paper 2 biology
1/113
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
114 Terms


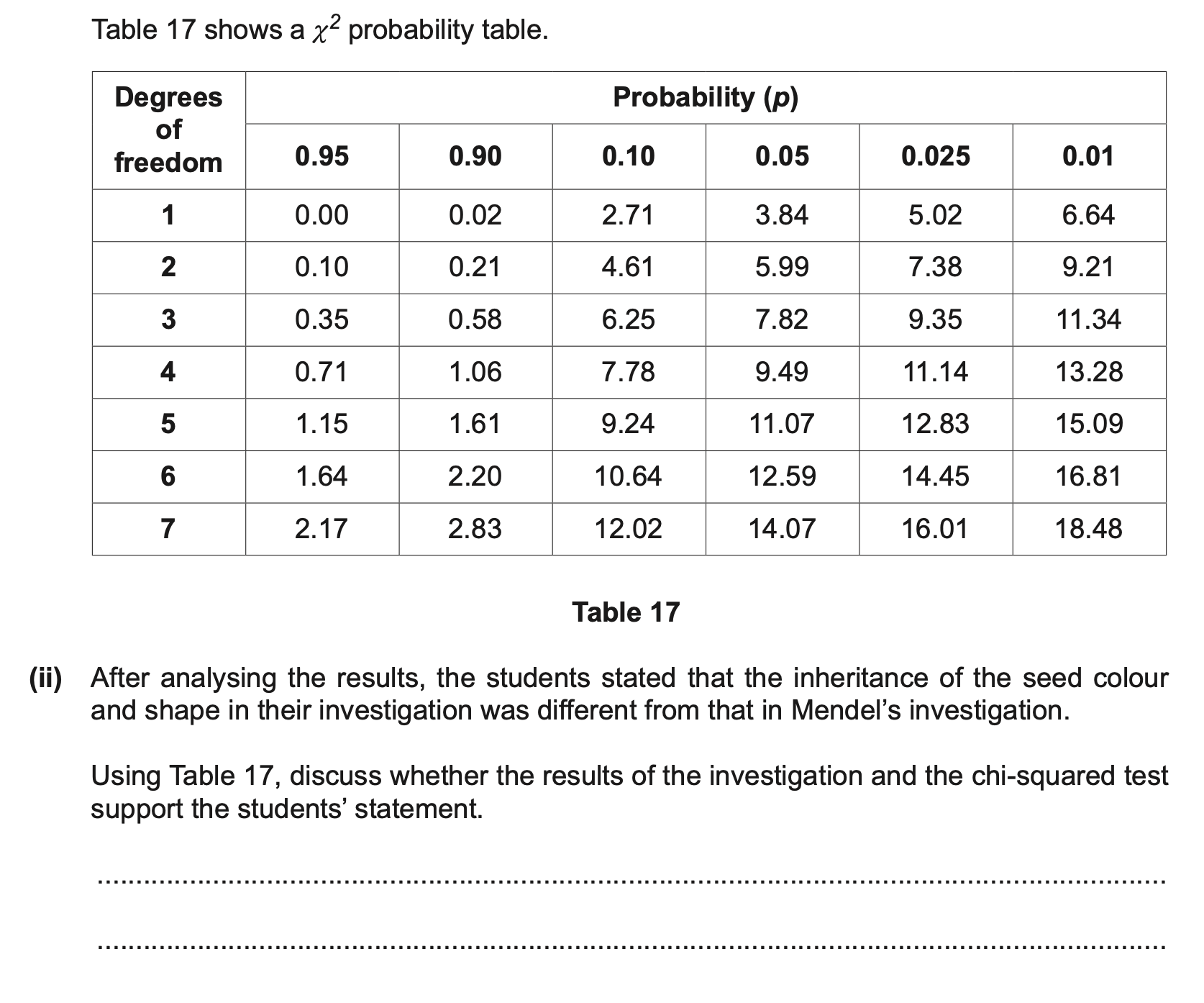
chi-squared value is 8.730
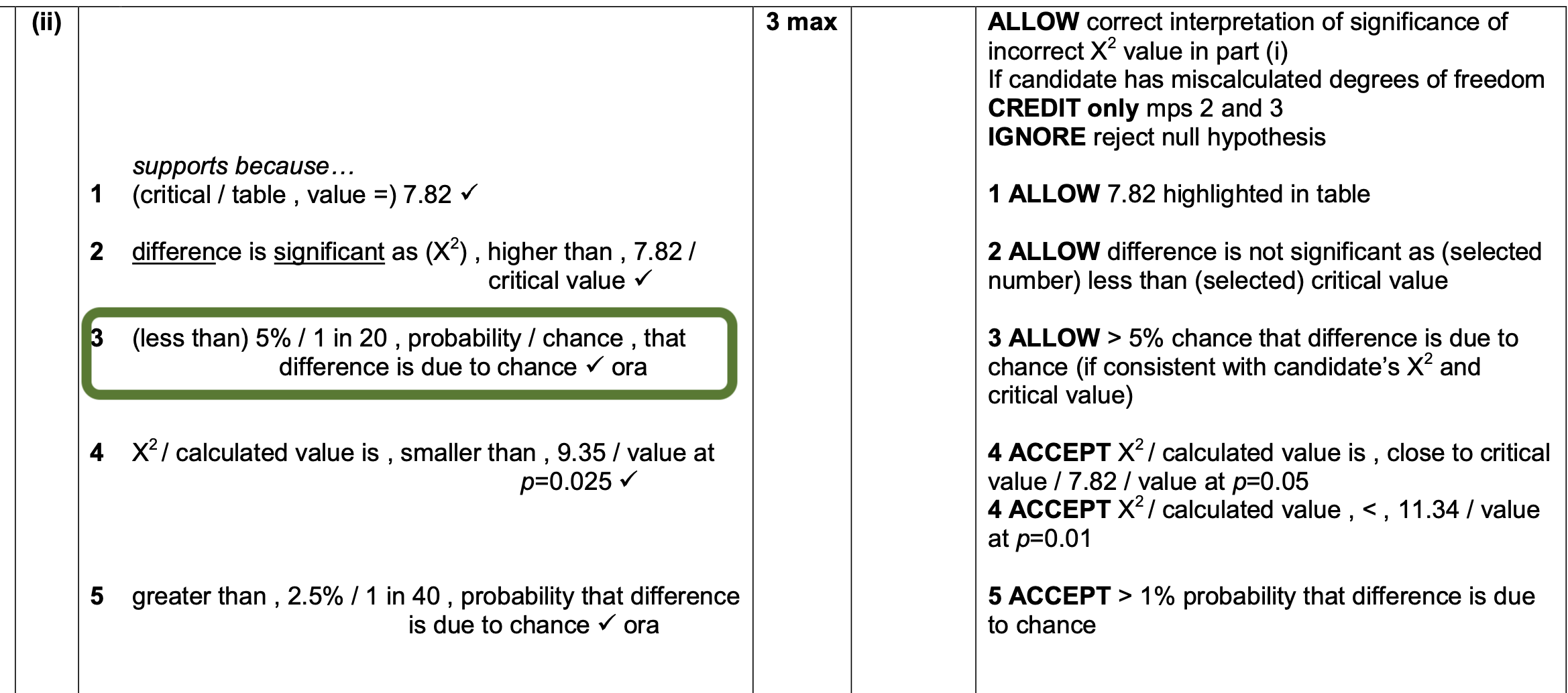

