Brain Functions, Overview, and Nerves
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
Function of Cerebrum
source of intellectual activities (memories, recognition, etc.)
Function of Cerebral Cortex
"higher order" functions like language and information processing
Function of Frontal Lobe
reasoning, planning, emotions, problem solving, and the coordination of speech and of muscle movements
Function of Motor Cortex
controls voluntary movement
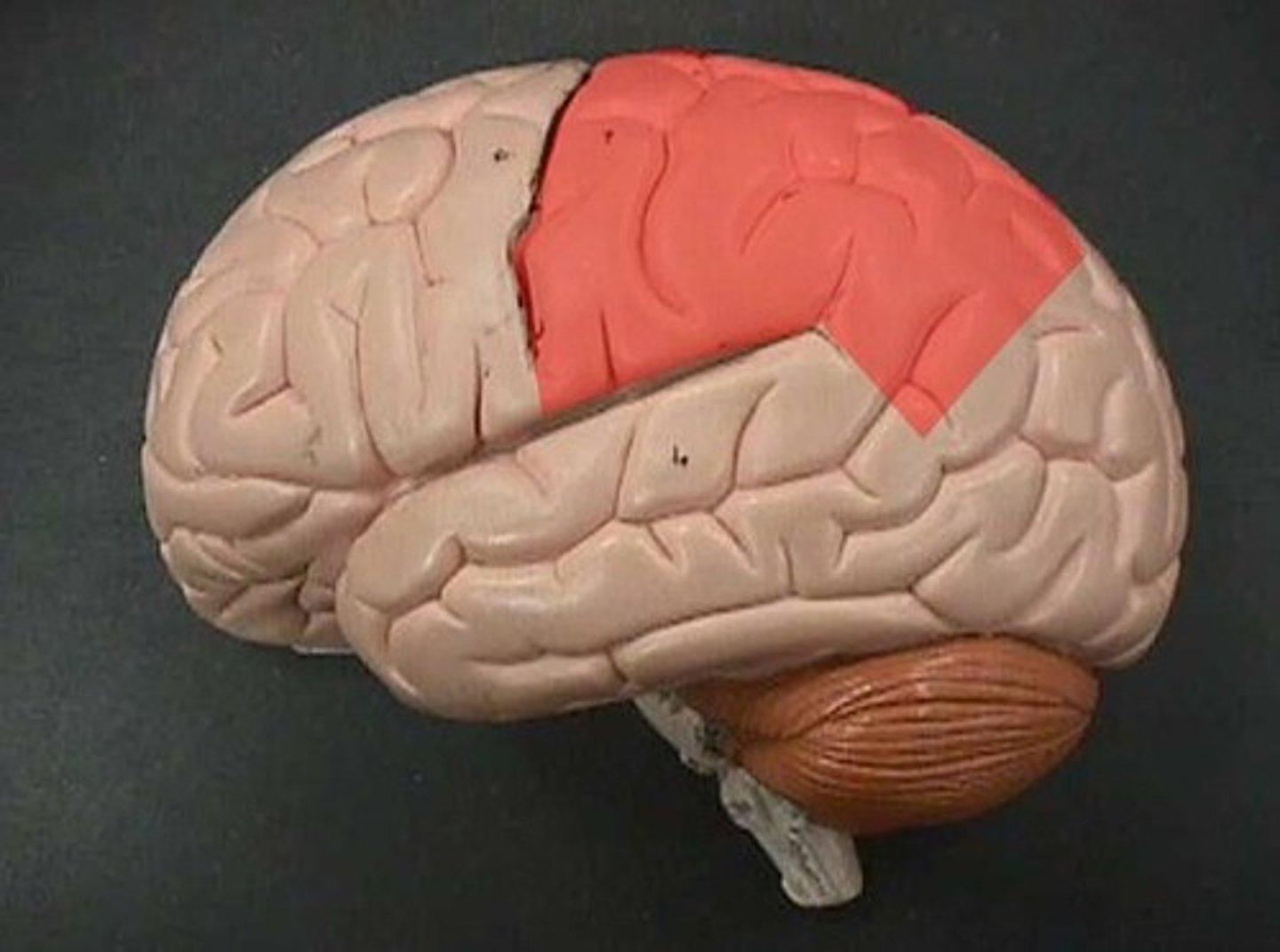
Function of Parietal Lobe
movement, orientation, recognition, perception of stimuli
Function of Sensory Cortex
facilitates the perception, interpretation, and understanding of touch, pressure, and pain
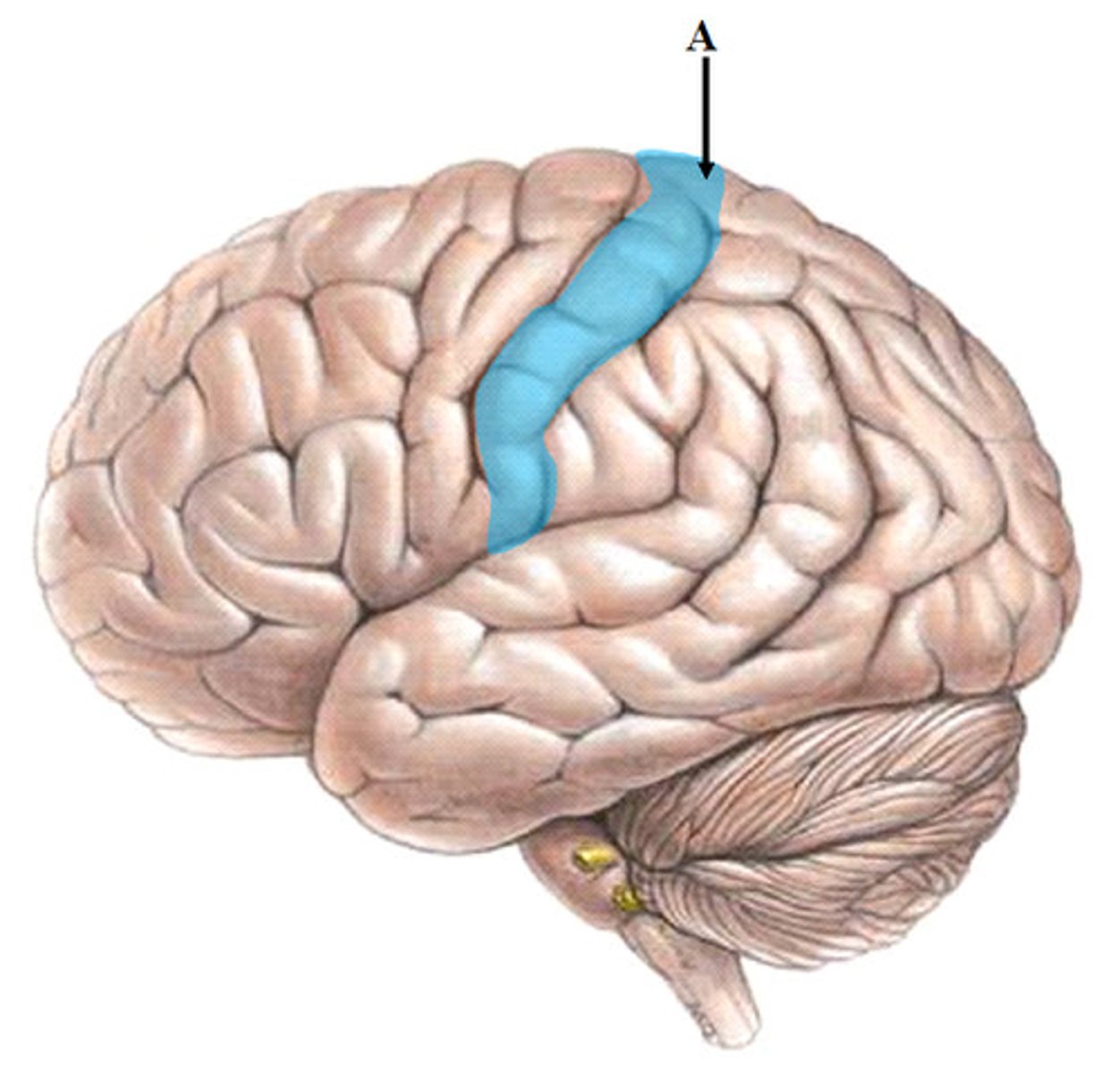
Function of Central Sulcus
separates frontal and parietal lobe
Function of Occipital Lobe
visual perception
Function of Temporal Lobe
perception and recognition of auditory stimuli, memory, and speech
Function of Cerebellum
regulation and coordination of movement, posture, and balance
Function of Brain Stem
vital life functions (breathing, heartbeat, blood pressure, etc.)
Function of Midbrain
vision, hearing, eye movement, and body movement.
Function of Pons
respiratory control, modifies respiration, sends info from forebrain to cerebellum; deal primarily with sleep, respiration, swallowing, bladder control, hearing, equilibrium, taste, eye movement, facial expressions, facial sensation, and posture.
