Exam II Review Problems, ICGW, and Case Studies
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms
Which of the following statements is NOT true about the “housekeeper wave”?
a) Undigested food is pushed into the small intestine at this phase.
b) It is responsible for grinding and mixing food in the stomach.
c) Enteric-coated tablets are normally emptied from the stomach during this wave.
b) It is responsible for grinding and mixing food in the stomach.
Enterohepatic recycling is mainly seen with drugs that are …
a) metabolized and eliminated by renal excretion
b) absorbed from the GIT and excreted in the bile unchanged
c) formulated as products that target the colon
d) metabolized in the gut wall before reaching the systemic circulation
e) the active drug form is recreated in the gut
b) absorbed from the GIT and excreted in the bile unchanged
and
e) the active drug form is recreated in the gut
According to the Noyes-Whitney equation, the dissolution rate of a drug increases with…
a) increasing solubility
b) decreasing particle size
c) increasing diffusion coefficient
d) increasing the boundary layer thickness
ALL except:
d) increasing the boundary layer thickness
Which of the following is true about OraVescent® technology?
a) it is a Type III Mucoadhesive delivery system.
b) it slows down the disintegration of the tablet and provides a sustained release of the drug.
c) it provides localized and transient pH changes that enhance both dissolution and permeability.
d) it contains a buffer that resists pH change and improves the stability of a drug.
e) All of the above
c) it provides localized and transient pH changes that enhance both dissolution and permeability.
Which of the following formulations may contain aspartame?
a) Chewable tablets
b) Oral granules
c) Orally disintegrating tablets
d) Coated oral tablets
e) Oral capsules
a) Chewable tablets
b) Oral granules
c) Orally disintegrating tablets
Isobutene and propane can be found in …
a) rectal enema
b) rectal suppository
c) rectal foam
d) rectal cream
c) rectal foam
Which of the following patients would benefit most from the use of an orally disintegrating tablet?
a) A 12-year-old male with appendicitis who has been ordered to have nothing by mouth
b) A 30-year-old female with persistent vomiting
c) A 44-year-old male with phenylketonuria
d) A 51-year-old male with schizophrenia who is adherent to monthly injections.
e) A 62-year-old female with dysphagia.
e) A 62-year-old female with dysphagia.
What is the purpose of potassium metabisulfite in Rowasa® (mesalamine) Rectal Enema?
a) Chelating agent
b) Antioxidant
c) Buffering agent
d) Preservative
e) Tonicity-adjustment
b) Antioxidant
Factors affecting drug absorption from the rectum include:
a) The pH of the rectal fluid
b) The presence of fecal matter
c) The presence of esterase in the rectal fluid
d) The location of the suppository within the rectum
b) The presence of fecal matter
AND
d) The location of the suppository within the rectum
Concerning diazepam rectal gel, which of the following is true?
a) The structural properties of the gel are specifically due to the hydrophilic polymers and the high water content of the formulation.
b) Diazepam rectal gel is formulated using long-chain hydrocarbons.
c) Diazepam rectal gel requires the addition of preservatives.
d) The solubility of diazepam in the gel is increased using co-solvents such as ethyl alcohol and propylene glycol.
e) Diazepam is water soluble, and therefore, its release from a water-soluble gel will be slow.
a) The structural properties of the gel are specifically due to the hydrophilic polymers and the high water content of the formulation.
c) Diazepam rectal gel requires the addition of preservatives.
d) The solubility of diazepam in the gel is increased using co-solvents such as ethyl alcohol and propylene glycol.
CP is a 12-year-old male experiencing nausea after his tonsillectomy. He has been prescribed ondansetron orally disintegrating tablets. His mother requests counseling on the prescription. Which of the following instructions should be included?
a) Dissolve the tablet in water or juice, then drink it immediately. (Effervescent tablets)
b) Drink a full glass of water after taking the tablet.
c) Hold the tablet under the tongue for 60 seconds before swallowing
d) Place the tablet on the tongue and wait for it to dissolve.
e) Push the tablet through the foil to remove it from the packaging.
d) Place the tablet on the tongue and wait for it to dissolve.
What will happen to digoxin if it’s given to a patient receiving cyclosporine?
a) Digoxin levels will decrease.
b) Digoxin levels will increase.
c) Digoxin levels will stay the same.
d) Both digoxin and cyclosporine levels will decrease.
e) No change in concentration will occur.
b) Digoxin levels will increase [Digoxin is a substrate of P-gp and cyclosporine inhibits P-gp. Cyclosporine can reduce the efflux of digoxin, leading to increased digoxin levels]
Which of the following are P-gp substrates?
a) Apixaban
b) Digoxin
c) Colchicine
d) St. John's wort
e) Phenytoin
a) Apixaban
b) Digoxin
c) Colchicine
Which of the following drugs interacts with grapefruit?
a) Tacrolimus
b) Lithium
c) Alendronate
d) Paroxetine
e) Metoprolol
a) Tacrolimus
A 65-year-old woman brings a new prescription for a monoamine oxidase inhibitor to the pharmacy. Which of the following foods should she be counseled to avoid?
a) Sauerkraut
b) Grapefruit
c) Potatoes
d) Walnuts
e) Fresh milk
a) Sauerkraut
A patient with asthma has been using theophylline for many years. The patient has been under a lot of stress lately and has started smoking again. About 15 – 20 cigarettes daily. Which of the following statements is correct about smoking?
a) Smoking will decrease the theophylline level.
b) Smoking will increase the theophylline level.
c) Smoking will not affect the drug levels.
a) Smoking will decrease the theophylline level.
