Speciation #16
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
Taxonomy
Def: the science of communicating evolutionary relationships
the process of naming, defining, and classifying groups of organisms
relies on phylogeny to help establish & define monophyletic taxa
has a hierarchical system of classification
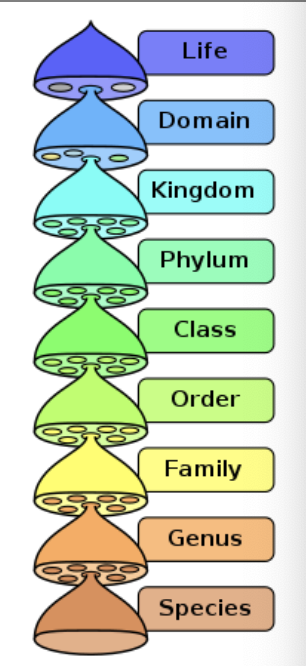
the science of communicating evolutionary relationships
Taxonomy
Species
Def: metapopulations that evolve independently from other metapopulations
communicating species
Communicating species
Microevolution
Def: the evolutionary processes and effects occurring within and between populations
evolution occurring below the species level
the evolutionary processes and effects occurring within and between populations
Microevolution
Macroevolution
Def: evolutionary processes and effects occuring between metapopulations
evolution occuring at or above the species level
evolutionary processes and effects occuring between metapopulations
Macroevolution
Metapopulation
Speciation
Def: the study of evolution occurring at that transition from Microevolution to Macroevolution
the evolutionary process by which gene flow between 2 populations stops, and those populations begin diverging into independent metapopulations
Barriers to reproduction that leads to populations diverging
Geographic barriers (allopatric vs parapatric vs sympatric)
Ecological barriers
Behavioral barriers
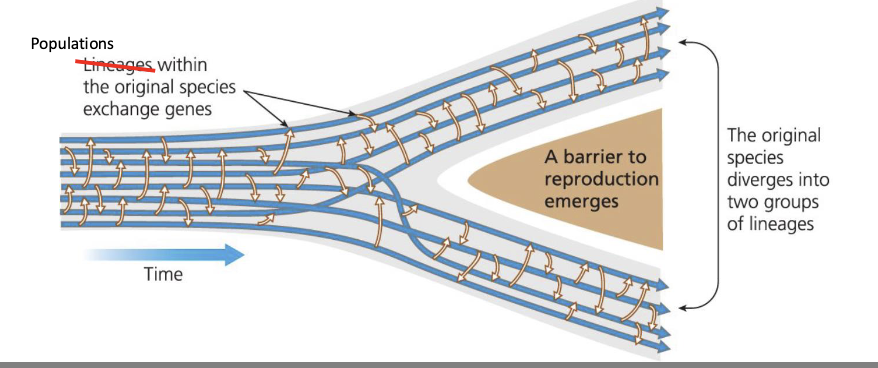
the study of evolution occuring at that transition from Microevolution to Macroevolution
Speciation
Allopatric speciation
Def: when populations become separated by geographic barriers that interfere with gene flow and create speciation events
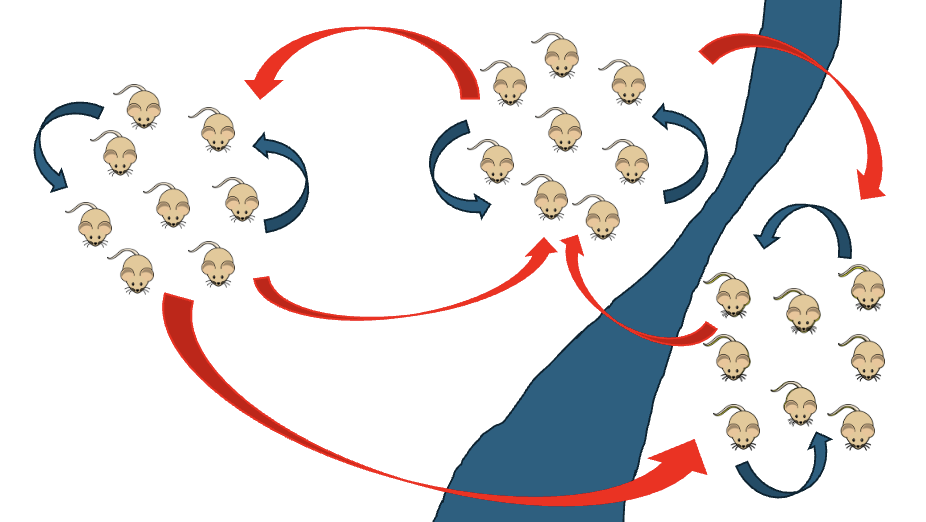
Allopatric speciation
What kind of speciation is this?
