Topic 1
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
Anthropocentrism
is a worldview that places humans at the centre of our value system (human interests and well-being are the primary focus). Nature is often seen as a resource for humans and is valued primarily for its usefulness, reflecting a utilitarian approach. views humankind as being the central, most important element of existence, and it splits into a wide variety of views

Biocapacity
The ability of a given biologically productive area to generate an ongoing supply of renewable resources and to absorb its wastes.
Biosphere
The part of the Earth inhabited by organisms that extends from the upper parts of the atmosphere to deep within the Earth's crust.
Citizen science
Science that uses the involvement of the public in scientific research to generate data.

Contexts
This describes when ESS "understandings" are applied in real life situations.

Decoupling
The disconnection of economic growth and environmental impact so that one no longer depends on the other.

Ecocentrism
A viewpoint that puts ecology and nature as central to humanity, seeing the natural world as having pre-eminent importance and intrinsic value

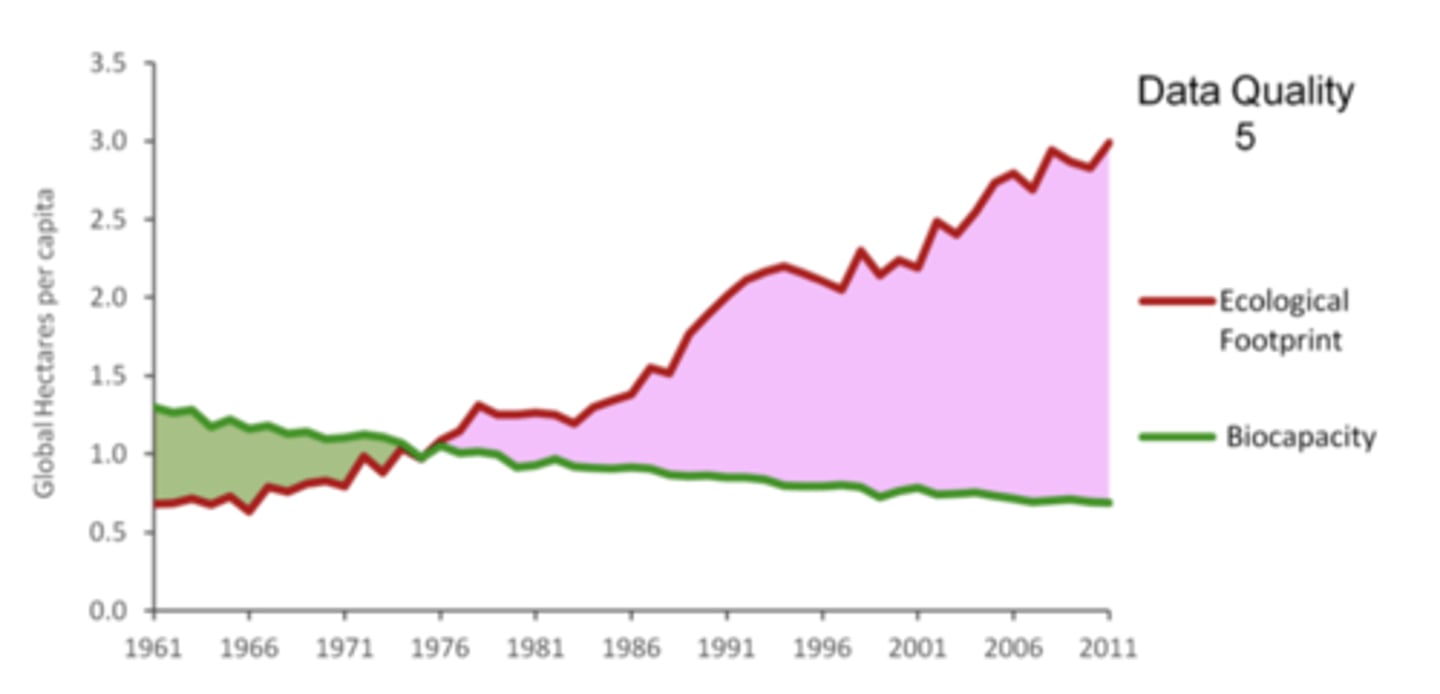
Ecological footprint
The area of land and water required to support a defined human population at a given standard of living; the measure takes account of the area required to provide all the resources needed by the population and the disposal of waste materials.

Emergent properties
Characteristics that are shown by a whole system but not by individual components of the system.
Environmental education
An education that teaches children and adults how to learn about and investigate their environment, and to make intelligent, informed decisions about how they can take care of it.

Environmental ethics
The branch of philosophy that studies the moral relationship of human beings to the environment, and the value and moral status of other species.

Environmental justice
the rights of all people live in an unpolluted environment and have equal access to natural resources.