Function of Medulla Oblongata
vital involuntary life processes, ex. Heart rate, respirations rhythm, blood pressure, visceral functions (vomit, swallow), decussation (crossover) of major motor tracts
Function of Spinal Cord
sends sensations from brain to body and returns motor commands
Function of Limbic System
group of interconnected structures that mediate emotions, learning, and memory
Function of Amygdala
emotional and social processing
Function of Thalamus
receive and relay sensory signals
Function of Function of Hypothalamus
maintain homeostasis
Function of Hippocampus
inhibition, memory storage, and space
Function of Diencephalon
sensory perception
Olfactory Nerve
Cranial nerve 1
*purely sensory
*sense of smell
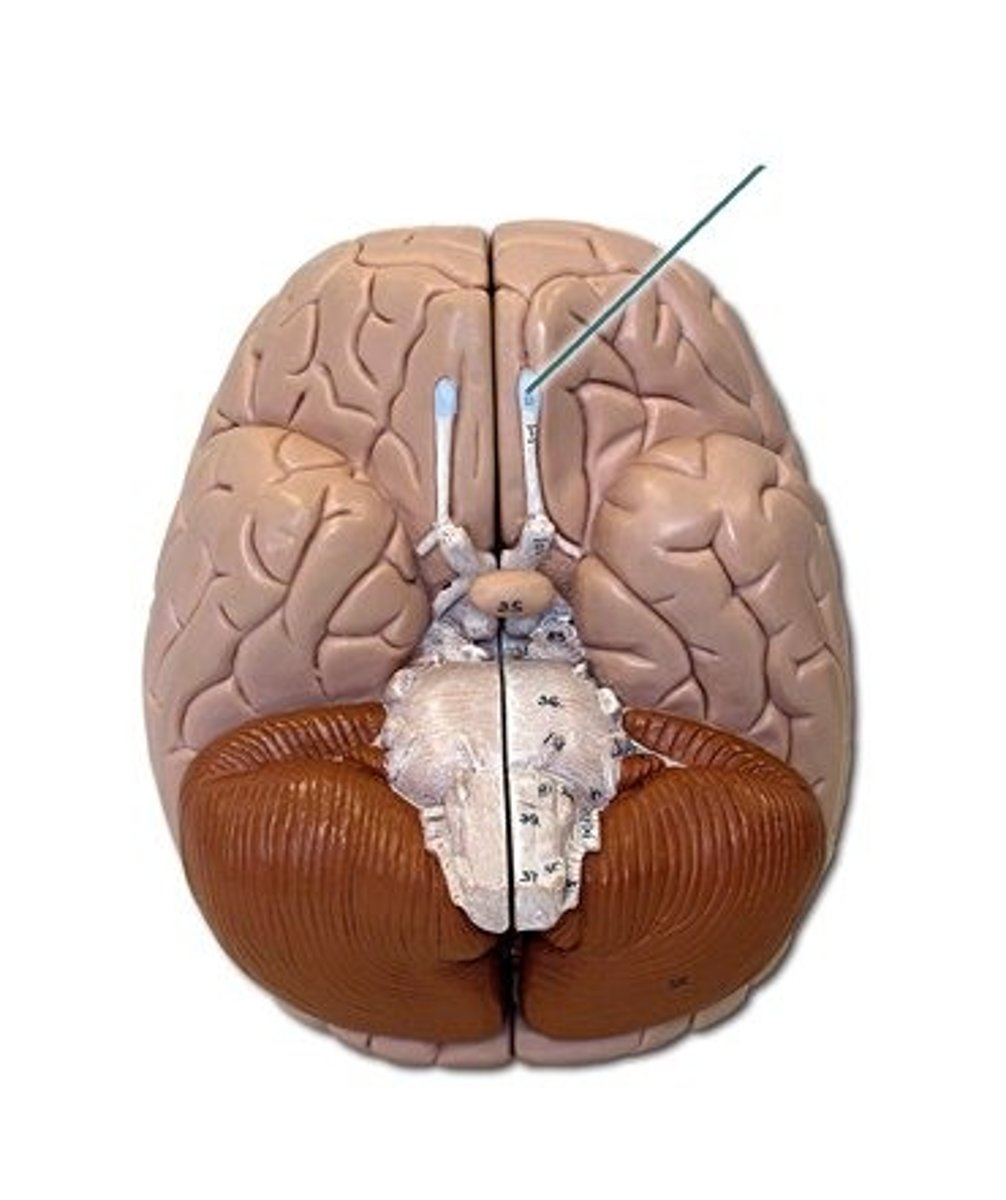
Optic Nerve
Cranial Nerve II
*purely sensory
*sense of sight
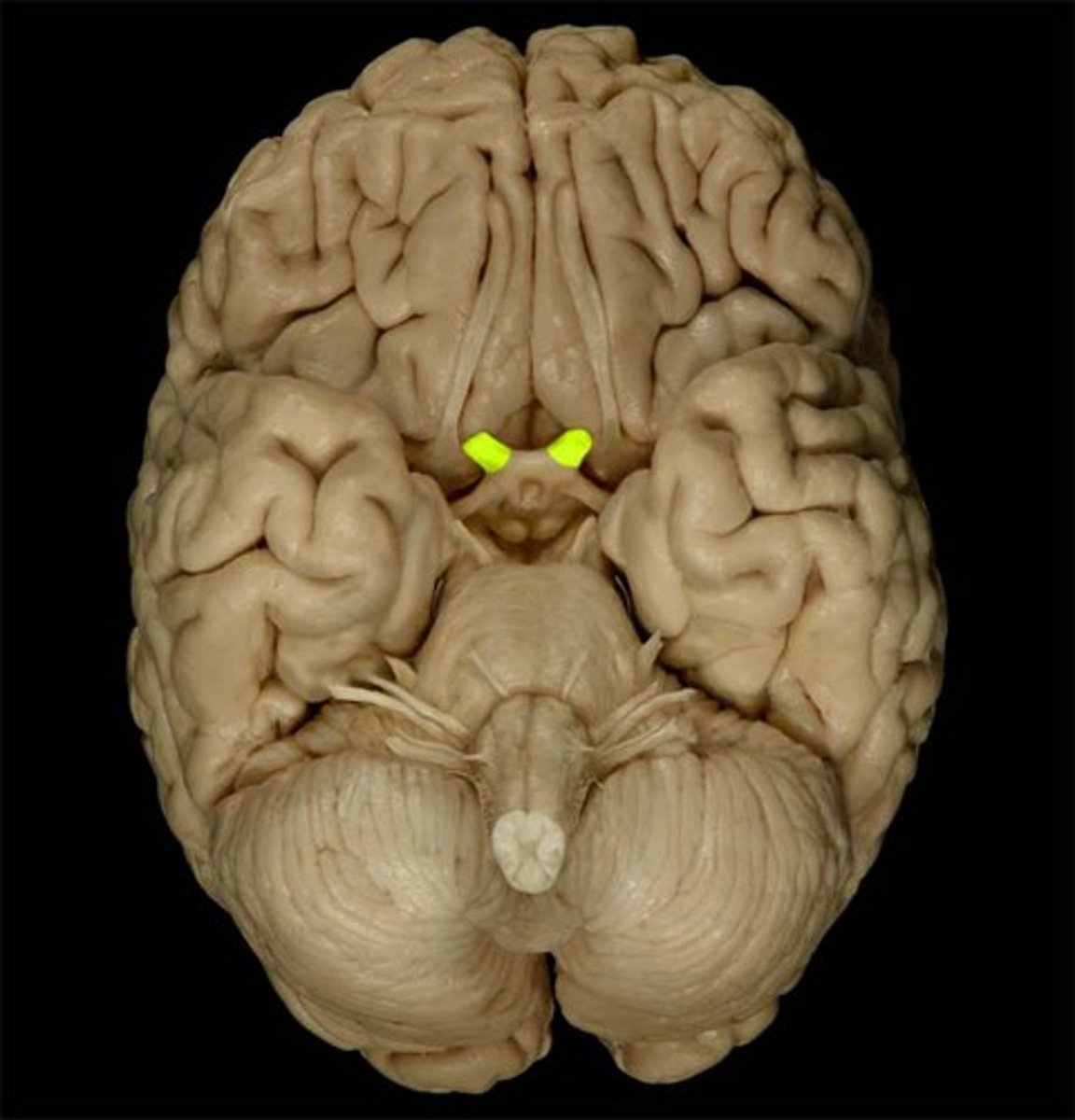
Oculomotor Nerve
Cranial Nerve III
*purely motor
*stimulates the ciliary smooth muscle - constrict pupil and bend lens (parasympathetic funcion
*moves eyeyball by controlling 4 eye skeletal muscles: medial rectus, inferior rectus, superior rectus, and inferior oblique
*attaches to the brainstem