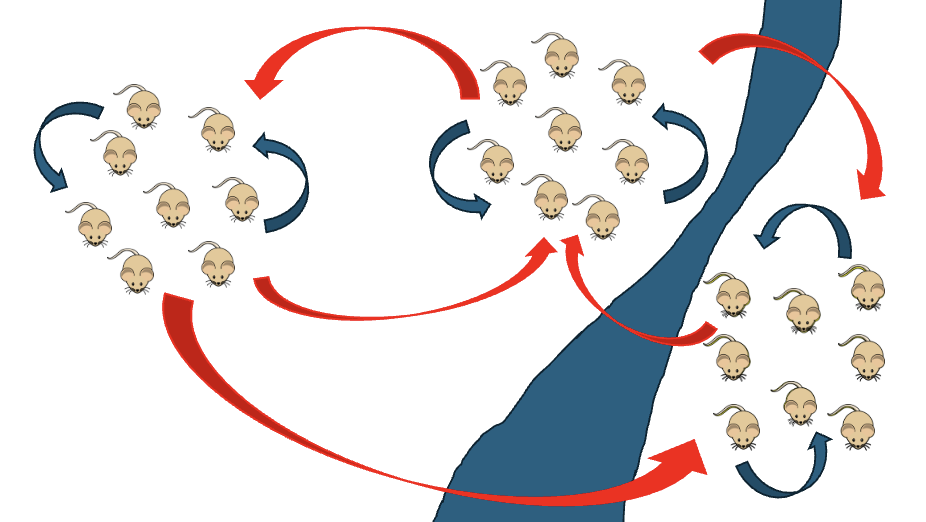
Parapatric
Def: speciation that occurs when diverging populations have distributions (genes) that remain adjacent (similar) to one another without total geographic isolation
an environmental or selection gradient forms across the total range of populations, causing population to diverge from one another
Parapatric
what kind of speciation is this?
Sympatric
Def: speciation that occurs even when the diverging populations are not geographically separated
disruptive force most often ecologically or behaviorally-based, leading to changes in niche partitioning or sexual selection pressures

Sympatric
What kind of speciation is this?

Hybridization
if separated populations occur in the same or overlapping geographic areas, and there is a potential for gene flow, we need to compare 3 diff fitness relationships:
If the fitness of the hybrid offspring are the same as the fitness of the true-breeding offspring → populations will NOT speciate
If the fitness of the hybrid offspring is lower than the fitness of the true-breeding offspring → populations will remain reproductively isolated
the populations will remain reproductively isolated because since the fitness of the hybrid offspring is lower, natural selection favors the true-breeding offspring, reducing gene flow and reinforcing reproductive isolation
If the fitness of the hybrid offspring is lower than the fitness of the true-breeding offspring → populations will remain reproductively isolated
why?
Reproductive Isolation
not good for the parent/species population to spend resources on a hybrid offspring that has a lower fitness
so selective pressures to prevent hybridization:
Pre-mating barriers = ecological or behavioral separation prevents mating
Pre-zygotic barriers = physiological incompatibility between mates or their gametes prevents successful fertilization
Post-zygotic barriers = hybrid offspring is produced, but it has a fitness of 0
Polyploidy
Def: Having three or more homologous chromosome sets
common in flowering plants
results from errors in cell division or hybridization between different species
how plants readily hybridize
hybrid offspring are fertile through self-pollination
even if they are not fertile
many can propagate themselves clonally (asexual reproduction)
a common source of diversity in plants
Having three or more homologous chromosome sets - how plants readily hybridize / a common source of diversity in plants
Polyploidy