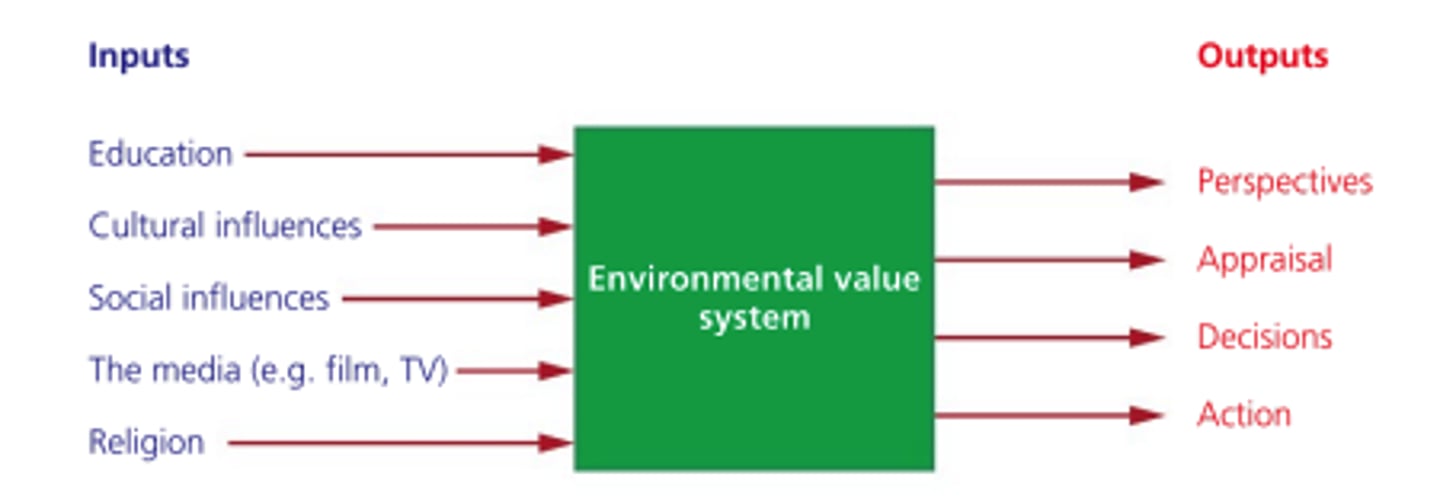
Environmental Value System (EVS)
A perspective that shapes the way an individual, or group of people, perceives and evaluates environmental issues, influenced by cultural, religious, economic and sociopolitical contexts.
Equilibrium
A state of balance among the components of a system.
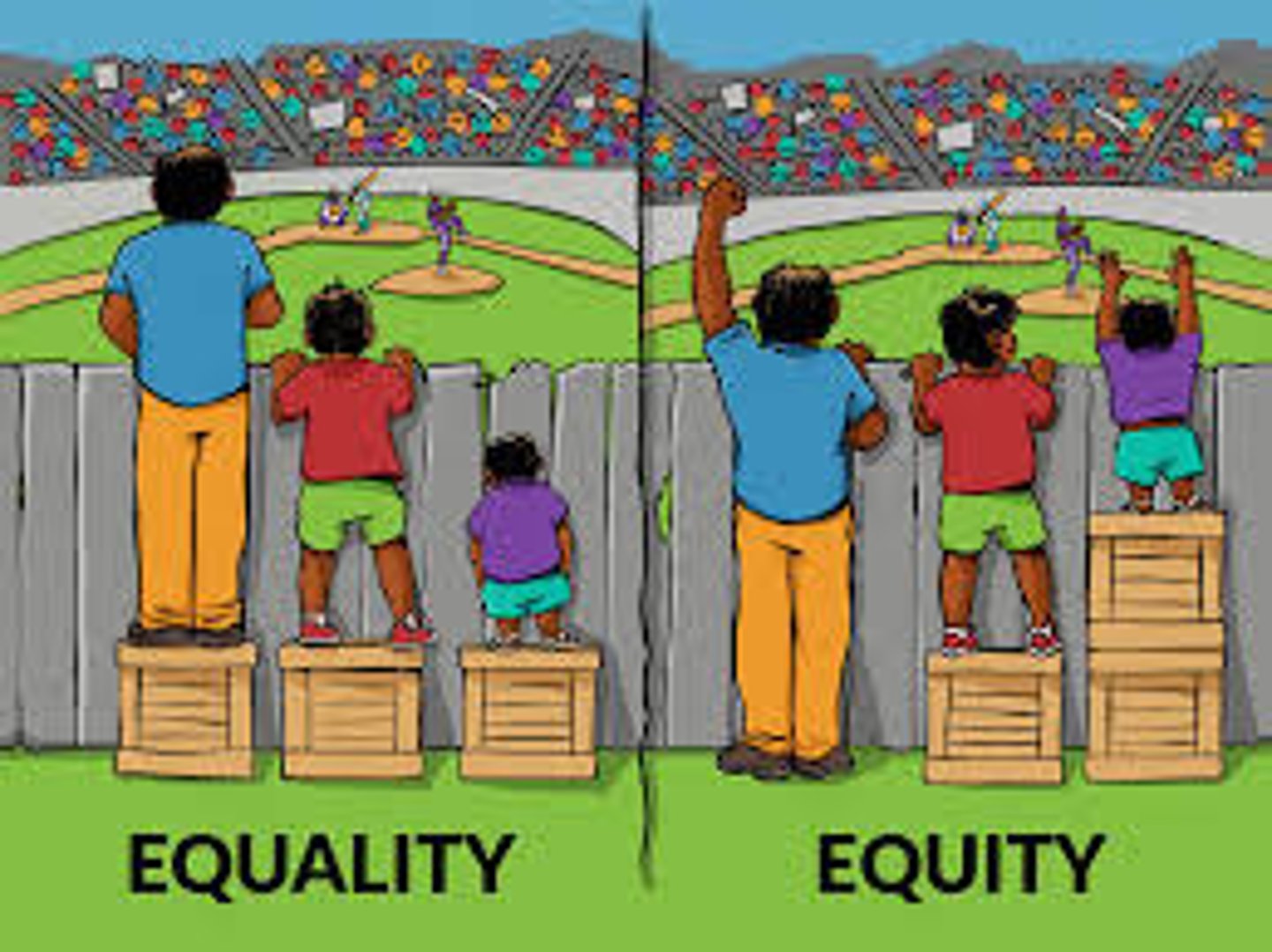
Equity