*tested to check for brainstem activity (pupils fixed and dilated means that it is not functioning properly)
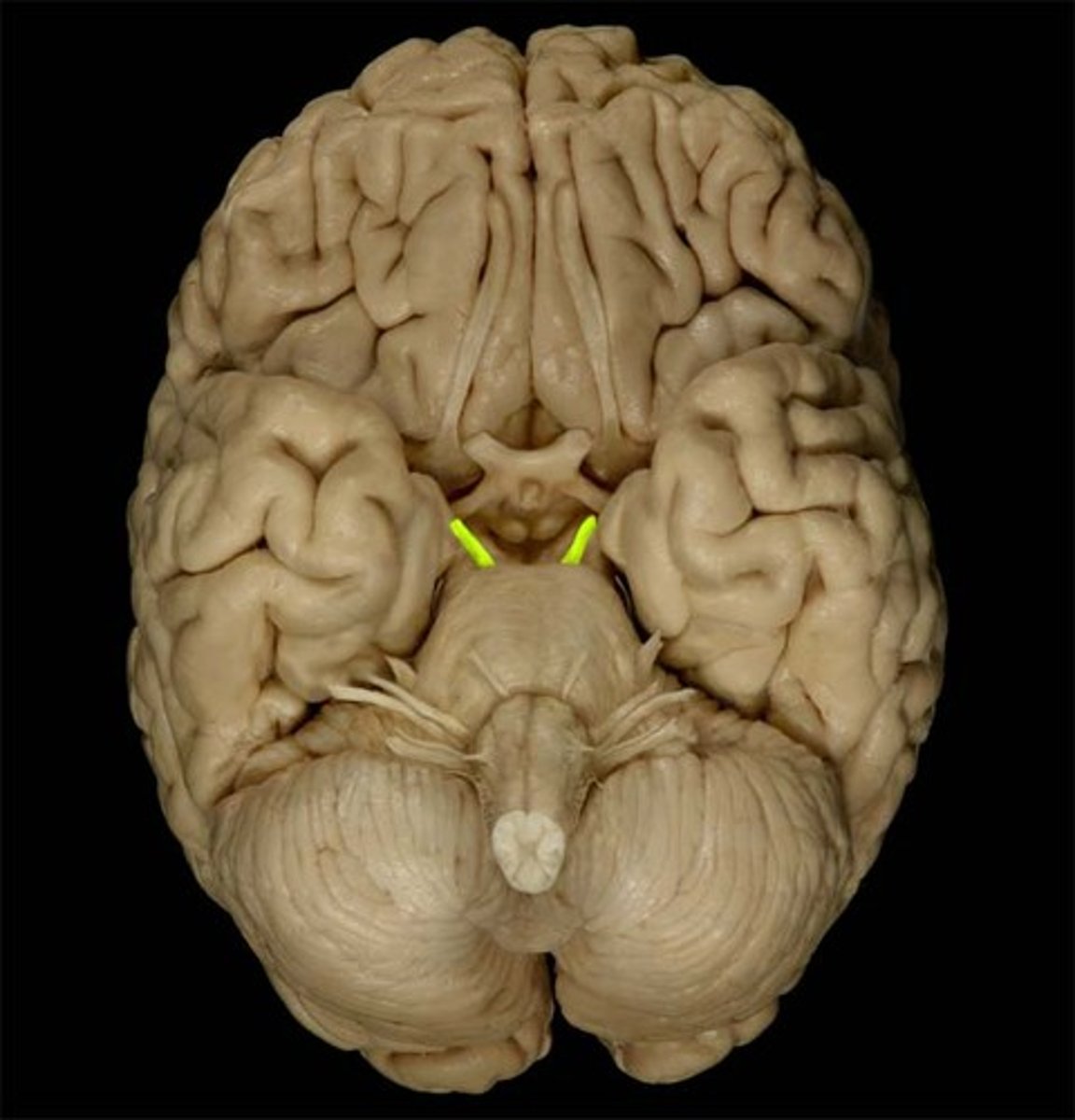
Trochlear Nerve
Cranial Nerve IV
*moves eyeball by controlling the superior oblique skeletal muscle
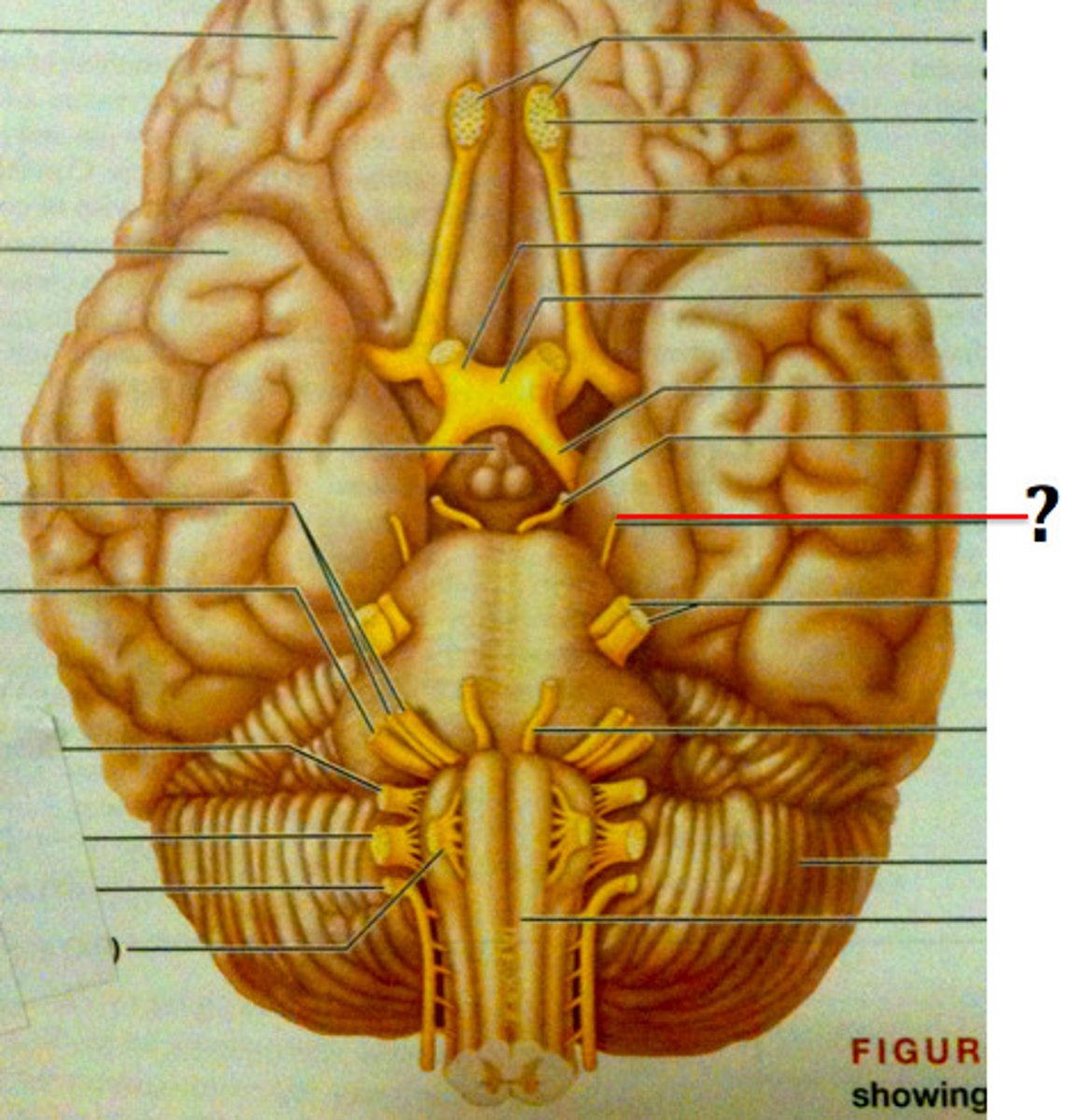
Trigeminal Nerve
*Cranial Nerve V
*responsible for sense of feeling on the face (three branches - forehead, upper jaw, and lower jaw)
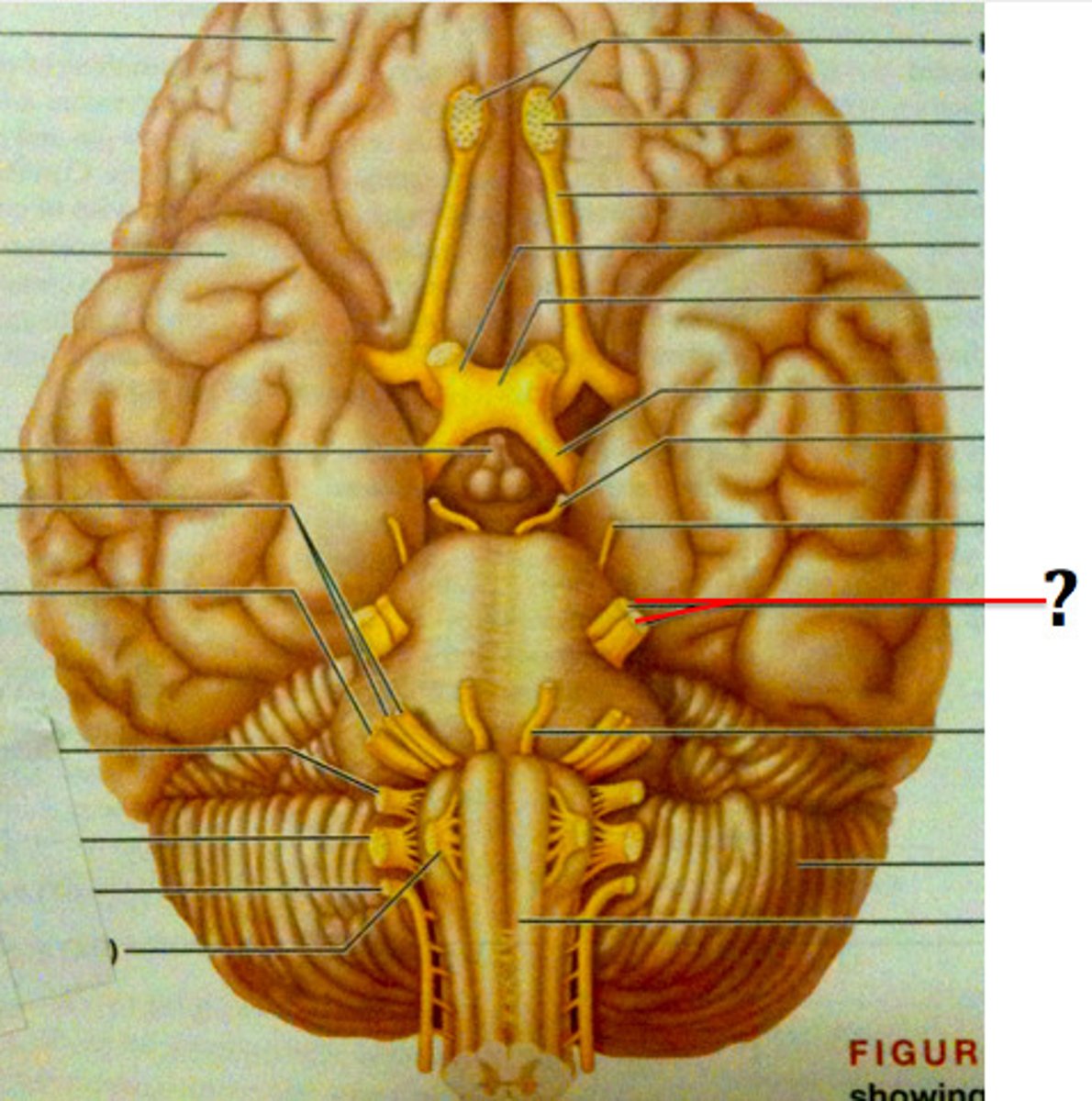
Abducens Nerve
Cranial Nerve VI
*purely motor
*moves eyeball (abducts it) by controlling the lateral rectus eye muscle
Facial Nerve
Cranial nerve VII
*Sensory - sense of taste for the front of the tongue. *Somatic Movement of the facial expression skeletal muscles
*parasympathetic stimulation of salivary and lacrimal glands.
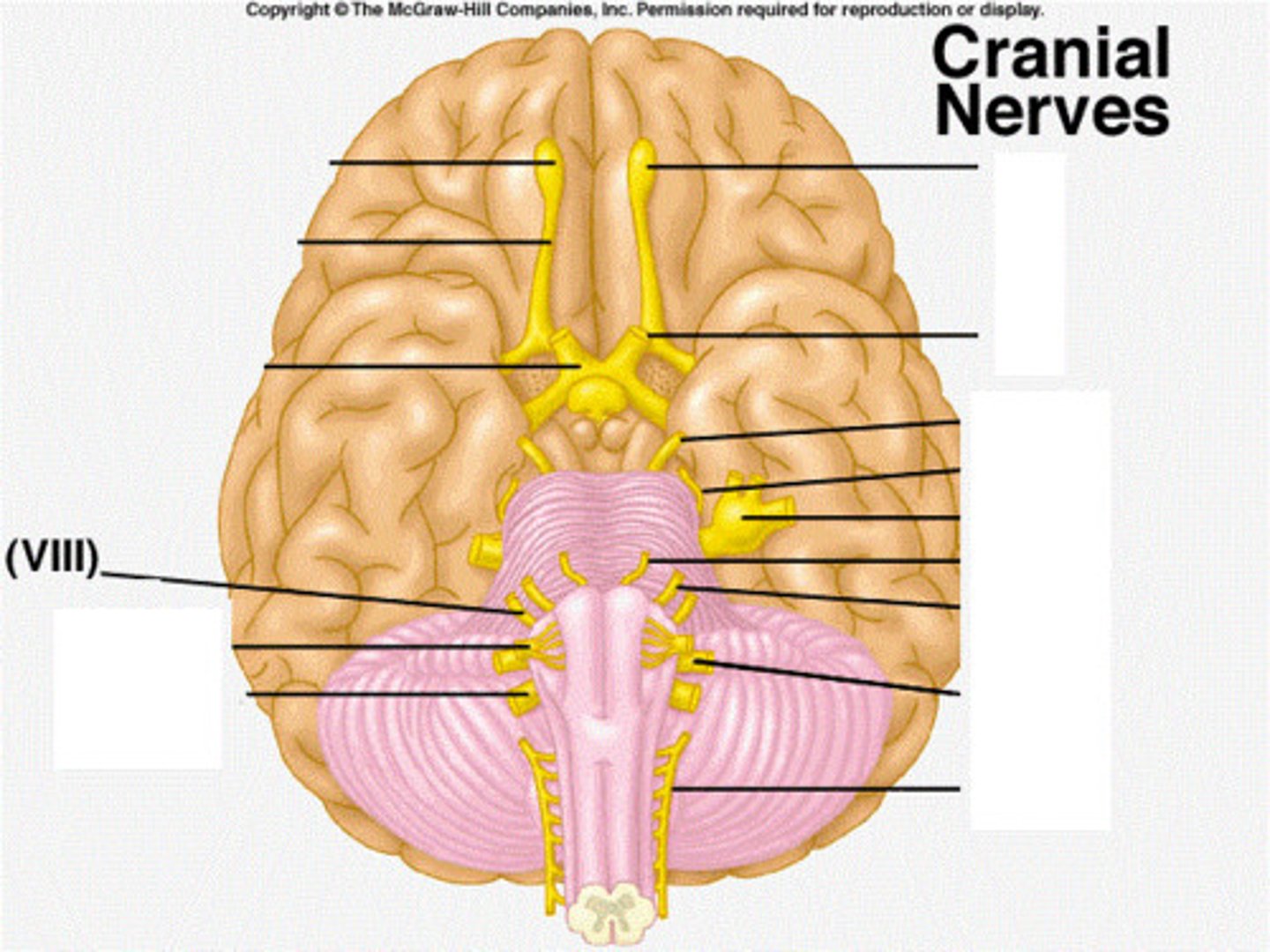
vestibulocochlear nerve
cranial nerve VIII
*purely sensory
*carries balance information and hearing to the temporal lobe for processing
glossopharyngeal nerve ("tongue and pharynx")
Cranial nerve IX.
*Sense of taste for the back of the tongue. *Somatic movement of the skeletal muscles for swallowing
*Parasympathetic stimulation of the parotid salivary glands.
