5.5 Chemistry - Creatinine, Uric Acid, BUN, and Ammonia
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
Creatinine is formed from the:
Oxidation of creatine
Creatinine is produced at a rate of approximately 2% daily from the oxidation of creatine mainly in skeletal muscle. Creatine can be converted to creatinine by addition of strong acid or alkali or by the enzyme creatine hydroxylase.
Creatinine is considered the substance of choice to measure endogenous renal clearance because:
It is completely filtered by the glomeruli
Creatinine concentration is dependent upon muscle mass, but varies by less than 15% per day. Creatinine is not metabolized by the liver, or dependent on diet, and is 100% filtered by the glomeruli. It is not reabsorbed significantly but is secreted slightly, especially when filtrate flow is slow. Plasma creatinine and cystatin C are the two substances of choice for evaluating the glomerular filtration rate (GFR).
Which statement regarding creatinine is true?
High serum levels result from reduced glomerular filtration
Serum creatinine is a specific but not a sensitive measure of glomerular function. About 60% of the filtration capacity of the kidneys is lost when serum creatinine becomes elevated. Because urine creatinine diminishes as serum creatinine increases in renal disease, the creatinine clearance is more sensitive than serum creatinine in detecting glomerular disease. A creatinine clearance below 60 mL/min indicates loss of about 50% functional nephron capacity and is classified as moderate (stage 3) chronic kidney disease.
Which of the following formulas is the correct expression for creatinine clearance?
Creatinine clearance = U/P x V x 1.73/A
Clearance is the volume of plasma that contains the same quantity of substance that is excreted in the urine in 1 minute. Creatinine clearance is calculated as the ratio of urine creatinine to plasma creatinine in milligrams per deciliter. This is multiplied by the volume of urine produced per minute and corrected for lean body mass by multiplying by 1.73/A, where A is the patient's body surface area in square meters. Separate reference ranges are needed for males, females, and children because each has a different percentage of lean muscle mass.
Which of the following conditions is most likely to cause a falsely high creatinine clearance result?
The patient empties his or her bladder at the start of the test and adds the urine to the collection
Urine in the bladder should be eliminated and not saved at the start of the test because it represents urine formed prior to the test period. The other conditions (choices A-C ) will result in falsely low urine creatinine or volume and, therefore, falsely lower clearance results. Error is introduced by incomplete emptying of the bladder when short times are used to measure clearance. A 24-hour timed urine is the specimen of choice. When filtrate flow falls below 2 mL/min, error is introduced because tubular secretion of creatinine occurs. The patient must be kept well hydrated during the test to prevent this.
The modification of diet in renal disease (MDRD) formula for calculating eGFR requires which four parameters?
Serum creatinine, age, gender, race
The National Kidney Foundation recommends screening for chronic kidney disease using the estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) because of the high frequency of sample collection errors associated with measuring creatinine clearance. The eGFR should be calculated according to the MDRD formula, and reported along with the serum or plasma creatinine.
eGFR (mL/min/1.73m^2) = 186 x Plasma Cr^(-1.154) x Age^(-0.203) x 0.742 (if female) x 1.21 (if Black)
What substance may be measured as an alternative to creatinine for evaluating GFR?
Cystatin C
Although all of the analytes listed are increased in chronic kidney disease as a result of low GFR, potassium, urea, and uric acid may be increased by other mechanisms and therefore, they are not specific for glomerular function. Cystatin C is an inhibitor of cysteine proteases. Being only 13 kilodaltons, it is completely filtered by the glomerulus then reabsorbed by the tubules. The plasma level is highly correlated to GFR because little is eliminated by nonrenal routes. Plasma levels are not influenced by diet, age, gender, or nutritional status. Low GFR causes retention of cystatin C in plasma and levels become abnormally high at clearance rates below 90 mL/min, making the test more sensitive than creatinine.
Which of the following enzymes allows creatinine to be measured by coupling the creatinine amidohydrolase (creatininase) reaction to the peroxidase reaction?
Sarcosine oxidase
The peroxidase-coupled enzymatic assay of creatinine is based upon the conversion of creatinine to creatine by creatinine amidohydrolase (creatininase). The enzyme creatinine amidinohydrolase (creatinase) then hydrolyzes creatine to produce sarcosine and urea. The enzyme sarcosine oxidase converts sarcosine to glycine producing formaldehyde and hydrogen peroxide. Peroxidase then catalyzes the oxidation of a dye (4-aminophenazone and phenol) by the peroxide forming a red-colored product. This method is more specific than the Jaffe reaction, which tends to overestimate creatinine by about 5% in persons with normal renal function.