The state, quality, or ideal of equality and justice between economic classes, ethnic and cultural groups, and the fair distribution of resources.
Feedback
This occurs when part of the output from a system returns as an input, and affects subsequent outputs.
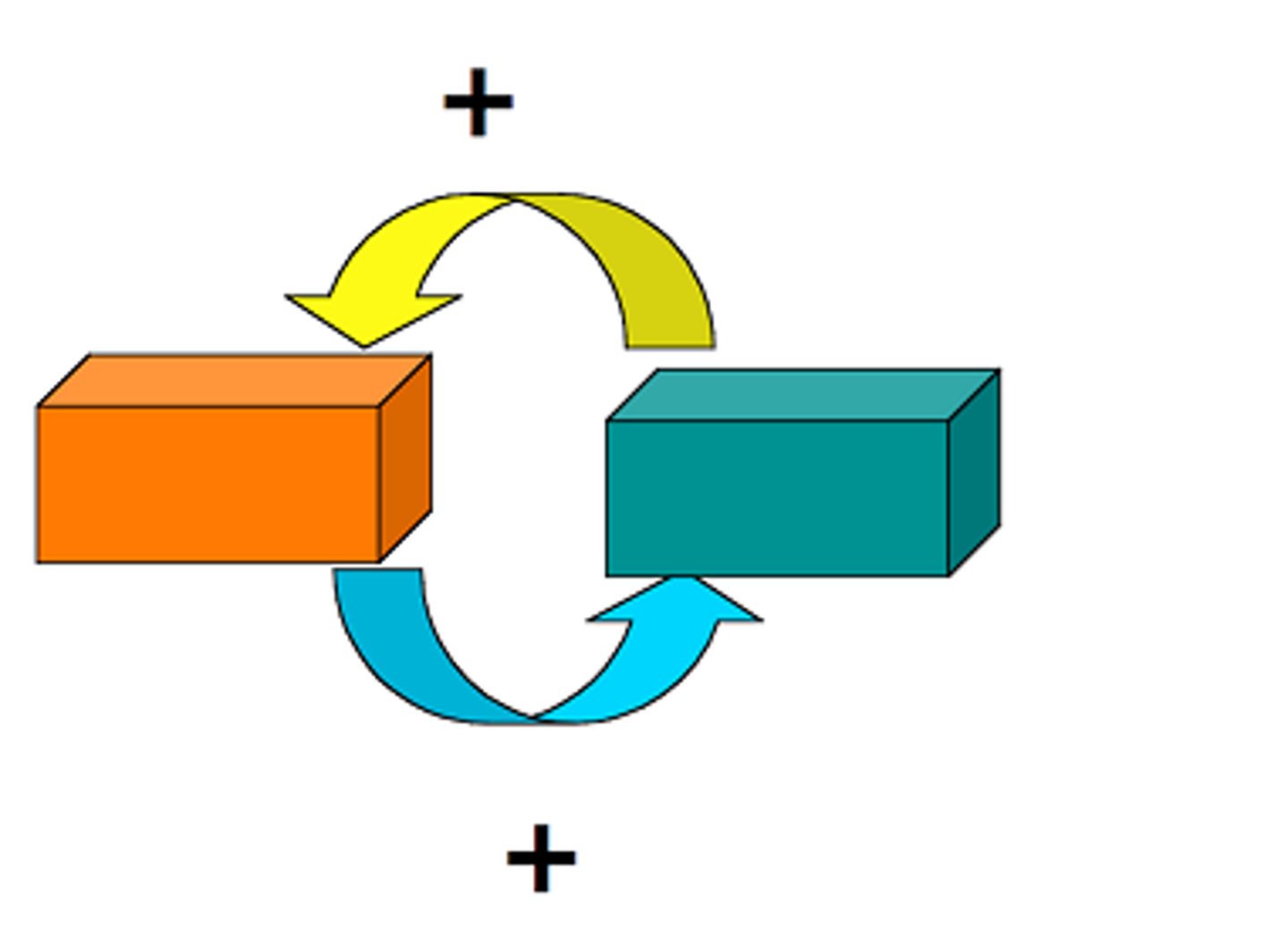
Flow
A movement of matter, energy or information between storages in a system.