*carries baroreptor information from the carotid sinuses
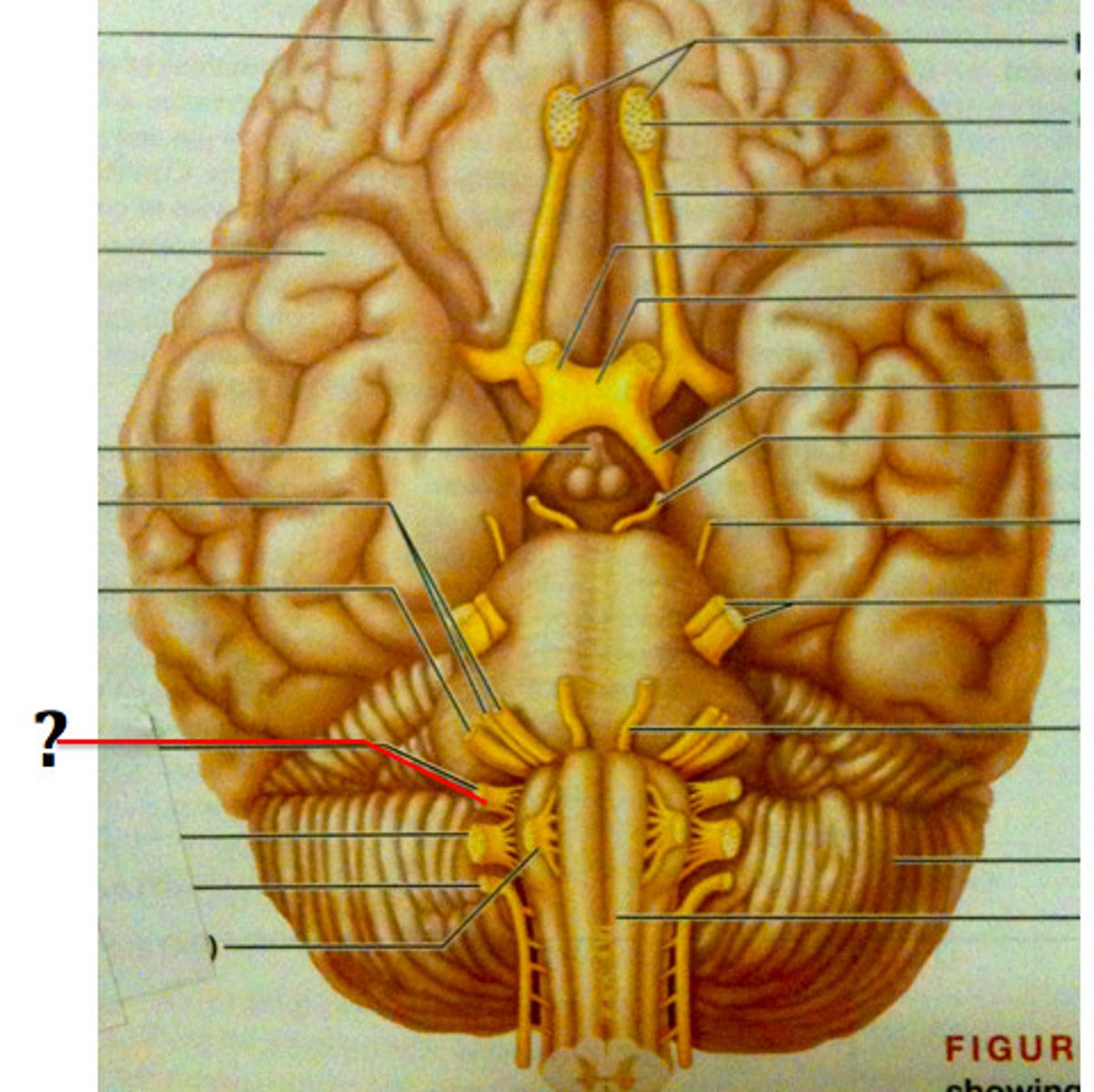
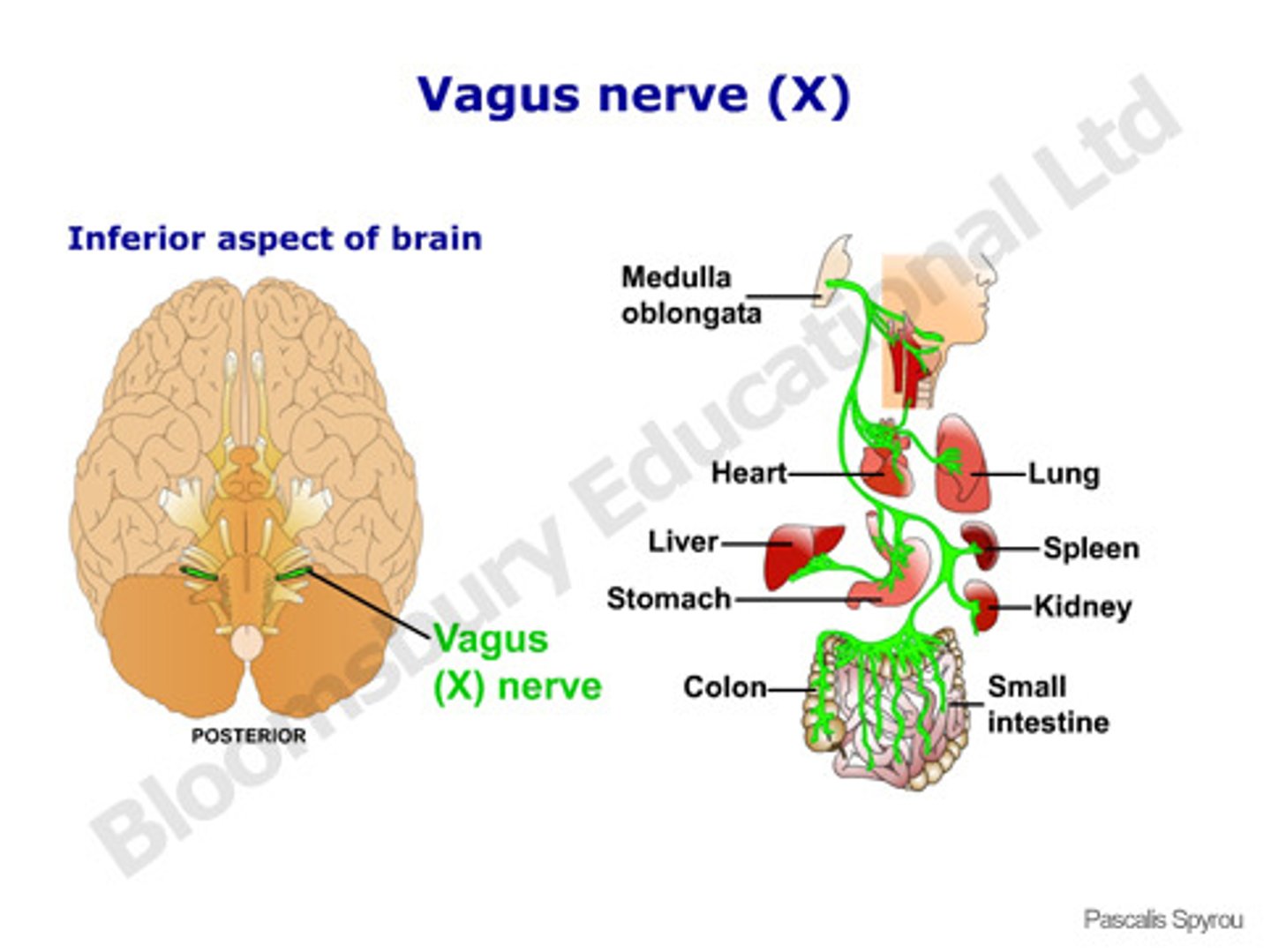
Vagus nerve ("wanderer")
Cranial nerve X.
*Sensory information from the internal organs -- particularly notable for connecting GI activity with the brainstem, and for carrying baroreceptor information from the heart to the brainstem.