The following agents may be used as a suppository base:
a) Triglycerides of higher saturated fatty acids
b) Polyacrylic acid
c) Polyethylene glycols
d) Cocoa butter
e) Benzyl alcohol
a) Triglycerides of higher saturated fatty acids
c) Polyethylene glycols
d) Cocoa butter
Which of the following statements is not correct?
a) passive diffusion involves the diffusion of drugs across the cell membrane and is driven by a concentration gradient, with drugs moving from high to low concentration
b) Carrier-mediated transport involves specific carrier proteins present in the cell membranes and can act either with a concentration gradient or against a concentration gradient
c) Endocytosis involves the internalization of substances by engulfment by the cell membrane which forms membrane-based vesicles within the cell, known as liposomes.
d) Some drugs can cross epithelia through gaps between the cells. This route is governed by passive diffusion and large hydrophilic molecules can pass through these gap junctions.
e) Drugs that are subjected to efflux processes include cytotoxic drugs such as steroids, immunosuppressants, and antibiotics.
c) Endocytosis involves the internalization of substances by engulfment by the cell membrane which forms membrane-based vesicles within the cell, known as liposomes.
and
d) Some drugs can cross epithelia through gaps between the cells. This route is governed by passive diffusion and large hydrophilic molecules can pass through these gap junctions.
What is the absorption rate of estrogen?
A. Fast
B. Slow
C. No absorption
A. Fast
What is the absorption rate of glycerol?
A. Fast
B. Slow
C. No absorption
B. Slow
What is the absorption rate of sucrose?
A. Fast
B. Slow
C. No absorption
C. no absorption
What is the absorption rate of acetic acid (pH = 1.5)?
A. Fast
B. Slow
C. No absorption
B. Slow
What is the absorption rate of acetic acid (pH = 7)?
A. Fast
B. Slow
C. No absorption
C. No absorption
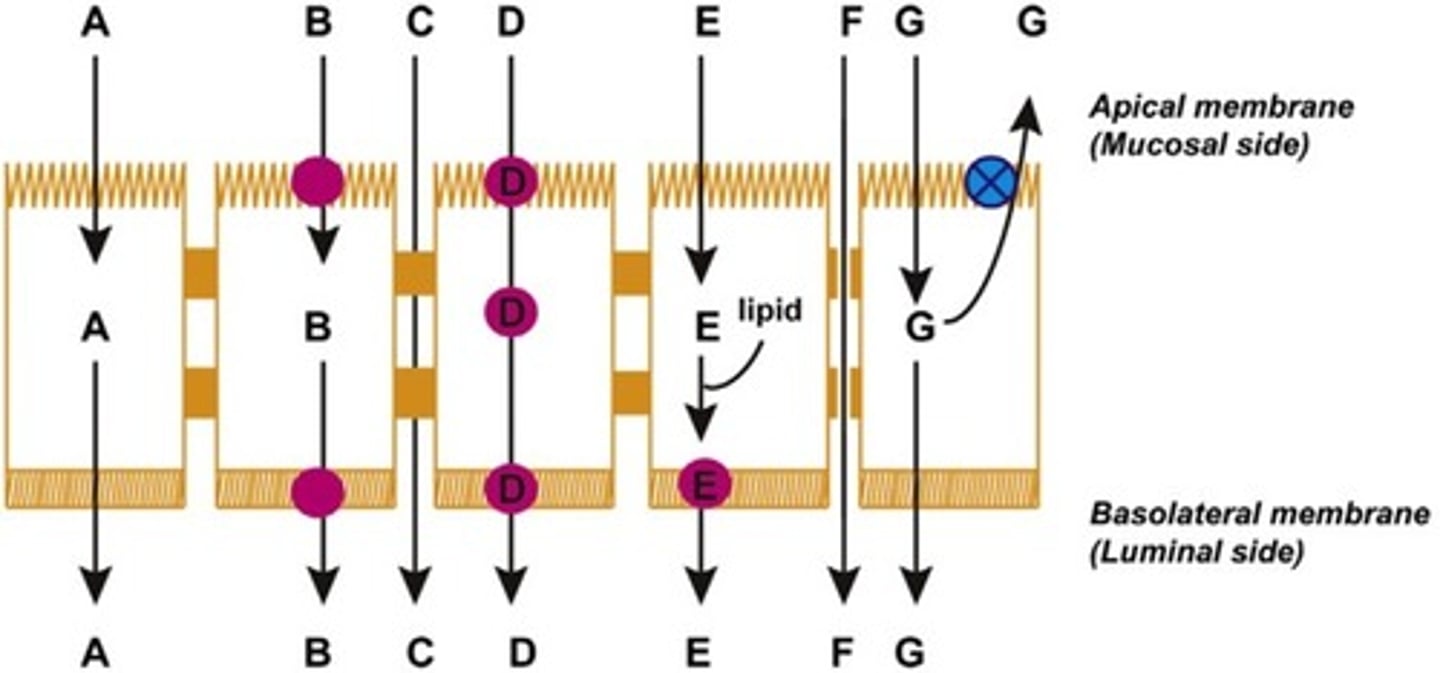
Which of the following is passive diffusion?