Select the primary reagent used in the Jaffe method for creatinine.
Saturated picric acid and NaOH
The Jaffe method uses saturated picric acid, which oxidizes creatinine in alkali, forming creatinine picrate. The reaction is nonspecific; ketones, ascorbate, proteins, and other reducing agents contribute to the final color. Alkaline CuSO4 is used in the biuret method for protein.
Interference from other reducing substances can be partially eliminated in the Jaffe reaction by:
Measuring the timed rate of product formation
The Jaffe reaction is nonspecific; proteins and other reducing substances such as pyruvate, protein, and ascorbate cause positive interference. Much of this interference is reduced by using a timed rate reaction. Ketoacids react with alkaline picrate almost immediately, and proteins react slowly. Therefore, reading the absorbance at 20 and 80 seconds and using the absorbance difference minimizes the effects of those compounds. Creatinine can be measured using an amperometric electrode. However, this requires the enzymes creatininase, creatinase, and sarcosine oxidase. The last enzyme produces hydrogen peroxide from sarcosine, which is oxidized. This produces current in proportion to creatinine concentration. Performing a sample blank does not correct for interfering substances that react with alkaline picrate.
Which of the following statements is true?
Cystatin C is measured immunochemically
Cystatin C can be measured by enzyme immunoassay, immunonephelometry, and immunoturbidimetry. However, there is no standardized calibrator as for creatinine, and therefore, results vary considerably from lab to lab. The coefficient of variation for these methods tends to be slightly higher than for creatinine. Since the enzymatic methods are specific, they give lower plasma creatinine results than the Jaffe method in persons with normal renal function. However, they tend to give higher clearance results than for inulin or iohexol clearance because some creatinine is secreted by the renal tubules.
In which case would eGFR derived from the plasma creatinine likely give a more accurate measure of GFR than measurement of plasma cystatin C?
Post-renal transplant
Cystatin C is eliminated almost exclusively by the kidneys and plasma levels are not dependent on age, sex, or nutritional status. However, plasma levels are affected by some drugs, including those used to prevent renal transplant rejection. Increased plasma levels have been reported in chronic inflammatory diseases and cancer. Formulas are available to calculate eGFR from plasma cystatin C, but unlike for creatinine, the formulas must be matched to the method of assay. The eGFR derived from cystatin C can detect a fall in GFR sooner and may be more sensitive for diabetic and other populations at risk for chronic kidney disease. As a screening test for eGFR, it has about the same predictive value as eGFR derived from creatinine.
A sample of amniotic fluid collected for fetal lung maturity studies from a woman with a pregnancy compromised by hemolytic disease of the newborn (HDN) has a creatinine of 88 mg/dL. What is the most likely cause of this result?
The fluid is urine from accidental puncture of the urinary bladder
Creatinine levels in this range are found only in urine specimens. Adults usually excrete between 1.2 and 1.5 g of creatinine per day. For this reason, creatinine is routinely measured in 24-hour urine samples to determine the completeness of collection. A 24-hour urine with less than 0.8 g/day indicates that some
of the urine was probably discarded. Creatinine is also used to evaluate fetal maturity. As gestation progresses, more creatinine is excreted into the amniotic fluid by the fetus. Although a level above
2 mg/dL is not a specific indicator of maturity, a level below 2 mg/dL indicates immaturity.
Which analyze should be reported as a ratio using creatinine concentration as a reference?
Urinary microalbumin
Measurement of urinary microalbumin concentration should be reported as a ratio of albumin to creatinine (e.g., mg albumin per g creatinine). This eliminates the need for 24-hour collection in order to avoid variation caused by differences in fluid intake. A dry reagent strip test for creatinine is available that measures the ability of a creatinine-copper complex to break down H2O2 , forming a colored complex. The strip uses buffered copper II sulfate, tetramethylbenzidine, and anhydrous peroxide. Binding of creatinine in urine to copper forms a peroxidase-like complex that results in oxidation of the benzidine compound. Also, 24-hour urinary metanephrines, vanillylmandelic acid, and homovanillic acid are reported per gram creatinine when measured in infants and children in order to compensate for differences in body size.