*Parasympathetic motor for internal (visceral) organs - slows heart, dilates bronchi, stimulates GI organs, etc.
accessory nerve
Cranial Nerve XI
*purely somatic motor to move trapezius and sternocleidomastoid
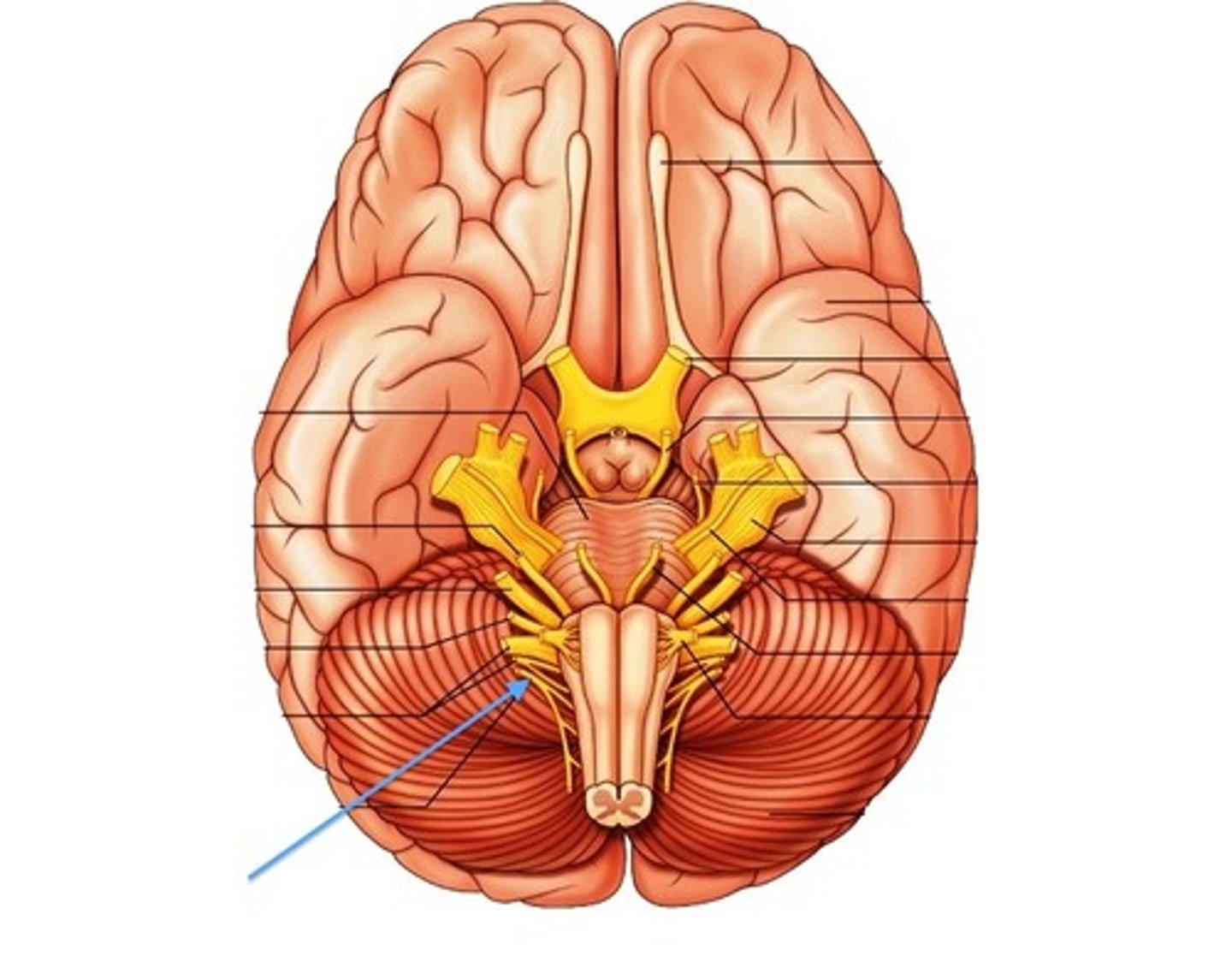
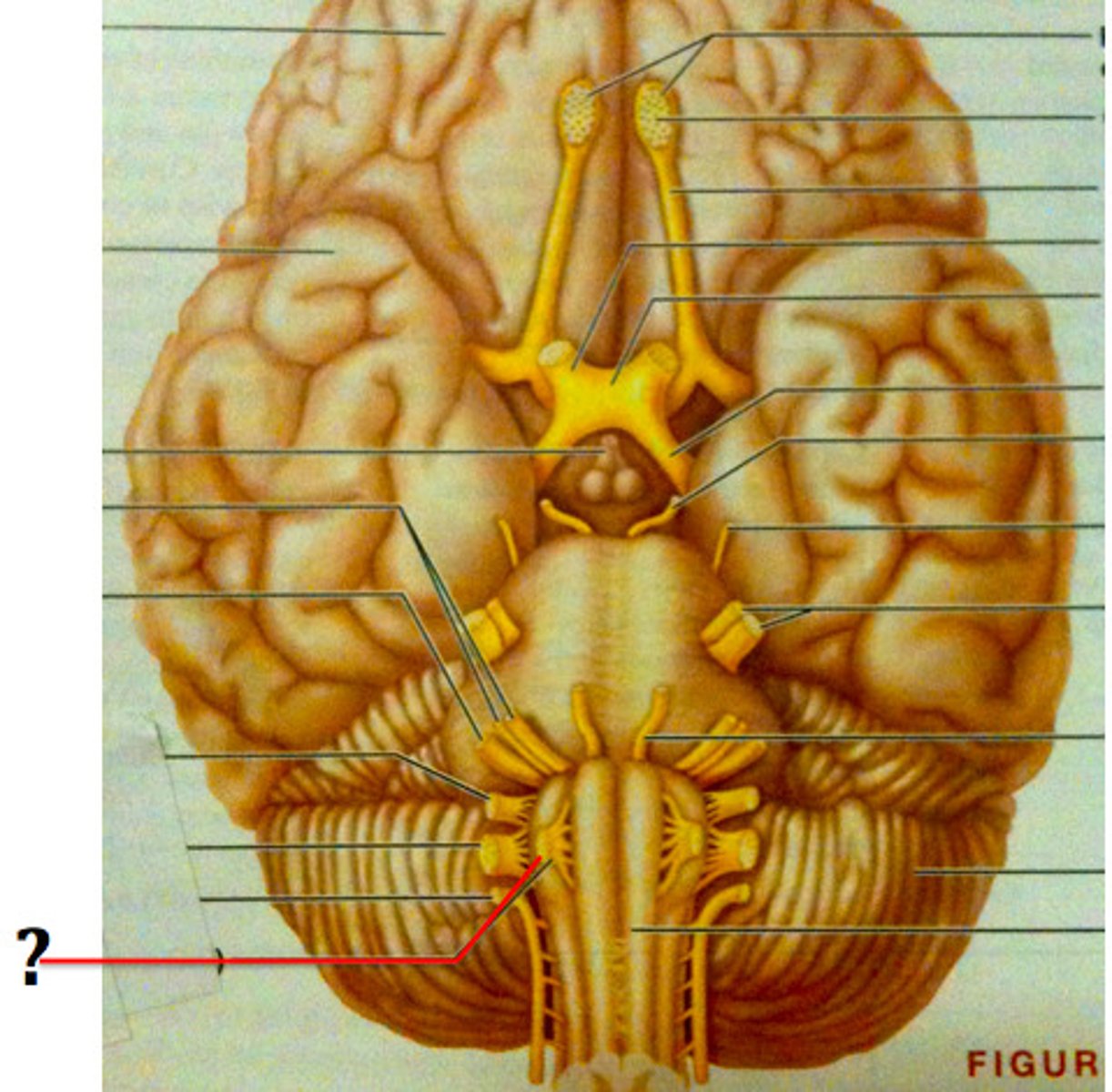
hypoglossal ("under tongue")
Cranial Nerve XII
*purely somatic motor
*controls tongue skeletal muscles
