Chapter 5: Cartilage
1/6
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
7 Terms
What is cartilage?
chondroblasts in lacunae of growing cartilage;
lacks nerve fibers and is avascular, so it heals slowly
Aging cartilage cells lose their ability to divide
Older cartilage tends to calcify and even ossify
matrix made of chondroitin sulfate, hyaluronic acid, and collagen fibers
resists tension and compression because it is 80% water
What are the types of cartilage?
hyaline, elastic, fibrocartilage, bone, blood
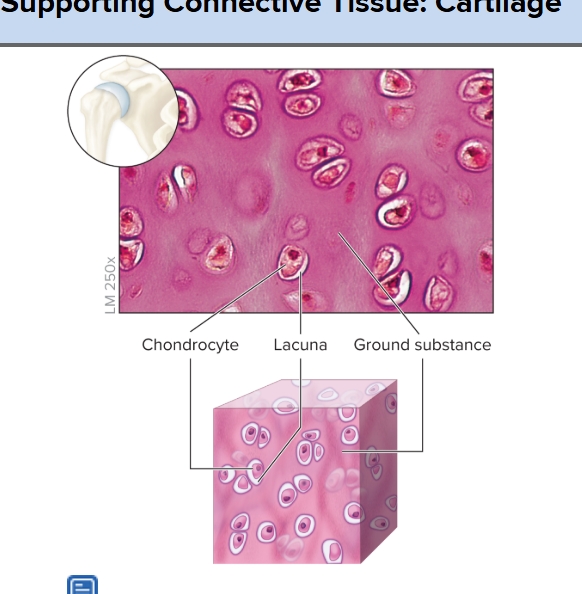
Hyaline
S: uniform collagen fibers in matrix for a glossy or glass-like appearance