Urea is produced from:
The catabolism of proteins and amino acids
Urea is generated by deamination of amino acids. Most is derived from the hepatic catabolism of proteins. Uric acid is produced by the catabolism of purines. Oxidation of pyrimidines produces orotic acid.
Urea concentration is calculated from the BUN by multiplying by a factor of:
2.14
BUN is multiplied by 2.14 to give the urea concentration in mg/dL.
BUN (mg/dL) = urea × (% N in urea ÷ 100)
Urea = BUN × 1/(% N in urea ÷ 100)
Urea = BUN × (1/0.467) = 2.14
Which of the statements below about serum urea is true?
BUN is elevated in prerenal as well as renal failure
Urea is completely filtered by the glomeruli but reabsorbed by the renal tubules at a rate dependent upon filtrate flow and tubular status. Urea levels are a sensitive indicator of renal disease, becoming elevated by glomerular injury, tubular damage, or poor blood flow to the kidneys (prerenal failure). Serum urea (and BUN) levels are influenced by diet and are low in necrotic liver disease.
A patient's BUN is 60 mg/dL and serum creatinine is 3.0 mg/dL. These results suggest:
Prerenal failure
BUN is affected by renal blood flow as well as by glomerular and tubular function. When blood flow to the kidneys is diminished by circulatory insufficiency (prerenal failure), glomerular filtration decreases and tubular reabsorption increases due to slower filtrate flow. Because urea is reabsorbed, BUN levels rise higher than creatinine. This causes the BUN:creatinine ratio to be greater than 10:1 in prerenal failure.
Urinary urea measurements may be used for calculation of:
Nitrogen balance
Because BUN is handled by the tubules, serum levels are not specific for glomerular filtration rate. Urea clearance is influenced by diet and liver function as well as renal function. Protein intake minus excretion determines nitrogen balance. A negative balance (excretion exceeds intake) occurs in stress, starvation, fever, cachexia, and chronic illness.
Nitrogen balance = (Protein intake in grams per day ÷ 6.25) - (Urine urea nitrogen in grams per day + 4), where 4 estimates the protein nitrogen lost in the feces per day and dividing by 6.25 converts protein to protein nitrogen.
BUN is determined electrochemically by coupling the urease reaction to measurement of:
The timed rate of increase in conductivity
A conductivity electrode is used to measure the increase in conductance of the solution as urea is hydrolyzed by urease in the presence of sodium carbonate.
Urea + H2O → 2NH3 + CO2
2NH3 + 2H2O + Na2CO3 → 2NH4+ + CO3^-2 + 2NaOH
Ammonium ions increase the conductance of the solution. The timed rate of current increase is proportional to the BUN concentration. Alternatively, the ammonium ions produced can be measured using an ion-selective electrode.
In the ultraviolet enzymatic method for BUN, the urease reaction is coupled to a second enzymatic reaction using:
Glutamate dehydrogenase
BUN is most frequently measured by the urease-UV method in which the urease reaction is coupled
to the glutamate dehydrogenase reaction, generating NAD+.
When the urease reaction is performed under first-order conditions, the decrease in absorbance at 340 nm is proportional to the urea concentration.
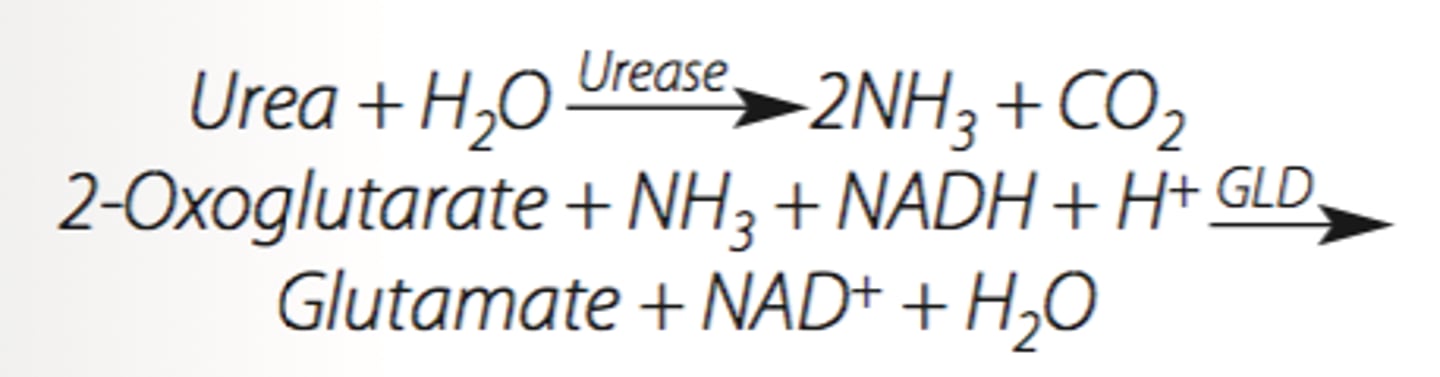
Which product is measured in the coupling step of the urease-UV method for BUN?
