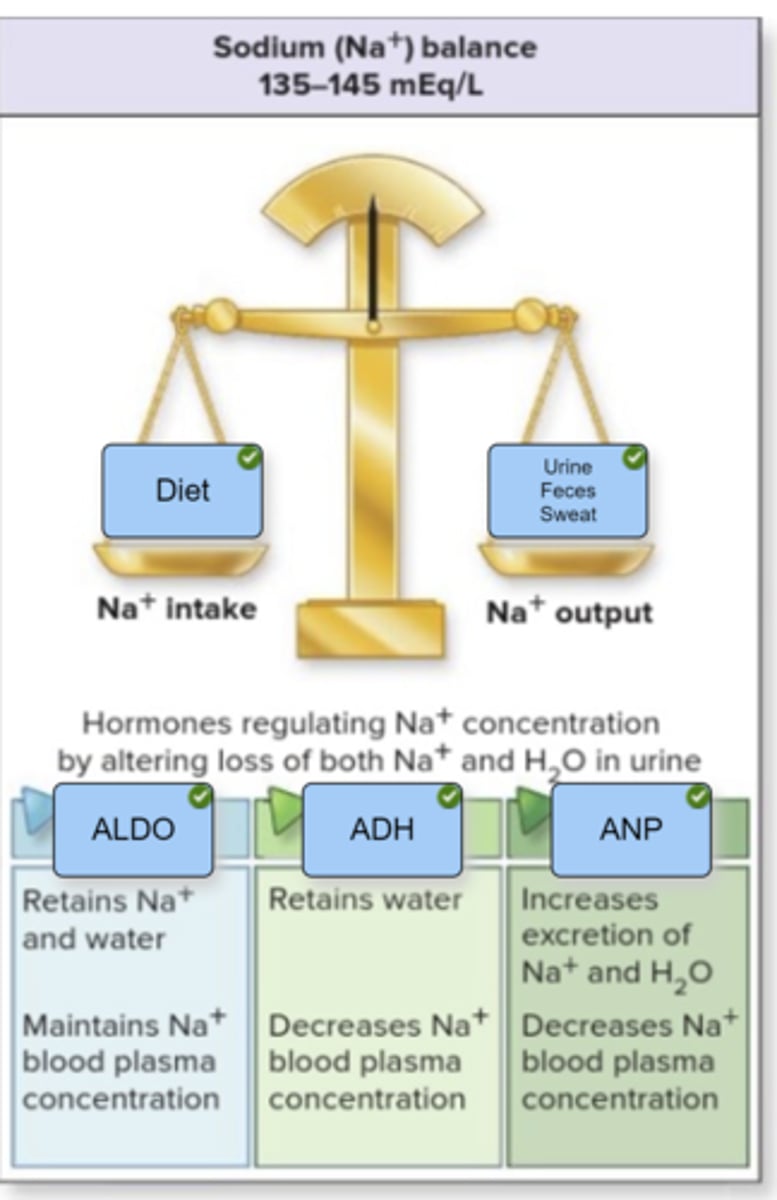
Approximately 99% of Na⁺ is in the ECF and only 1% in the ICF, a gradient that is maintained by Na⁺/K⁺ pumps. It is usually present in the form of either sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO₃) or sodium chloride (NaCl).
The ECF becomes temporarily hypertonic if Na⁺ concentration increases from either elevated Na⁺ content or decreased water content. Consequently, water moves from the other compartments into the blood plasma in an attempt to reestablish the normal Na⁺ concentration.
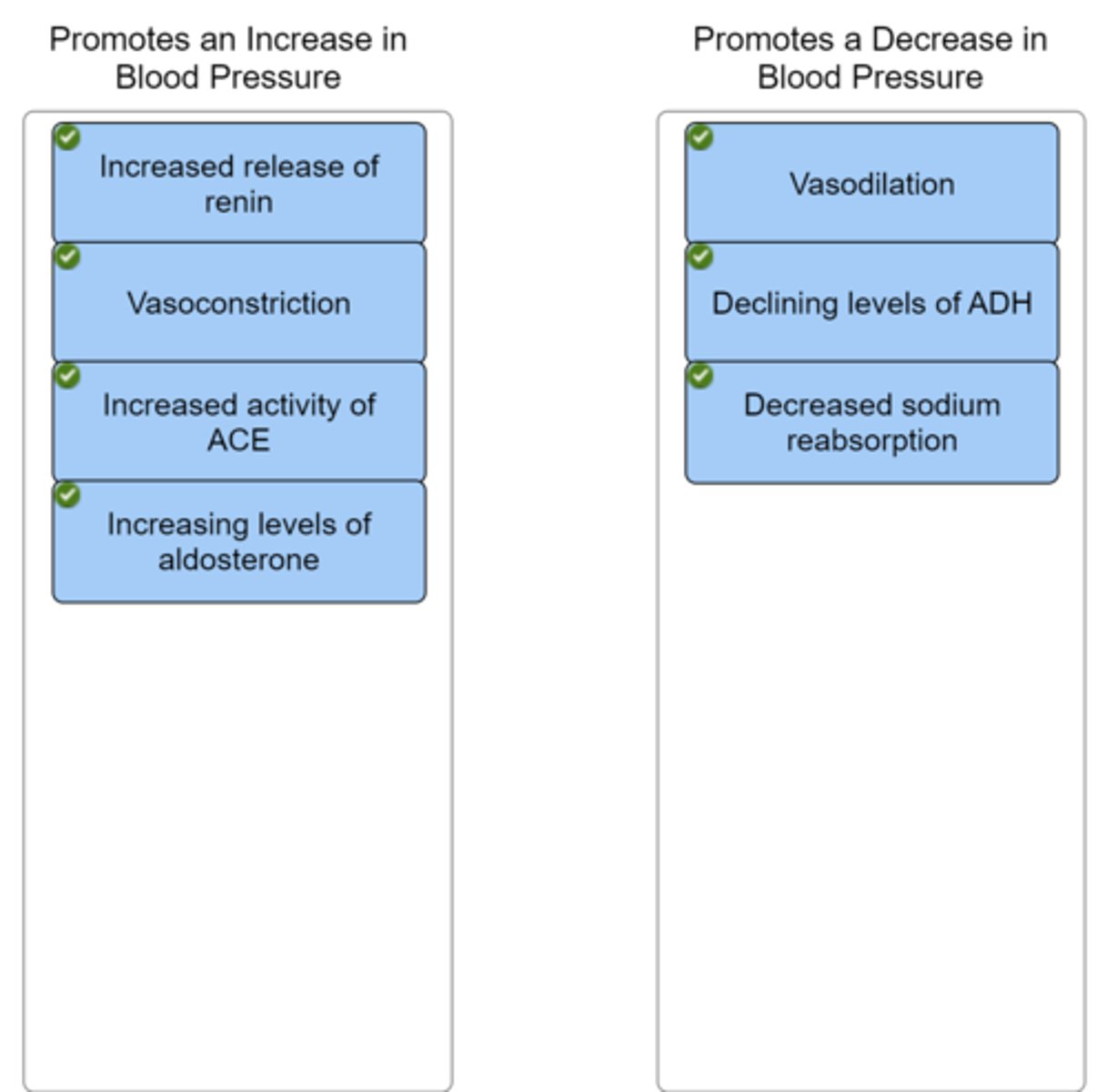
Identify whether each circumstance provided will promote an increase or decrease in blood pressure
Select all that are possible sources of fixed acids.