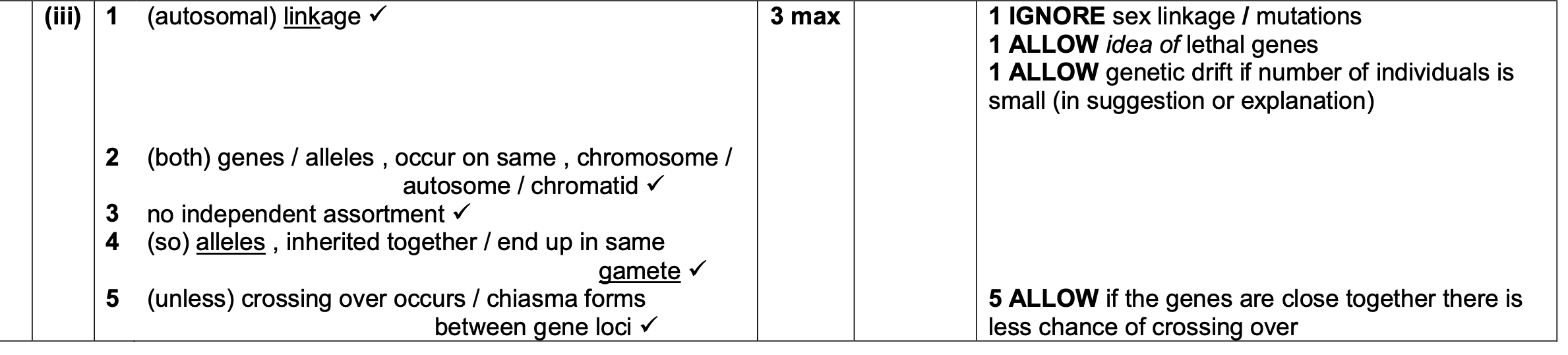
How could a plant respond to an infection?
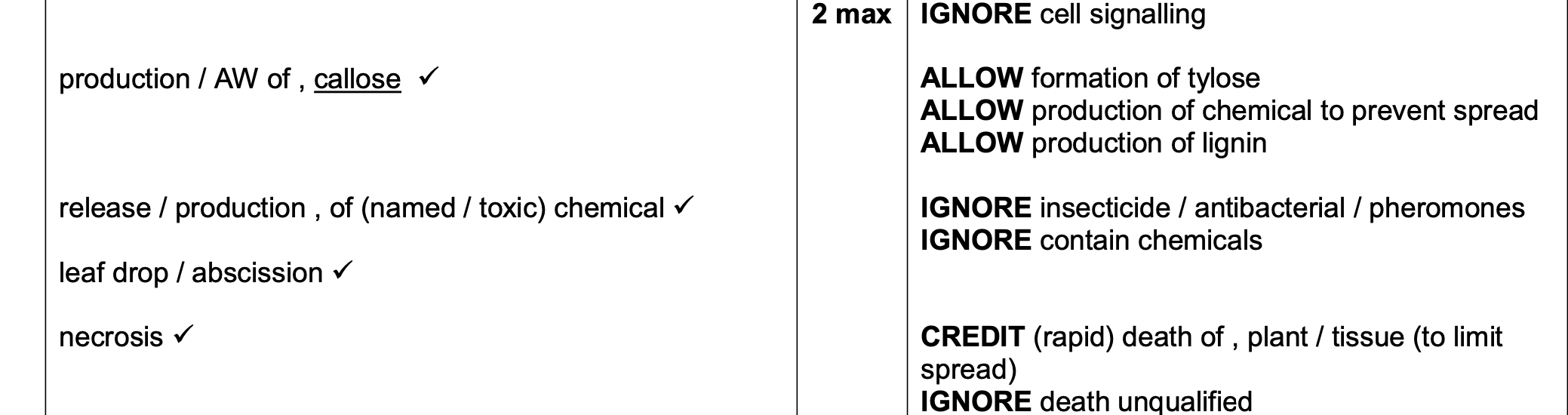
why would an experiment use clones?
to prevent genetic diversity and increase validity
to ensure consistent results and isolate the effect of the independent variable.
control variables that may affect DV

