Sociology Final Exam Review
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
deviance
nonconformity to a set of norms that a significant number of people in a community or society accept
What is regarded as deviant is as variable as the norms and values that distinguish different cultures and subcultures from one another.

crime
The result of any action that contravenes the laws established by a political authority
anomie
to refer to a situation in which social norms lose their hold over individual behavior
Created by Durkheim

norms
principles or rules that people are expected to observe; they represent the "dos and don'ts" of society

laws
Rules of behavior established by a political authority and backed by state power
formal positive sanctions
the offering of rewards for conformity applied by a specific group or agency to ensure that a particular set of norms is followed

formal negative sanctions
punishment for behavior that does not conform applied by a specific group or agency to ensure that a particular set of norms is followed

informal positive sanctions
spontaneous reactions to nonconformity with the offering of rewards for conformity
Informal negative sanctions
spontaneous reactions to nonconformity with punishment for behavior that does not conform

deviant subcultures
A subculture whose members hold values that differ substantially from those of the majority

mass incarceration
a situation where vastly greater numbers of people are held in prisons than in earlier periods of history or in comparison to similar countries (especially African American males)
ethnic breakdown of America's prison population
African Americans make up around 33 percent of the current prison population (make up 12% of US)
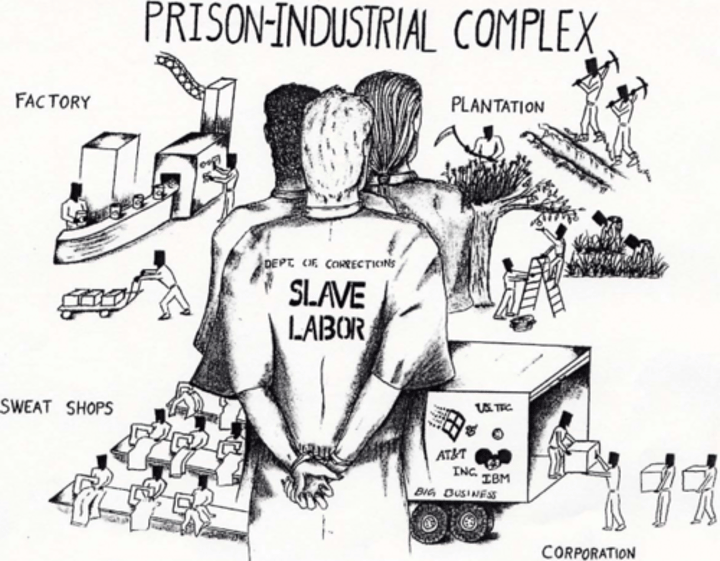
prison-industrial complex
the corporations and agencies with an economic stake in building and supplying correctional facilities and in providing services (Large numbers of people—including bureaucrats, politicians, and prison employees—have vested interests in the existence and further expansion of the prison system)
5 sociocultural theories of crime
1. functionalist theory 2. labeling theory 3. conflict theory 4. control theory 5. broken windows theory
1. functionalist theory (Emile Durkheim & Robert Merton)
Deviance serves the function of creating solidarity among the larger society
2. Labeling theory
An approach to the study of deviance that suggests that people become "deviant" because certain labels are attached to their behavior by political authorities and others
3. conflict theory
The argument that deviance is deliberately chosen and often political in nature due to the inequities of the capitalist system
4. control theory (Travis Hirschi)
The theory that views crime as the outcome of an imbalance between impulses toward criminal activity and controls that deter it.
broken windows theory (Phillip Zimbardo)
Wilson and Kelling (arose from Phillip Zimbardo's study) argued that any sign of social disorder in a community, even the appearance of a broken window, encourages more serious crime.
One unrepaired broken window is a sign that no one cares, so breaking more windows—that is, committing more serious crimes—is a rational response by criminals to this situation of social disorder. Thus, minor acts of deviance lead to a spiral of crime and social decay
social stratification
inequalities among individuals and groups that are determined not so much by individual personality or small-scale social situations but, more broadly, by attributes such as gender, age, race, ethnicity, or religious affiliation
slavery
an extreme form of stratification and inequality in which some individuals are literally owned by others as property
caste
A social system in which one's social status is held for life (associated with the cultures of the Indian subcontinent and the Hindu belief in rebirth. all individuals must remain at the social level of their birth throughout their life. individuals who fail to abide by the rituals and duties of their caste will be reborn in an inferior position in their next life. Caste systems structure the type of contact that can occur between members of different ranks)
class
a large-scale grouping of people who share common economic resources that strongly influence the type of lifestyle they are able to lead
life chances
a person's opportunities for achieving economic prosperity, coined by Max Weber

