Chapter 13 - Altering the Genetic Material: Mutation and DNA Repair
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
What is a heritable change in the genetic material?
A mutation
Mutations are essential to the ? of life; they are the source of variation for ??
Continuity of life; variation for natural selection
New mutations are more likely to be..
Harmful than beneficial
DNA repair systems ? most DNA damage before ? mutation can occur.
Reverse, Permanent mutation
A ? mutation affects only a single base pairs within the DNA
Point Mutation
A ?? involves a change where one base is replaced by another.
Ex?
Base Substitution
Ex: T was replaced by G, and corresponding A was replaced with C

A single base pair can be ? or ? and cause a point mutation.
Ex?
Added or deleted
Ex: A single base pair (A-T) has been added to the sequence.

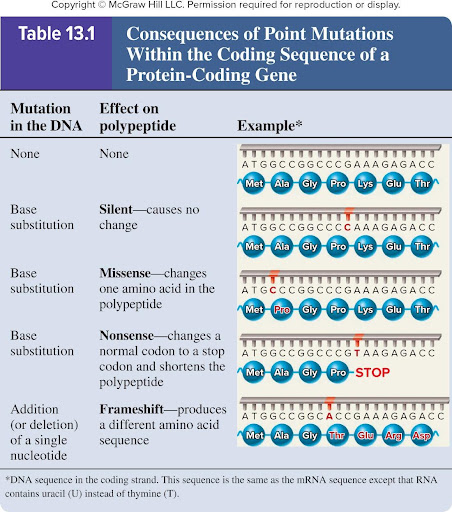
A point mutation within the coding region may be classified as a ? mutation, ? mutation, ? mutation, or ? mutation based on the impact on the ?
Silent, Missense, Nonsense, Frameshift
On the Polypeptide
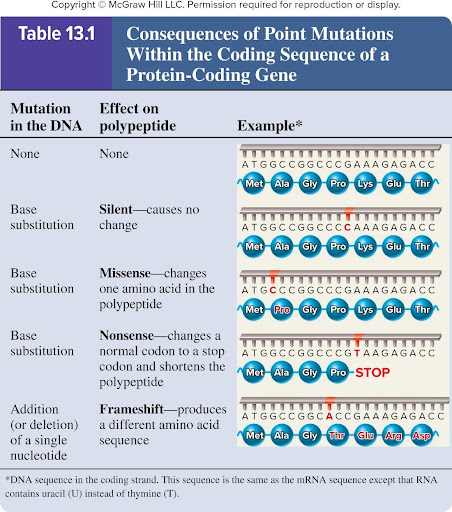
Silent mutation
Mutation in DNA?
Effect on Polypeptide?
Base substitution
Causes no change
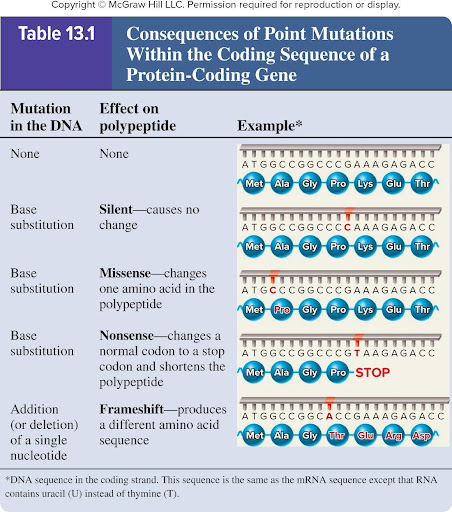
Missense mutation
Mutation in DNA?
Effect on Polypeptide?
Base substitution
Changes ONE amino acid in the polypeptide
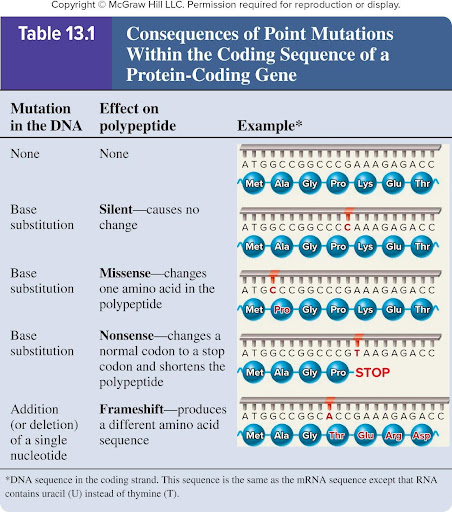
Nonsense mutation
Mutation in DNA?
