1.2 Bonding 🪢
1/23
Earn XP
Description and Tags
GCSE CCEA Specification GCSE Chemistry Double Award Science, Triple Award Science Unit 1: Structures, Trends, Chemical Reactions, Quantitative Chemistry and Analysis
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
Bonding
way in which molecules and structures are held together
Molecule
particle consisting of two or more atoms chemically bonded together
Compound
substance consisting of two or more elements chemically combined
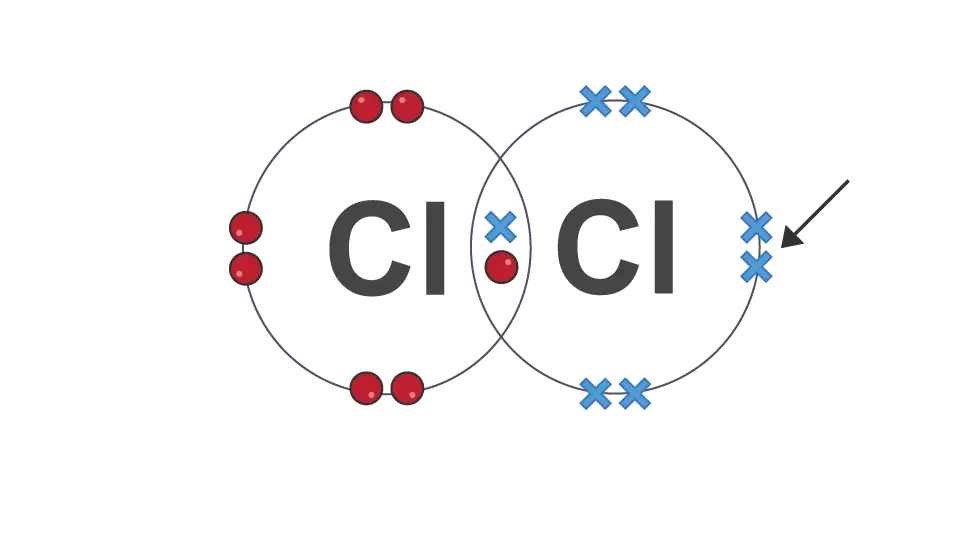
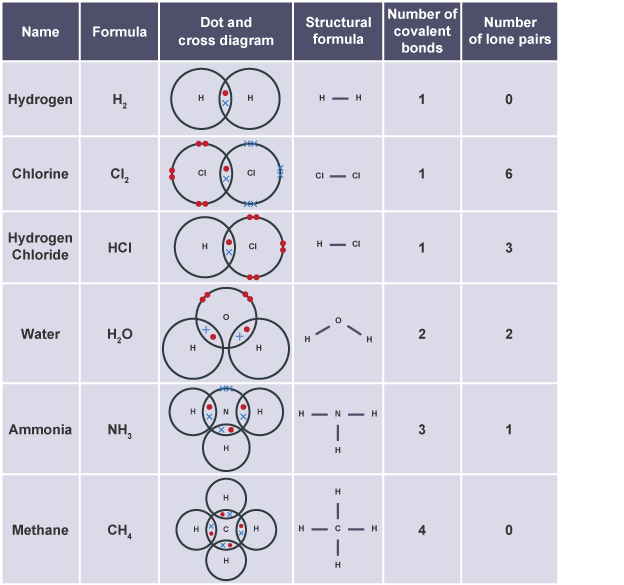
Dot and cross diagram
shows arrangement of atoms or ions, same elements have same electrons (✕ / ⬤)
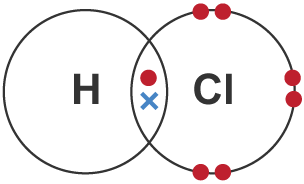
Covalent bond
formed by shared pair of electrons between non-metals, neutral charge
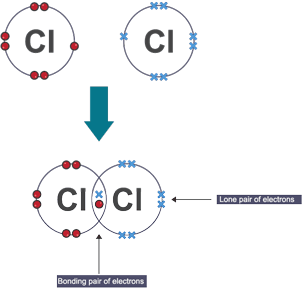
Lone pair electrons
Electrons paired up but not part of covalent bond
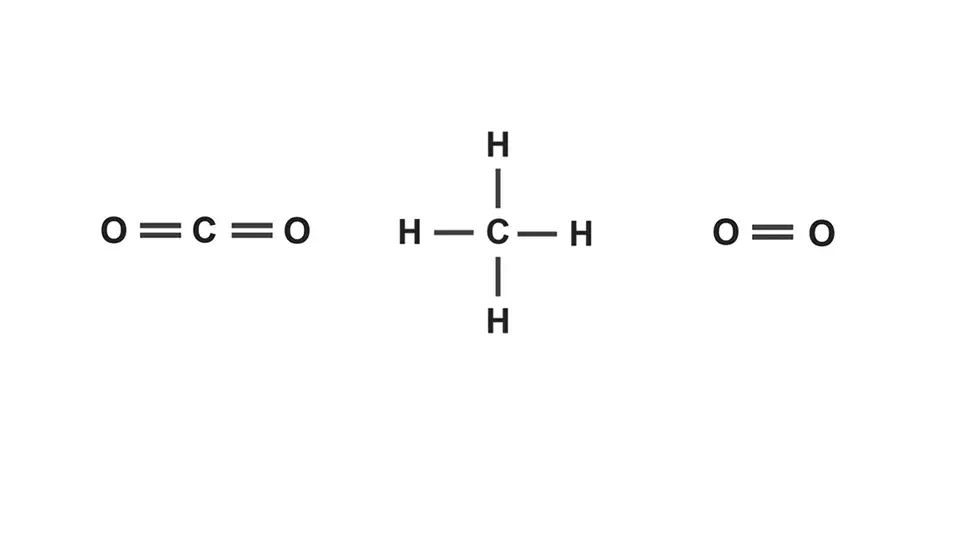
Stick diagram/ structure
single line for covalent bond, double line for double covalent etc
Strength of covalent bonds
Very strong and takes large amount of energy to break
Common covalent substances
H2, Cl2, HCl H2O, NH3, CH4
Diatomic
two atoms covalently bonded in a molecule
Diatomic elements
H2, N2, O2 + Group 7
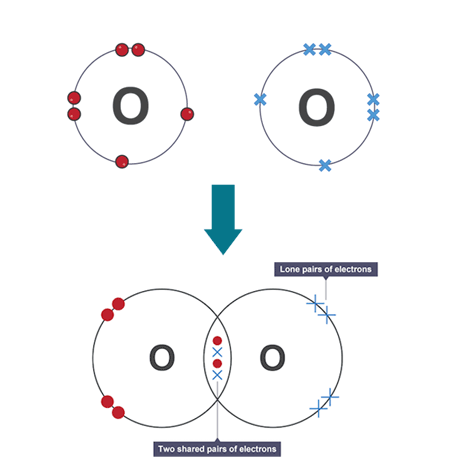
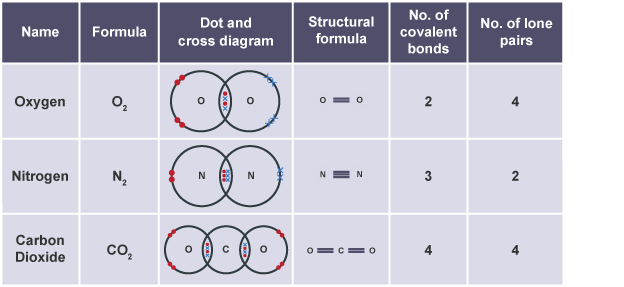
Double covalent bond
bond which atoms share two pairs of electrons e.g carbon dioxide or oxygen