F: firm support with some pliability
L: ends of long bones, tip of nose, costal cartilage (between sternum and ribs), respiratory passages, embryonic skeleton and epiphyseal plate
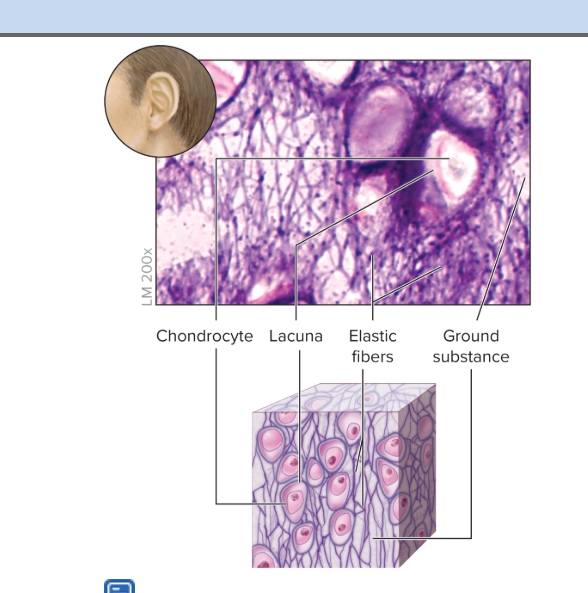
Elastic
S: matrix has more elastic fibers than hyaline cartilage
F: gives strength and exceptional stretchability
L: found in external ear (pinna) and epiglottis
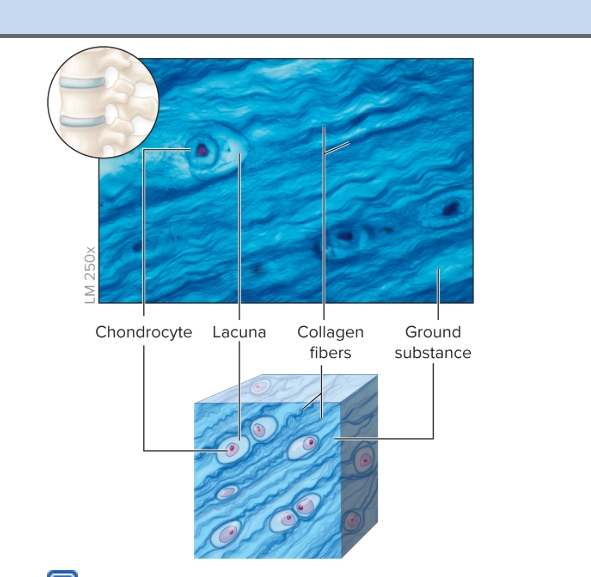
Fibrocartilage
S: chondrocytes in rows that alternate with collagen
F: resist heavy pressure and tension
L: between vertebrae, pubic bones, and forms meniscus of knee
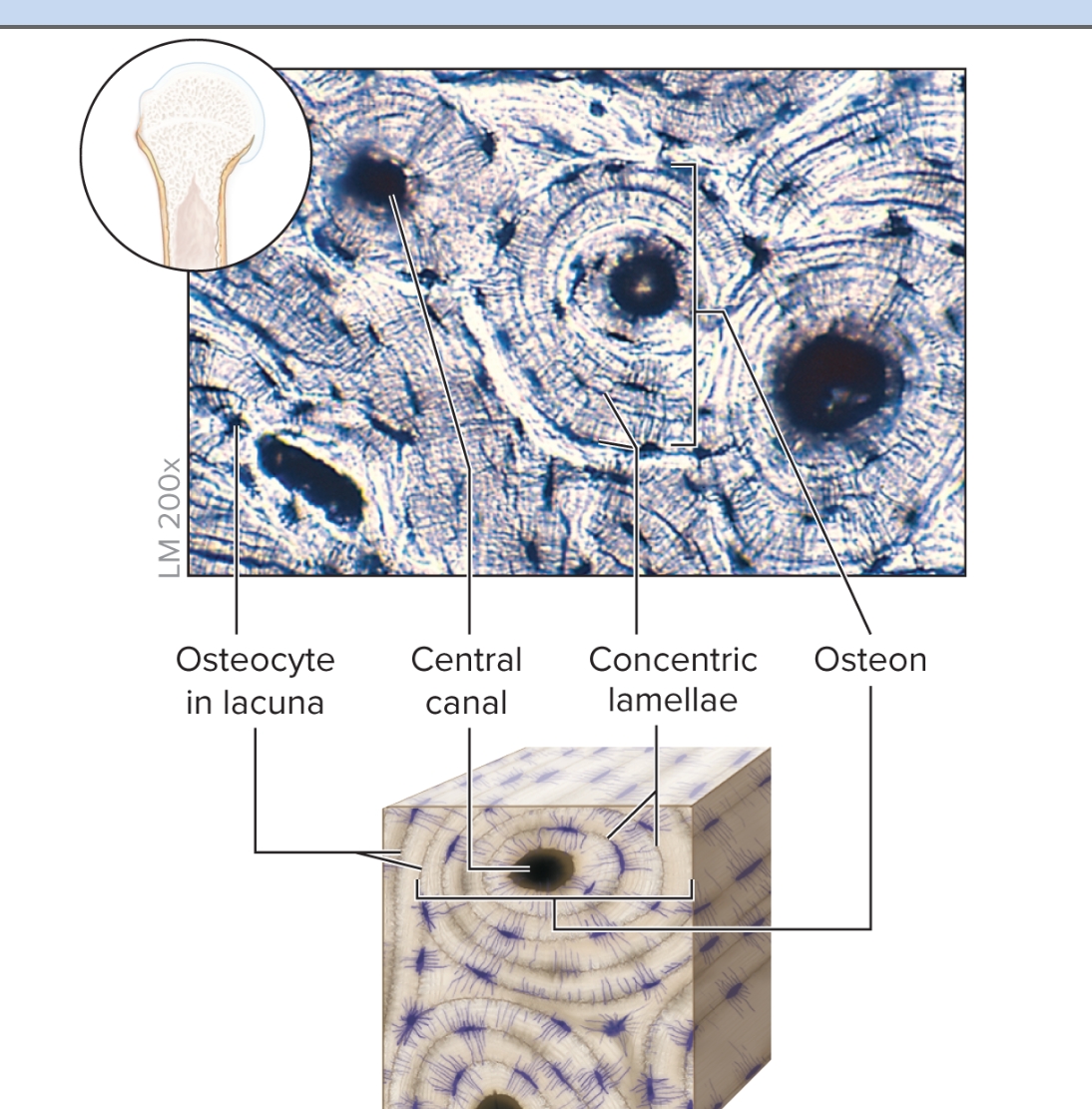
What is bone?
