Meristems and primary growths
1/27
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
define a tissue
a tissues is a group of one or more cell types which carries out specialized functions(s)
what are meristems? describe them
plants have undifferentiated tissues called meristems, consisting of cells which constantly divide under suitable conditions and produce new cells
-some of these cells then elongate and differentiate to produce new tissues of the plant body and others remain as meristems.
-meristems may have dormant periods.
-due to the action of meristem new cells are added
-subsequently these cells get differentiated and therefore plant growth occurs by making new plant tissues
what are some characteristics of meristematic cells?
all cells in meristems have common characteristics.
-they are isodiametric (roughly spherical)
-they are living cells
-they are structurally and functionally undifferentiated
-they have a central nucleus
-they have a dense cytoplasm
-they have the ability to multiply
what are the 3 stages of a meristem?
in meristem there are 3 overlapping zones of cells consisting of cells at successive stages of
-cell division
-cell elongation
-differentiation
what are the 3 types of meristems?
-apical meristems
-lateral meristems
-intercalary meristems
what are the locations of apical meristems?
root tips and shoot tips
what is the role of apical meristems?
they add new cells that enable increase in length
describe primary growth
meristems located at shoot tips and root tips adding new cells that enable increase in length
describe apical meristems
these meristems are located at root tips and shoot tips. they add new cells that enable increase in length. this process is known as primary growth
what are the 2 types of lateral meristems? what do they each produce?
vascular cambium- produces secondary xylem and secondary phloem
cork cambium-produces thick and tough periderm, replacing epidermis
where are lateral meristems found and what do they involve in?
they are found in woody plants and involve in the secondary growth in increasing circumference of roots and stems
describe lateral meristems