income
Money received from paid wages and salaries or earned from investments
wealth
Money and material possessions held by an individual or group
cultural capital (Pierre Bourdieu)
Noneconomic or cultural resources that parents pass down to their children, such as language or knowledge.
social mobility
Movement of individuals or groups between different social positions

intragenerational mobility
Movement up or down a social stratification hierarchy within the course of a personal career

intergenerational mobility
Movement up or down a social stratification hierarchy from one generation to another

structural mobility
Mobility resulting from changes in the number and kinds of jobs available in a society
downward mobility
an exchange of positions such that more talented people in each generation move up the economic hierarchy, while the less talented move down
absolute poverty
Not meeting the minimal requirements necessary to sustain a healthy existence
relative poverty
Poverty defined according to the living standards of the majority in any given society
poverty line
An official government measure to define those living in poverty in the United States
working poor
People who work but whose earnings are not enough to lift them above the poverty line
feminization of poverty
An increase in the proportion of the poor who are female
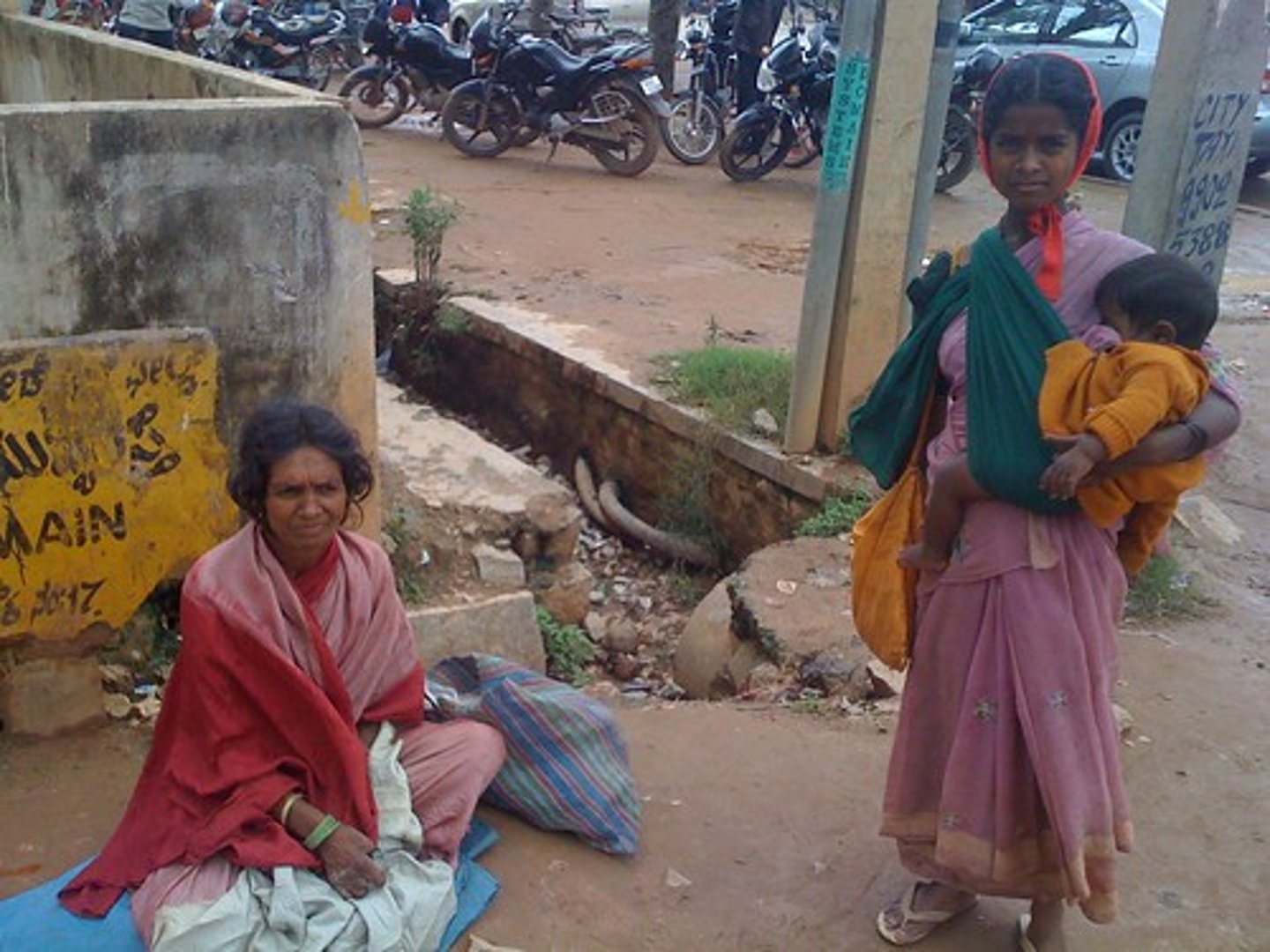

