Carbohydrate Metabolism [Glycogenesis, Glycogenolysis, The Cori Cycle, and The Pentose Phosphate Pathway]
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
Glycogen
Branched polymeric form of glucose
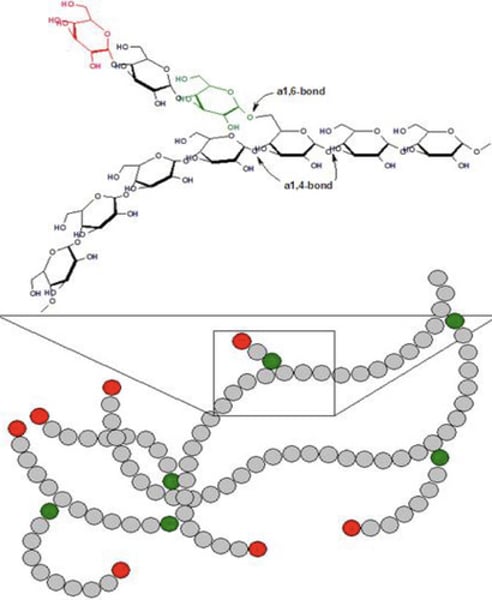
Glycogen
Storage form of carbohydrates in humans
Glycolysis
In muscle, it is the source of glucose for (?)
Liver
In (?) tissue, it is the source of glucose required to maintain normal blood glucose levels
A
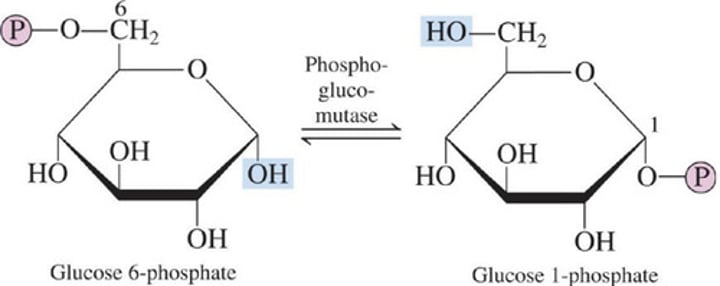
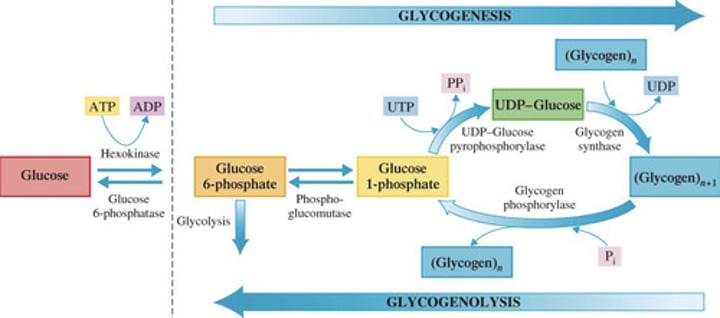
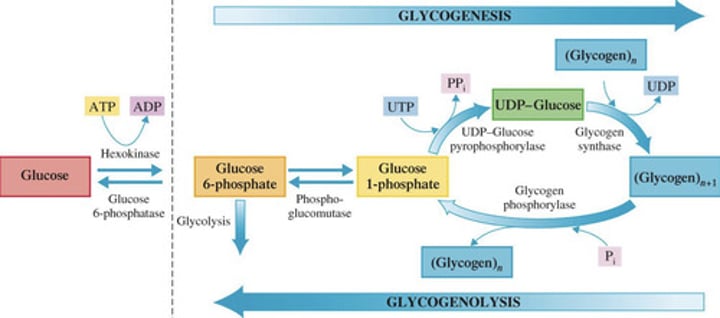
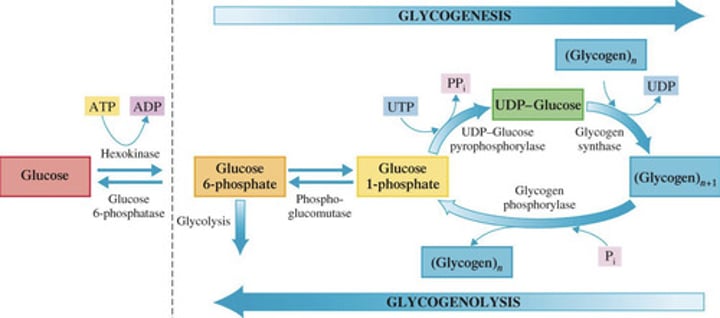
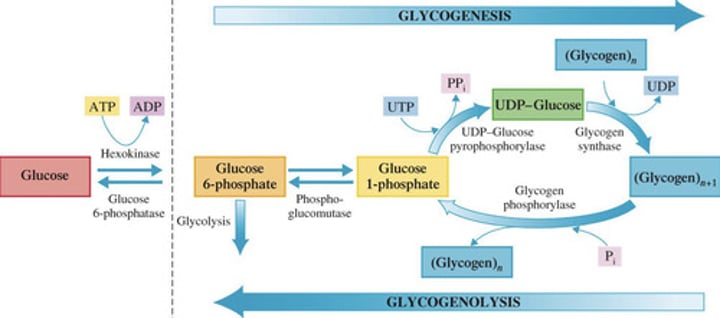
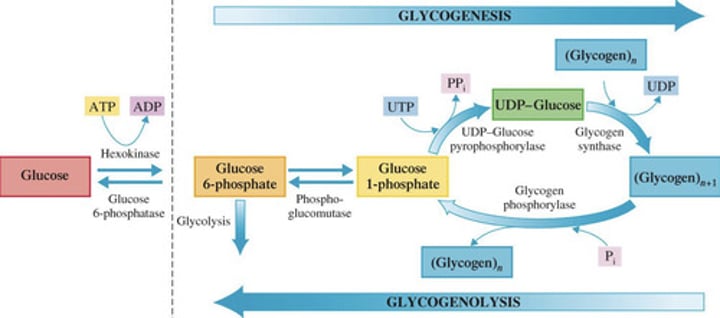
Identify the step in Glycogenesis
1.) Starting material is glucose 6-phosphate (available from the first step of glycolysis)
A.) Step 1: Formation of glucose 1-phosphate
