ecology unit test
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/55
Last updated 9:56 PM on 5/7/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
56 Terms
1
New cards
ecology
how organisms interact in an environment
how orgs affect each other in the world
how orgs affect each other in the world
2
New cards
ecosystem
* combo of abiotic and biotic factors
* energy flow (nitrogen cycle, photosynthesis, cellular respiration)
* usually some kind of unit (woods,swamp, lake, etc)
* energy flow (nitrogen cycle, photosynthesis, cellular respiration)
* usually some kind of unit (woods,swamp, lake, etc)
3
New cards
niche
* what a species eats
* where a species lives
* physical and invisible spaces a species inhabits in an ecosystem
* where a species lives
* physical and invisible spaces a species inhabits in an ecosystem
4
New cards
population
group of organisms of the same species in the same place at the same time
5
New cards
energy
the ability to do work
* usually measured in calories
* usually measured in calories
6
New cards
producer
* an autotroph
* convert sunlight into chemical energy
* convert sunlight into chemical energy
7
New cards
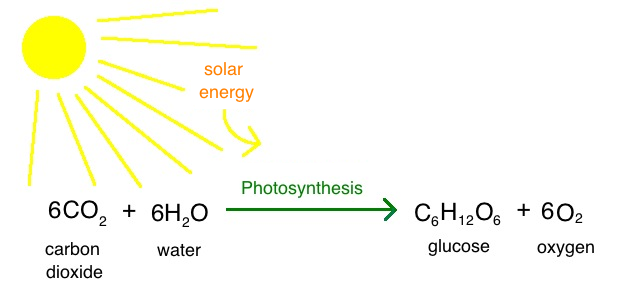
photosynthesis
* plants use CO2 during process to make glucose
* removes CO2 from the atmosphere
* removes CO2 from the atmosphere
8
New cards
consumer
* eat producers
* need to consume other organisms for their energy
* whatever they don’t use for energy they store or use as heat
* need to consume other organisms for their energy
* whatever they don’t use for energy they store or use as heat
9
New cards
trophic level
a level in an ecosystem
* consumer
* producer
* primary consumer
* etc
* consumer
* producer
* primary consumer
* etc
10
New cards
biomass
* mass of biotic factors in an environment
* typically looked at in individual trophic levels
* pyramid used by ecologists to determine if an ecosystem is able to support itself
* typically looked at in individual trophic levels
* pyramid used by ecologists to determine if an ecosystem is able to support itself
11
New cards
why does water cycle matter
* plants
* plants = unable to grow w/o water
* habitats
* bodies of water are used as habitats and breeding ground for things born in water
* life
* water provides essential nutrients and minerals for physical life
* plants = unable to grow w/o water
* habitats
* bodies of water are used as habitats and breeding ground for things born in water
* life
* water provides essential nutrients and minerals for physical life
12
New cards
evaporation
turning liquid into gas
13
New cards
transpiration
evaporation from plants and leaves
14
New cards
condensation
turning gas into a liquid
15
New cards
precipitation
rain, snow, sleet, hail, etc.
16
New cards
infiltration
water trickling into soil
17
New cards
groundwater
water is located in the ground in aquifers
18
New cards
runoff
water that collects on top and runs into streams, oceans, rivers, etc.