A
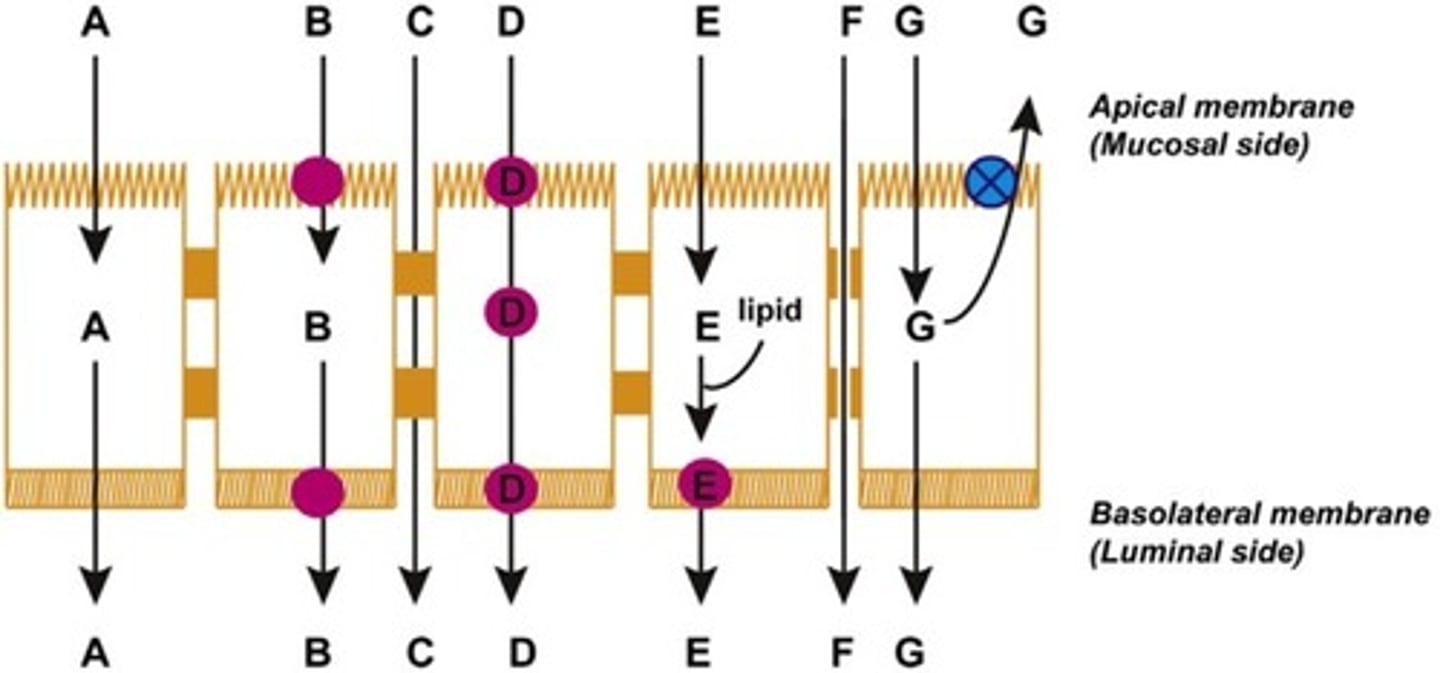
Which of the following is convective transport?