NAD+
In the urease-UV method, urease is used to hydrolyze urea, forming CO2 and ammonia. Glutamate dehydrogenase catalyzes the oxidation of NADH, forming glutamate from 2-oxoglutarate and ammonia. The glutamate dehydrogenase reaction is used for measuring both BUN and ammonia.
Which enzyme deficiency is responsible for phenylketonuria (PKU)?
Phenylalanine hydroxylase
PKU is an overflow aminoaciduria resulting from the accumulation of phenylalanine. It is caused by a deficiency of phenylalanine hydroxylase, which converts phenylalanine to tyrosine. Excess phenylalanine accumulates in blood. This is transaminated, forming phenylpyruvic acid, which is excreted in the urine.
Which of the following conditions is classified as a renal-type aminoaciduria?
Fanconi syndrome
Fanconi syndrome is an inherited disorder characterized by anemia, mental retardation, rickets, and aminoaciduria. Because the aminoaciduria results from a defect in the renal tubule, it is classified as a (secondary-inherited) renal-type aminoaciduria. Wilson's disease (inherited ceruloplasmin deficiency) causes hepatic failure. It is classified as a secondary-inherited overflow-type aminoaciduria because the aminoaciduria results from urea cycle failure. Hepatitis is classified as a secondary-acquired overflow-type aminoaciduria. Homocystinuria is a primary-inherited overflow-type aminoaciduria, and is caused by a deficiency of cystathionine synthase.
Which aminoaciduria results in the overflow of branched chain amino acids?
Homocystinuria
Valine, leucine, and isoleucine accumulate due to branched-chain decarboxylase deficiency in maple syrup urine disease. These are transaminated to ketoacids that are excreted, giving urine a maple sugar odor. Alkaptonuria is caused by homogentisic acid oxidase deficiency, causing homogentisic aciduria. Homocystinuria is a no-threshold-type aminoaciduria that usually results from cystathionine synthase deficiency.
In addition to phenylketonuria, maple syrup urine disease, and homocystinuria, what other aminoaciduria can be detected by tandem MS?
Citrullinemia
Most states use electrospray ionization tandem-mass spectroscopy (MS/MS), which can detect over 20 inborn errors of metabolism from a single blood spot. Typically, this includes phenylketonuria, tyrosinemia, maple syrup urine disease, homocystinuria, citrullinemia, and argininosuccinate acidemia. The latter two are errors of the urea cycle.
Of the methods used to measure amino acids, which is capable of measuring fatty acids simultaneously?
Tandem-mass spectroscopy
All four methods are able to separate each amino acid (up to 40 species); however, tandem-mass spectroscopy with electrospray ionization can measure amino acids, organic acids such as methylmalonic
acid, and fatty acids. The acids are eluted from the dried blood spot with methanol after addition of internal standards and then derivatized with butanol-hydrochloric acid. Soft ionization of the butyl esters of the amino acids and butyl acylcarnitines of organic and fatty acids yields parent ions, and these are fragmented by collision with argon in the second mass filter to produce daughter ions. A process called multiple reaction monitoring identifies both parent
ions and neutral fragments that identify the acids. Carnitines are quarternary ammonium compounds that carry the acids across the mitochondrial membrane.
Blood ammonia levels are usually measured in order to evaluate:
Hepatic coma
Hepatic coma is caused by accumulation of ammonia in the brain as a result of liver failure. The ammonia increases central nervous system pH and is coupled to glutamate, a central nervous system neurotransmitter, forming glutamine. Blood and cerebrospinal fluid ammonia levels are used to distinguish encephalopathy caused by cirrhosis or other liver disease from nonhepatic causes and to monitor patients with hepatic coma.