*Body cells
*Diet rich in animal protein
Select all that are possible causes of respiratory acidosis.
Pulmonary edema
Emphysema
Airway blockage
Label the figure with the items provided
The process of moving a bolus through the GI tract as a result of involuntary muscle contractions is referred to as
peristalsis.
Hydrochloric acid is secreted in the
stomach.
Most nutrient absorption occurs in the
small intestine.
What organ produces bile?
Liver
Which of the following is the correct order for the major parts of the gastrointestinal tract?
Mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine
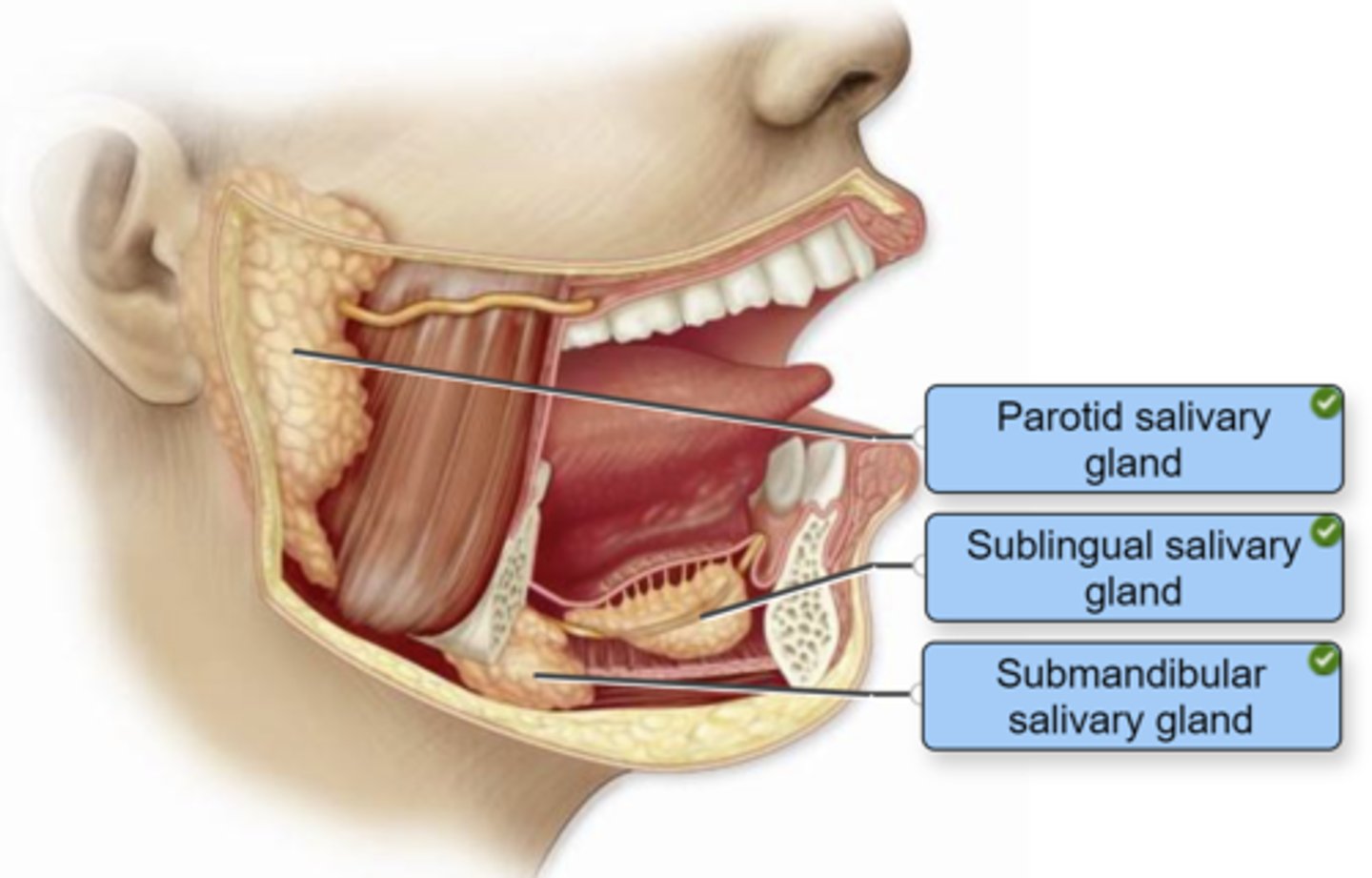
Identify the salivary glands in the figure.
Tony's symptoms of Crohn's disease were typical; they included all of the following except
Vomiting
Smokers have an increased risk of developing Crohn's disease. This statement is
true
An important diagnostic feature of Crohn's disease is full-thickness inflammation. To better understand this, put in proper sequence the layers of the bowel gastrointestinal wall, from the lumen to the serosa.