F
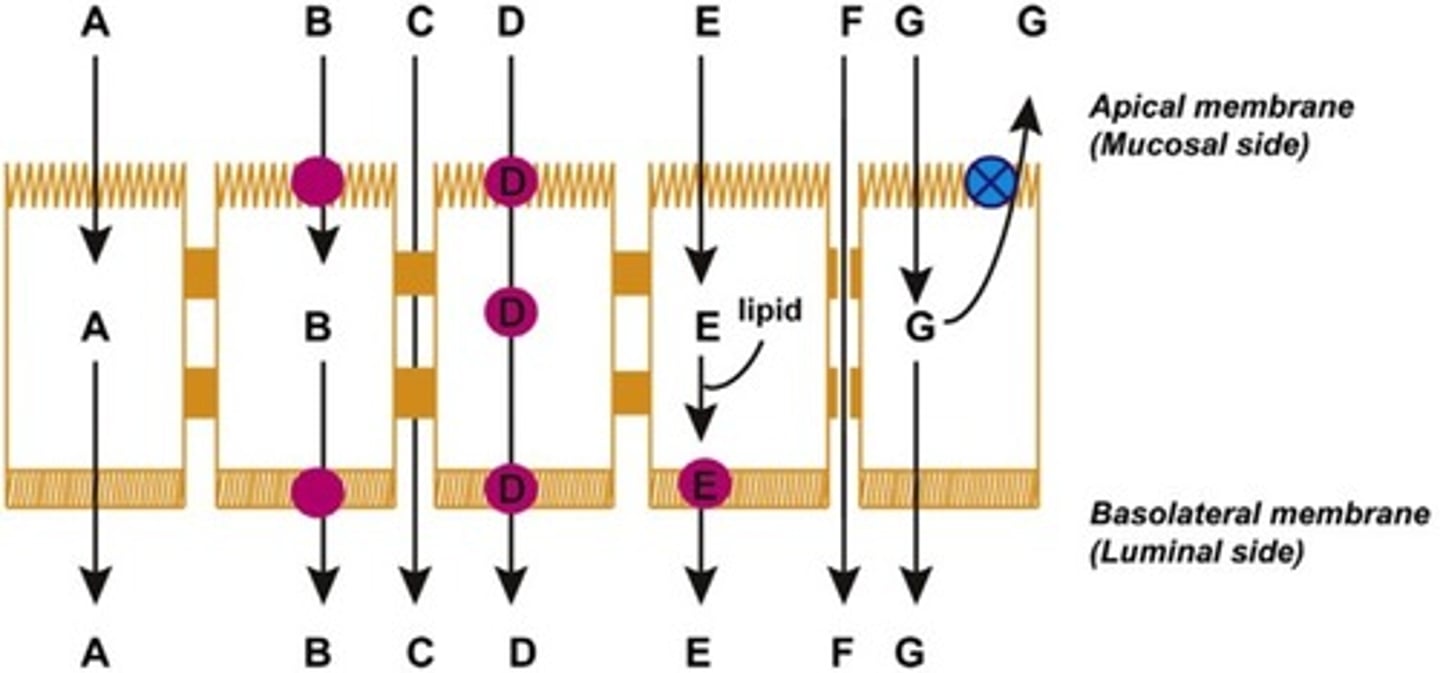
Which of the following is active transport?
B
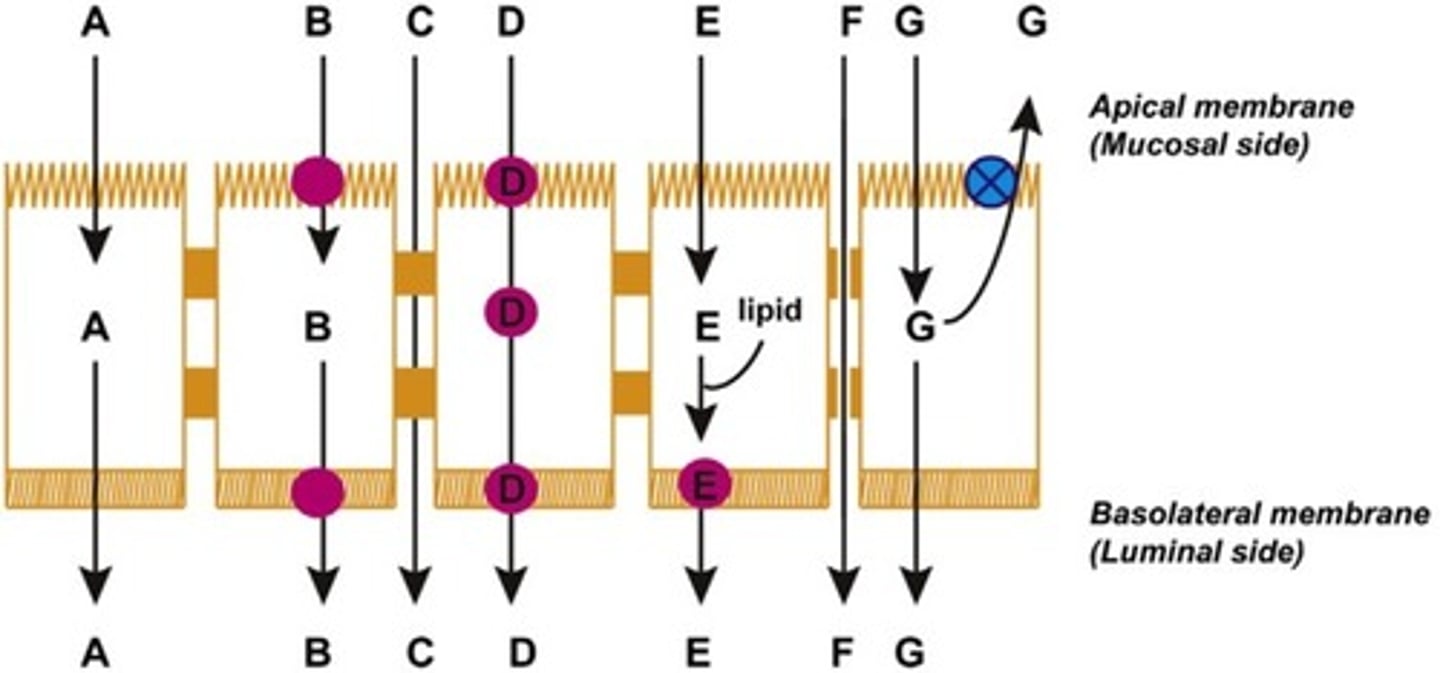
Which of the following is facilitated transport?