B.) Step 2: Formation of UDP-glucose
A
Identify the step in Glycogenesis
2.) Enzyme phosphoglucomutase effects the change from a 6-phosphate to a 1-phosphate
A.) Step 1: Formation of glucose 1-phosphate
B.) Step 2: Formation of UDP-glucose
B
Identify the step in Glycogenesis
1.) High-energy compound UTP (uridine triphosphate) activates glucose 1-phosphate to form uridine diphosphate glucose (UDP-glucose)
A.) Step 1: Formation of glucose 1-phosphate
B.) Step 2: Formation of UDP-glucose
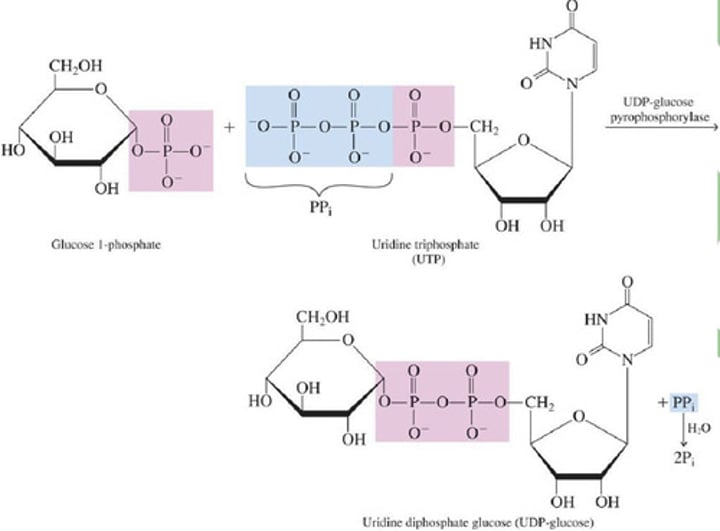
UDP
Glucose transfer to a glycogen chain
1.) Glucose unit of UDP-glucose is attached to the end of a glycogen chain and (?) is produced
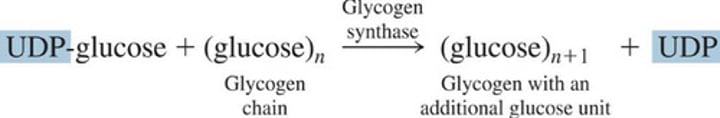
Pentose Phosphate Pathway
This is the pathway in which glucose 6-phosphate is used to produce NADPH, ribose 5-phosphate (a pentose phosphate), and numerous other sugar phosphates.