vascular cambium and cork cambium are lateral meristems. they are found in woody plants and involve in the secondary growth in increasing circumference of roots and stems. vascular cambium produces secondary xylem and secondary phloem. the cork cambium produces thick and tough periderm, replacing epidermis
where may intercalary meristems be found?
at the bases of stems and leaves of some monocots such as grasses
what is the role of intercalary meristems?
they allow rapid regroth in damaged leaves
describe intercalary meristems
some monocots such as grasses show meristematic activity at the bases of stems and leaves. they are known as intercalary meristems. they allow rapid regrowth in damaged leaves
define the primary growth of the root
elongation of root due to the activity of primary meristems located on root apex
what are the processes taking place during growth? write a feature of them
during the growth three processes take place
i)cell division - due to mitotic division
ii)cell elongation
iii)cell maturation - due to differentiation
-these stages are found in 3 overlapping regions starting from meristems
why does cell division occur?
due to mitotic division
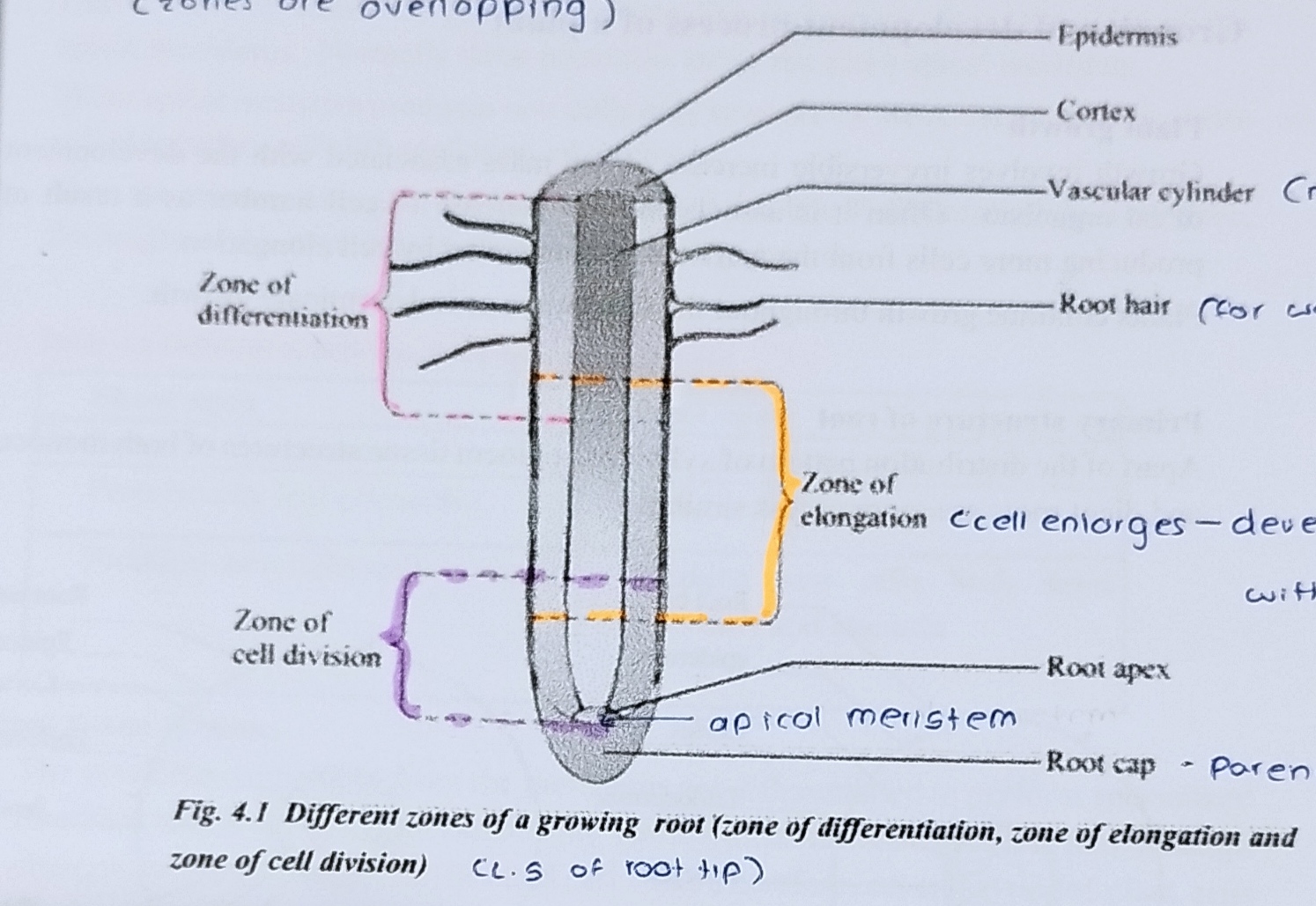
what is the function of root cap and what cells produce it?
cells produced outward to the apical meristem are differentiated to form root cap which prevents damaging the root apical meristem from friction when grows through soil
describe the events of the 3 processes
-the zone of cell division includes the root apical meristem and its derivatives. in this region, new cells are produced to both sides. cells produced outward to the apical meristem are differentiated to form root cap which prevents damaging the root apical meristem from friction when grows through soil.
-cells produced inward to the meristem undergo elongation, in the zone of cell elongation. root cells elongate, sometimes to more than 10 times their original length. hence the root is pushed forward through soil.
-in the zone of maturation, the cells begin specializing in structure and function where cells complete their differentiation and become functionally mature. primary structure of the root is formed as a result of primary growth.