B
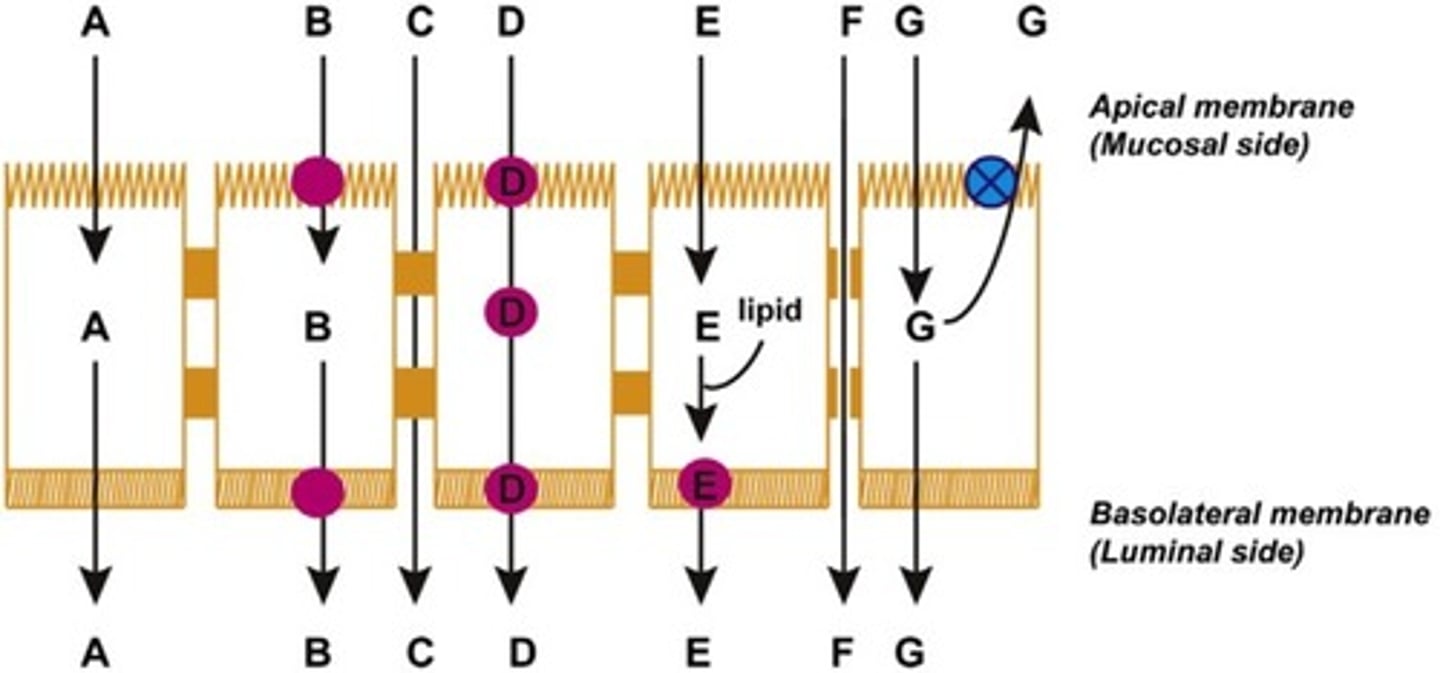
Which of the following is transcytosis [endo/pino]?