UTP; ADP
Glucose transfer to a glycogen chain
2.) UDP reacts with ATP to form (?) and (?)
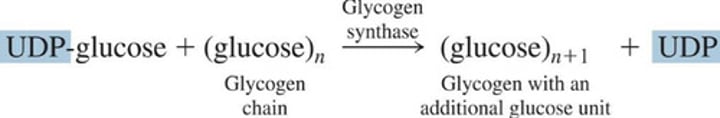
Glycogenolysis
Breakdown of glycogen to glucose
Glycogen
Glycogenolysis
Once the blood glucose levels are low, it will utilize the stored (?) to replenish it.
2
How many steps are there in Glycogenolysis?
Glycolysis
Pentose Phosphate Pathway
When ATP demand is high, the pathway continues to its end products, which enter (?).
B
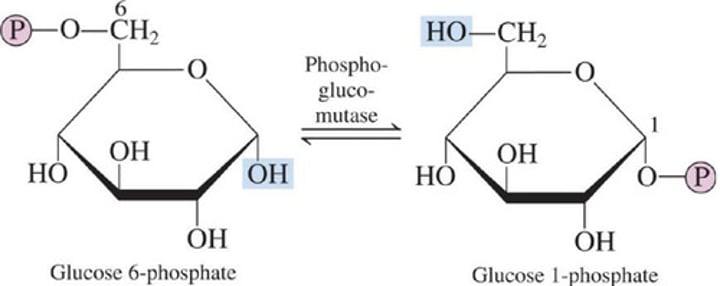
Two-step process of Glycogenolysis
Phosphoglucomutase catalyzes the isomerization process whereby the phosphate group of glucose 1-phosphate is moved to the carbon 6 position (reverse of the first step of glycogenesis)
A.) Phosphorylation of a glucose unit
B.) Glucose 1-phosphate isomerization
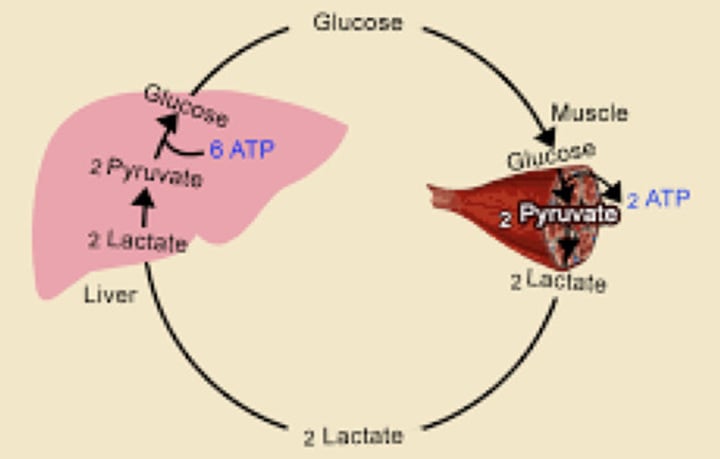
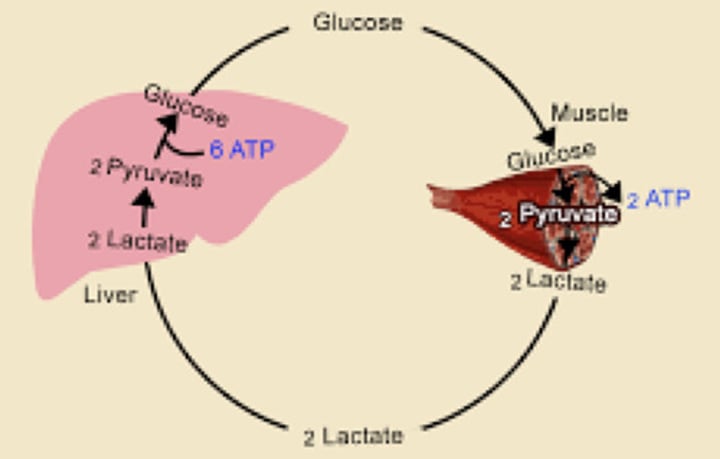
Cori Cycle
The cycle of lactate to glucose between the muscle and liver
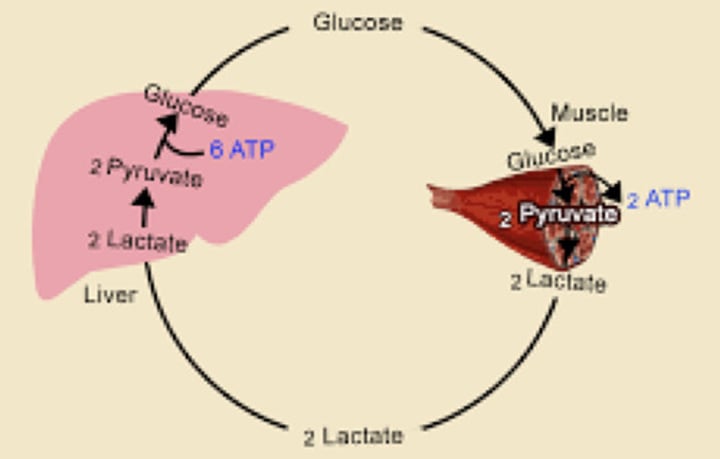
pyruvate
Cori Cycle
Gluconeogenesis uses lactate as a source of (?)