Green economy
An economy that is low carbon, resource efficient and socially inclusive.

Green GDP
This measures environmental costs and subtracts these from GDP.

Intrinsic value
A characteristic of a natural system that has an inherent worth, irrespective of economic considerations, such as the belief that all life on Earth has a right to exist.

Issues
These are important topics in ESS, for example resource management, pollution, globalization and energy security

Justice
The idea that people are treated impartially, fairly, properly and reasonably by others, the law and arbiters of the law.

Model
A simplified version of reality and can be used to understand how a system works and to predict how it will respond to change.
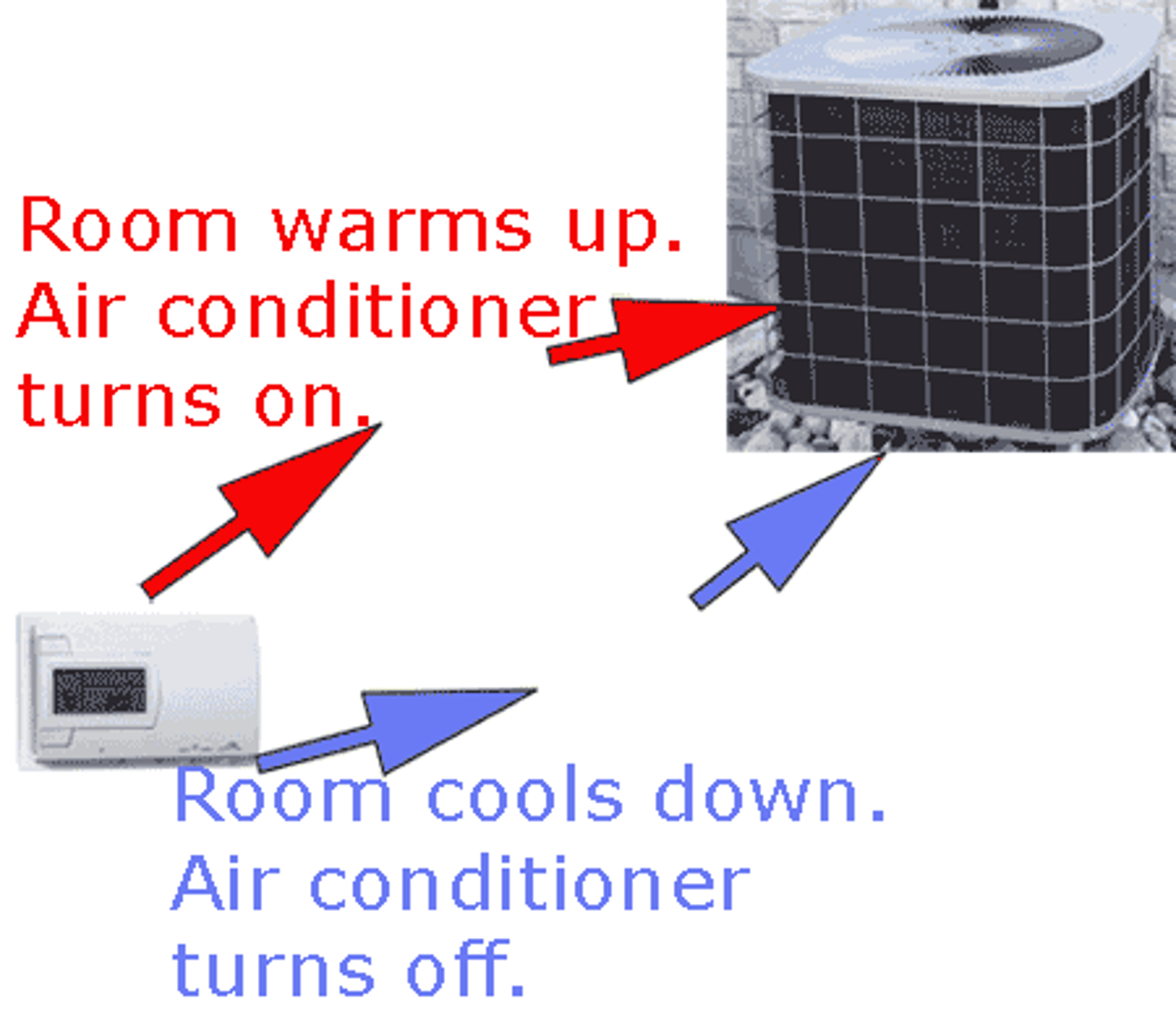
Negative feedback
Feedback that tends to counteract any deviation from equilibrium and promotes stability.
Open system
A system that exchanges both matter and energy with its surroundings (for example, an ecosystem).
Perspectives
Particular viewpoints, which may vary between different interest-groups, that can exist at a variety of scales

