Cystic Fibrosis and Bronchiectasis
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
Cystic Fibrosis
an autosomal recessive genetic disorder affecting the respiratory, digestive, and reproductive systems
CFTR, common, Caucasians, genetic, chloride, mucus, damage
Introduction to Cystic Fibrosis
-Cause: mutation in the ____ gene
-Incidence: most ________ life-threatening genetic disease in Caucasians
-Carrier frequency: 1 in 25 __________ carry a CFTR mutation
-Risk factors: family history, _______ predisposition
-Primary Issue: dysfunctional _______ transport → thick _____ production → multi-organ _________
chloride, epithelial, mucus, infections, pancreatic, infertility
Cystic Fibrosis Pathophysiology
-CFTR gene mutation leads to: defective _______ and water transport across _________ membranes. It also leads to thick, sticky ______ accumulation in lungs, pancreas, and other organs
-Affected systems include: respiratory, gastrointestinal, and reproductive.
-Respiratory: mucus obstruction, chronic _________, and bronchiectasis
-Gastrointestinal: ___________ insufficiency, malabsorption, meconium ileus
-Reproductive: ________ in males due to congenital bilateral absence of the vas deferens
cough, infections, polyps, vitamin, liver, imbalances, thrive
Cystic Fibrosis Clinical Presentation
-Pulmonary Symptoms: chronic ______ with thick mucus, recurrent respiratory ___________, digital clubbing, nasal _______, and sinusitis
-GI Symptoms: failure to thrive, steatorrhea, _______ deficiencies, pancreatitis, _____ disease
-Other: electrolyte __________ and infertility in males
-Neonates: meconium ileus, failure to _______
trypsinogen, chloride, pilocarpine, CFTR, obstructive, FEV1, lipase
Cystic Fibrosis Diagnosis
-Newborn screening: immunoreactive ____________ (IRT) test
-Sweat chloride test: gold standard (>60 mmol/L _______ on two occasions after __________ administration confirms diagnosis)
-Genetic testing: ____ mutation analysis
-Pulmonary function tests (PFTs): shows ____________ pattern with reduced ____, irreversible
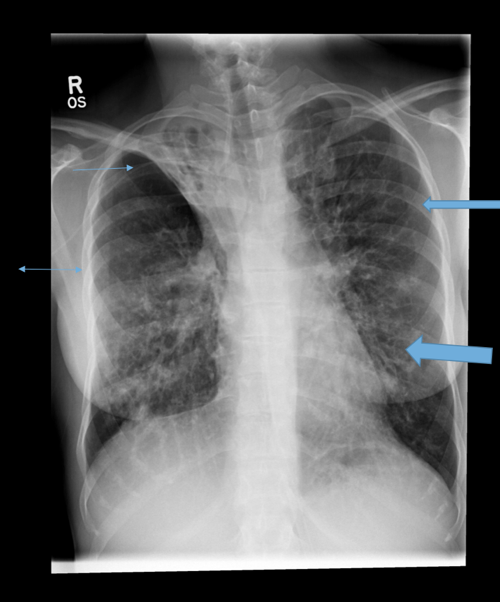
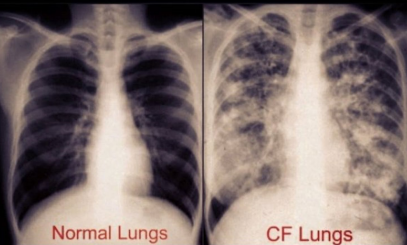
-CXR: bronchiectasis, hyperinflation of lungs
-Other labs: hyponatremia, metabolic alkalosis, elevated _______ (pancreatitis)
physiotherapy, saline, mucolytic, chronic, tobramycin, infections, CFTR, transplant
Cystic Fibrosis Treatment and Management: Pulmonary
-Airway clearance therapies: chest _______________, oscillatory devices, hypertonic ________, dornase alfa (_________), and bronchodilators
-Antibiotic therapy: _______ suppressive therapy (Azithromycin), inhaled ___________ for Pseudomonas colonization, and antibiotics for acute pulmonary ____________
-____ modulators: Ivacaftor, lumacaftor/ivacaftor, tezacaftor, elexacaftor
-Lung and/or liver _______: considered in end-stage disease
pancreatic, vitamin, diabetes
Cystic Fibrosis Treatment and Management: Nutrition and GI
-___________ enzyme replacement therapy (PERT)
-Fat-soluble ________ supplementation (A, D, E, K)
-High-calorie, high-protein diet
-Treatment of CF-related __________ (CFRD) if present
failure, infections, obstruction, improving
Cystic Fibrosis Complications
-Respiratory complications: chronic respiratory _________, bronchiectasis, and increased risk of respiratory ___________.