osteocytes imbedded in a mineral matrix, in an orderly arrangement called osteons
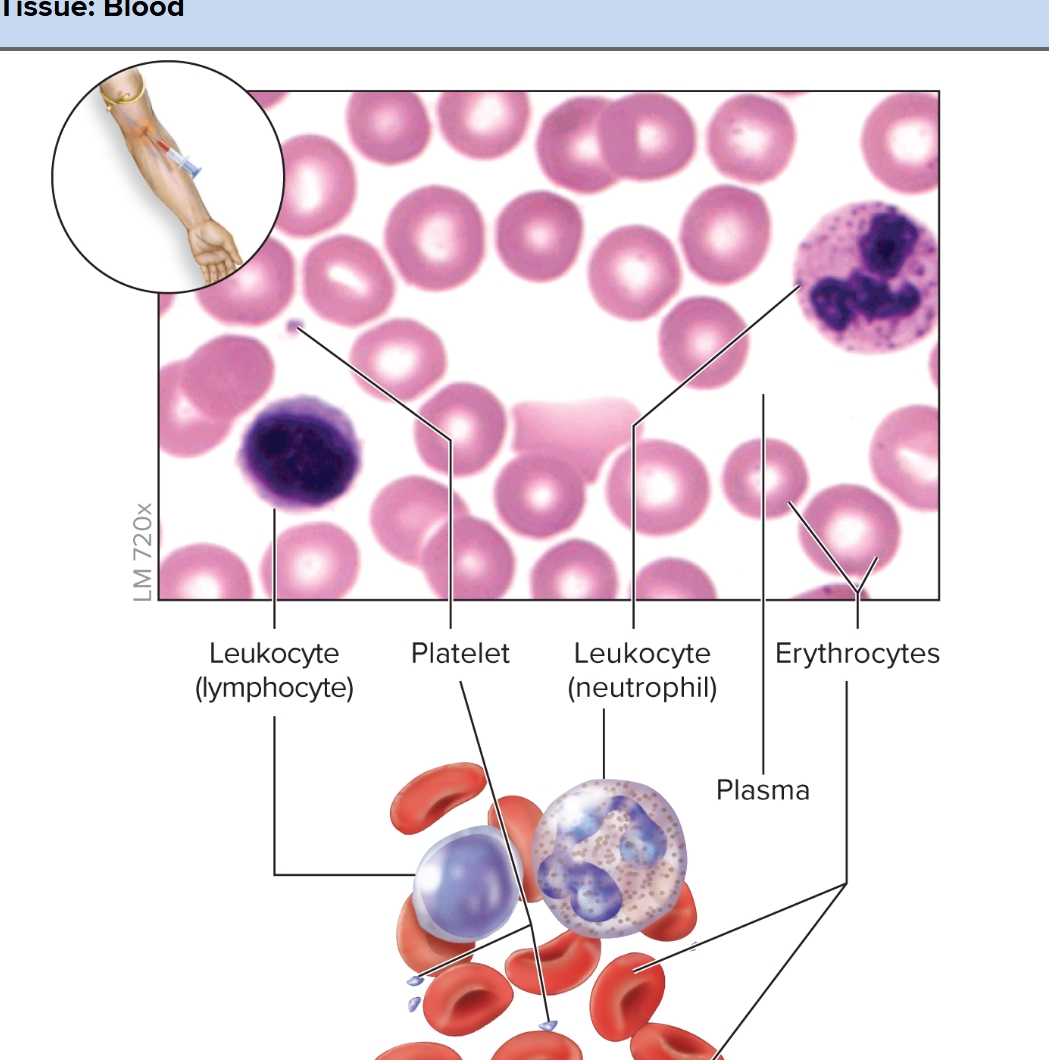
What is blood?
formed elements (cells called erythrocytes (RBC’s), leukocytes (WBC’s) and thrombocytes (platelets)) in a fluid matrix