Biology Vocab 3.1-3.3
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
Organic Compounds
Carbon based molecules
Hydrocarbons
Compounds composed of only carbon and hydrogen
Carbon skeleton
The chain of carbon atoms in an organic molecule — a backbone/structure
Isomers
Compounds with the same formula but different structures — Differing in positioning of double bonds (a feature that changes the molecule) — The different structures effect the way they link together
Functional groups
Groups of atoms that usually participate in chemical reactions and give specific chemical properties to organics
Hydroxyl groyp
A hydrogen atom bonded to an oxygen atom — makes molecules polar
Carbonyl group
A carbon atom linked by a double bond to an oxygen atom — Typically sugars
Carboxyl group
Carbon double-bonded to an oxygen and a hydroxyl group — acts as an acid by contributing hydrogen and becoming ionized
Carboxylic acids
Compounds with carboxyl groups
Amino group
Nitrogen atom bonded to two hydrogen atoms — acts as a base by picking up hydrogen from a solution
Amines
Organic compounds with an amino group — building blocks of proteins
Phosphate group
Phosphorus atom bonded to four oxygen atoms — Often involved in energy transfer — Usually ionized and attached to the c skeleton
Estradiol
A female sex hormone
Testosterone
A male sex hormone
Single bond
Covalent bond where two atoms share one electron pair (-)
Double bond
Covalent bond where two atoms share two electron pairs (=)
Macromolecules
Large biological molecules made up of smaller units — carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids
Polymers
Long chains of repeated smaller units called monomers
Monomer
Small molecules that link together to form polymers — building blocks of protein
Dehydration reaction/synthesis
Removes a molecule of water; removes hydrogen and hydroxyl from a polymer chain and the two create water (OH-) + (H+) = H2O — After water is taken away, it is now unstable and can join together to make one large polymer
Hydrolosis
Opposite of dehydration; means to break down with water — Transition into two small monomers
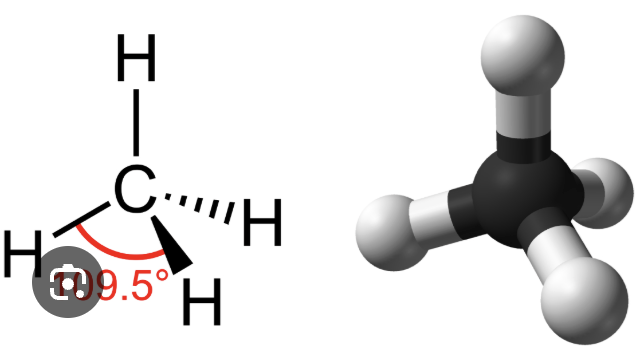
Tetrahedron
Object with four triangular slides — Occurs whenever a carbon atom participates in four single bonds
List the four classes of macromolecules
Carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids
What kind of charge to all hydrocarbons (C - H) have?
Non-polar
What do the functional groups do?
Help determine the properties of organic compounds
Ball and stick model
Building a polymer chain — One small polymer and another monomer that you want to bond BUT they already have a charge and are fat and happy. SO take a hydroxide from the polymer and a hydrogen from the monomer (dehydration synthesis). Now both of them can link up because you got rid of their charge
Space filling model
The opposite of the ball and stick model — placing water between the bond of the polymer and monomer (hydrolosis)