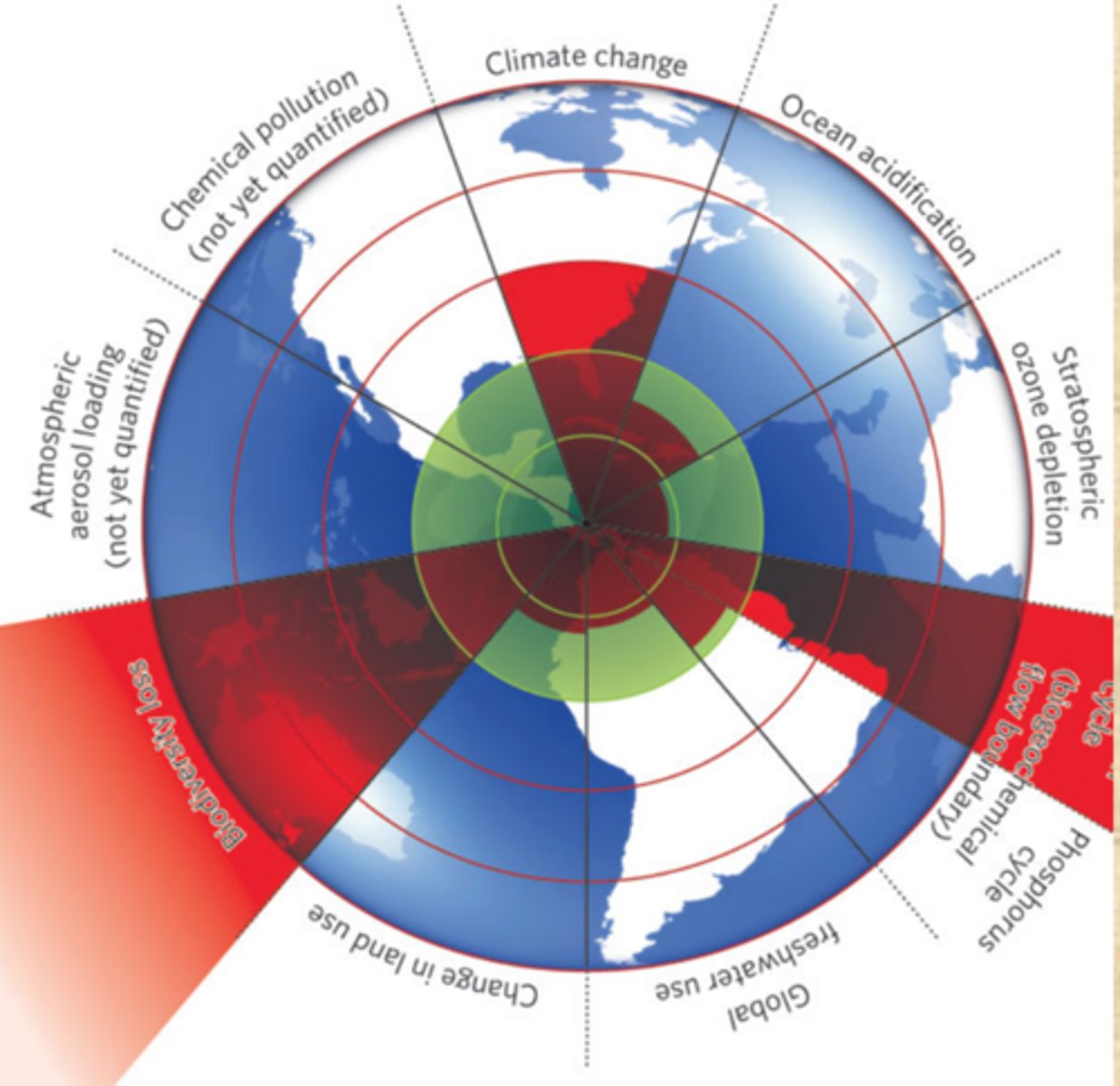
Planetary boundaries
Processes that regulate the stability and resilience of the Earth system, within which humanity can continue to develop and live sustainably; crossing these boundaries increases the risk of creating sudden, extensive or irreversible environmental changes.
Positive feedback
Feedback that increases change; it promotes deviation away from an equilibrium.
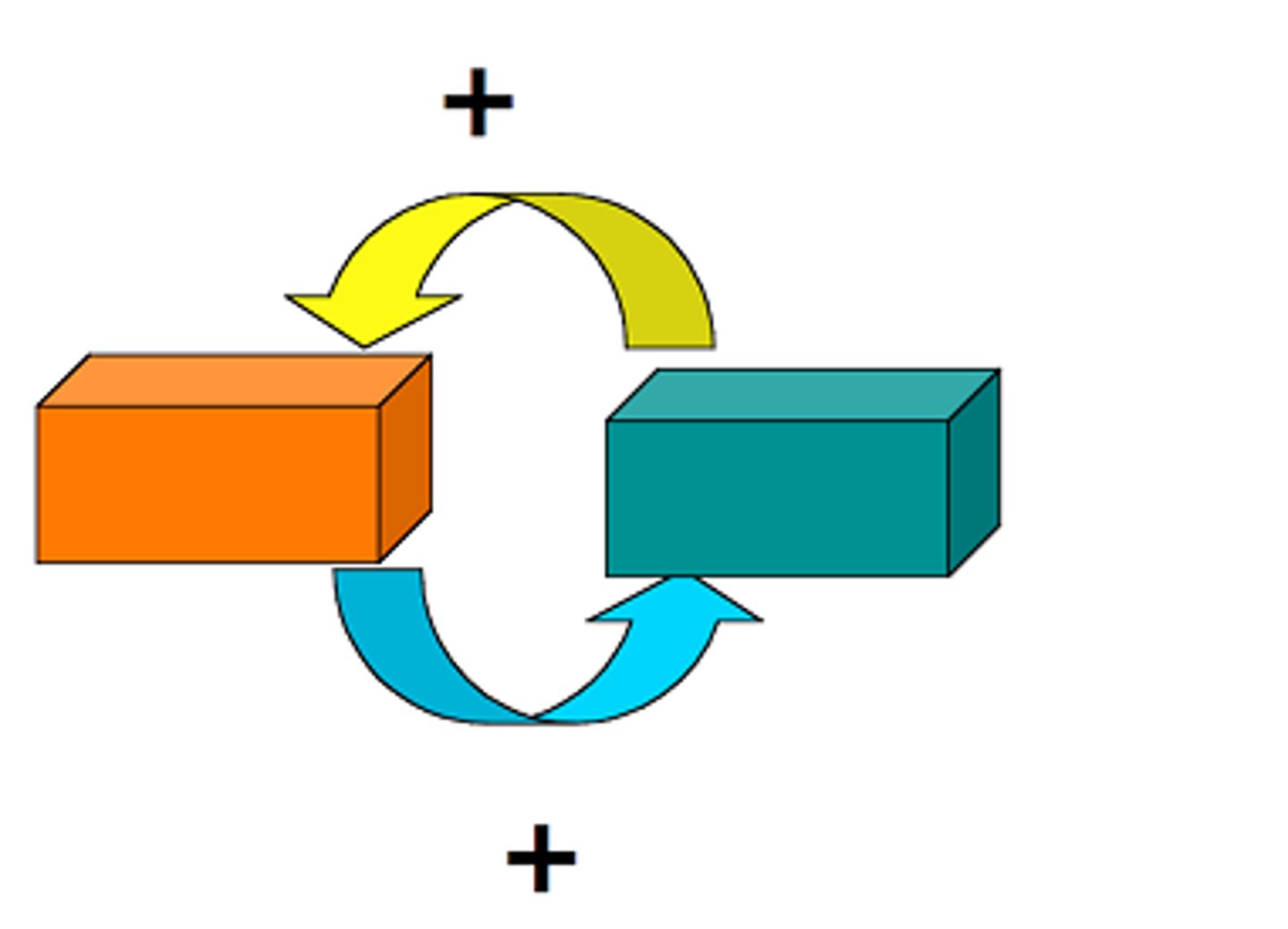
Product stewardship
An environmental management strategy that means whoever designs, produces, sells, or uses a product takes responsibility for minimizing the product's environmental impact throughout all stages of the product's life