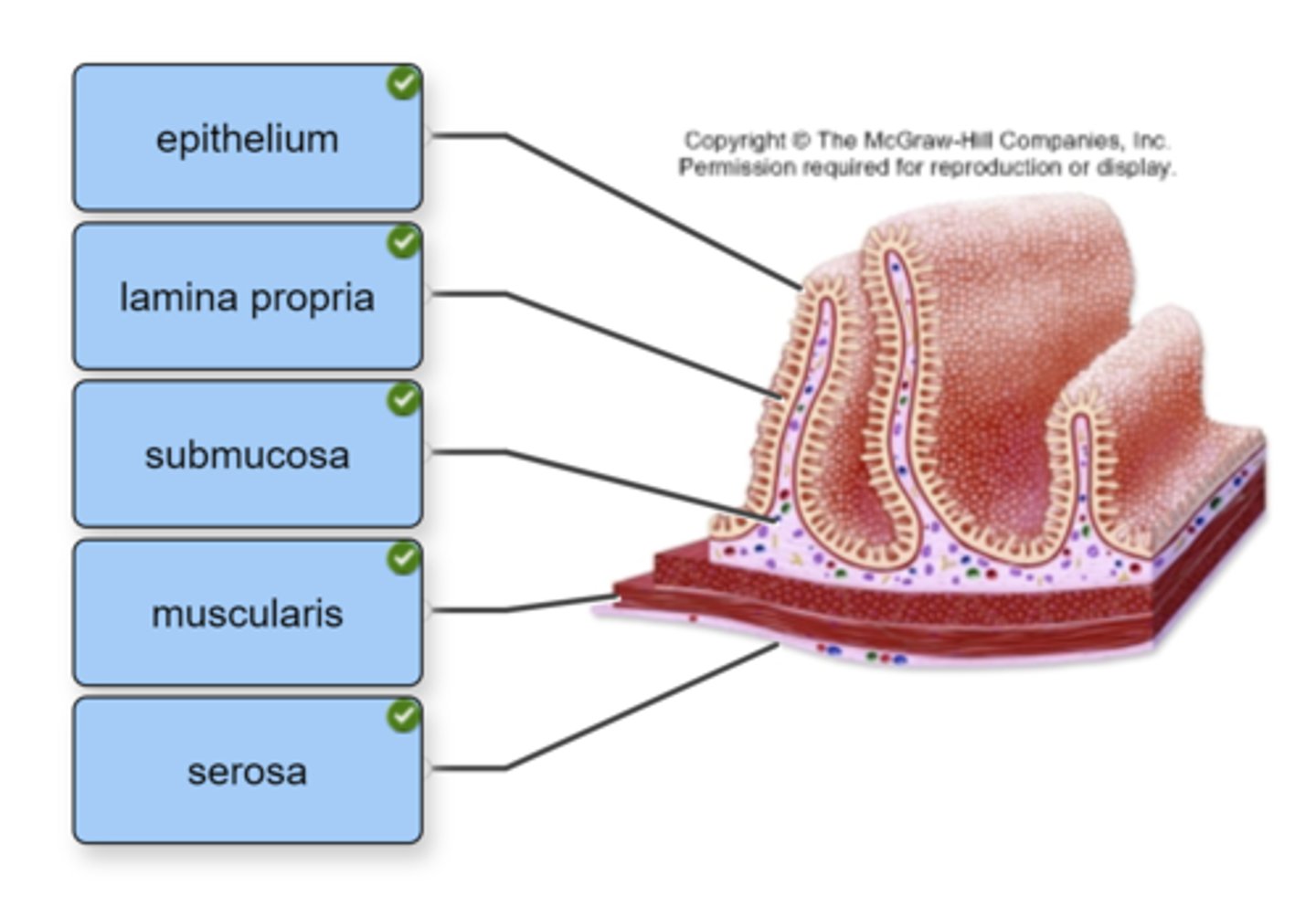
Pathological consequences of full-thickness inflammation of the bowel wall in Crohn's disease include all of the following except
weight gain
Known cures for Crohn's disease include
use of anti-inflammatory agents such as 5-aminosalicylic acid.
use of broad spectrum antibiotics.
surgical removal of affected segments of the bowel
None of these are correct.
Classify the given terms or examples with the appropriate category.
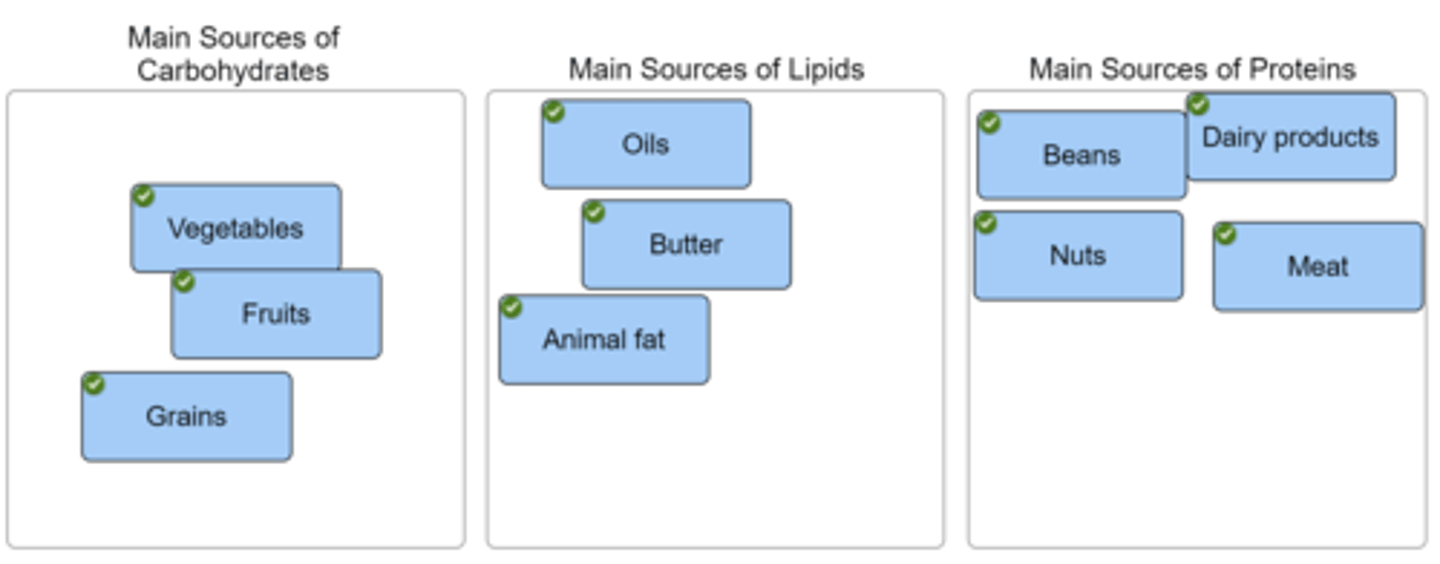
Classify the given terms or examples with the appropriate category.

Complete the sentences with the terms given. Not all terms will be used.
Nutrition is the study of how ingested chemicals interact in the body.
A nutrient is any element or compound necessary for or contributing to an organism's metabolism, growth, or other function.
Six nutrient groups exist, classifiable as those that provide energy; such as carbohydrates, protein, and fats.
Other nutrients are those that support metabolic processes in the body; such as vitamins, minerals, and water.
Some nutrients are essential because they cannot be synthesized in the body and must be obtained from a food source.
What function do many B vitamins serve in the production of energy?
They function as coenzymes.
Enzymes assist in the occurrence of reactions by
lowering the activation energy.
Consuming B vitamins in excess of need will
increase B vitamins in the urine.
Which B vitamin is found in egg yolk (and other foods) and functions as part of coenzyme A?