A
Two-step process of Glycogenolysis
Glycogen phosphorylase effects the removal of an end glucose unit from a glycogen molecule as glucose 1- phosphate
A.) Phosphorylation of a glucose unit
B.) Glucose 1-phosphate isomerization
Liver
Cori Cycle
Lactate is formed during strenuous exercise. It diffuses from muscle cells into the bloodstream and is transported to the (?)
2 ATP
Glucose transfer to a glycogen chain
3.) Adding one glucose unit to a glycogen chain requires the investment of (?) molecules
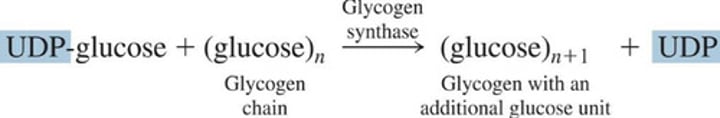
Pyruvate; Lactate; Pyruvate; Glucose
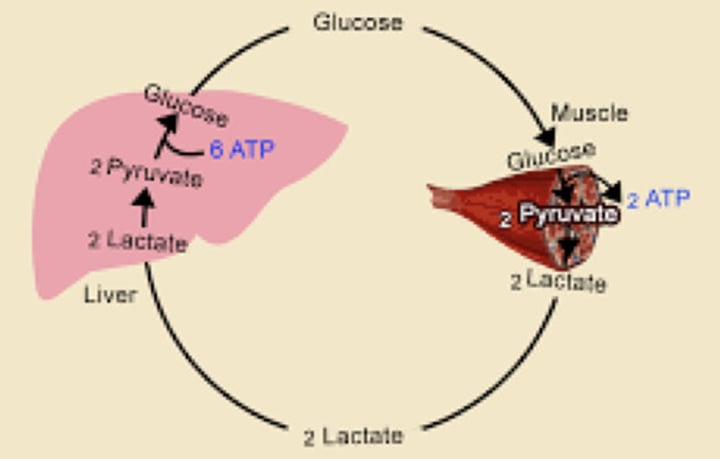
Cori Cycle
Glucose → (?) → (?) [then goes to liver] → (?) → Glucose-6-Phospate → (?) → Goes back to the cell to perform glycolysis
![<p>Cori Cycle</p><p>Glucose → (?) → (?) [then goes to liver] → (?) → Glucose-6-Phospate → (?) → Goes back to the cell to perform glycolysis</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/bc201f41-b54c-4830-adb4-037f2eb7fb0f.image/jpeg)
Lactate dehydrogenase
Cori Cycle
Which enzyme converts lactate to pyruvate in the liver?