Resilience
The tendency of a system to avoid tipping points and maintain stability through steady-state equilibrium.

Society
An arbitrary group of individuals who share some common characteristics, such as geographical location, cultural background, historical time frame, religious perspective, value system and so on.

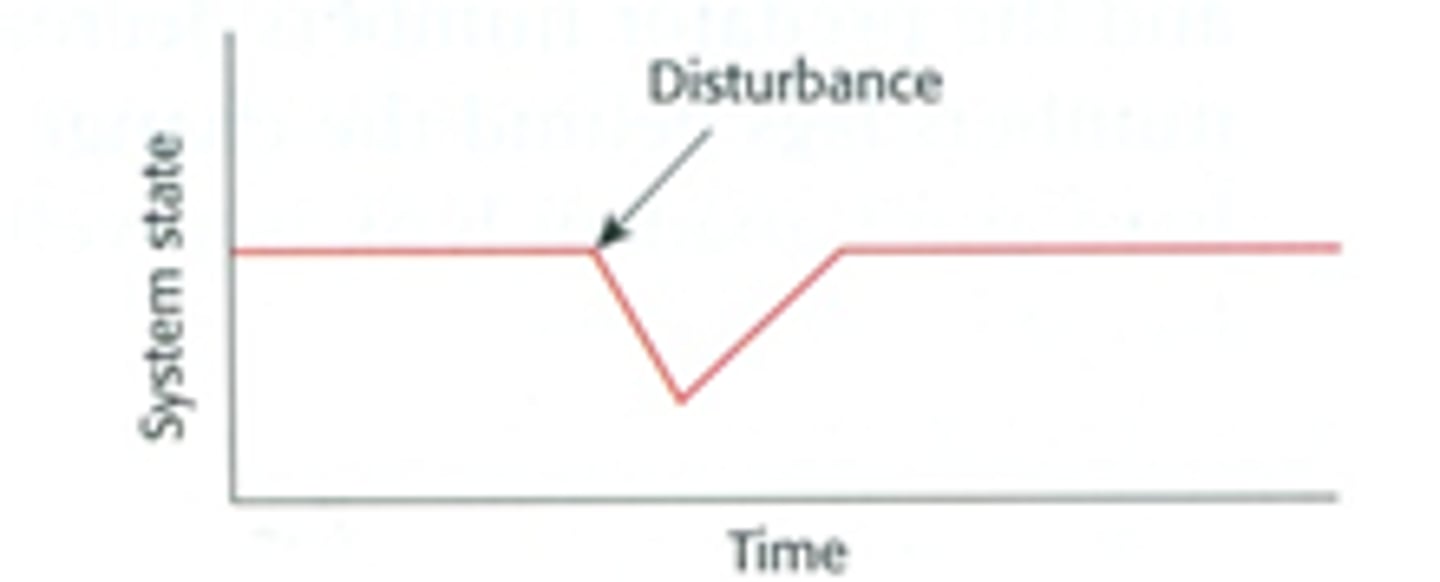
Stable equilibrium
The tendency in a system for it to return to a previous equilibrium condition following disturbance.
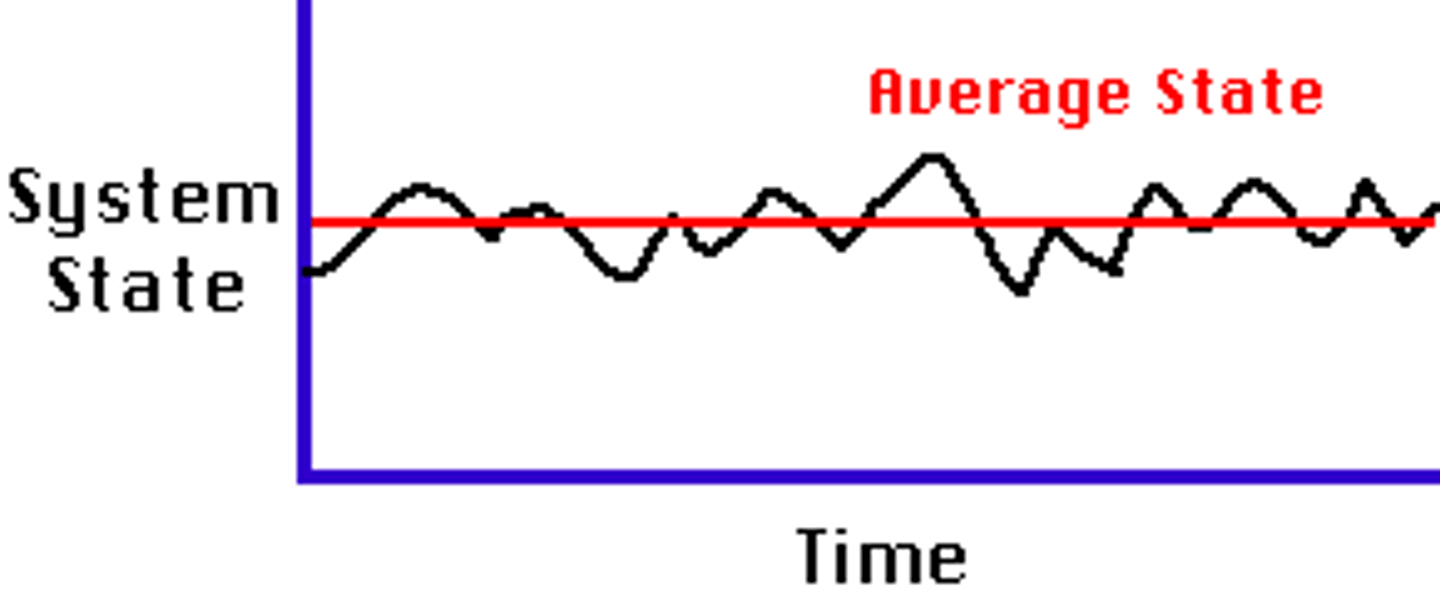
Steady-state equilibrium
The condition of an open system in which there are no changes over the longer term, but in which there may be oscillations in the very short term.
Stewardship
The responsible management and protection of something that is considered worth caring for and preserving.