Effect on Polypeptide?
Base substitution
Changes a normal codon to a stop codon and shortens the polypeptide
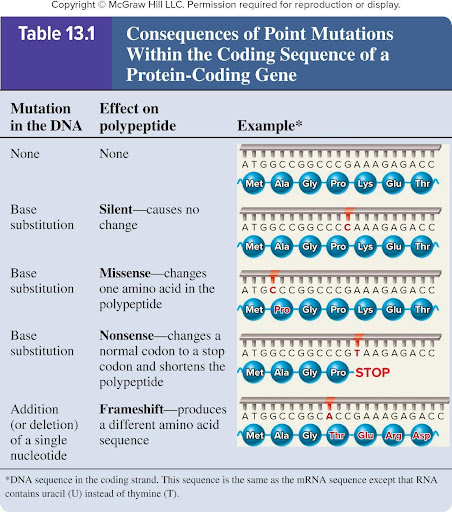
Frameshift mutation
Mutation in DNA?
Effect on Polypeptide?
Addition (or deletion) of a single nucleotide
Produces a different amino acid sequence
People are affected by ? of genetic disease
Thousands
The ? and ? of a mutation determines its severity and heritability
Time and Location
Germ-line cells give rise to…
Gametes (sperm and egg cells) and somatic cells are all other body cells.
Only mutations in ?-line cells can be passed from parents to offspring
Germ-line
The experiments of ? and ?? addressed questions about the cause of mutations
Joshua and Esther Lederberg
Joshua and Esther documented the presence of ? cells that were resistant to T1 bacteriophage.
Presence of E. coli
Data from Joshua and Esther indicated that mutations happened…
Before expose to the virus, consistent with these mutations occurring randomly
In addition to ? mutations that occur at a background rate, various ? and ? agents can ? mutations.
Spontaneous, chemical and physical, induce
Spontaneous mutations result from…
Ex?
Abnormalities in biological processes
Ex: mistake during DNA replication
Induced mutations are caused by…
Environmental agents called MUTAGENS, that alter the structure of DNA
What do Mutagens do?
Alter the structure of DNA
Common causes of mutation
Spontaneous:
Induced:
Spontaneous: Errors in DNA replication, toxic metabolic products, changes in nucleotide structure, transposons
Induced: Chemical agents, physical agents.
Chemical mutagens can cause…
Covalent modifications, act as base analogs, or cause distortion of the double helix.
Chemical Mutagens and their effects on DNA structure:
Physical Mutagens and their effects on DNA structure:
Chemical: -Nitrous acid: deaminates bases
-Nitrogen mustard: Alkylates bases
-Ethyl methanesulfonate: Alkylates bases
-5-Bromouracil: Acts as a base analogue
-2-Aminopurine: Acts as a base analogue
-Benzo[a]pyrene: Inserts between bases in the DNA double helix and causes additions or deletions
Physical: -Xrays (ionizing): cause base deletions, single nicks in DNA strands, crosslinking, and chromosomal breaks.
-UV light(nonionizing): promotes thymine dimer formation, which involves covalent bonds between adjacent thymines.
Physical agents such as ? and ? light can ? DNA structure.
X-rays, and UV lights, damage
Ionizing radiation
Ex?
Has high energy and penetrates deeply to create free radicals.
Can cause deletions or break in one or both DNA strands
Ex: X-rays
Nonionizing radiation
Ex?
Has less energy and can only penetrate the surface.
Ex: UV light
UV rays can cause ? dimers to form; if not repaired, these dimers can cause gaps or incorporation of incorrect bases.
Thymine dimers
The Ames test investigates whether…
A substance is a mutagen
All living organisms require the ability to:
Repair damage to DNA in order to minimize mutation.
Direct repair
A repair enzyme recognizes an incorrect structure in the DNA and directly restores the correct structure
Base excision and nucleotide excision repair
An abnormal base or nucleotide is recognized, and a portion of the strand containing the abnormality is removed. The complimentary DNA strand is then used as a template for synthesizing a normal DNA strand.
Mismatch repair
Similar to excision repair, except that the DNA defect is a base-pair mismatch in the DNA, not an abnormal nucleotide. The mismatch is recognized, and a strand of DNA in this region is removed. The complementary strand is used to synthesize a normal strand of DNA.
Nucleotide excision repair (NFR) is the
Most common DNA repair system; it is found in all eukaryotes and prokaryotes.