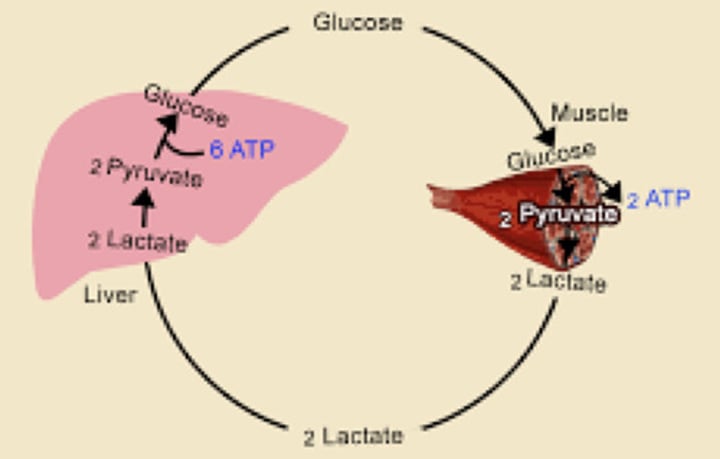
recycled
Pentose Phosphate Pathway
When NADPH demand is high, intermediates are (?) to glucose 6-phosphate (the start of the pathway), and further NADPH is produced.
It helps generate ribose 5- phosphate for nucleic acid and coenzyme production
Muscles
Cori Cycle
Pyruvate is then converted to glucose via gluconeogenesis. The glucose enters the bloodstream and is transported to the (?)
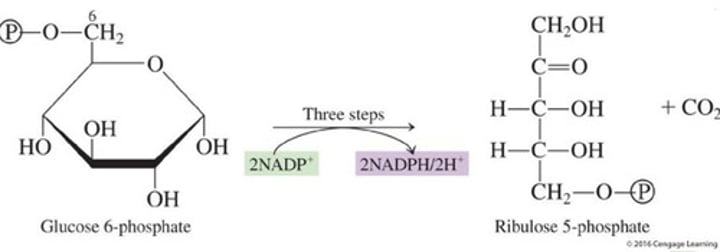
Oxidative; Non-Oxidative
What are the two stages of Pentose Phosphate Pathway?
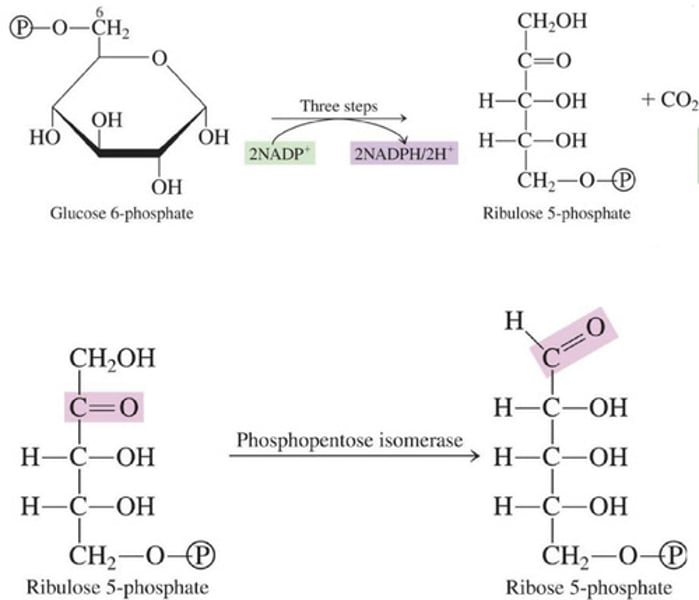
Oxidative stage
Pentose Phosphate Pathway
Identify the stage:
Involves three steps through which glucose 6-phosphate is converted to ribulose 5-phosphate and CO2
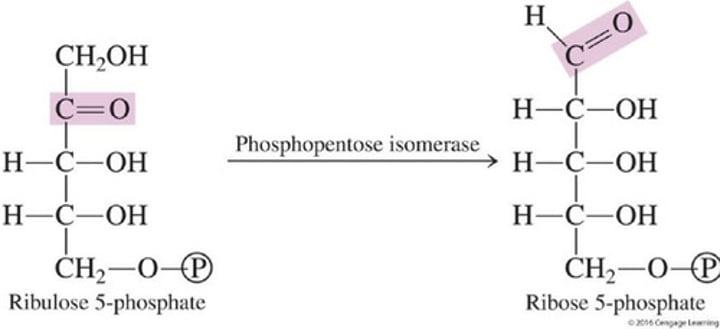
Non-Oxidative stage
Pentose Phosphate Pathway
Identify the stage:
In the first step, ribulose 5-phosphate (a ketose) is isomerized to ribose 5-phosphate (an aldose)