Enzymatic measurement of ammonia requires which of the following substrates and coenzymes?
Subtrate: α-Ketoglutarate; Coenzyme: NADH
Enzymatic assays of ammonia utilize glutamate dehydrogenase (GLD). This enzyme forms glutamate from α-ketoglutarate (2-oxoglutarate) and ammonia, resulting in oxidation of NADH. The rate of absorbance decrease at 340 nm is proportional to ammonia concentration when the reaction rate is maintained under first-order conditions.
Which statement about ammonia is true?
Hepatic coma can result from Reye's syndrome
Ammonia produced in the intestines from the breakdown of proteins by bacterial enzymes is the primary source of plasma ammonia. Most of the ammonia absorbed from the intestines is transported to the liver via the portal vein and converted to urea. Blood ammonia levels will rise in any necrotic liver disease including hepatitis, Reye's syndrome, and drug-induced injury such as acetaminophen poisoning. In hepatic cirrhosis, shunting of portal blood to the general circulation causes blood ammonia levels to rise. Ammonia crosses the blood- brain barrier, which accounts for the frequency of central nervous system complications and, if severe, hepatic coma.
SITUATION: A sample for ammonia assay is taken from an IV line that had been capped and injected with lithium heparin (called a heparin lock). The sample is drawn in a syringe containing lithium heparin, and immediately capped and iced. The plasma is separated and analyzed within 20 minutes of collection, and the result is 50 μg/dL higher than one measured 4 hours before. What is the most likely explanation of these results?
Stasis of blood in the line caused increased ammonia
Falsely elevated blood ammonia levels are commonly caused by improper specimen collection. Venous stasis and prolonged storage cause peripheral deamination of amino acids, causing a falsely high ammonia level. Plasma is the sample of choice since ammonia levels increase with storage. Lithium heparin and EDTA are acceptable anticoagulants; the anticoagulant used should be tested to make sure it is free of ammonia. A vacuum tube can be used if filled completely. Serum may be used provided the tube is iced immediately, and the serum is separated as soon as the sample clots. The patient should be fasting and must not have smoked for 8 hours because tobacco smoke can double the plasma ammonia level.
Uric acid is derived from the:
Catabolism of purines
Uric acid is the principal product of purine (adenosine and guanosine) metabolism. Oxidation of proteins yields urea along with CO2, H2O, and inorganic acids. Catecholamines are oxidized, forming vanillylmandelic acid (VMA) and homovanillic acid (HVA).
Which of the following conditions is associated with hyperuricemia?
Renal failure
Excessive retention of uric acid results from renal failure and diuretics (or other drugs) that block uric acid excretion. Hyperuricemia may result from overproduction of uric acid in primary essential gout or excessive cell turnover associated with malignancy and chemotherapy. Overproduction may also result from an enzyme deficiency in the pathway forming guanosine triphosphate (GTP)
or adenosine monophosphate (AMP) (purine salvage). Hyperuricemia is also associated with ketoacidosis and lactate acidosis, hypertension, and hyperlipidemia. Xanthine oxidase converts xanthine to uric acid; therefore, a deficiency of this enzyme results in low serum levels of uric acid. Paget's disease of bone causes cyclic episodes of bone degeneration and regeneration and is associated with very high serum ALP and urinary calcium levels.
Orders for uric acid are legitimate stat requests because:
Levels above 10 mg/dL cause urinary tract calculi
Uric acid calculi form quickly when the serum uric acid level reaches 10 mg/dL. They are translucent compact stones that often lodge in the ureters, causing postrenal failure.
Which uric acid method is associated with negative bias caused by reducing agents?
Uricase coupled to the Trinder reaction
The peroxidase-coupled uricase reaction is the most common method for measuring uric acid in serum or plasma. Uricase methods form allantoin, carbon dioxide, and hydrogen peroxide from the oxidation of uric acid. When peroxide is used to oxidize a Trinder dye (e.g., a phenol derivative and 4-aminoantipyrine), some negative bias may occur when high levels of ascorbate or other reducing agents are present. Rate UV methods are free from this interference. Reduction of phosphotungstic acid by uric acid forms tungsten blue. This colorimetric reaction is nonspecific, resulting in falsely elevated uric acid caused by proteins and many other reducing substances.