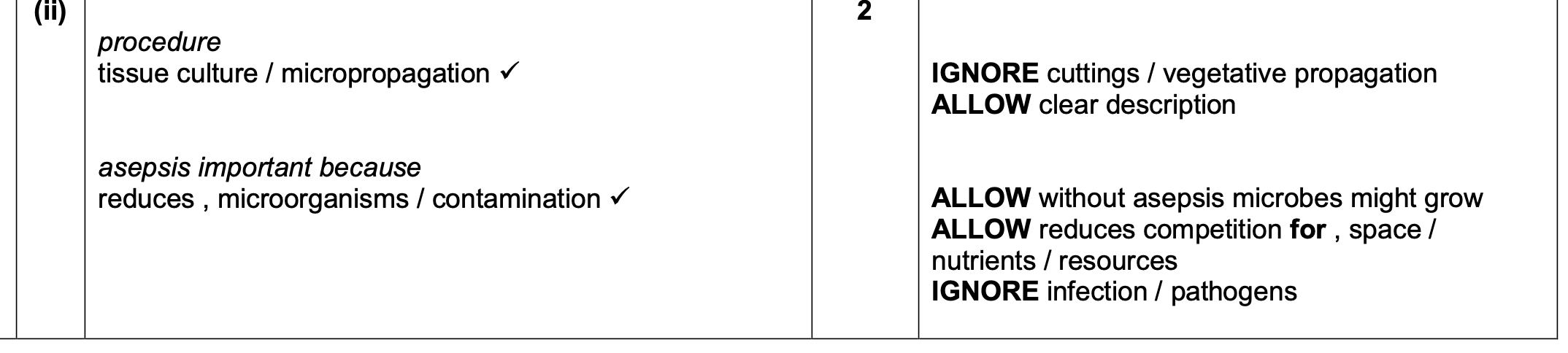
Variables that need to be controlled when growing plants/clones for an experiment

principles of classification



what does lactose permease do
digests lactose by facilitating its transport across cell membranes.