Pantothenic acid
When Charles was a baby the initial CF symptoms were caused by
the thick and gooey mucus from his gastrointestinal tract, the buildup of which resulted in multiple physical obstructions producing complete blockage
People with CF have frequent respiratory infections because
mucus plugs that occur within their bronchi keep bacteria laden particles from being coughed out. As a result, the bacteria are free to proliferate distal to the plug, causing infections
The cause of the pancreatic destruction in a person with CF is
the thick and tenacious mucus in the pancreatic duct. The mucus obstructs the movement of pancreatic juices and enzymes, thus allowing the digestive enzymes to destroy pancreatic tissue.
CF patients develop deficiencies of fat soluble vitamins because
once the pancreas is destroyed, no lipase is produced and no fats can be absorbed. Since fat soluble vitamins must accompany fats absorbed from dietary intake, no fat soluble vitamins can be absorbed either
Fat soluble vitamins include all the following except
C
Even though one in 25 people of European descent carry one copy of a gene that can cause CF, the disease is not nearly that common because
in order to express the disease, both copies a person inherits must be defective
CF treatment can include
prevention and control of pulmonary infections and the use of specially formulated versions of the fat-soluble vitamins, although there is no cure
Fill in the blanks with the terms provided. Not all terms will be used
Although the vast majority of the total body K+ is located within the ICF, it is only the approximate 2% of the K+ in the ECF that is continually regulated. Small changes in blood plasma K+ levels can readily lead to a K+ imbalance—the most lethal of the electrolyte imbalances. Changes to the neuromuscular organs are the most significant effects of a K+ imbalance. Potassium is generally obtained from fruits and vegetables, but input is increased with salt substitutes that contain K+. Only small amounts of K+ are lost from the body through sweat and feces. Most K+ (approximately 80–90%) is lost in urine
Classify the given terms or examples with the appropriate category.
Metabolic Acidosis:
*Blood H+ increases
*Blood (HCO3)- decreases
*Causes increased respiration
Metabolic Alkalosis:
*Blood H+ decreases
*Causes decreased respiration
*Blood (HCO3)- increases
Use the words "increase" or "decrease" to complete the sentence.
An increase in ADH production results in a(n) increase in water reabsorption in the kidneys, whereas a decrease in ADH production results in a(n) decrease in water reabsorption in the kidneys.
The net filtration pressure (NFP) is calculated by
subtracting the net colloid osmotic pressure from the net hydrostatic pressure
The term 'congestive heart failure' refers to
the backup and congestion of blood in the pulmonary circulation and on the venous side of the systemic circulation due to a weakly contracting left ventricle
The NFP of the pulmonary capillary bed of a patient is calculated to be -5 mmHg. You would expect this patient's pulmonary edema to be
non-existent. The NFP is negative and that will promote fluid movement into the capillary lumens, rather than out
Fill in the blanks with the terms provided. Not all terms will be used
In respiratory acidosis, respiratory rate decreases, blood CO₂ increases, and H₂CO₃ increases. In respiratory alkalosis the respiratory rate increases, blood CO₂ decreases, and H₂CO₃ decreases. In metabolic acidosis, blood H⁺ increases and (HCO₃)⁻ decreases. The respiratory system compensates for this by increasing the respiratory rate. Finally, in metabolic alkalosis, blood H⁺ decreases and (HCO₃)⁻ increases. In this situation the respiratory system compensates by decreasing the respiratory rate.
Which stimulus for increasing thirst and water intake is monitored by the thirst center directly?
Increased blood osmolarity
Complete each sentence by dragging the proper label into the appropriate position. Not all terms will be used.
Low blood pressure causes the kidneys to increase the secretion of renin from the juxtaglomerular cells. This leads to the formation of angiotensin II.
The hormone angiotensin II stimulates widespread vasoconstriction, release of ADH from the posterior pituitary, as well as the release of aldosterone from the adrenal cortex.
Aldosterone acts on the principal cells of the kidney tubules to reabsorb greater amounts of sodium from the tubular fluid. Additional water is reabsorbed as a result.
The hormone ADH stimulates the kidney to increase water reabsorption from the urine, as additional aquaporins are inserted into the collecting tubules and ducts.
The net result of angiotensin II, aldosterone, and ADH is a(n) increase in blood pressure resulting in part from increased blood volume.
Elderly people have the lowest body fluid percentage of all age groups, and are therefore _________ likely to develop a fluid imbalance.
More
Bile from the liver and digestive juices from the pancreas enter which section of the small intestine?
Duodenum
Which of the following might stimulate the cephalic phase of gastric secretion?
The thought of food
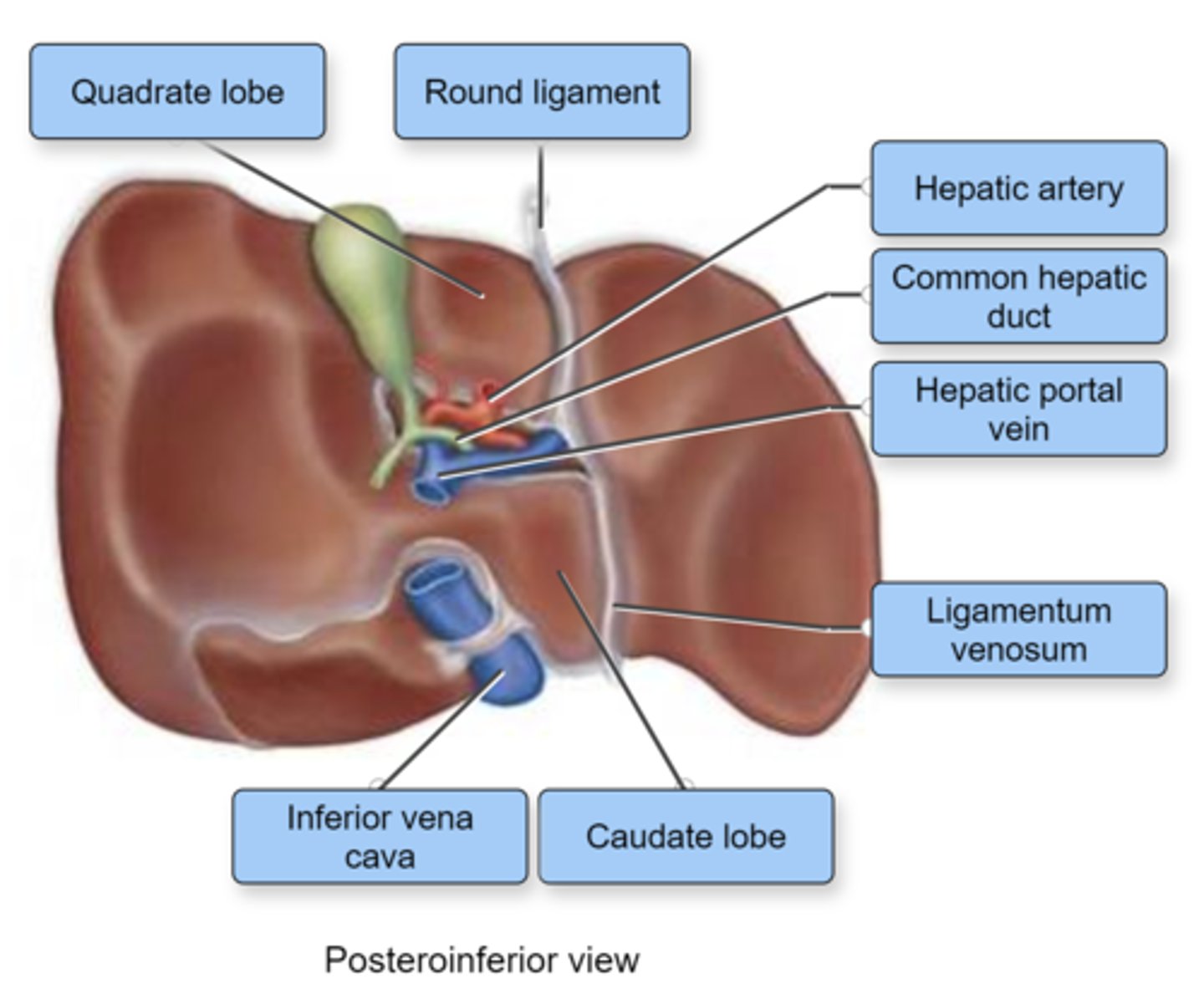
Structurally, the human liver is divided into how many lobes?