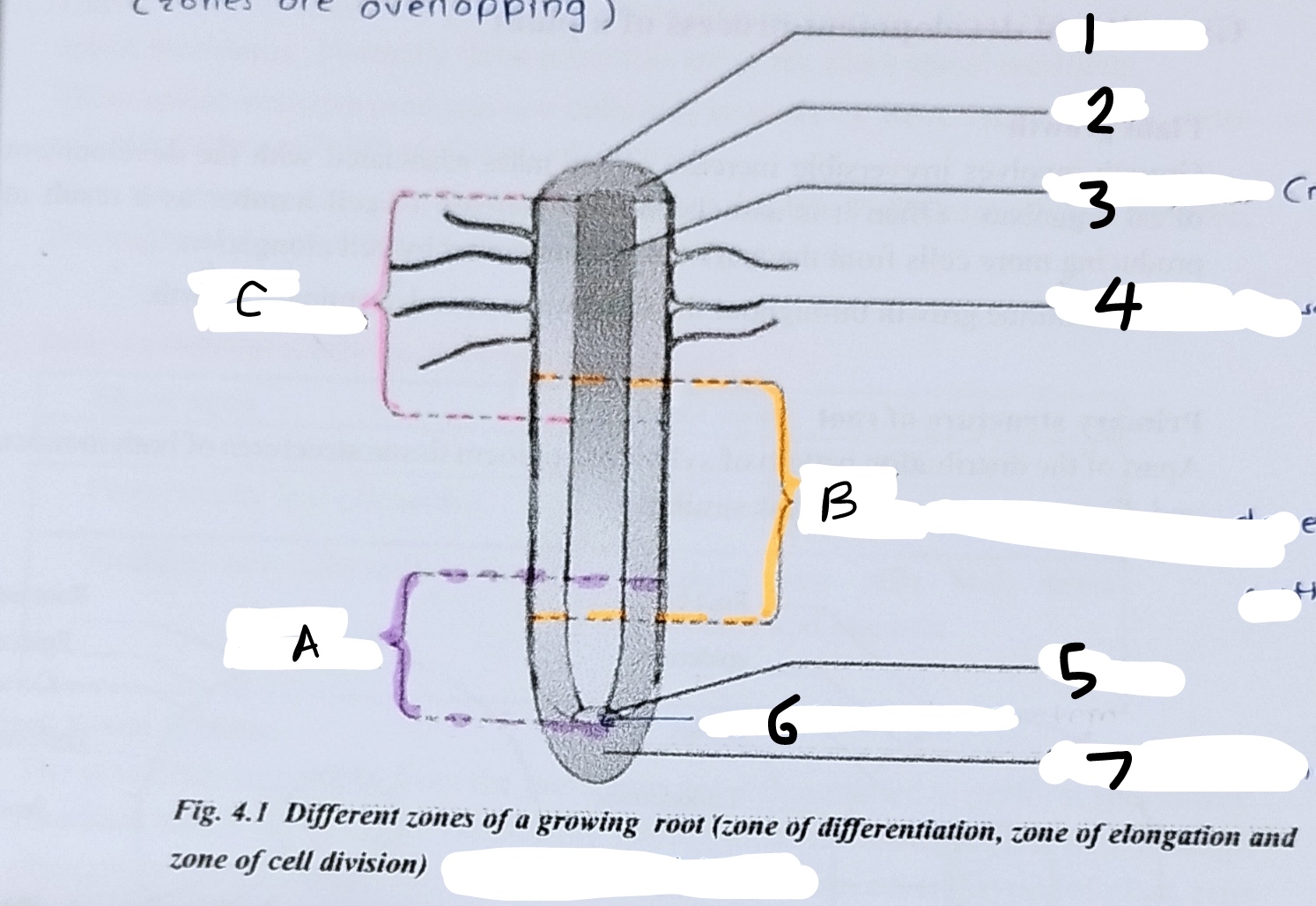
Write what parts are labelled and what the overall diagram is
define the primary growth of the shoot
elongation of shoot is due to the activity of primary meristem located in shoot apex
what is a shoot apical meristem?
