consumer behavior exam 2
1/144
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
145 Terms
what is a self?
a person's essential being that distinguishes them from others, especially considered as the object of introspection or reflexive action.
what is an identity?
distinguishing characteristics of an
individual – seen internally or externally
who is Erving Goffman?
sociologist
what is erving goffman’s take on the whole deal of “self”? (dramaturgical perspective)
he believes the self is something we are NOT and rather something we do
our self is defined by others
what is self-concept?
summarizes the beliefs a person holds about his own attributes and how he
evaluates the self on these qualities.
what is self esteem?
refers to positivity of a person’s self concept.
low self esteem —> expect not to perform well
high self esteem —> confidence
what is the collective self?
Identity driven by membership or association with others
what is the ideal self?
our conception of how we would like to be
what is the actual self?
our more realistic appraisal of the qualities we have
how are products related to the ideal and actual self?
they help us reach ideal self while also being consistent with actual self
what is impression management?
we work to “manage” what others think of us
what is the digital self?
The personas we create online
Online Avatars
Twitter and Instagram
Facebook
Others?
Does your Instagram account accurately reflect who
you actually are?
what do marketers do when it comes to multiple selves?
pitch products needed to facilitate active role identities
what does it mean to have multiple selves?
means recognizing and engaging with different, distinct aspects of your personality that may vary by situation, social role, or internal state.
what is an example of multiple selves:
looking glass self
what is the looking glass self?
When we imagine ourselves from an outside perspective we are using what is
referred to as the looking-glass self.
We tend to overestimate how much other people are paying attention to us
We also are somewhat bad at estimating what others actually think
“everyone hates me”
what is the extended self?
the concept that a person's identity is not limited to their body and mind but includes possessions, people, places, and even their digital footprint.
how do marketers use the extended self?
to connect with consumers by positioning products as integral to their identity, which includes possessions, people, places, and group values.
what is self-consciousness in us?
self monitors us
having public self consciousness
___are a form of self presentation
selfies
what does you are what you consume refer to?
Social identity is influenced by individual consumption behaviors
Inference of personality based on consumption patterns
people who have incomplete sense of self complete this identity
what is self/product congruence?
consumers demonstrate their values through their purchase behavior
product usage = self-image
ex: harley davidson users
what does self-image congruence models refer to?
we choose products when attributes matches the self (or ideal self)
what are the 4 levels of self?
individual
family
community
group
what does the individual level of self refer to?
personal possessions (cars, clothing)
what does the family level of self refer to?
residence and furnishings
what does community level of self refer to?
neighborhood or town where you live
what does group level of self refer to?
social or other groups
what does embodied cognition refer to?
power posing — enclosed cognition
the behaviors we emit influence our sense of self and who we are
ex: wonder woman/superhero pose leads to being more confident
gender and sex roles in socialization look like what…
gender role vary by culture but change over time
many societies. experience traditional roles
what are agentic roles?
men are expected to be assertive and have certain skills
what are communal roles?
women are taught to foster harmonious relationships
sex-types traits are?
characteristics we stereotypically associate with one gender or the other
what are sex-types products
take on
masculine or feminine
attributes
Doll houses
Race Cars
Wine Coolers
Jagermeister
what is the stereotype when it comes to beauty?
Exemplar of appearance
“What is beautiful is good” stereotype
Favorable physical features:
Attractive faces
Good health and youth
Balance/symmetry
Feminine curves/hourglass body shape
“Strong” male features
why do people change their body?
to fit in or stand out
examples include:
Body anxiety
Cosmetic surgery
Body decoration and
mutilationBody piercing
what is personality?
influences the way he or she responds to marketing stimuli, but efforts to use this information in marketing contexts meet with mixed results.
how do we measure personality?
through psychometric assessments like self-report questionnaires, which ask individuals to rate their own feelings and behaviors on scales, and observer ratings from others.
who was freaud?
father of psychoanalysis and talk therapy
before him no therapists talked to you, was other way around
what were freuds detractors?
wrote extensively on cocaine benefits
focused on sex & sexual conflict
researchers say much of his theory makes no sense
what is ID?
part of you that wants good things all the time (pleasure seeking)
what is the ego?
the in between of both, evaluates both sides
what is super-ego?
rule follower, concerned about future, cautious side
what does motivational research and consumption motives tell us (dichter)?