Four
The enzyme carbonic anhydrase catalyzes the formation of bicarbonate from carbon dioxide and hydrogen
False
Match the swallowing phase with its description.
Bolus passes from pharynx to esophagus.
Pharyngeal phase
Bolus passes from esophagus to stomach.
Esophageal phase
Chewing forms a bolus.
Voluntary phase
Answer the following True/False questions regarding the structure and location of the esophagus.
1. The esophagus extends from the nasopharynx to the stomach. False
2. The esophagus is about 25 meters long. False
3. The esophagus lies anterior to the trachea. False
4. The muscularis of the esophagus is different from other parts of the digestive tract because the superior part of the esophagus consists of skeletal muscle. True
5. The esophagus contains both an upper and a lower esophageal sphincter that regulates the movement of materials into and out of the esophagus. True
6. The esophagus contains numerous mucous glands that produce a thick, lubricating mucus that coats the inner surface of the esophagus. True
The majority of triglyceride digestion occurs in the small intestine facilitated by the enzyme
pancreatic lipase.
The accessory organs of the lower GI tract include the liver, gallbladder, and
Pancreas
Fill in the blanks with the terms provided. Not all terms will be used.
Food groups were initially organized by the USDA into a food guide pyramid that consisted of breads/grains, vegetables, fruits, dairy, proteins, and fats/oils/sweets.
This organization provided a general approach for the number of servings that should be consumed daily from each category. In 2011, the USDA revised this structure to MyPlate. It provides a visual of the relative proportions of the types of foods we need to stay healthy.
One half of these relative proportions is vegetables and fruit and the other half is protein and grains, with dairy off to the side.
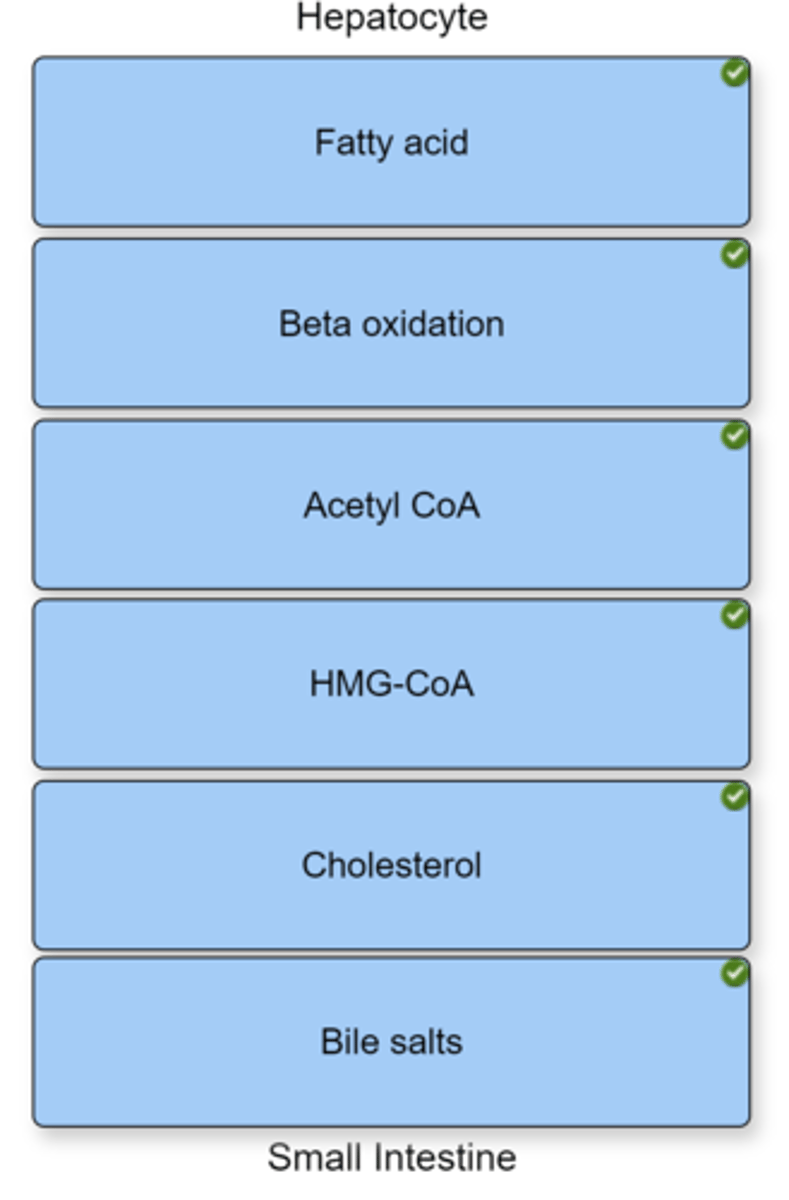
Place the events of cholesterol synthesis in the correct sequence from beginning to end.
In order to complete each sentence, click and drag each word or phrase from the left into the appropriate blank on the right. Not all terms will be used.
In the liver, the amine group is removed from glutamic acid.