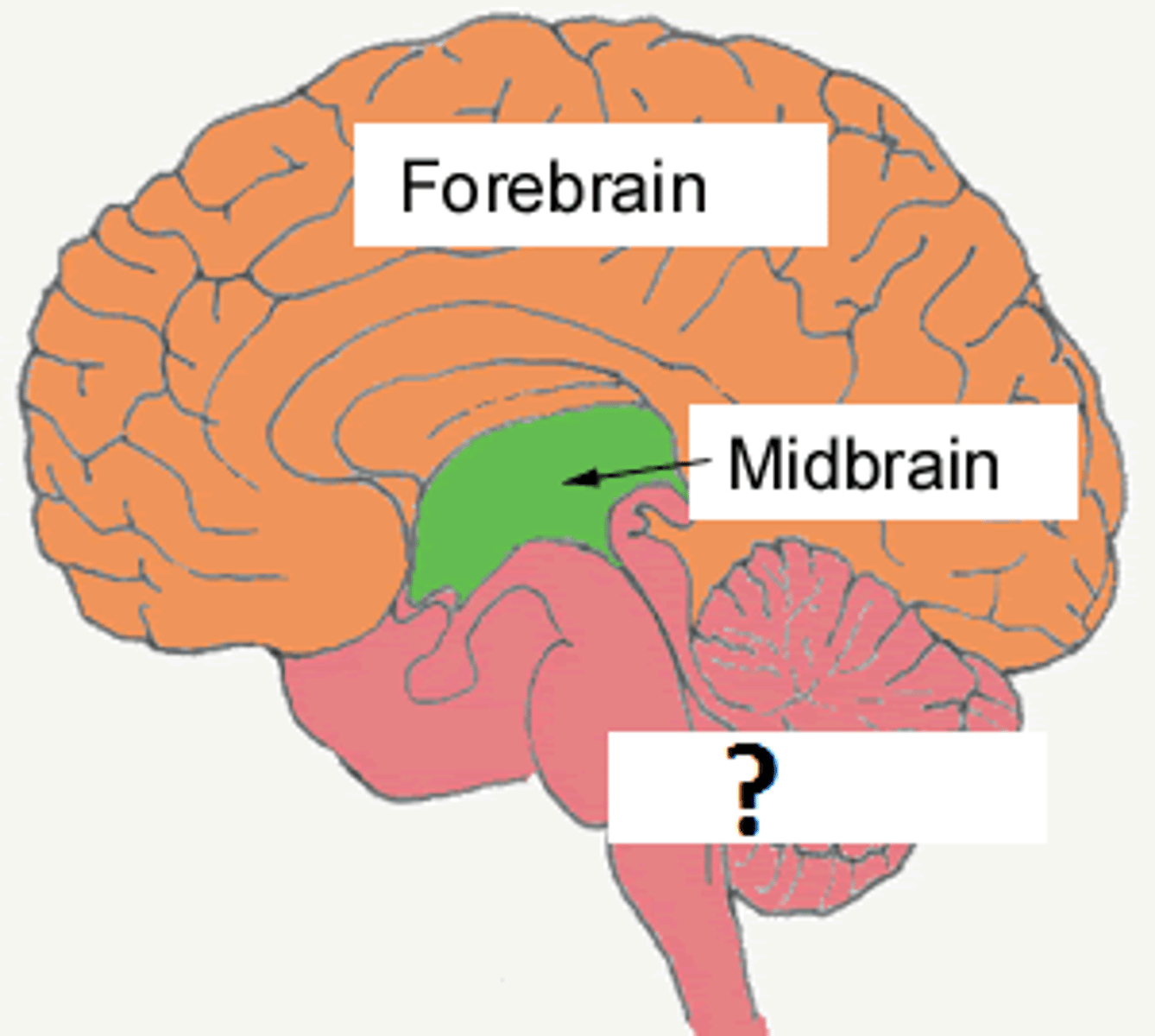
Forebrain
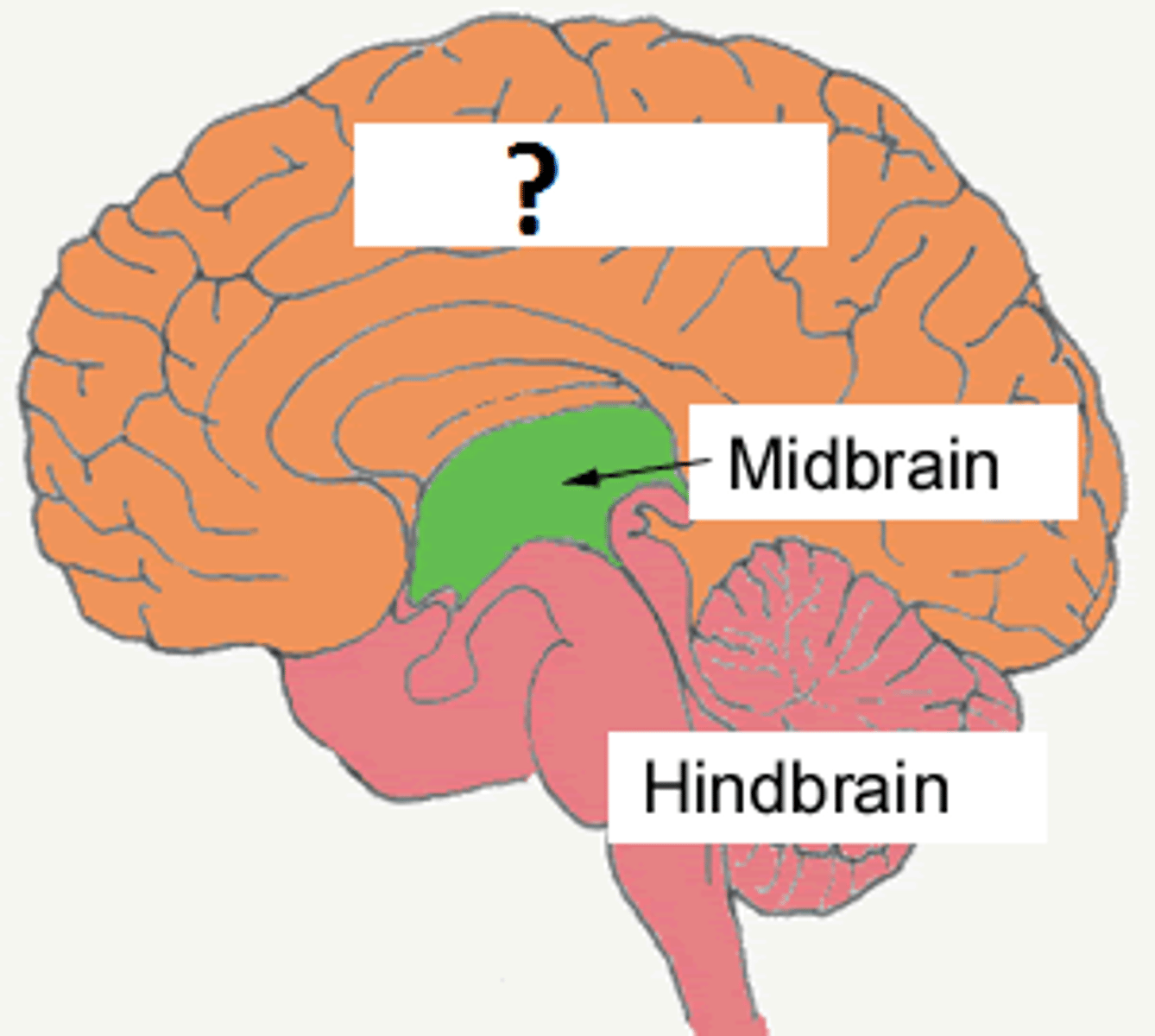
Midbrain (Mesencephalon)
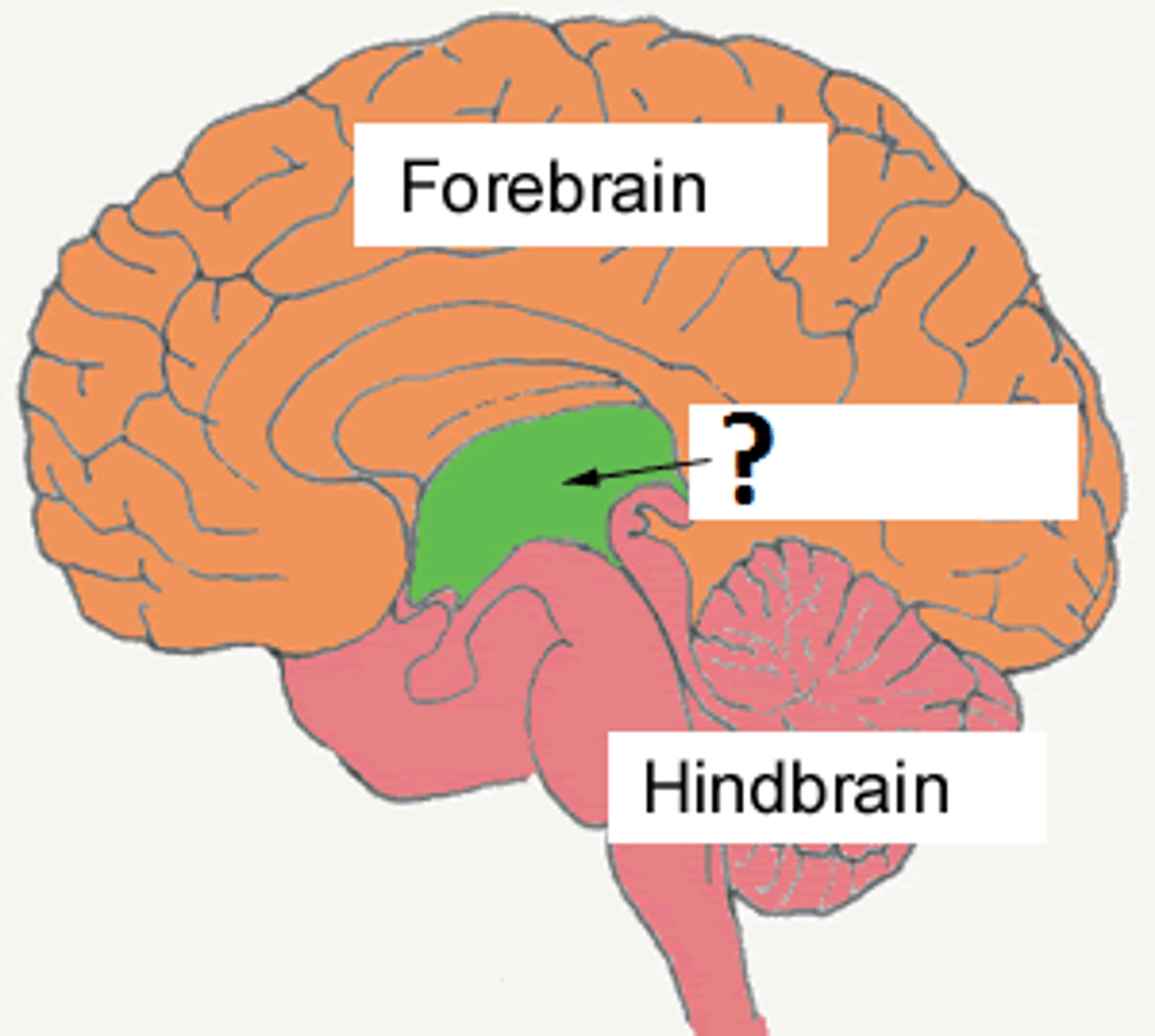
Hindbrain
Cerebrum
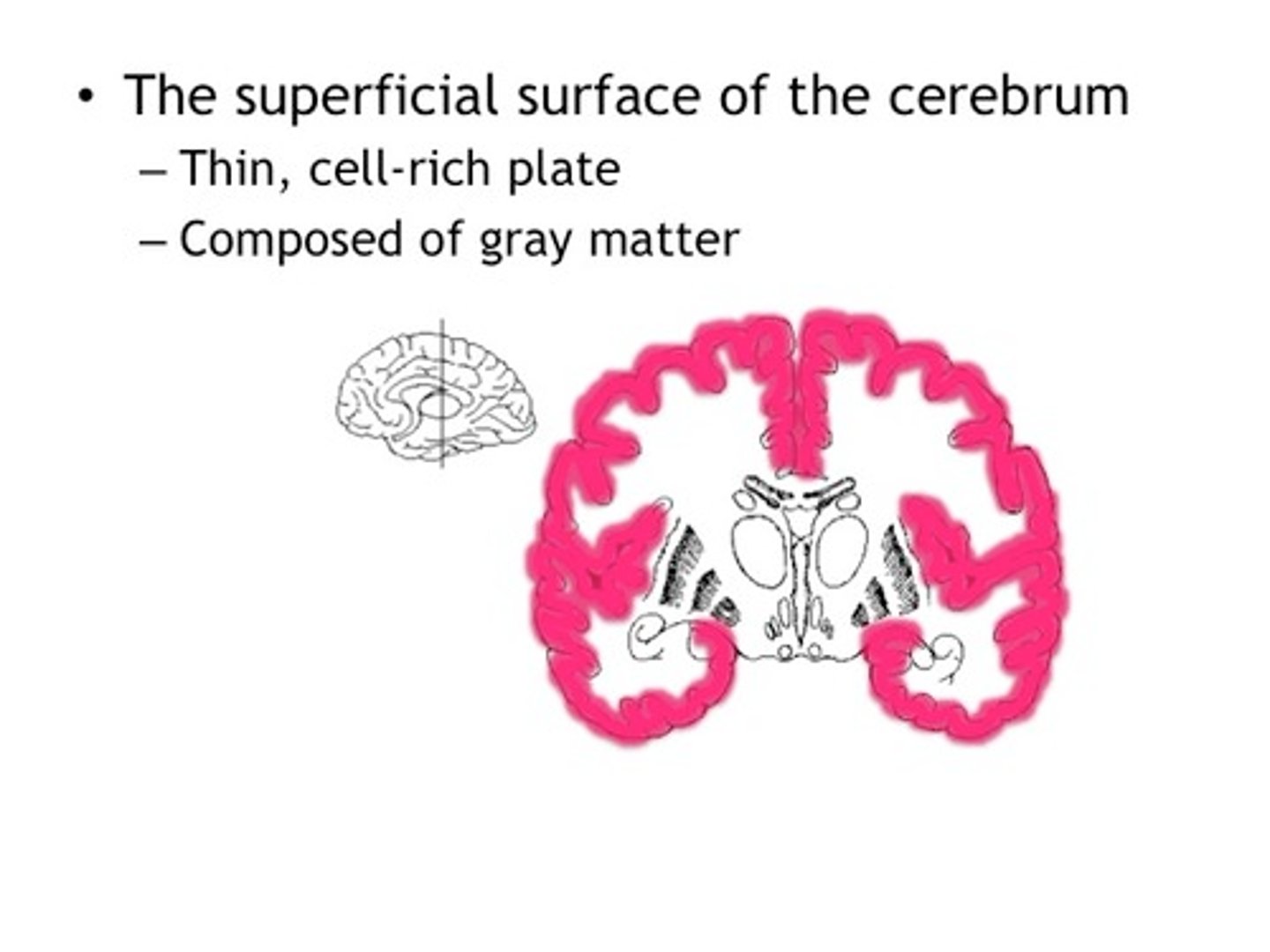
Cerebral Cortex
Outer layer of cerebrum, gray matter
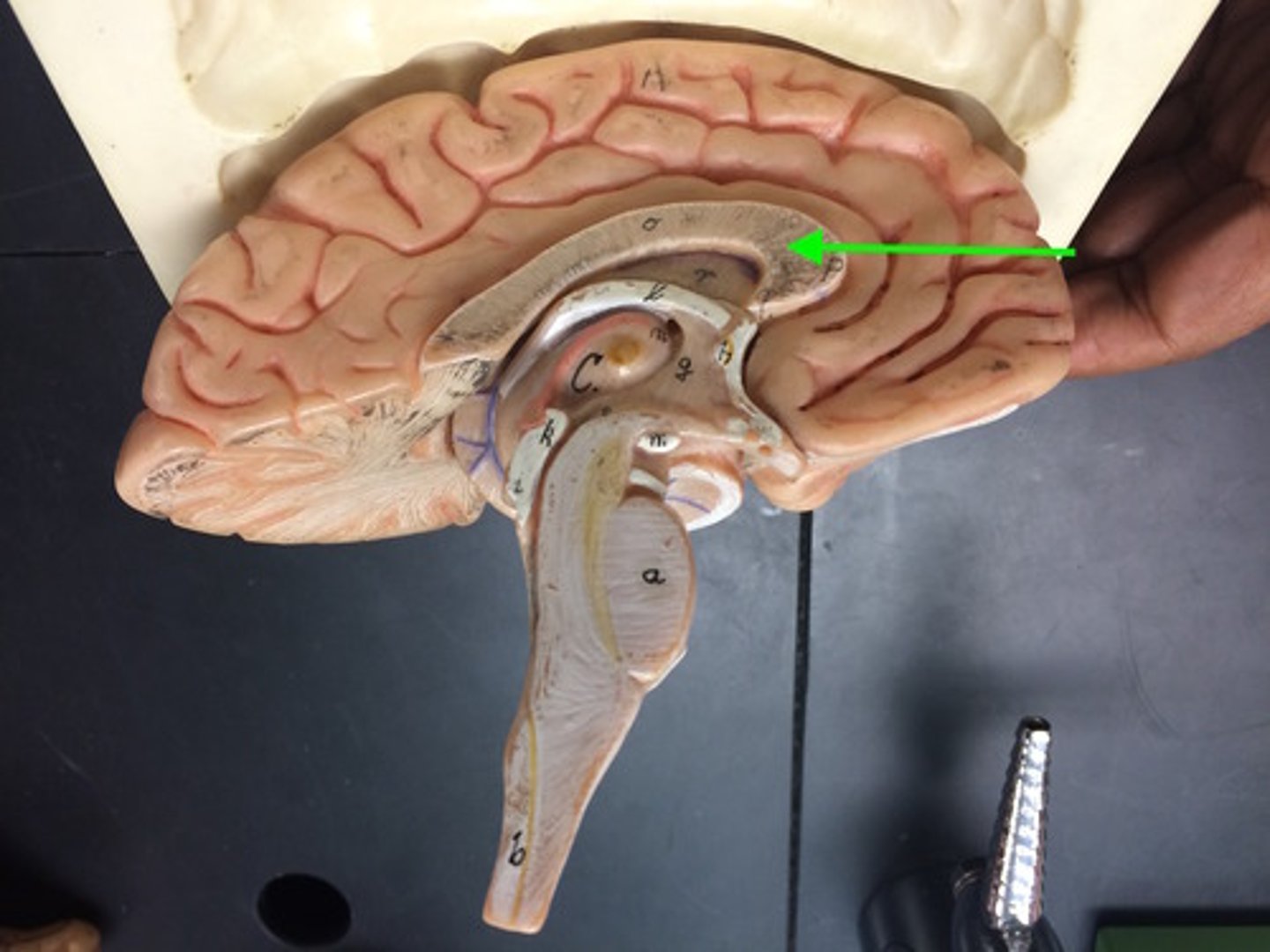
Corpus Collosum
connect right and left hemisphere of the brain, contain maximum white matter
