AP Pscyh: Unit 0 Vocab and etc
1/90
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
91 Terms
Psychodyanamic Perspective
It is the hidden part of our minds. How our unconcious thoughts or feelings influence our decisions and personality. Built from experiences (child hood experiences)
-created by Sigmund Freud
Behavioral Perspective
Focuses on observable behaviors wihtout refrencing our mental proceses
role of enviroment in our behaviors (reinforcment or punishment), or how we observe other indivifuals and copy them
Sociocultural perspective
Focuses on a persons experiences and influences in thie rlife to understand how culture shapes an individual
how mores, culture, expectations influence them and their decision
Humanistic Perspective
emphasizez our potential as humans to grow as an individual and free will
-motivation to grow
Cognitive Perspective
Focuses on how we as individuals interpret, process, and remember information and how it influences people behavior
Biological Perspective
seeks to link our biological, physiological, and psychological processes
-how different brain chemicals like hormones, neurotransmitters etc and genes
-allows us to understand medications and differnt illnesses
Biosychosocial Persopective
Focuses on interconncetedness of biological, phycological, and social factors in our behavior and mental processes
-”the whole picture”
Evolutionary Perspective
how natural selection and adpatation influence behavior
-our behaviors are to survive
-ex: fear of certain things
What are the different perspectives of psychology
Psychodynamic, Socialcultural, Biological, Evolutionary, Behavioral, Cognitive, Biopsychosocial, humanistic
Psychology
the scientific study of the
mental processes - thinking parts
behavior - what we do and how we act
Confirmation Bias
The tendency to look for information that confirms existing beliefs or our point of view and dismiss what is against our perspective
Hindsight Bias
Tendency to think that one could have anticipated the outcome of the event or experiment after it has already occurred
“I knew it”
Overconfidence Bias
when people think they more than they actually do
overestimating the accuracy of ones beliefs
Emperical evidence
information aquired by observation or experimentation
Scientific Method
a systematic approach to research where a problem is idntified, relevant data is fathered, a hypothesis is formed, and it is tested
Hypothesis
a testable prediction
Falsifiable
A hypothesis must be worded so it can be wrong or right
Why is it important to consider cogntivie biases
in some situations when the biases were present, information was missapplied to differnt groups
ex: using it for racism
What is a falsifiable hypothesis and why is it nessecary?
it means that it can be tested and potentially be proven false and not just and only right
this make sures that results are true
Peer Review
a process in which research articles and studies are evaluated by other experts before being published
Replication
the action of repeating a study, using the same methods to see of the original results can be consistlety reproducued
Reliability
the consistiency of the research study or a measuring test
Validity
the extnt or how good the test measures or predicts what its supposed to
accurately measures what it intends to measure
ex: a valid driving test should include a practical driving component and not just a theoretical test of the rules of driving
American Psychological Association (APA)
a professional organiziation representing the pscyhologist in the United States.
Research Design
the overall plan that outlines how the research study will be conducted and will adresss the research question
ex: experimental, corrolational, descriptive
Methodology
specific techniques, systematic procdeures and techniques to conduct research
ex: Methodology includes decisions about sampling procedures, data collection methods (e.g., surveys, interviews, observations), data analysis techniques (e.g., statistical tests, qualitative coding), and quality assurance measures.
Quantitative Data
information about quantities that can be measured and written down with numbers and looks for percise relationship and predictions
Qualititative Data
descriptive information which comes from interviews, focus groups, photographs and other artistic depictions, and observations of behavior
Likert Scales
a way to get quantitative data
a psychometric scale used in questionares and surverys
ex: Strongly agree, agree ….