D
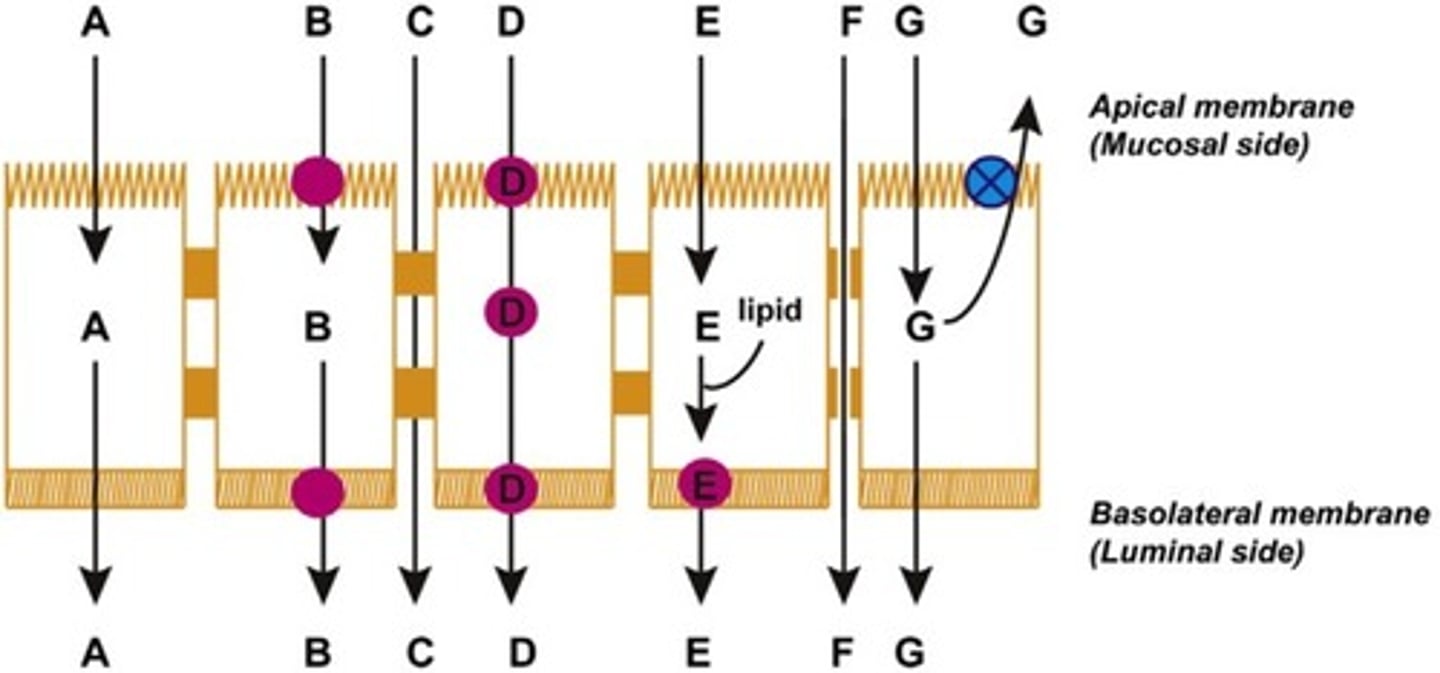
Which of the following is paracellular permeation?
C
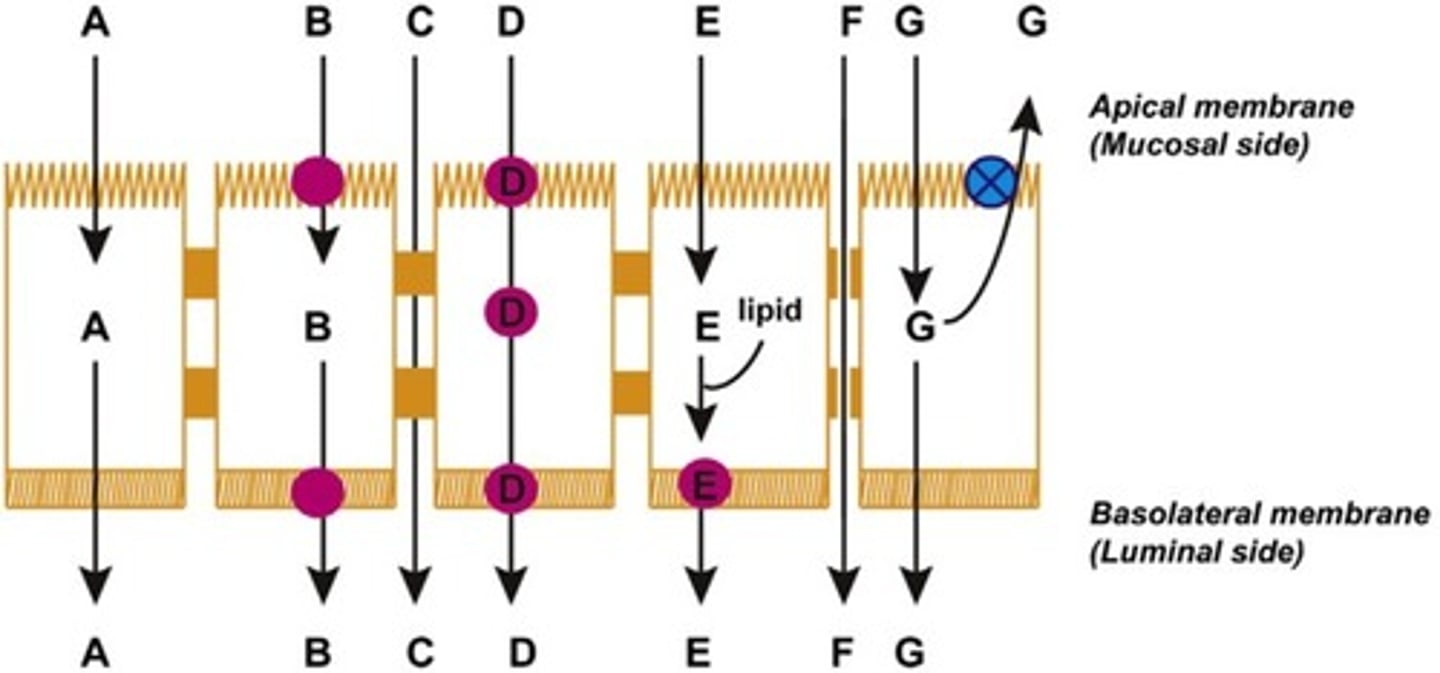
Which of the following is efflux transport?
