Phonetics & Phonology Vocabulary
1/24
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards for Phonetics and Phonology review.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
Phonetics
The study of speech sounds, focusing on their physical properties.
directly observed , not particular language
Phonology
The study of the sound system of a language and the contrastive sounds. Speaker’s head
studied indirectly, specific language
Phoneme
The smallest meaning-distinguishing unit in a language.
Allophone
A variant form of a phoneme.
Phones that are realizations of the same phoneme – with regard to their phonological status.
Vowel Quadrilateral
Representing the mouth shape and tongue position in cross-section.
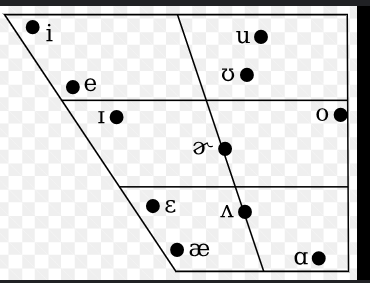
Monophthongs
Vowels that remain relatively unchanged during production.
Diphthongs
Vowels that change during production.
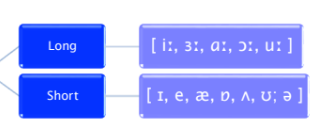
Monophthongs are sometimes labelled:
Pure Vowels
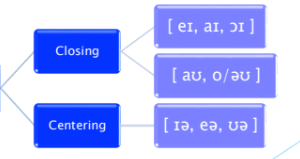
Closing Diphthongs
Diphthongs where the articulation moves from a lower vowel to a higher vowel.
[ eɪ, aɪ, ɔɪ ] [ aʊ, o/ǝʊ ]
Centering Diphthongs
Diphthongs where the articulation moves from a higher vowel to a lower vowel. [ ɪǝ, eǝ, ʊǝ ]
phonetic properties
contrastive
non-contrastive
Non-contrastive(phonetic properties)
Those that provide more detailed description of sound but do not distinguish one sound (or word) from another

Contrastive(phonetic properties)
Those that distinguish one sound from another
When two words contrast (have different meanings) with only one distinctive sound, we call this a minimal pair

Allophones
sounds whose description includes 1 or more non-distinctive properties. These are variant forms of a phoneme, e.g. [th] and [t̪]
Phones that are realizations of the same phoneme – with
regard to their phonological status.
![<p>sounds whose description includes 1 or more non-distinctive properties. These are variant forms of a phoneme, e.g. [th] and [t̪]</p><p>Phones that are realizations of the same phoneme – with</p><p>regard to their phonological status.</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/7383fe57-ec58-45f4-90de-0c8540f800ce.png)
Phonemes
defined by distinctive phonetic properties
(aka features), e.g. /t/ and/p/ (differ: place of articulation; share: manner, voice, aspiration, etc.)

Phone
Actual speech sound; smallest sound segment in a stream of speech without regard to its possible phonological status.
[p] voiceless bilabial plosive
Phonemic transcription:
transcribe the presumed underlying representations of sounds (the speaker’s stored mental idea). What you find in a dictionary.
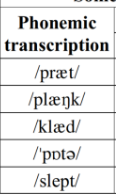
Phonetic transcription:
real-life detailed transcription< it shows lik person talk according to their accent dialect
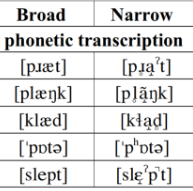
Diacritics
small marks or sylables that added to letters or phonetics symbles E.g.
Minimal Pair Test
A method used in phonetics to identify contrasting phonemes in a language by comparing pairs of words that differ by only a single sound. The results help determine which sounds are phonemic in a given language.
Contrastive Distribution
two or more sounds that occur in identical environments and for which at least one minimal pair can be found
/p/ vs. /b/
pat → /pæt/
bat → /bæt/
🔁 Swapping /p/ and /b/ changes the meaning → so they are in contrastive distribution.
➡ Therefore, /p/ and /b/ are different phonemes in English.
Complementary Distribution
Phones never occur in identical environments
Example (English): [pʰ] vs. [p]
These are both versions of the phoneme /p/.
[pʰ] → aspirated, with a puff of air
Occurs at the beginning of a stressed syllable:
pin → [pʰɪn]
[p] → unaspirated
Occurs after /s/:
spin → [spɪn]
🔄 You can’t swap them — saying [spʰɪn] sounds odd or foreign, but it doesn’t change the word into something new.
“free variation”
contrasts are suspended in specific words
“either” [iðɚ] vs [ɑɪðɚ]
”booth” [buθ] vs [buf]
Phonotactics
refer to rules in a language about how sounds can be arranged in words
Start of a word:
✅ /st/ as in "stop" → allowed
❌ /tl/ — tlip is not a possible English word
End of a word:
✅ /ŋ/ as in "sing" → allowed
❌ /h/ — sih (with /h/ at the end) is not allowed in English
Vowel patterns:
English allows consonant–vowel–consonant (CVC) patterns like "cat" /kæt/
Some languages (like Hawaiian) might not allow words to end in a consonant at all
Phonotactic Rules
Based on position within a word (mainly consonants)
Based on the structure of a syllable