Structured Interviews
-research method in which predtermined questions asked in the same order
-this allows for consistient data collection and compares partcipants
-relaible results
Qualitative data
Survey Technique
a research technique that involves the collection of information from a sample of indivudials thruogh their responses to questions
-tields both qualitiative and quantitative data
Wording effect
the effect that question phrasing and order have on survery data
on how people respond - can lead to biased responses if worded wrong
Social desirability bias
a tendency to give socially approved answers to questions about oneself
influenced by social norms rather than putting the right answers
Naturalistic Observation
observing subject in their natural enciroment without manipulation or control by the researcher
Not the best because it’s only for a small time not prolonged
Not cause effect
Case Study
in depth study of a single person, group, event, community, or phenomenon
cannot be generalized
Not cause and effect
Correlational Research
a non experimental resaerch method,
studies the relationship between 2 variables with the help of statistical analysis
“correlelation is not causation”
Third Variable Problem
A form of confounding variable that leads to a mistaken relationship between 2 variables
Usually in correlational studies
ex: more sports → worse academic scores -wrong bc its probably because of less study time
Scatterplot
a graphical representation of the values for a set of data
Coerrelation Coefficient
ranges [-1,1'], and represented by “r”
the closer it is to -1 or 1, the stronger it is
(-) means negative correlation while (+) means positive correlation
the stronger it is, the better it can be used to predict certain things
Positive correlation
a relationship in which both variables move in the same direction
up and up
down and down
Negative Correlation
a relationship between 2 variables that move the opposiute directions
one goes up another goes down
Experimental Method
a method of research where the researcher controls the settings and manipulates the indpendent variables and studie show the dependent variable is affected
“cause and effect:
Independent Variable
the variable that is being changed or manipulated by the researcher
the factor that might or might not cause change to the other variable
The cause
Dependent Variable
the variable being measures or observed in an experiment
influenced or not influenced by the. independent variable
The effect
Confounding variables
a variable that influences both the dependent and indepdnet bariable causing a spruious association - affects the results and is not accounted for
Operational Defininitions
specifies how a researcher will manipulate (indpendent variable) or measure the dependent variable
Allows others to replicate the study to test the reliability of the results
ex: regular exercise is defined as 150 min per week
or happiness Is measured with this test
Experimental group
the group that is exposed to the indepdent variable and are testedc
Control Group
is the group that is not exposed to the indepdnet variable
used as a baseline
Random Assignment
assignining participants to experimental and control groups by chance, thus minimizing preexisting differnces between those assigned to the differnt groups
Experimenter Bias
the researchers influence results to potray a certain outcome or how results are conducted
-way to reduce this is with double blind studies so the researcher doesnt know what group is experimental or control and will intrerpet resutls authentically
Placebo Effect
phenomoneon where individuals experience change in condition beacuse of thier beleifs rather than physiological mechanisms
Placebo Conditions
aa condition in which treatment is not administered by the subject beleives that it was
-intended to test if a medicine is truly wokring or if its just the beleif
-the participants think they got it
-usually given to the control group
Single Blind Study
a resaerch design where participants are unaware of wether they belong to the experimental or the control group but the reserchers do know
to reduce the placebo effect
-participants don’t know what they got
Double Blind Study
both the participants the researchers conducting the study are unaware who belongs in the experimental or control group
Sample
a subset of indiviuduals from a larger population(group studied), used to conduct research
Represenative Sample
a sample that acfuractly reflects the characteristics of a population as a whole
-includes many races, ages, gender, backgrounds etc
a good representative sample study can be generalized
Random Sample
everyone from a population has an equal chance of getting into the study
minimizes the researcher bias
increases generalizibility
Sample bias
a bias that occurs when some people are more likley to be in the study compared to another group
may not be repredentative
Generalizability
the extent to which the study’s results can be applied to a larger population
this depdents on how good the representation of the sample is
Statistics
a branch of mathematics dealing with the collection, analysis, interpretation, and presentation of masses of numerical data
Descriptive Statistics
refer to numerical measures used to sumarize and describe the characteristics of a data set
central tendency: mean meadian mode
Inferential Statistics
involes using data from a sample to make inferences or predictions about a larger population - generalization
Test if data is significantly significant
Measures of central tendency
tools used to describe the central or average value of a set of data.
