hit to lead 1
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
explain the importance of solubility
important to run in vitro assays and in vivo deliver of the drug to determine drug absorption and bioavailability, target is >100 microM
describe lipophilicity/hydrophilicity balance
balance is required to ensure sufficinet membrane permeability without excessive fat deposition or toxicty, target is 0-3
describe microsomal toxicity
this assay measures compound clearance by the liver enzymes to give an idea of how quickly will the drug be cleared in vivo
target < 30 microL/ min mg protein
describe cyp450 inhibition
cyp450 enzymes do phase 1 metabolism by introducing polar groups to increase water solubility, its inhibition can lead to drug accumulation and toxicity
target >10 microM
describe caco-2 permeability
it measures drug's ability to cross intestinal epithelial membrane, important for gut absorption
target > 1x10^-6 cm-1
describe MDCK permeability
evaulates the impact of efflux pumps like p-glycoprotein, which can pump the drug out and reduce absorption
target < 10x10^-6 cm-1
describe HepG2 hepatotoxicity screening
assess liver specific toxicity, target is 50x IC50 or EC50
describe cytotoxicity assays
check general cell toxicity in other tissues like heart, muscle, lung
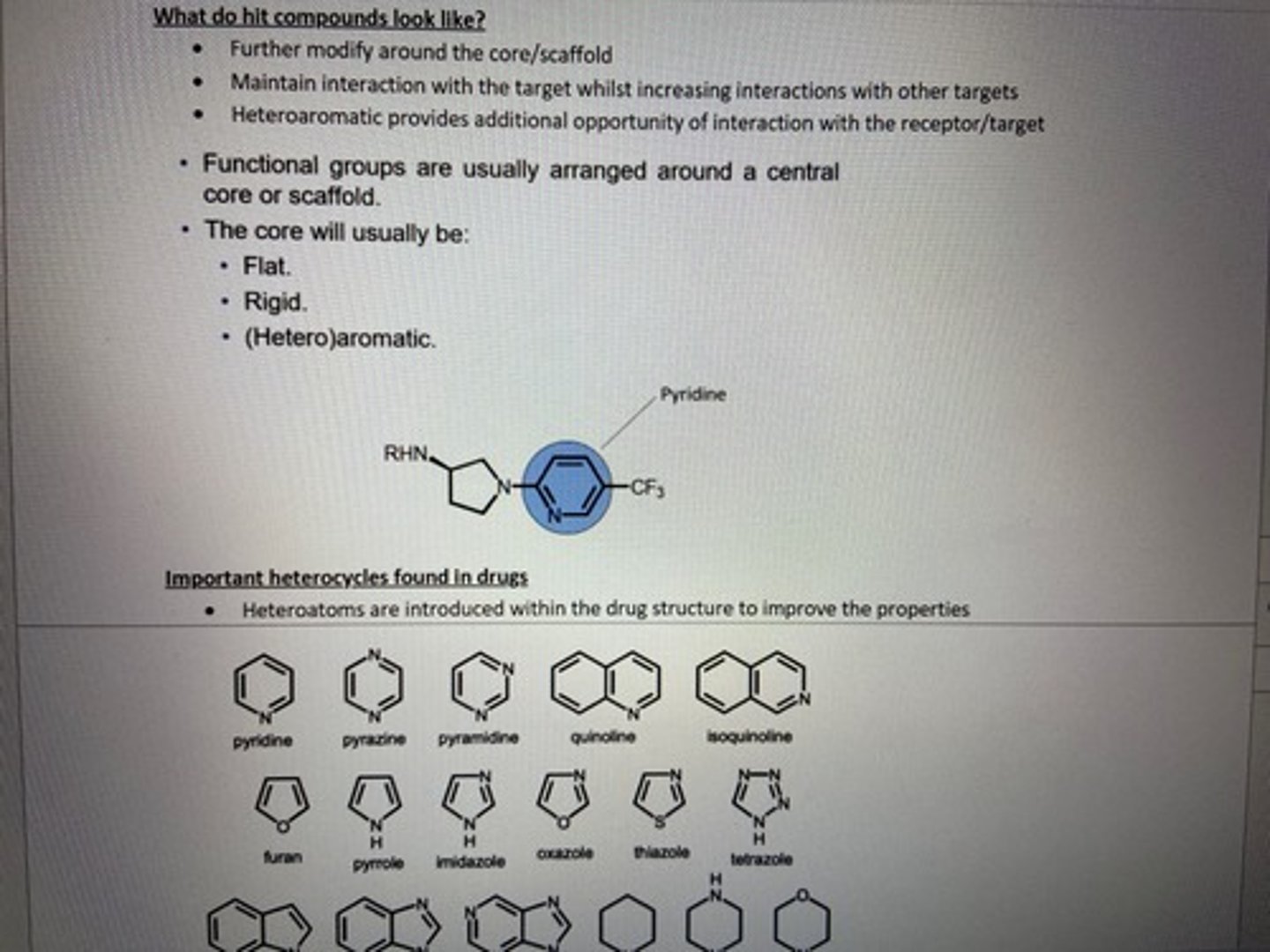
what is the importance of heterocyclic core
function groups are arranged around flat, rigid, heteroaromatic, small core that allows rapid synthesis of analogues, optimise Log P, solubility etc, template hopping to novel IP
6 membered ring- pyradine, quinolone
5 membered ring- imidazole,thiazole
fused system- purine, indole
saturated system- piperidine
what is the criteria to move hit to lead
reproducable in vitro efficacy, >100 fold selectivity for the target, favourable drug ADME properties, chemical tractability( simple synthetic pathway and commercially available starting material), patentable structure, no toxicity or mutagenicity
give an hit to lead example
hit started with a known protein kinase inhibitor as the core
lead optimization modified the core to create analogues and used x-ray crystallogrphy to identify binding sites founding Imatinib- myeloid leukemia
Describe how Caco-2 works
form a monolayer of 2 cells, in the apical side add the drug and allow the drug to cross through semi-permeable membrane, in the basal lateral side sample the drug and use LCMS or chromatogrpahy to determine the concentration between apical and basolateral, if a drug has high permeability then a high level of it has moved to basolateral side
What is bioavailability?
how mcuh of the drug actually reaches systemic circulation
describe the importance of plasma protein binding
high binding can affect dose, half-life and cause toxicity
FU (fraction unbound) >90 %
what is druggability DMPK assessment
A-absorption Caco-2 and MDCK
D- distribution plasma protein binding
M-metabolism CYP450, microsomal stability
E-excretion PK screening w urine analsys