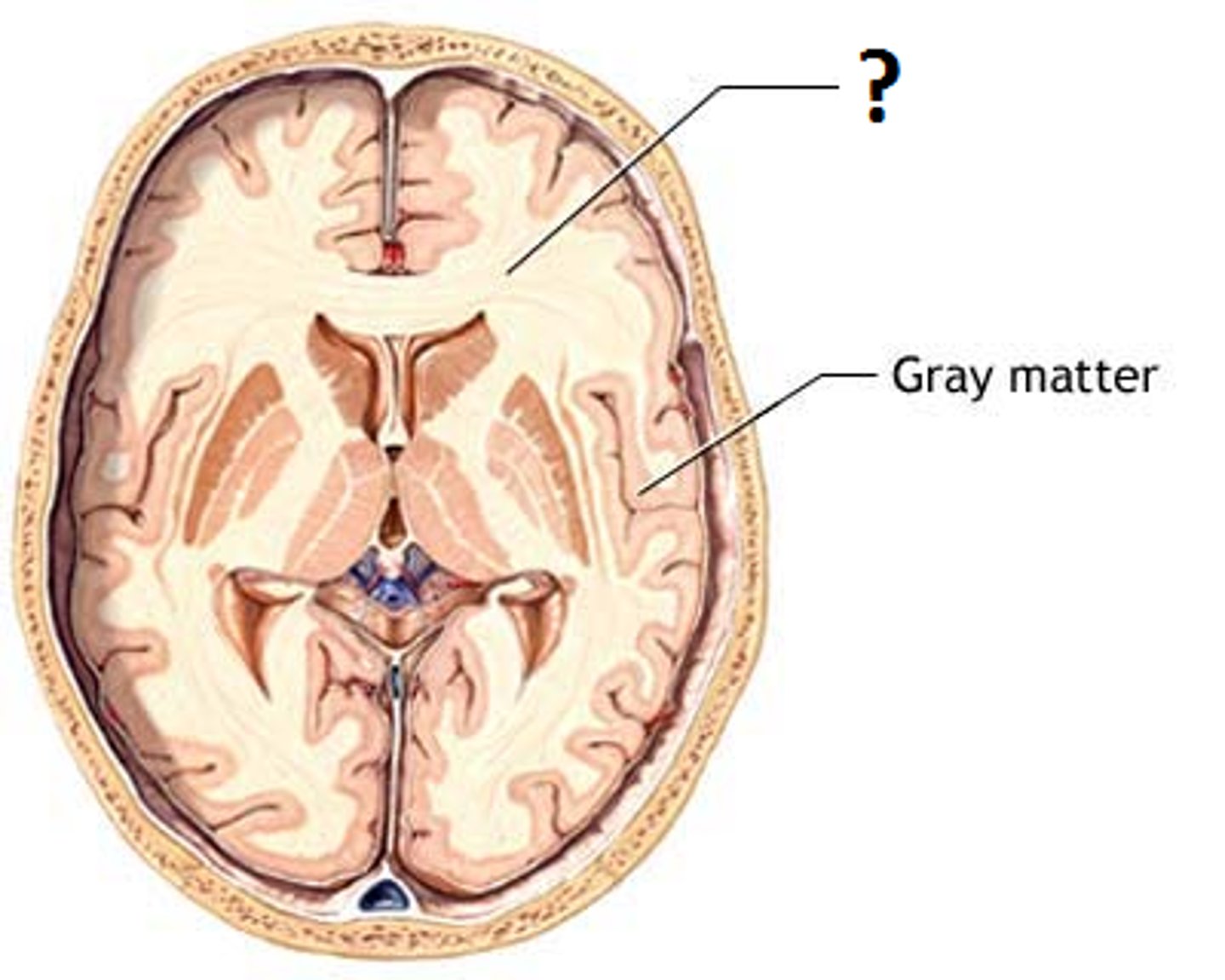
White Matter
Deep, allow different parts of brain to communicate with each other
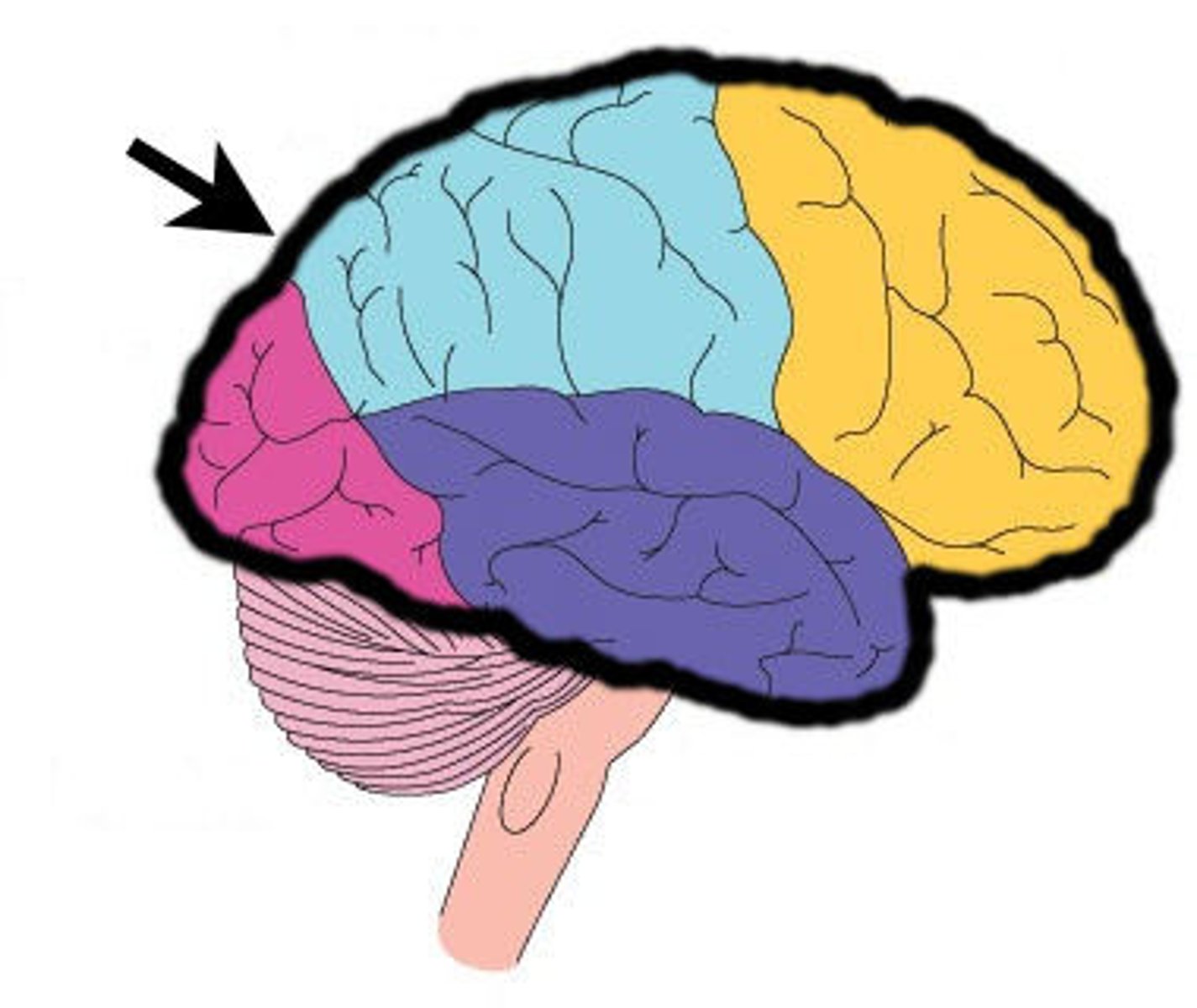
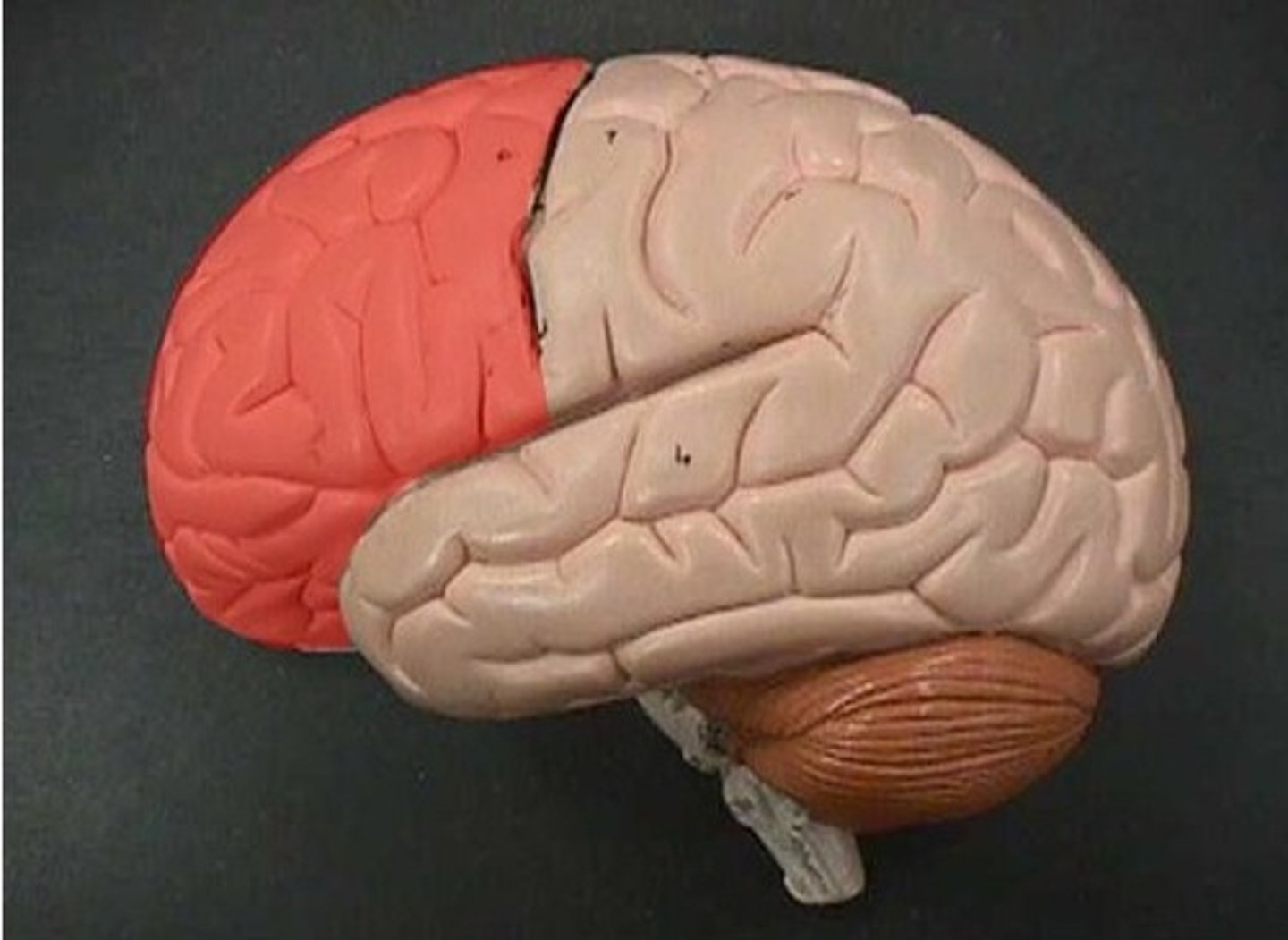
Frontal Lobe
Motor Cortex (prefrontal gyrus)
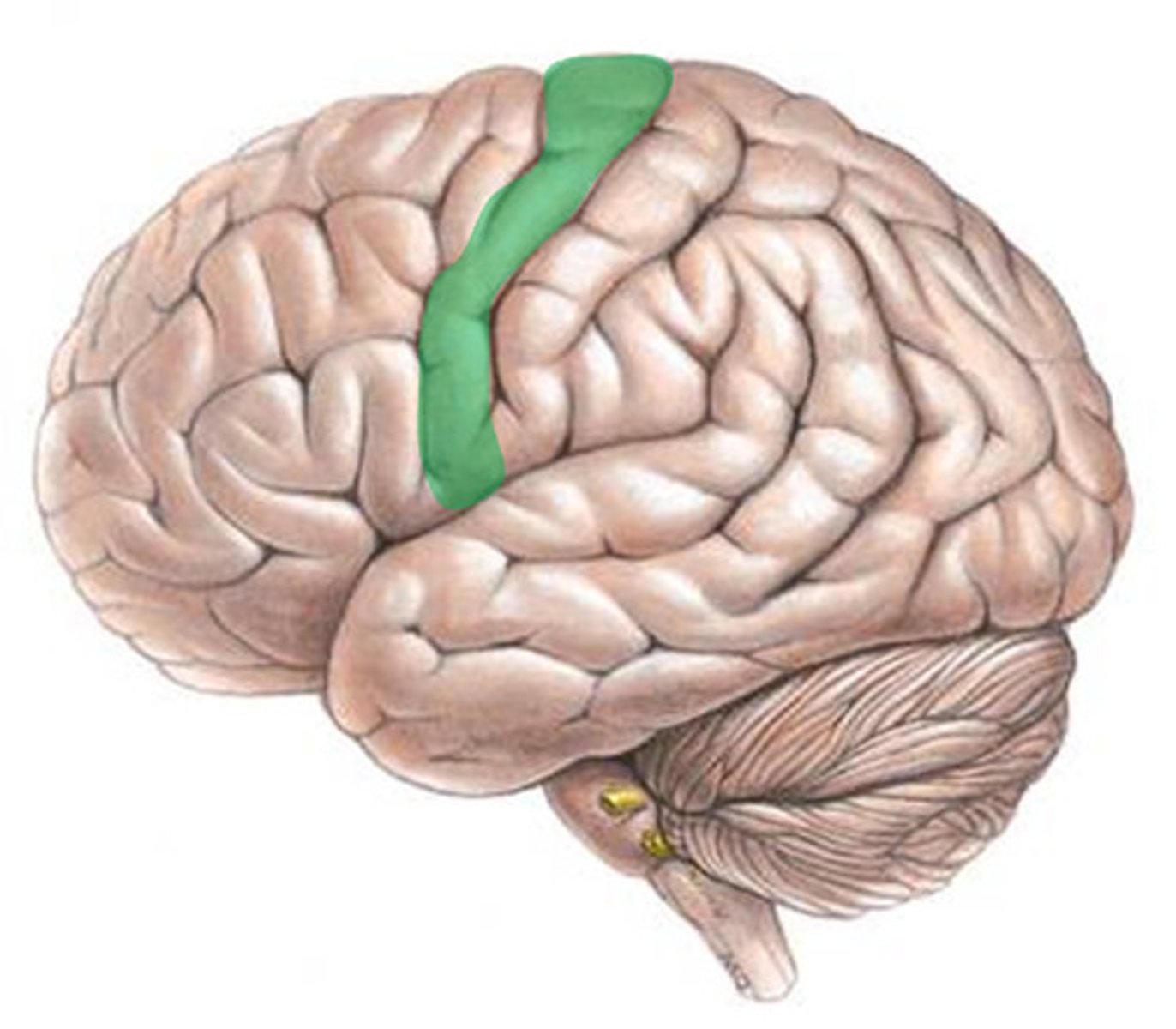
Central Sulcus
Parietal Lobe
Sensory Cortex (Postcentral Gyrus)