The -NH₂ then becomes ammonia by the addition of a hydrogen atom.
The liver quickly combines the ammonia with carbon dioxide to form urea.
This nitrogenous waste is then excreted via urine
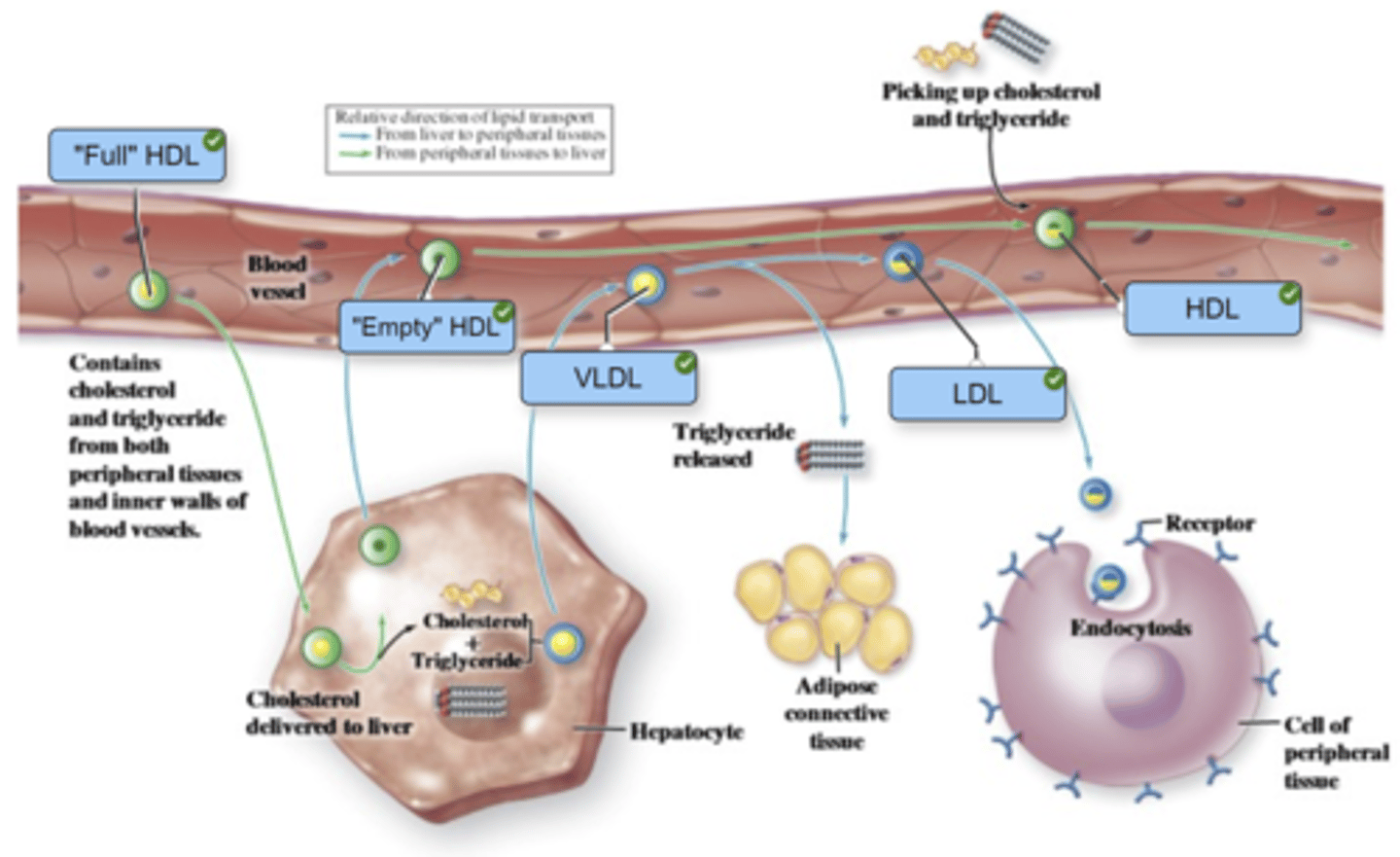
Label the figure with the items provided.
Which B vitamin is found in egg yolk (and other foods) and functions as part of coenzyme A?
Pantothenic acid
When protein is converted to glucose or fat, how is nitrogen eliminated from the body?
Through the kidneys
Complete each sentence by dragging the proper label into the correct position. Not all terms will be used.
Ascorbic acid, more commonly known as vitamin C, is a powerful antioxidant found in citrus where deficiency causes scurvy.
An important component of photodetection, retinol, or vitamin A, is found in lipid-rich sources such as fish oil, eggs, cheese, and milk.
Calcitriol, or vitamin D, is synthesized in a complex set of reactions involving the skin, liver, and kidneys. It is found in varying amounts in fortified milk, fish, and fish oils.
Nuts and vegetable oils are good sources of the lipid-soluble antioxidant vitamin E, which is also known by its chemical name, alpha-tocopherol.
Phylloquinone, or vitamin K, is synthesized almost entirely by bacteria in the large intestine and is involved with blood coagulation.
Which carbohydrate is a good source of fiber in our diet?
Cellulose
Fixed acid is regulated by the _____ through the absorption and elimination of _____.
kidney; bicarbonate and H+
Renin is released from the juxtaglomerular apparatus in response to
low blood pressure or decreased NaCl in the fluid within the distal convoluted tubule.
Aldosterone exerts effects on principal cells of the kidney by causing
increased numbers of Na+/K+ pumps.
The hormone ANP
increases urine output and decreases blood volume.
If a physiologic condition resulted in blood pH reaching 7.2, but then physiological buffering systems brought the pH to 7.4, that increase in pH would be called
compensation.
Aerobic cellular respiration and dehydration synthesis reactions result in
metabolic water intake.
The most abundant cation within cells is
potassium.
The development of hypoxia can limit the effectiveness of respiratory compensation for metabolic
alkalosis
If an individual's respiratory rate decreases, then blood CO2 levels
rise, blood H+ levels rise, and blood pH falls.
Renal compensation for acidosis results in
urine with a low pH and an elevation of blood bicarbonate levels.
The molecule HCl is an example of a(n)
electrolyte
Insulin causes blood plasma levels of potassium to ________ by _______ activity of the Na+/K+ pumps.
decrease; stimulating
Respiratory acidosis occurs when the partial pressure of
carbon dioxide rises
Water lost through feces is considered ___________ water loss.
sensible, obligatory
An individual who consumes many antacids for stomach upset and many diuretics for high blood pressure will be at risk for metabolic
alkalosis.