-Gastrointestinal complications: liver disease, intestinal _____________
-Prognosis: median survival ___________ with advanced therapies. Early diagnosis and multidisciplinary care improve outcomes
genetic, sweat, CFTR, essential
Cystic Fibrosis Pearls
-Cystic fibrosis is a _________ disorder affecting multiple organ systems
-______ chloride test is the gold standard for diagnosis
-Pulmonary and gastrointestinal management are key to improving outcomes
-____ modulators have revolutionized treatment
-Multidisciplinary care is ___________ for long-term survival
permanent, bronchi, mucus, damage
Intro to Bronchiectasis
-Bronchiectasis is a chronic lung disease characterized by __________ and irreversible dilation of ______ due to recurrent infections and inflammation
-Key features: ______ accumulation, recurrent infections, and airway ______
imaging, fibrosis, ciliary, autoimmune, inflammation
Bronchiectasis Epidemiology
-Prevalence: increasing due to better __________ and recognition
-Risk Factors: cystic _________ (CF-related vs non-CF bronchiectasis), recurrent respiratory infections, primary _________ dyskinesia, immune deficiencies, _____________ diseases, and aspiration or chronic pulmonary _____________
injury, mucus, damage, dilation
Bronchiectasis Pathophysiology
Cycle of Infection & Inflammation:
Airway ________ due to infection or inflammation
Mucociliary clearance dysfunction → ______ accumulation
Recurrent infections lead to further bronchial _______
Airway ________ and remodeling
productive, purulent, infections, damage, clubbing, wheezing
Bronchiectasis Clinical Presentation
-Chronic ____________ cough with large amounts of _________ sputum (thick, dark brown)
-Recurrent respiratory __________ (Pseudomonas, Haemophilus, Staph Aureus)
-Dyspnea, wheezing, and fatigue
-Hemoptysis (due to airway ________, bronchial artery erosion)
-___________ of fingers (in advanced cases)
-Physical Exam: + crackles, _____________, and rhonchi
abnormal, opacities, HRCT, diagnosis, dilation, obstructive, bacterial, underlying
Bronchiectasis Diagnosis
-CXR: _________, but non-specific with linear atelectasis, tram-track appearance, __________, and increased bronchial markings
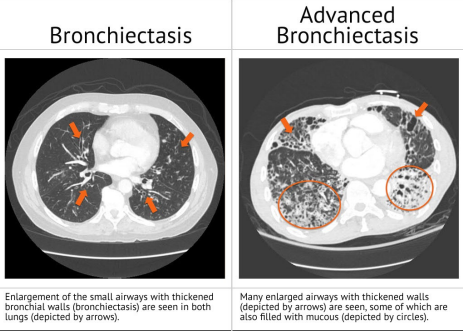
-High-resolution CT (____) scan: gold standard for __________. Shows bronchial ________, thickened airway walls, and lack of tapering
-PFTs: often show __________ pattern, decreased FEV1/ratio/FVC
-Sputum cultures: identify ____________ colonization (e.g., Pseudomonas)
-Bronchoscopy: used in select cases to rule out obstruction or malignancy
-Workup for __________ conditions: immunoglobulin levels, CFTR genetic testing, and ciliary function testing
clearance, oscillatory, saline
Bronchiectasis Treatment: Airway ___________ Therapy
-Chest physiotherapy (percussion, postural drainage)
-High-frequency ___________ devices (e.g., vest therapy)
-Hypertonic ________ nebulization (mucolytics)
-Dornase alfa (for CF-related bronchiectasis)
empiric, Fluoroquinolone, aminoglycosides
Bronchiectasis Treatment: Antibiotic Therapy
-Acute exacerbations: ________ coverage based on sputum culture, no culture results start with _______________
-Chronic suppressive therapy: inhaled _______________ (tobramycin for Pseudomonas)
SABAs, corticosteroids
Bronchiectasis Treatment: Bronchodilators and Anti-Inflammatory Therapy
-_______ or LABAs
-Inhaled ______________ (for airway inflammation)
surgical, transplant, immunoglobulin, hemoptysis
Bronchiectasis Treatment: Surgical and Advanced Therapies
-__________ resection: considered in localized disease unresponsive to medical therapy
-Lung __________: for severe, end-stage disease
-Treatment of underlying conditions: _________________ replacement for immune deficiency
-Bronchial artery embolization for ___________
exacerbations, hemoptysis, infections
Bronchiectasis Complications
-Frequent _____________ and respiratory decline
-Massive __________ (due to bronchial artery hypertrophy)
-Pulmonary hypertension and right heart failure (cor pulmonale)
-Secondary ___________ (e.g., Nontuberculous Mycobacteria- NTM)
permanent, HRCT, clearance, underlying
Bronchiectasis Pearls
-Bronchiectasis is a chronic lung disease with _____________ airway dilation
-____ is the gold standard for diagnosis
-Treatment focuses on airway __________, infection control, and inflammation management
-Recognizing and treating __________ causes is crucial
infections, fibrosis, obstruction
Three Hallmark Symptoms of Bronchiectasis
Recurrent respiratory ________
Peribronchial ________
Airway ___________
Tram-Track
sign on chest imaging indicative of bronchiectasis, characterized by parallel lines representing thickened bronchial walls.