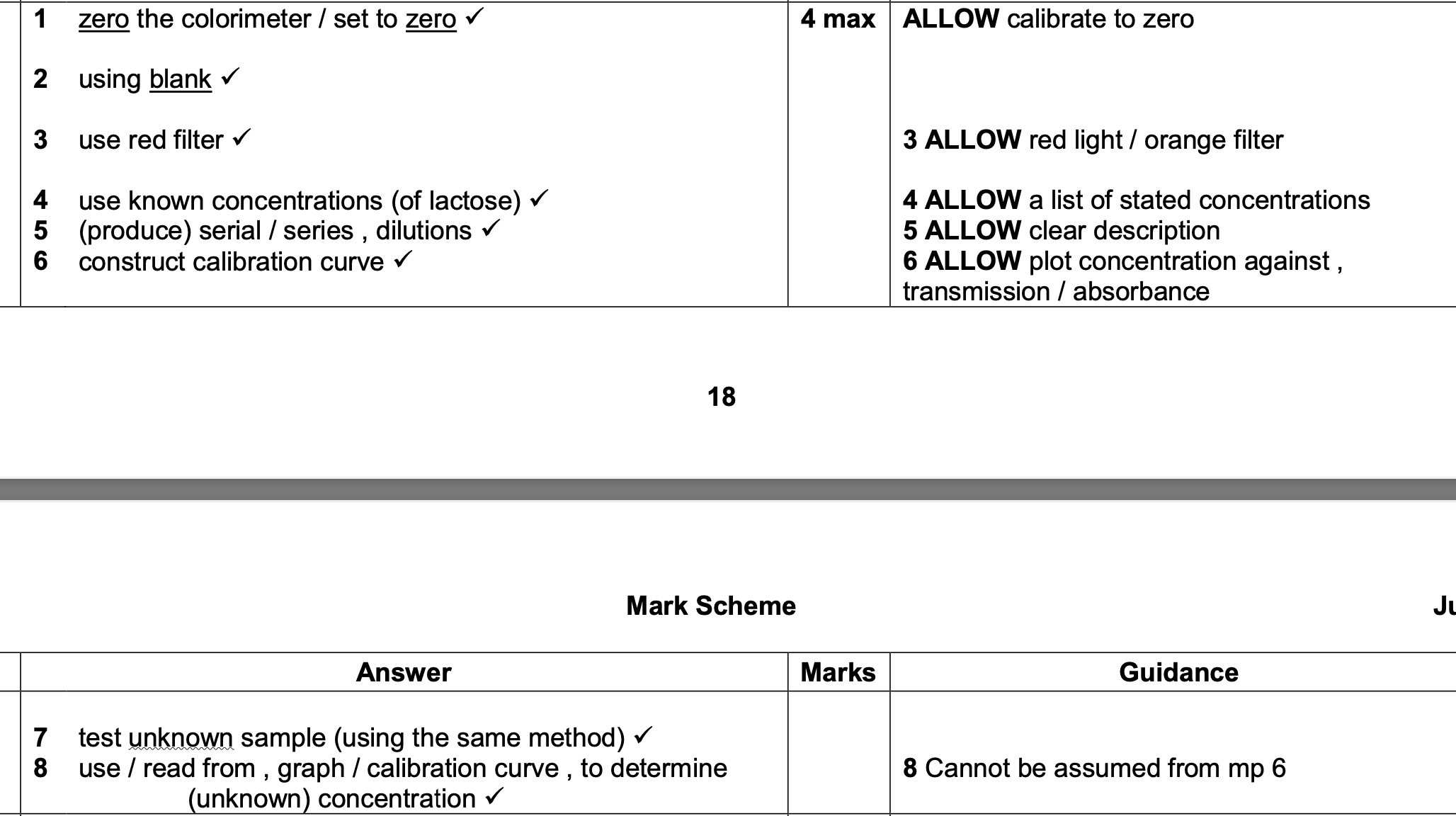
what is happening when the modified bacteria and the isolated DNA are put together?

How can scientists determine that the bacteria successfully took up the DNA?

concern about genetic modification of bacteria?
increase in antibiotic resistance
DO NOT CREDIT immune
apoptosis
enzymes break down cell cytoskeleton (it’s a protein)
the cytoplasm becomes dense with tightly packed organelles
the plasma membrane changes and small protrusions called blebs form
chromatin condenses, nuclear envelope breaks down and DNA breaks into fragments.
what are homeobox genes
regulatory genes, 180 base pairs, code for homeodomain which is part of a protein and homeobox genes contain hox genes.
suckers
stems that grow from roots to plants
runners or stolen
stems that grow on the surface of the ground
rhizomes
stems that grow underground
where can cuttings be taken from?
root cuttings
scion cuttings
leaf cuttings
embryo splitting
a zygote is created in IVF
zygote divides by mitosis to form a ball of cells
the cells are separated and allowed to continue dividing
each small mass of cells is placed into the uterus of a surrogate mother
(phenotype unknown until birth)
SCNT
an egg cell is obtained and its nucleus is removed (enucleation)
a normal body cell (somatic cell) from the adult is isolated and may have its nucleus removed
the complete adult somatic cell or its nucleus is fused with the empty egg cell by applying an electric shock
the shock triggers the egg cell to start developing
the cell undergoes mitosis to produce a small ball of cells
the young embryo is placed into the uterus of a surrogate mother.
(known phenotype, only way to clone an adult)