19
New cards
aquifers
bodies of saturated rock and sediment thru which water can move
20
New cards
why is carbon cycle important
* energy
* carbon provides energy that fuel global economy
* temperature
* carbon creates greenhouse effect in order to regulate the Earth’s temperature
* food
* carbon makes up food we eat
* carbon provides energy that fuel global economy
* temperature
* carbon creates greenhouse effect in order to regulate the Earth’s temperature
* food
* carbon makes up food we eat
21
New cards
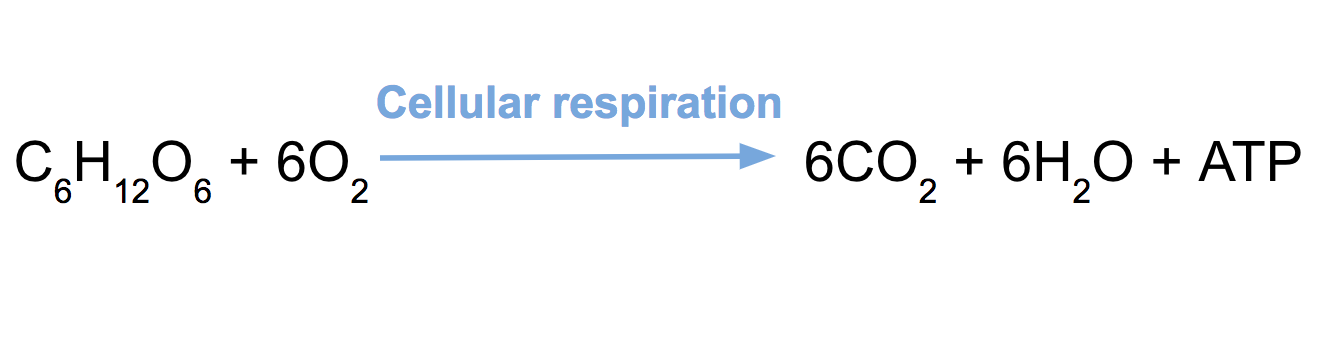
cellular respiration and equation
* process that produes CO2
* done by animals
* glucose used to make ATP which is a usable form of energy
* done by animals
* glucose used to make ATP which is a usable form of energy
22
New cards
fossil fuels
things like coal, oil, and gas are made of them
23
New cards
decomposition
process of rotting and decay
* turns organisms into fossils
* turns organisms into fossils
24
New cards
atmosphere CO2
carbon exists in the atmosphere as CO2
25
New cards
why do we care about nitrogen cycle and nitrogen
* nitrogen makes up proteins and nucleic acids
26
New cards
limiting factor
* the amount of nitrogen we have in the global ecosystem limits how much we can grow
27
New cards
nitrogen fixing bacteria
* usable nitrogen only enters the ecosystem through plants
* we can’t breath it in or use it if not usable
* creates usable nitrogen for producers and then consumers eat the plants
* we can’t breath it in or use it if not usable
* creates usable nitrogen for producers and then consumers eat the plants
28
New cards
atmosphere N2
* unusable because it’s triple bond is too strong to break down easily
* it is 80% of available nitrogen
* it is 80% of available nitrogen
29
New cards
Biosphere
all of Earth and the atmosphere
30
New cards
biome
a large area with same climate patterns
31
New cards
ecosystem
all of abiotic and biotic factors in a location
32
New cards
community
a group of dif species living together
33
New cards
population
a group of the same species living together
34
New cards
individual
a single organism
35
New cards
primary consumers
* consume producers
* whatever they dont’t use they store or use as heat
* whatever they dont’t use they store or use as heat
36
New cards
secondary consumers
* eat another consumer
* omnivore or carnivore
* predator or scavenger
* omnivore or carnivore
* predator or scavenger
37
New cards
tertiary consumers
* eat secondary consumers
* omnivore or carnivore
* predator or scavenger
* omnivore or carnivore
* predator or scavenger
38
New cards
decomposers
consumer that eats dead and rotting things
* returns nutrients to the ground for the producers to use
* returns nutrients to the ground for the producers to use
39
New cards
where does energy that isn’t used go?
* is stored for the next level to use when the organism is consumed
* is released as heat
* is released as heat
40
New cards
10% rule
* each level only gets 10% of the energy from the level below it
* makes ecosystems have a lot of producers and not as many consumers
* as you go up the pyramid there are less organisms bc there is not enough energy at that level to sustain more organisms
* makes ecosystems have a lot of producers and not as many consumers
* as you go up the pyramid there are less organisms bc there is not enough energy at that level to sustain more organisms
41
New cards
energy flow and energy flow pyramids
* energy enters an ecosystem through the sun
* w/o sun we wouldn’t have energy and we would be mega cold
* only flows in 1D
* producers use photosynthesis to turn light energy into sugar and oxygen
* consumers use cellular respiration to convert O2 from breathing and glucose from consuming into ATP
* w/o sun we wouldn’t have energy and we would be mega cold
* only flows in 1D
* producers use photosynthesis to turn light energy into sugar and oxygen
* consumers use cellular respiration to convert O2 from breathing and glucose from consuming into ATP
42
New cards
competition
* 2 species have the same limiting resource
* limiting resource = a resource species have in common that is limited (food, water, space, etc.)