Triple covalent bond
bond which atoms share three pairs of electrons e.g nitrogen
Metallic bonding
attraction between delocalised electrons and positive ions in regular lattice
Metals typically form
positive ions (cations) by delocalising outer electrons
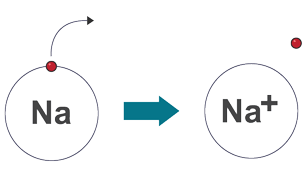
Ionic bonding
electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions, metal and non-metals
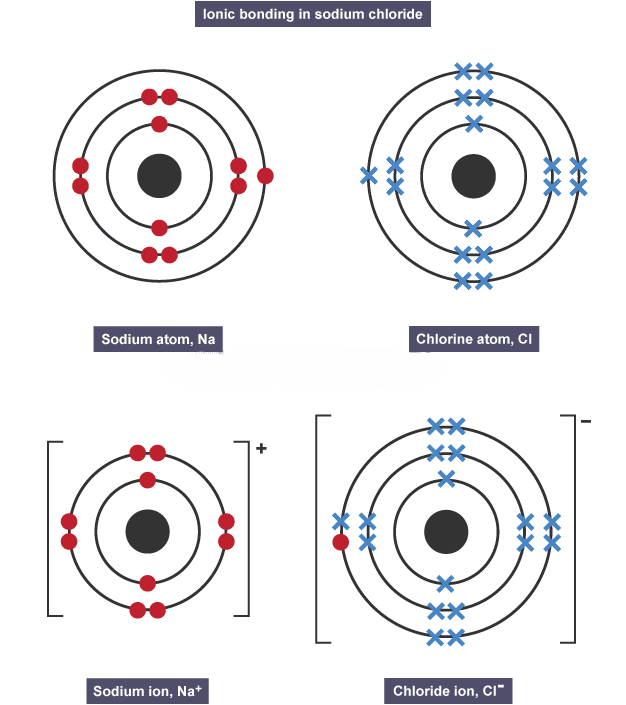
Electrons in ionic bonding
transferred from metal atom to non-metal atom
Examples of Ionic compounds
NaCl, MgO
Drawing ionic bonds
draw electronic configuration of each atom
work out how many electrons are transferred
draw configuration of ions formed
write the charge of each ion [ ]±
![<ol><li><p>draw electronic configuration of each atom</p></li><li><p>work out how many electrons are transferred</p></li><li><p>draw configuration of ions formed</p></li><li><p>write the charge of each ion [ ]<sup>±</sup></p></li></ol><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/cd769447-db8a-441e-84a0-6fb2ae6d7f77.png)
Ionic formula
simplest whole number ratio of the ions in giant ionic lattice
Ion
charged particle formed when an atom gains or loses electrons
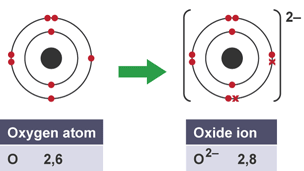
Anion
negatively charged ion, ends in -ide
Cation
positively charged ion
Molecular ion (back of data leaflet)
charged particle containing more than one atom e.g OH-