Storage
The locations where matter, energy or information is held in a system.

Sustainability
Definitions of sustainability begin with the idea that development should meet the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their needs. It refers to limiting the degree to which the current generation's activities create harmful environmental outcomes involving resource depletion or degradation that will negatively affect future generations. Sustainability is increasingly important as planetary boundaries are pushed to their limit. Sustainability today has three integrated aspects: environmental, sociocultural (including political) and economic.

Sustainable development
Development that meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs. (Brundtland, 1987)

System
An assemblage of parts and the relationships between them, which together constitute an entity or whole.
Systems approach
A system is composed of interrelated and interdependent elements that can be collectively regarded as a unitary whole. A systems approach explores connections and interdependencies between the elements and within the system as a whole.
Technocentrism
A viewpoint that argues that technological developments can provide solutions to environmental problems.

Tipping point
A critical threshold when even a small change can have dramatic effects and cause a disproportionately large response in the overall system.

Transfers
Processes that involve a change in location within the system but no change in state.
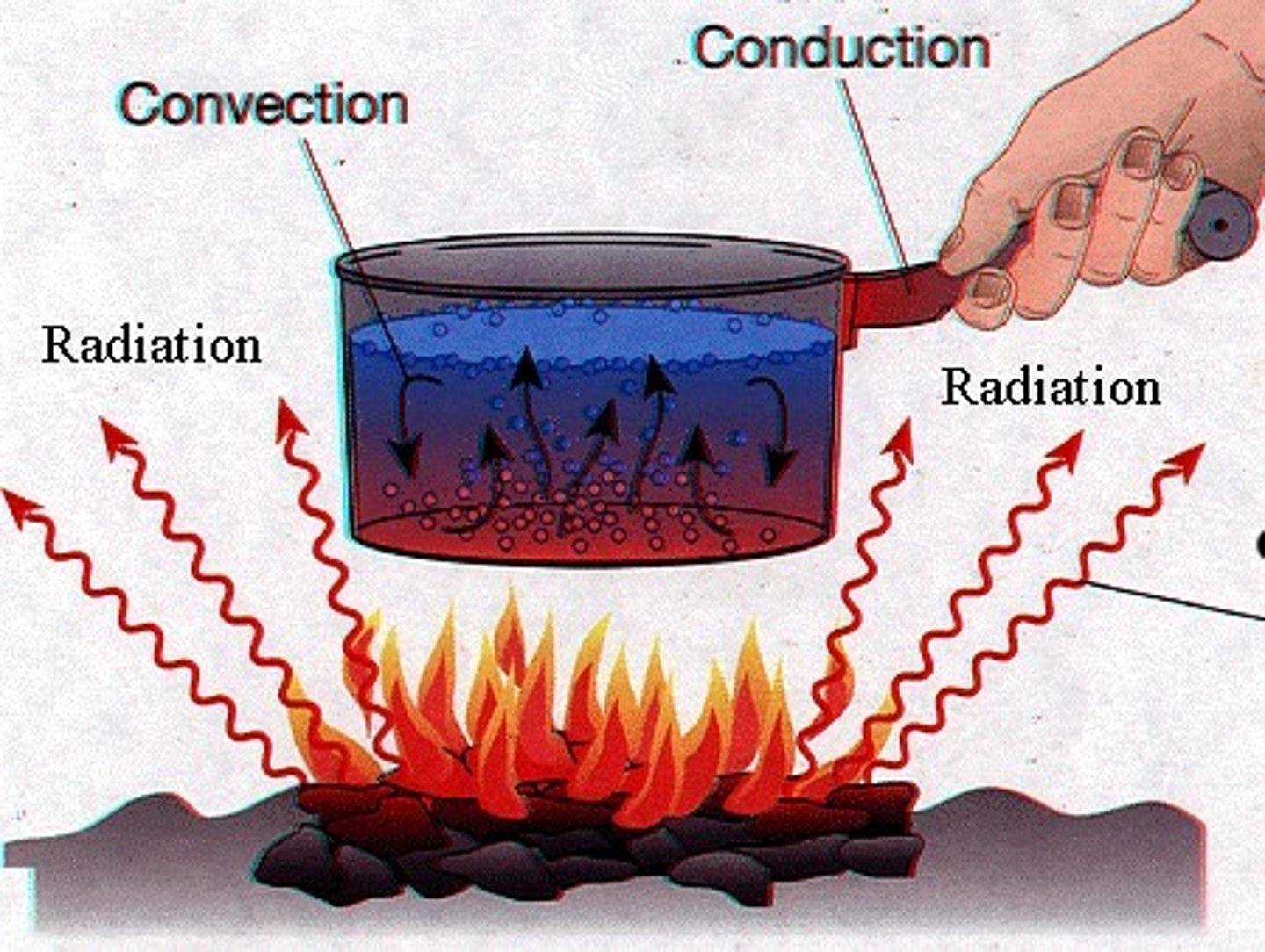
Transformations
Processes that lead to the formation of new products or involve a change in state.
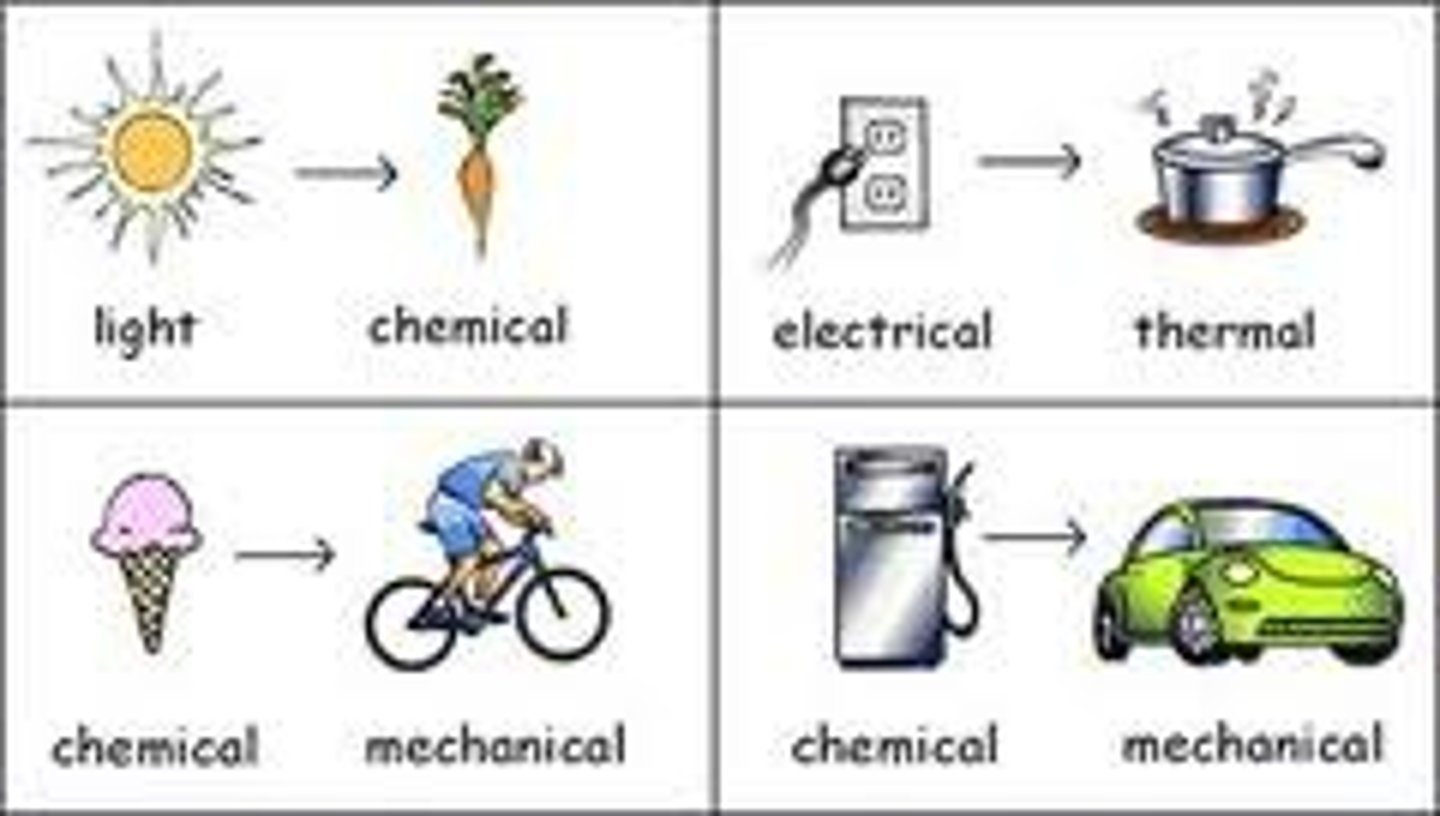
Worldview
Lenses, often shared by groups of people, through which they perceive, make sense of and act within their environment. They shape people's values and perspectives through
culture, philosophy, ideology, religion and politics
Values
The qualities or principles that people feel have worth and importance in life.
Values surveys
used to investigate the perspectives shown by a particular social group towards environmental issues.