G
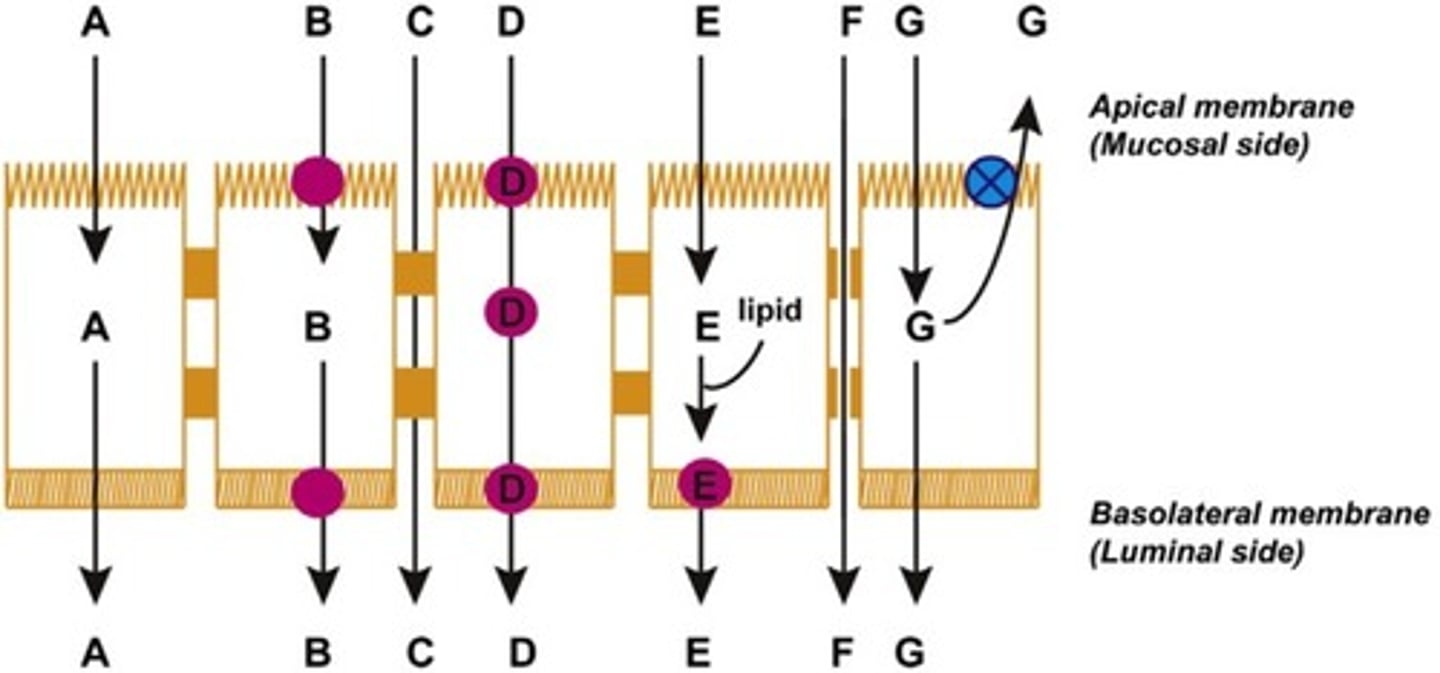
Which of the following is transcellular diffusion and incorporation into lipid particles?
E
The faster onset of action of Aleve tablets is due to?
A. increased solubility
B. increased permeability
A. increased solubility
Which drug form shows a pH-dependent water solubility?
A. naproxen
B. naproxen sodium
C. both
A. naproxen
What is the BCS class of naproxen?
A. Class I
B. Class II
C. Class III
D. Class IV
B. Class II
Which dosage form is the most affected by food?
A. Aleve® tablet
B. Naprosyn®
C. EC-Naproxen®
D. Naprelan® ER tablet
E. All of the above dosage forms are equally affected
C. EC-Naproxen®
Transmucosal fentanyl formulations are not advised for managing acute or postoperative pain in patients who are not tolerant of opioids. Why is this the case?