children in poverty
Given the high rates of poverty among families headed by single women, it follows that children are the principal victims of poverty in the United States; The economic well-being of racial minority children and children of single mothers is even more dire
homelessness
People who have no place to sleep and either stay in free shelters or sleep in public places not meant for habitation
relative depravation
Deprivation a person feels by comparing himself with a group

net worth
all the assets one owns (for example, cash, savings and checking accounts, investments in stocks and bonds, and real estate properties) minus one's debts

types of debt
home mortgages, credit card balances, loans that need to be repaid ?
income distribution
The way the national income is divided into "shares" ranging from the poor to the rich
how does class differ from caste? describe the main 3 differences
1)Class is fluid. (you can move up and down)
2)Class is partially achieved. (based on achievement, you can move up and down)
3)Class is economically based. (divided into social classes)
what are the 3 key predictors of social class? aka Pierre Bourdieu
1)Economic cultural
2) Social capital
3)Cultural capital
what are the 5 main classes in the US? describe social characteristics of each (% of total population, educational attainment, race/ethnicity, income level, voting behavior, etc)
upper class ("A social class broadly composed of the more affluent members of society, especially those who have inherited wealth, own businesses, or hold large numbers of stocks/shares),
middle class (social class composed broadly of those working in white-collar and lower managerial occupations),
working class (broadly composed of people working in blue-collar, or manual, occupations), lower class (those who work part-time or not at all and whose household income is typically lower than $31,000 a year),
poor
what is the current federal minimum wage?
$7.25 per hour
anthropocene
term used to denote the current geological epoch, in which many geologically significant conditions and processes are profoundly altered by human activities

environmental ecology
The scientific study of the distribution and abundance of life and the interactions between organisms and their natural environment
global warming
An increase in the average temperature of the earth's atmosphere (especially a sustained increase that causes climatic changes)
sustainable development
Development that meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs

negative formal sanction example
getting a ticket for speeding
negative informal sanction example
getting yelled at for talking in class
positive formal sanction example
being on time for class or work and BEING REWARDED OR THANKED
a college diploma
positive informal sanction example
praising a women for wearing a dress or makeup
What percentage of the social class is the super rich?
1%
What percentage of the social class is the upper class?
20%
What percentage of the social class is the middle class?
40%
What percentage of social class is the working class and lower class?
30%
What are two examples of non-economic indicators of one's social class?
1)Education
2)Lifestyle
What are the root causes of crime according to control theory?
Crime results from a lack of social and physical control that deters it.
In which social class are you most likely to find mid-level corporate managers and high income professionals?
Upper middle class
Putting locks on mailboxes is an example of
target hardening