a single value that is represneative of an entire distrubition
provide single value that represents the center or typical value of a distrobultion
Mean
the average of a set of numerical values
Median
the middle value of the data set
arange the numbers in order and find the middle
Mode
the value that appears the most in a data set
Range
represents the difference between the highest and lowest values in a data set
subtract the smallest from the largest number in the data set
Outliers
numbers that are far off in the data set and may skew our mean which is why we might want to use the median more sometimes
Normal Curve or Bell curve
the majority of data follows this bell curve
the majority of the data are concentrated in the middle
fewer values are on the side
Regression to the mean
the phenomenon that if there is an extrreme value tend to get closer to the average when measures agian
-extreme scores may be from temporary factors
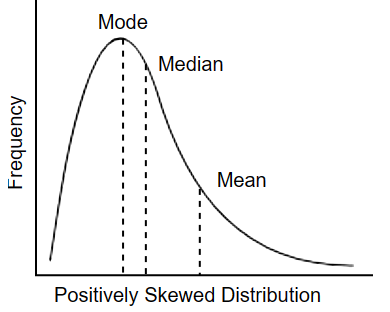
Positive Skew
the majority of data is on the left side but there are some extremly high values, causing the mean to go towards the right, but the mode is on the left
sugest outliers or unusually high values
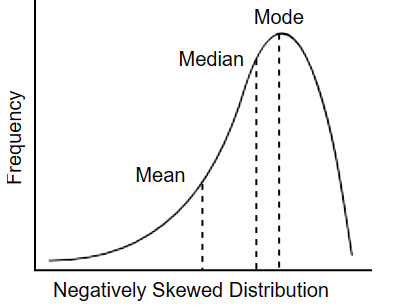
negative skew
this is when the majority of data falls onto the higher values or on the right
but there are some extreme low values outliers, making the mean lower
the mode is on the right
Standard Deviation
a measure od that amount of data variation or dispersion in a set of values in relation to the mean,
usually a bell curve 64 percent are middle …
symbolised by the sigma symbol
if the deviation is small, then most scores are close to the average
but when the deviation is large, then it means that the scores are more spread out
standard decision is usually 68% for normal distribution
Percentile Rank
percentange of people lower or the same than the given score
50th percentile: 50 are taller,50 is shorter
Bimodal Distribution
A distribition that shows 2 differnt peaks or modes
Statistical Signifiance
the likleyhood that observed results in a resarch study are not due to chance for interdental statistics
P value,
if it is greater than 5 perent, then occurred by chance
if less than 5 percent, then it didn’t occur by chance - rejects the null hypothesis- accepts the alternate hypothesis
If it was 90 percent- data is probably by chance and accept null hypothesis
Effect Sizes
Inferential statistic method
a large effect size indicates that the indepdnet vartiable has a big impact on the dependent variable
If there is a small effect size then the independent variable has a little impact on the dependent variable
Meta Analysis
A statistican analysis that combines the results of multiple scientific studies and make a conclusion
Insitutional Review Boards (IRB)
are commitiees responsible for reviewing and apporving resaerhc proposals to ensure that they meet ethical standards and protect the rights and welfare of resaerch participants
Informed Consent
permission granted with the knowledge of potential consequences given from the patient. Agreement to participiate in the research stidy
Informed Assent
the parents or a guardian will give legal consent to a child or someone who cant decide by themselves
Confidentiality
the requirement of the researcher to handle sensitive data and information obtained during the study and keep it with discretion
Deception
the researchers may not mislead the participants of the true purpore or nature of the study, procedures or expected outcomes
unless its absoltuley and ethically nessecary for the study
Confederates
individuals who are part of the resaerch study but are collaborating with the researchers and know about the study
debreifing
this is required to do by the researcher and tell the participants the true nature of the study, the data, purpose, and deceptions used
Descriptive method
describe behaviors
Methodology includes case studies, surveys, observations
Theory
Supported by data from completed research and explains a question though or phenomenon
Quasi experiment
Does not include random assignment
Not for cause and effect
x score
Negative is below mean
Positive is grater than mean
Defensive claim
Claim is specific and takes a stance, statement presented as truth
Must have emperical evidence to support it that is reliable