Assumes that we channel socially unacceptable needs into acceptable outlets (unstated goals of consumption)
what is the reality principle?
is a psychological concept, central to Freudian theory, that governs the ego and dictates the ability to assess the external world and delay immediate gratification in favor of long-term, realistic goals.
who is carl jung?
father of analytical psychology
disciple of freud
believed in idea concept of collective unconscious that recognizes common behavior patterns/personality types
explained creation of archetypes
what were carl jung’s archetypes?
old wise man
earth mother check slides for more info
what are personality traits?
identifiable characteristics that define a person
what are traits relevant to consumer behavior?
innovativeness
materialism
self-consciousness
need for cognition
what are traits in consumer research?
frugality
impulsiveness
trait anxiety
bargaining proneness
trait vanity
what are the big five personality dimensions?
openness to experience
conscientiousness
extroversion
agreeableness
neuroticism (emotional instability)
what does openness to experience mean?
the degree to which a person is open to new ways of doing things
how is openness to experience measured?
thinking of new ways of doing things
what is conscientiousness?
the level of organization and structure a person needs
how is conscientousness measured?
how prepared someone is
what is extroversion?
how well a person tolerate stimulation from other people
how is extroversion measured?
talking to a lot of different people at parties
what is agreeableness?
the degree to which we defer to other people
how is agreeableness measured?
their ability to take time out for others
what is neuroticism (emotional instability)?
how well a person copes with stress
how is neuroticism measured?
how upset someone can get/how easily they get upset
what is MBTI (based on jung)
Focus of attention
Information processing
Decision making
Dealing with outer world
ISTJ, ENFP
what is an example of brand personalities?
pilgrim on quaker oats, pillsbury dough boy
what are brand personalities based on?
Competence
Excitement
Ruggedness
Sincerity
Sophistication
who was David Aaker?
he said there was dimensions of brand personality
definition of brand personality:
set of traits people attribute to a product as if it were a person
what is the reader response theory?
all is interpreted by observers
what are the trait theories?
traits relevant to consumer behavior:
innovativeness
materialism
self-consciousness
need for cognition
what is consumer segmentation?
what are attitudes/where they stem from?
Relatively enduring overall evaluations of objects, products, services, issues,
or people.
definition of attitudes:
a lasting, general evaluation of people, objects, advertisements, or issues
what is an attitude object?
anything toward which one has an attitude
what are the ABC’s of attitudes?
Affect
Behavior
Cognition
example of ABC approach to attitudes:
Affect: “I really like my Toyota Corolla.”
Behavior: “I always buy Toyota products.”
Cognition: “My Corolla gets good gas mileage.”
how does the hierarchy of effects work when it comes to attitudes?