Feelings of thirstiness are brought on by
decreases in salivary secretions and increases in blood osmolarity
Low levels of calcium within cells are maintained by
pumps that move calcium out of cells or into the sarcoplasmic reticulum.
Label the figure with the items provided. Not all labels will be used
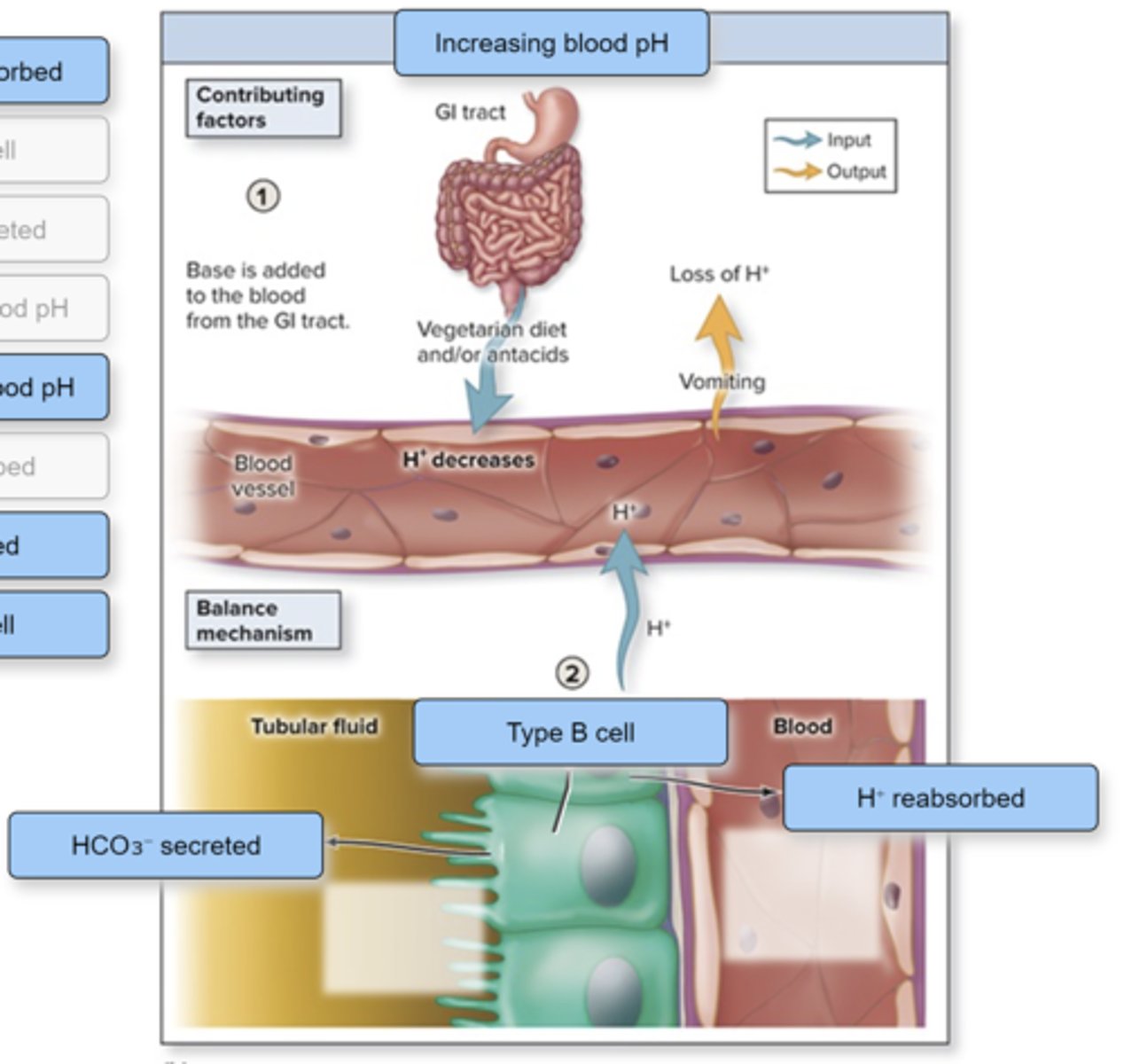
Label the figure with the items provided
Indicate whether the given act would create water retention or water loss in the body.
Stenosis (constriction) of the hepatopancreatic ampulla would interfere with
the transport of bile and pancreatic juice.
The buccal, lingual, and labial salivary glands are __________ salivary glands.
intrinsic
An enzyme found within saliva is salivary
amylase.
Manufacturers of some medications used to treat heartburn advertise that their products shut down the acid-producing pumps in the stomach. Where are these "acid-producing pumps"? In other words, which type of gastric gland cell secretes acid?
Parietal cells
The gastroenterologist has just determined that you have a blockage in your jejunum and he will have to perform surgery, making a small incision in the wall to remove the obstruction. Which tunic will be cut first?
Serosa
The projections on the superior surface of the tongue, some of which house taste buds, are the
papillae
The lining of the gastrointestinal tract that allows for absorption and secretion is
simple columnar epithelium.
What is the correct order for the list of structures of the large intestine, starting at the cecum and ending at the rectum?a: Left colic flexure
b: Ascending colon
c: Transverse colon
d: Right colic flexure
e: Sigmoid colon
f: Descending colon
b, d, c, a, f, e
An increased secretion of watery saliva will result when the
salivary nuclei of the brainstem activate parasympathetic pathways to salivary glands.
What material is transported in the sinusoids of the liver?
Mixed arterial and venous blood
Duodenal glands (Brunner glands) that secrete a viscous mucus into the small intestine are located in the
submucosa
The central cavity of a tooth is filled with
pulp
Lipid molecules that are absorbed from the GI tract enter
lymphatic capillaries.
Secretin is a hormone that is secreted by the
small intestine.
The esophagus
contains both smooth and skeletal muscle fibers.
"Segmentation" within the small intestine refers to the
back-and-forth motion that mixes chyme with glandular secretions.
The enzyme pepsin becomes active when pH is
low.