* limiting resource = a resource species have in common that is limited (food, water, space, etc.)
43
New cards
predation/defense mechanisms
* predator hunting down prey
* eat live organisms
* controls amount of prey
* drives evolution (coevolution)
* defense mechanisms
* animals
* skunks spray predators
* porcupines have quills
* camouflage
* venom/ poison
* plants
* throns
* causes rashes
* eat live organisms
* controls amount of prey
* drives evolution (coevolution)
* defense mechanisms
* animals
* skunks spray predators
* porcupines have quills
* camouflage
* venom/ poison
* plants
* throns
* causes rashes
44
New cards
symbiosis
a long-term close relationship between 2 species
* mutualism
* positive relationship between two species where both benefit
* sometimes they can’t live w/o each other
* parasitism
* one sided relationship
* one organism benefits while the other one is harmed
* commensalism
* one sided relationship
* one organism benefits while other isn’t affected
* mutualism
* positive relationship between two species where both benefit
* sometimes they can’t live w/o each other
* parasitism
* one sided relationship
* one organism benefits while the other one is harmed
* commensalism
* one sided relationship
* one organism benefits while other isn’t affected
45
New cards
biodiversity
* total number of organisms
* relative abundance
* variety of all living things and their interactions
* relative abundance
* variety of all living things and their interactions
46
New cards
why is biodiversity important?
we need it for a balanced healthy ecosystem
47
New cards
threats to biodiversity: natural causes
* disease
* often occur naturally and can wipe out portions of a population
* predators
* naturally control the population of prey
* geographic change
* natural disasters affect habitats and therefore what can survive
* natural erosion also affects habitats
* often occur naturally and can wipe out portions of a population
* predators
* naturally control the population of prey
* geographic change
* natural disasters affect habitats and therefore what can survive
* natural erosion also affects habitats
48
New cards
threats to biodiversity: pollution
* man made elements and items make their way into the environment
* fossil fuels
* litter
* oil spills
* fossil fuels
* litter
* oil spills
49
New cards
threats to biodiversity: habitat destruction
* loss of habitat usually cue to human involvement
* logging
* deforestation
* farming
* logging
* deforestation
* farming
50
New cards
threats to biodiversity: global climate change
* both natural and human induced changes to climate
* natural
* natural disasters
* natural drying
* natural erosion
* human
* fossil fuel emissions
* over-use of resources
* natural
* natural disasters
* natural drying
* natural erosion
* human
* fossil fuel emissions
* over-use of resources
51
New cards
threats to biodiversity: human activity
* any human activity that destroys or changes the environment
* deforestation
* industrial fishing
* industrialization
* farming
* overharvesting
* habitat fragmentation
* deforestation
* industrial fishing
* industrialization
* farming
* overharvesting
* habitat fragmentation
52
New cards
threats to biodiversity: invasive species
* species that aren’t native to an area move there
* some introduced accidentally
* some introduced on purpose but not always ill intentioned
* species ultimately take over an ecosystem
* some introduced accidentally
* some introduced on purpose but not always ill intentioned
* species ultimately take over an ecosystem
53
New cards
carrying capacity
* maximum population a particular environment can sustain
* when we exeed carrying capacity the environment breaks down →decreases carrying capacity
* when we exeed carrying capacity the environment breaks down →decreases carrying capacity
54
New cards
carrying capacity: birth rate
how many organisms are born each year
55
New cards
carrying capacity: death rate
how many organisms die each year
56
New cards
carrying capacity: migration
* movement of organisms into (immigration) or out of (emmigration) an ecosystem