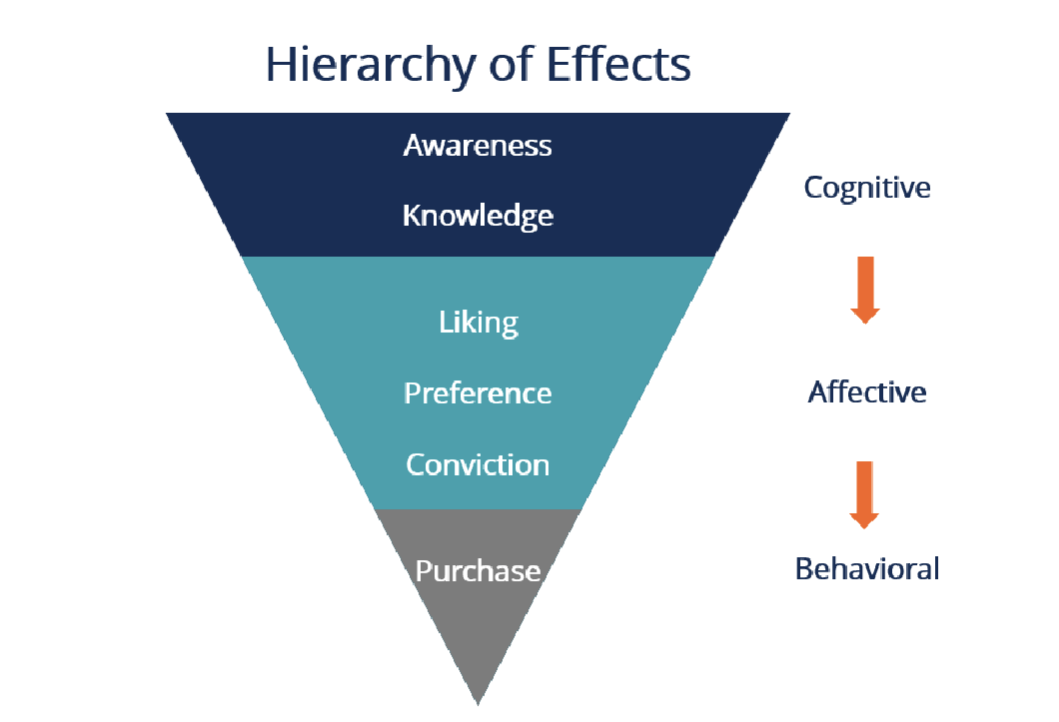
what is the purchase context of high involvement?
belief — affect — behavior
what is the purchase context of low involvement?
belief — behavior — affect
what is the purchase context for experiential?
affect — behavior — belief
what is the purchase context for behavioral influence?
behavior — belief — affect
what are the functional theories of attitudes?
utilitarian function
value-expressive function
EGO-defensive function
knowledge function
what is the utilitarian function?
relates to rewards and punishments — we tend to like people/stuff that is nice to us
what is value-expressive function?
expresses consumer’s values or self concept
what is the EGO-defensive function?
protect ourselves from external threats or internal feelings
what is the knowledge function?
help us navigate the world — need for order, structure, or meaning
what are the three parts of attitude commitment?
internalization
identification
compliance
how do we discuss how committed someone is to an attitude?
you can observe and discuss their consistent behaviors, the consistency between their words and actions, and their willingness to be accountable for their choices
what is internalization?
Highest level of attitude commitment: deep-seeded attitudes become part of
consumer’s value system
what is identification?
Mid-level of attitude commitment: attitudes formed in order to conform to another person or group
what is compliance?
Lowest level of attitude commitment: consumer forms attitude because it gains rewards or avoids punishments
what is the consistency principle?
We value/seek harmony among thoughts, feelings, and behaviors and change components to make them consistent
Relates to the theory of cognitive dissonance
what is the balance theory?
Considers how a person might perceive relations among different attitude objects and how he might alter attitudes to maintain consistency
what are the triad attitude structures related to balance theory?
person
Perception of attitude object
Perception of other person/object
what do self perception theories tell us?
WE INFER ATTITUDES FROM OUR BEHAVIORS
what is the foot-in the door technique?
Consumer is more likely to comply with a request if they have first agreed to comply with a smaller request
what is the low-ball technique?
Person is asked for a small favor and is informed after agreeing to it that it will be very costly.
what is the door in the face technique?
Person is first asked to do something extreme (which they refuse), then asked to do something smaller.
what is the fishbein model?
Salient Beliefs
Object-Attribute Linkages
Evaluation
what is something to note about the ATO model?
Important to note attitudes don’t have to be about concrete things
what is the social judgment theory?
We assimilate new information about attitude objects in light of what we already
know/feel
Initial attitude = frame of reference
Latitudes of acceptance and rejection in social judgment theory?
Assimilation effects
Contrast effects
Example: “Choosy mothers choose Jif Peanut
Butter”