WH Exam 1
1/159
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
160 Terms
How many deaths per 100,000 live births?
How many are preventable?
19, ½
___ women die every day during pregnancy and childbirth in the US
2-3
Normal menstrual cycle duration ___ days. Can vary: ___
28; 21-35
__ phase involves forming a mature egg.
Follicular
__ phase lasts 10-14 days
Follicular
During the follicular phase, ___ is released.
FSH
__ phase lasts 1 day
Ovulation
During ___, the mature follicle ruptures in response to a surge in LH.
ovulation
during ovulation, an ____ is released
ovum
The ___ begins at ovulation and lasts until the menstrual phase of the next cycle.
luteal
The follicle after rupturing forms the ___ which secretes progesterone.
corpus luteum
During luteal phase, the body temp increases ___ F
0.5-1
What hormone is involved in maintaining a pregnancy?
progesterone
__ preserves the corpus luteum and progesterone production
hCG
What is a zygote?
Fertilized ovum
hCG levels __ every 48-72 hours in the early weeks of pregnancy
doubles
amniotic fluid is composed of:
98% water and 2% organic matter
__ contains albumin, urea, uric acid, creatinine, bilirubin, lecithin (mix of fats), sphingomyelin (lipid found in myelin sheath), epithelial cells, vernix & lanugo
amniotic fluid
< 500 mL of amniotic fluid is referred to as ___
oligohydraminos
>2000 mL of amniotic fluid is referred to as ___
polyhydramnios
oligohydramnios is associated with: ___
uteroplacental insufficiency and renal insufficiency
polyhydramnios is associated with: __
maternal diabetes, neural tube defects, chromosomal variations, malformations of the CNS, GI alterations
__ is a polyploidy condition that is diagnosed by genetic testing
Down syndrome
Patient presents with small, low set ears, hyperflexibility, muscle hypotonia , wide spaced eyes , ulnar loop on the second digit , simian crease , fat facial profile, small white spots on irises, open mouth with protruding tongue. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Down Syndrome
This condition follows an autosomal recessive inheritance that is characterized insufficient activity of the enzyme hexosaminidase A.
Tay Sachs Disease
Immunoglobulin that crosses the placenta is called __
IgG
What immunoglobulin is found in the colostrum?
IgA
The __ is made up of 1 large vein (O2) and 2 small arteries (CO2) surrounded by Wharton's Jelly
umbilical cord
__ is made by the placenta and functions to maintain endometrium, decrease contractility of the uterus, stimulate maternal metabolism & breast development
progesterone
__ preserves the corpus luteum and its progesterone production
hCG
__: enlargement of the women’s breast, uterus, and external genitalia.
Estrogen
___ Stimulates myometrial contractility (Braxton Hicks)
estrogen
__ relaxation of the pelvic ligaments, softens the cervix in preparation of birth
Relaxin
__ regulates fetal and maternal metabolism, development of breast for lactation, decreases maternal glucose utilization (increase glucose avail to fetus)
hPL/hCS
Protecting the fetus from immune attack by mothers immune system is a function of the __
placenta
Weeks of gestation for full term
37-42 weeks
number of times a woman has been pregnant
G
term births (after 37 weeks)
T
pregnancies delivered from 20-37 weeks
P
number of miscarriages ending before 20 weeks
A
number of living children
L
First day of LMP - 3 months + 7 days + 1 year
Naegele’s rule
How to determine delivery day if the patient has irregular periods?
Ultrasound
CBC, blood typing, Rh factor, rubella titer, urinalysis, renal function, pap smear are all __
prenatal labs
tuberculin skin test, STI, HIV, hep B surface antigen, VDRL, RPR testing, glucose tolerance are all __
prenatal tests
Pregnant blood volume should increase 50% above non pregnant levels by the __th week
30
Increase in blood volume begins at __ weeks and peaks at __ weeks.
10-12, 32-34
Maternal HR should increase __ bpm
10-15
BP should decrease 5-10 mm Hg by the __ trimester.
2nd
Pregnancy makes the woman __ due to an increase increase in fibrin, plasma, fibrinogen levels.
hypercoagulable
Amenorrhea, fatigue, breast tenderness, n/v, urinary frequency are all __
presumptive signs
hyperpigmentation, fetal movement, uterine enlargement, & breast enlargement are all __
presumptive signs
braxon hicks contraction, abdominal uterine enlargement and positive pregnancy test are all __
probable signs
Ballottement can be done in how many weeks?