"The absorption pharmacokinetics of fentanyl from the oral transmucosal dosage form is a combination of an initial rapid absorption from the buccal mucosa and a more prolonged absorption from the swallowed fentanyl from the GI tract." As a result, patients who are not tolerant to the medication may be at risk for overdose due to the high potency of fentanyl, the prolonged action of this dosage form, and the variation in absorption.
A patient keeps the OTFC lozenge in the mouth for a long time (more than the recommended 15 minutes) and tries not to swallow the saliva during that period. What will happen to the bioavailability of fentanyl, in terms of rate and extent of absorption?
It is recommended that the lozenge be finished in 15 minutes. If you finish it too quickly, you will swallow more of the medicine and get less relief. If the lozenge is not finished in 15 minutes and the patient continues to have it in their mouth for a longer duration, the opposite will happen and the patient may experience more relief than appropriate. The bioavailability would increase from the original 25%, the rate of absorption would decrease, and the extent of absorption would increase.
What would happen to fentanyl bioavailability, if a patient chewed and swallowed the OTFC lozenge instead of sucking?
The bioavailability in this example would decrease because the drug would be solely in the GIT.
Calculate (estimate) the bioavailability of fentanyl if the patient chews and swallows the OTFC medication.
According to the reading, "only 33% (1/3) of the swallowed fentanyl reaches the systemic circulation. Thus, the observed 50% bioavailability of OTFC was due to the rapid transmucosal absorption (25%) and the slower GI absorption (i.e., 25%, one-third of the 75%)." As a result, if the patient were to chew and swallow the OTFC medication the amount of swallowed fentanyl would be less than the 75% expected from correct administration. Essentially 100% goes to the GIT, so one-third of that would reach systemic circulation at 33% bioavailable which is lower than 50%.
During the administration of fentanyl, Cmax and AUC increased in a dose-dependent manner. What is the advantage of this "linear pharmacokinetics"?
The advantage of linear pharmacokinetics is the predictability this provides. It would be easier to monitor the patient, make dose adjustments, and/or titrate the patient in both directions.
OTFC and Fentora are not bioequivalent with each other. We shouldn't substitute one product for another on an "mcg" per "mcg" basis. Why do these products show different pharmacokinetics?
The amount of first-pass metabolism differs between the two medications. Fentora has 50% reaching systemic circulation from the buccal administration and so 50% heads to the GIT. From the GIT about 15% will reach systemic circulation. Therefore, the total is roughly 65% for Fentora. As a result, the dosage for Fentora will not match OTFC. For example, 200mcg of Fentora will have more systemic circulation then 200mcg of OTFC; therefore, switching between an equal mcg dosage could be harmful for the patient.
Which transmucosal dosage forms are associated with application site reactions, ranging from paresthesia to ulcerations and bleeding?
A. Fentora
B. OTFC
C. Both
A. Fentora
What makes mesalamine products more favorable than sulfasalazine (Azulfidine®) for managing IBD?
Mesalamine has fewer adverse effects as compared to sulfasalazine
Are the mesalamine products designed for local or systemic action?
Local
Would an immediate-release oral capsule of mesalamine be effective for treating ulcerative colitis?
No! The efficacy of mesalamine depends on achieving a high concentration at the disease site. An immediate-release product (such as an oral suspension) has a systemic bioavailability of 80%. Rapid and extensive absorption means less amount of drug will be available for the local action against IBD.
Will the Canasa rectal suppository melt or dissolve in the rectum?
Melt
What does the excipient Carbomer 934P in Rowasa do?
A. suspending/thickening agent
B. chelating agent
C. preservative
D. buffer/pH adjustment
E. antioxidant/reducing agent
A. suspending or thickening agent
What does the excipient xanthan gum in Rowasa do?
A. suspending/thickening agent
B. chelating agent
C. preservative
D. buffer/pH adjustment
E. antioxidant/reducing agent
A. suspending or thickening agent
What does the excipient edetate disodium in Rowasa do?
A. suspending/thickening agent
B. chelating agent
C. preservative
D. buffer/pH adjustment
E. antioxidant/reducing agent
B. chelating agent
What does the excipient sodium benzoate in Rowasa do?
A. suspending/thickening agent
B. chelating agent
C. preservative
D. buffer/pH adjustment
E. antioxidant/reducing agent
C. preservative
What does the excipient potassium acetate in Rowasa do?
A. suspending/thickening agent
B. chelating agent
C. preservative
D. buffer/pH adjustment
E. antioxidant/reducing agent
D. buffer or pH adjustment
What does the excipient potassium metabisulfite in Rowasa do?
A. suspending/thickening agent
B. chelating agent
C. preservative
D. buffer/pH adjustment
E. antioxidant/reducing agent
E. antioxidant or reducing agent
Which products are preferred for patients with ulcerative proctitis? (multiple answers)
A. Canasa
B. Rowasa
C. Lialda
D. Apriso
E. Sf Rowasa
A, B, and E
Why is bedtime dosing recommended for rectal products?
Bedtime dosing is recommended because it's easier to retain the product in the rectum to ensure a longer duration of action (for approximately eight hours).
Less leak out.