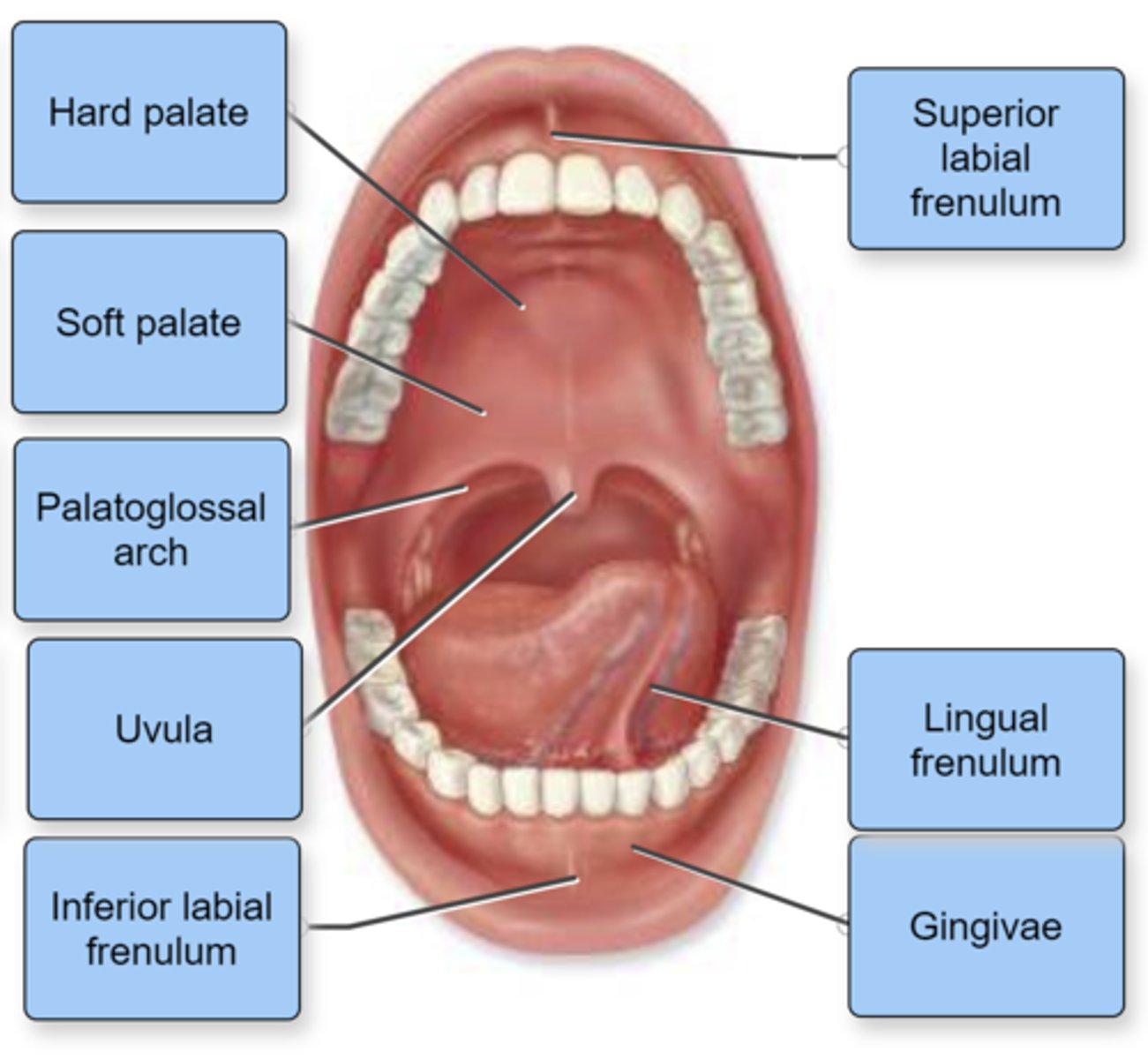
Label the structures of the oral cavity in the figure.
Label the structures of the liver.
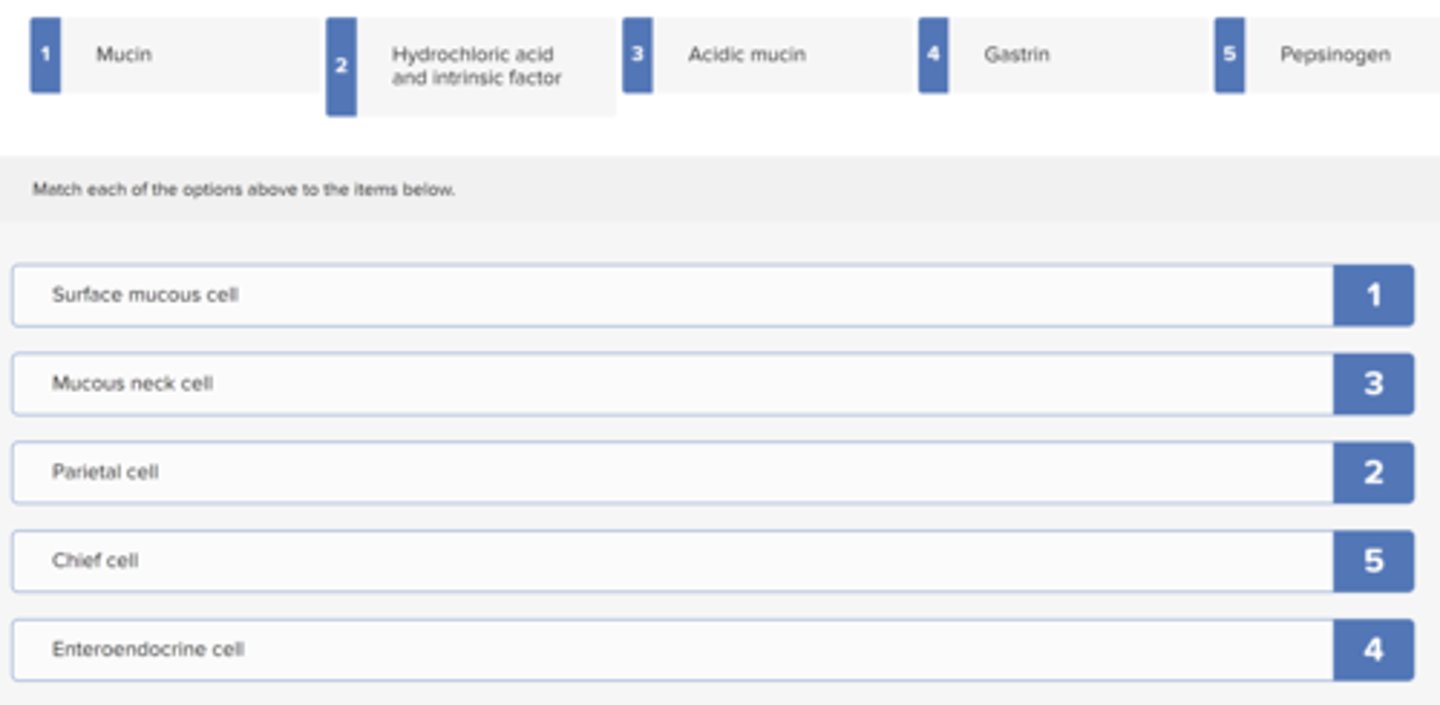
Match the secretory cell of the stomach with its secretion.
A deficiency in vitamin _____ may result in night blindness as well as dry, flaky skin.
A