16-28
Ballottement is a
probable sign
Hegar sign can be done in how many weeks
6-12
Hegar sign is a
probable sign
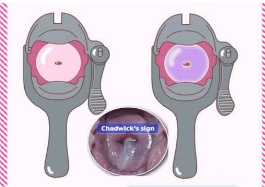
Chadwick’s sign can be checked in how many weeks?
6-8
Chadwick’s sign is a
probable sign
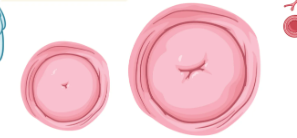
Goodell's sign can be checked at how many weeks
5
Goodell's sign is a
probable sign
What is this
Ballottement
What this
Hegars sign
What is this
Chadwick’s sign
What is this
Goodell’s sign
Ultrasound, fetal movement felt by experienced clinician, and auscultation of fetal heart tones via doppler are all
positive signs
Measuring __ involves using a tape measure and measuring from the top of the uterus to top of pubic bone
fundal height
__ presents as decreased CO, BP, and increased orthostatic stress. Advised to encourage patient to lay on her side.
Vena cava syndrome
Excessive salivation or __ is one of the GI signs during pregnancy
Ptyalism
__ conflicting feelings is the most common in the first trimester
Ambivalence
__: mother become increasingly preoccupied with herself and her fetus (early part of pregnancy)
Introversion
__: physical changes of the growing fetus, enlarging abdomen and fetal movement, bring reality and validity to the pregnancy (second semester)
Acceptance
__: Emotional lability is characteristic throughout most pregnancies
Mood swings
__: pregnancy affects a woman’s body image varies greatly from person to person
Changes in body image
__ occurs d/t progesterone, estrogen, and melanocyte stimulating hormone levels
Hyperpigmentation
__ aka mask of pregnancy occurs in about 70% of pregnant women
melasma
__: pigmented line down middle of abdomen
Linea nigra
__: stretch marks reduce connective tissue strength at 6-7 months
Striae gravidarum
__ occur due to poor circulation and uterus compression
Varicose veins
__ refers to spontaneous, irregular, painless contractions
Braxton hicks contractions
Advise a patient to hydrate, rest in side lying position, and teach breathing techniques if they are experiencing
braxton hicks
Amount of water recommended per day for pregnant women
8 glasses
Fetal movement starts in ___ weeks
16-20
If fetal movement lasts longer than __ call the HCP
2 hours
decrease fluid intake before bedtime, reduce caffeinated beverages, and kegel exercises are all interventions for ___
Urinary frequency/incontinence
Side lying position, release pressure in blood vessels is a recommendation for a pregnant woman experiencing
Fatigue
Eat small frequent meals, bland, low fat is a recommendation for a pregnant woman experiencing
N/V
Wear larger bra with good support is a recommendation for pregnant woman experiencing
breast tenderness
__ is the flow of a whitish, yellowish, or greenish discharge from the vagina of the female that may be normal or that may be a sign of infection
Leukorrhea
shark, swordfish, king mackerel, orange roughy, ahi tuna, tilefish are all things that should be __ during pregnancy
avoided
Hot dogs, lunch meat, deli meat should be __ during pregnancy
avoided
soft cheese should be __ during pregnancy
avoided
Refrigerated pate or meat spreads should be __ during pregnancy
avoided
Refrigerated smoked seafood should be __ during pregnancy
avoided
Refrigerated smoked seafood should be __ during pregnancy
avoided
artificial sweeteners should be __ during pregnancy
avoided
shrimp, canned light tuna, salmon, pollock, catfish, tilapia, cod should be __ during pregnancy
eaten
Peanuts, almonds, sunflower seeds, broccoli, salmon, kale, and molasses all include __
calcium
Lactose free dairy products or calcium enriched orange juice or soy milk should be given as a Ca replacement for __
lactose intolerance
__: omit red meat, fish, and poultry but eat eggs, milk, and dairy products along with plant-based foods.
Lacto-ovo-vegetarians