a shoot apical meristem is a dome shaped mass of dividing cells located at the shoot tip
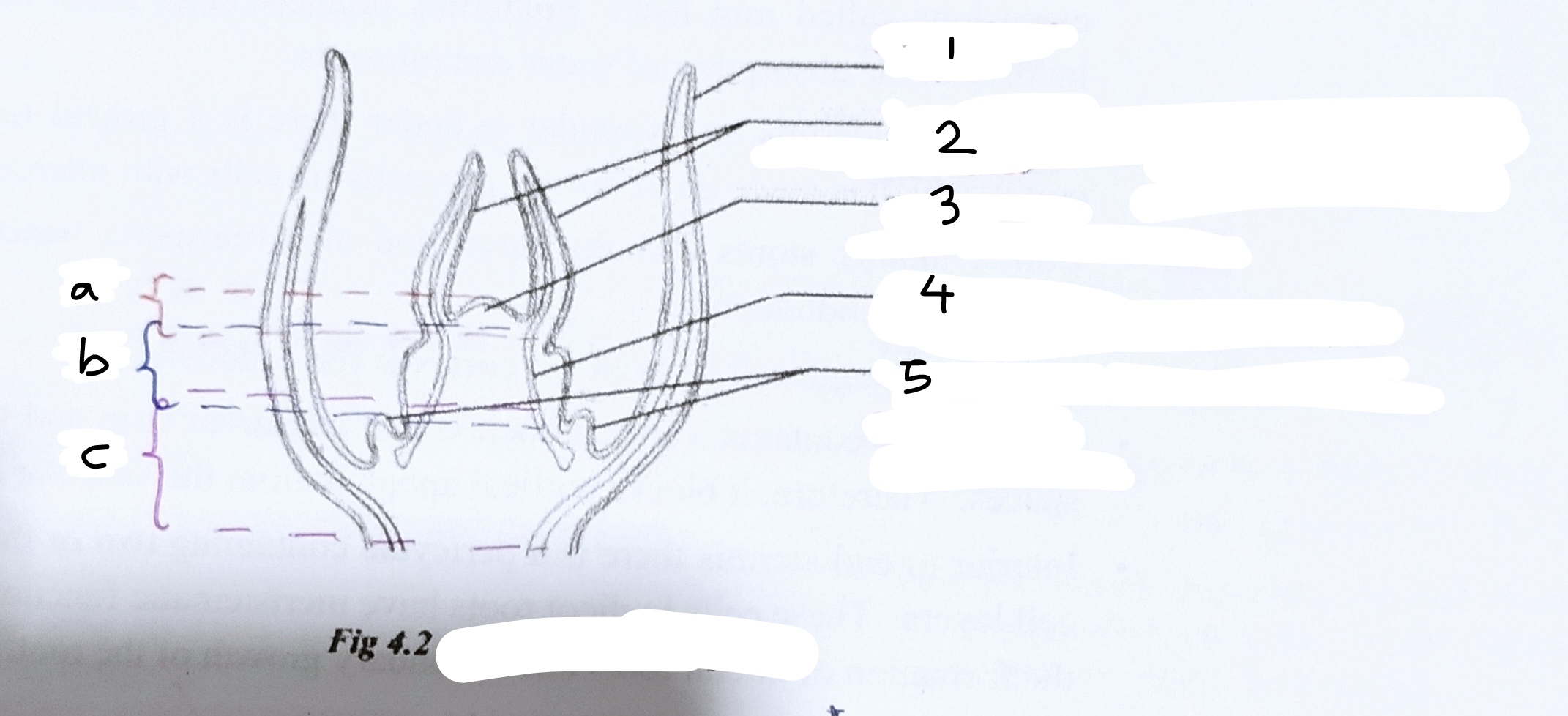
Write what parts are labelled and what the overall diagram is
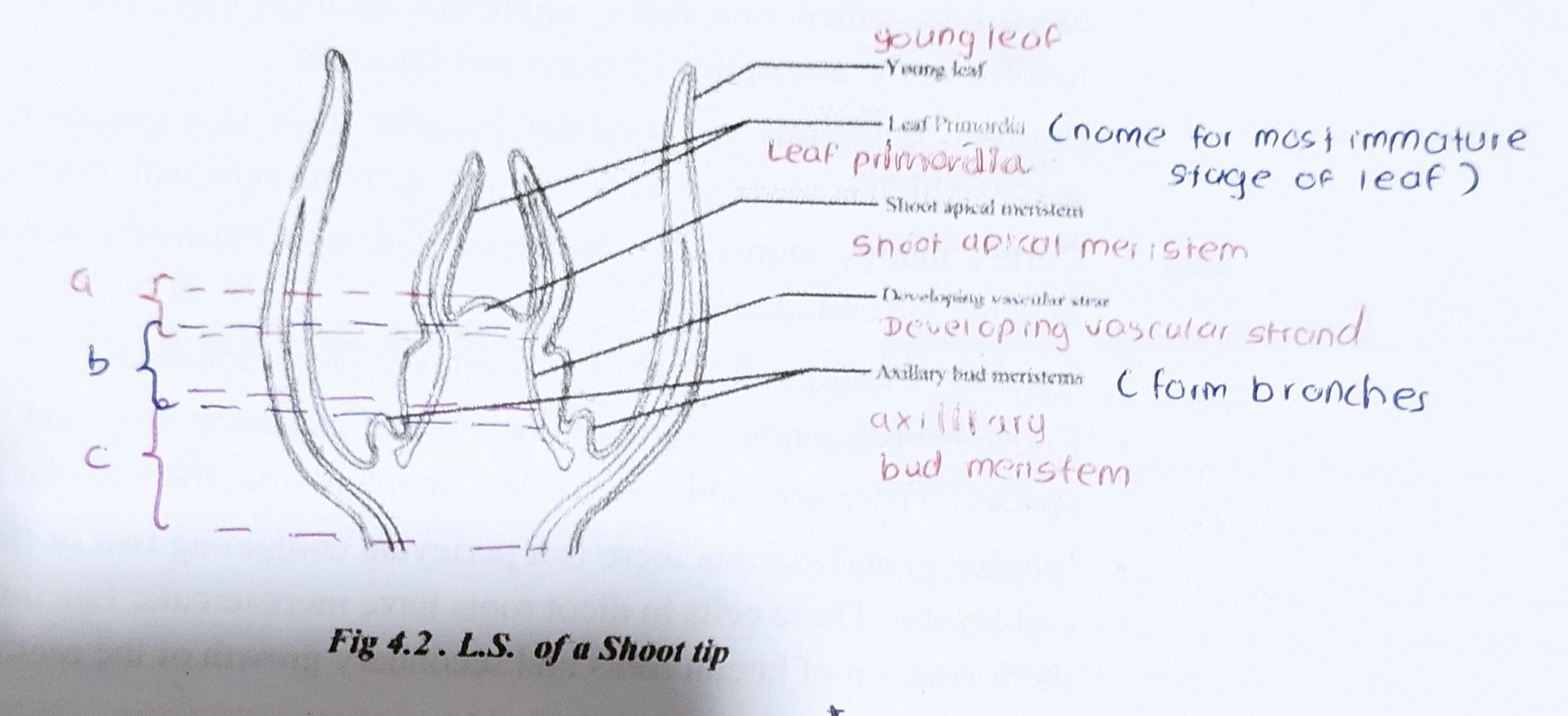
what are leaf primordia?
leaves develop from leaf primordia, finger-like projections along the sides of the apical meristems. normally these primordia cover the shoot apical meristem
describe the 3 processes of growth of shoot apical meristem
shoot apical meristem produces new cells only towards the stem, due to mitosis. around the end of cell elongation, cell differentiation takes place. then the primary tissues of the stem are formed due to cell differentiation. therefore, the height of the stem is increased due to primary growth
what are the similarities between root and shoot apical meristem?
-both have 3 overlapping zones of cells
-both have apical meristem
what are the differences between shoot apex and root apex?
-shoot apex is found at tips of shoot but root apex is found at the tip of the root
-shoot apex is protected by leaf primordia but root apex is protected by root cap
-shoot apex produces new cells only inwards but root apex produce new cells both sides outwards and inwards