Parietal Lobe-Wernicke's area
Formation of language
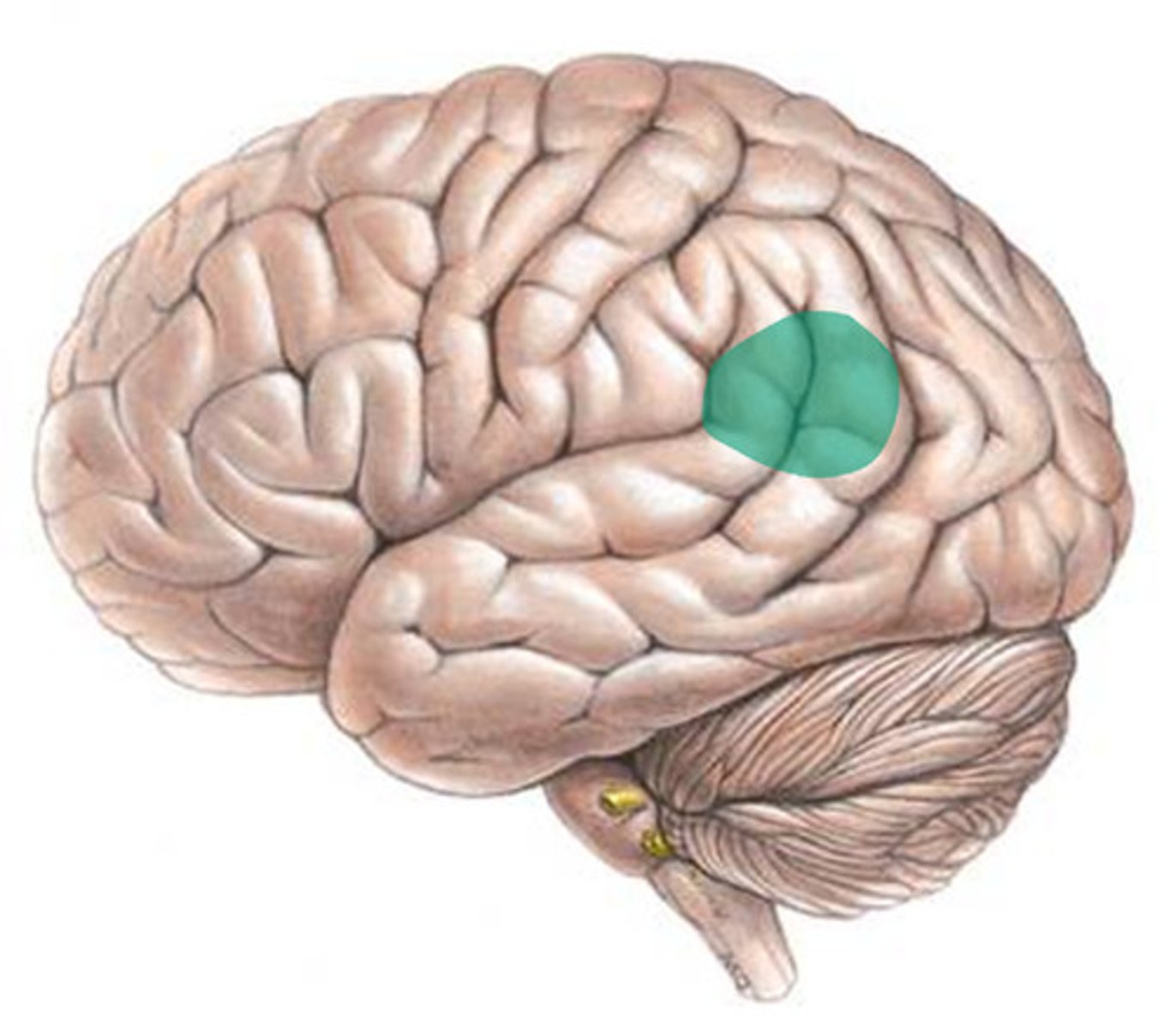
Occipital Lobe
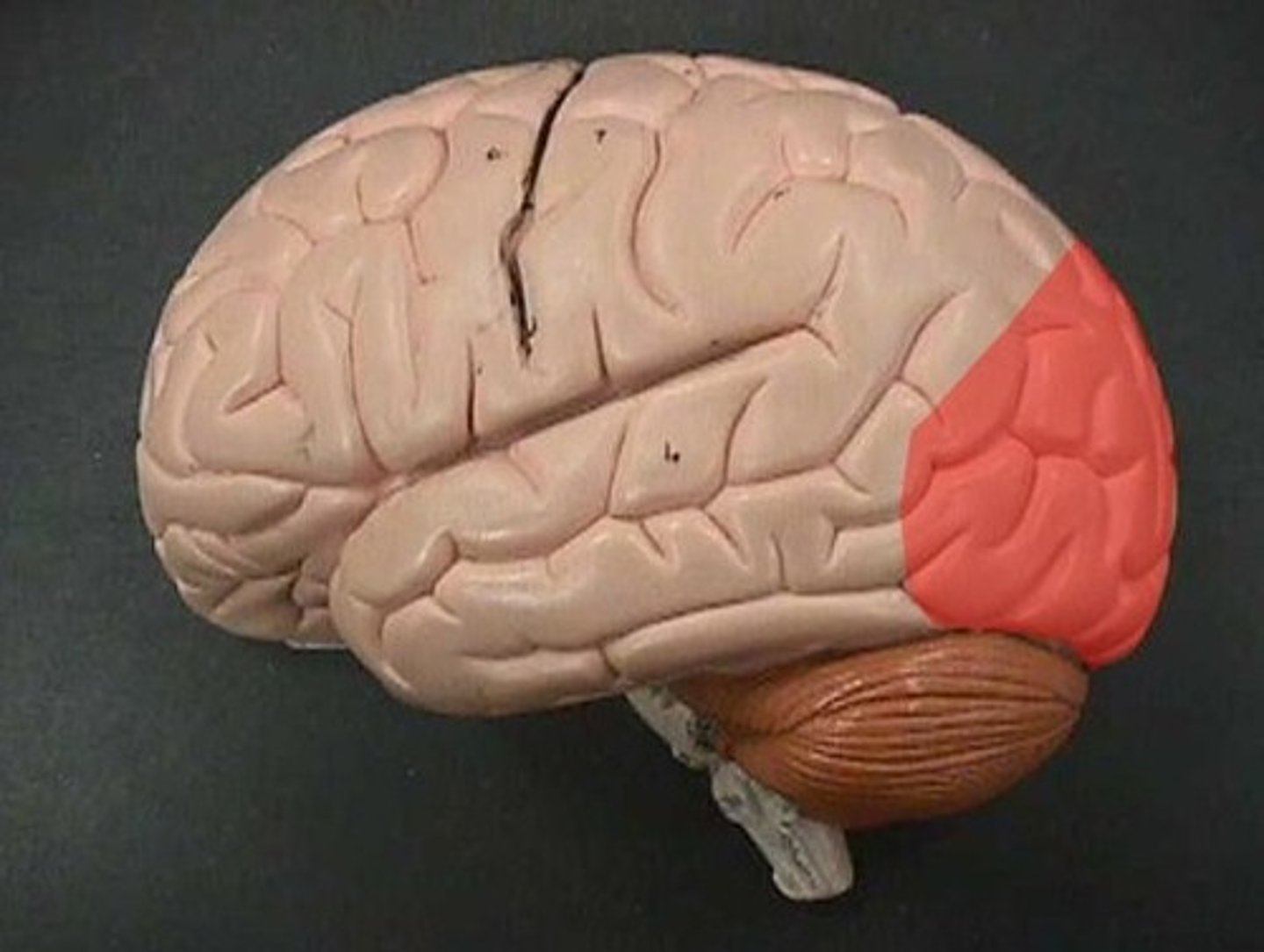
Temporal Lobe
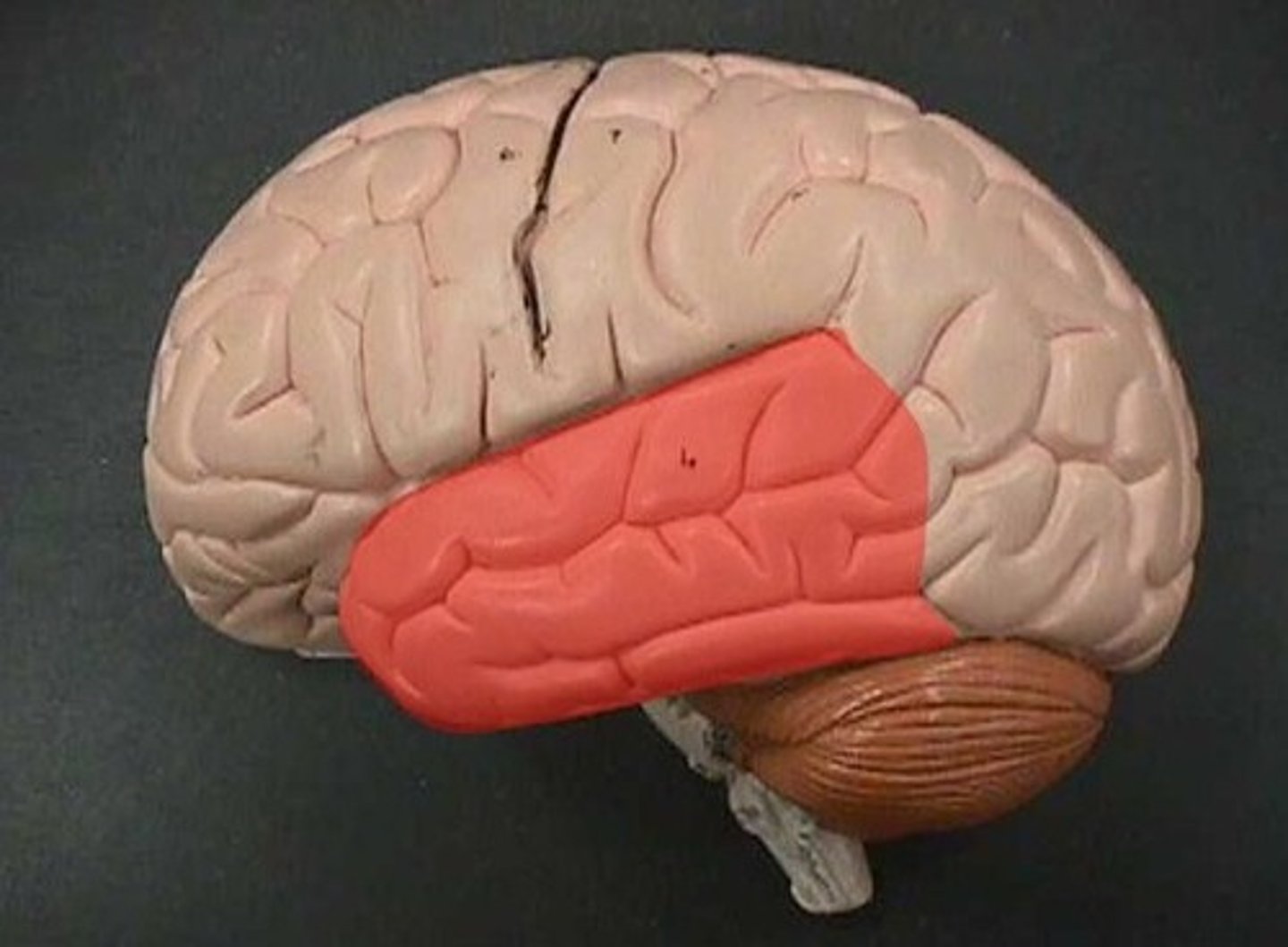
Function of Left Hemisphere
Langauge and Reasoning
Function of Right Hemisphere
Creativity, artistic, imagination
Sulcus (sulci plural)
Shallow depressions of the cerebrum
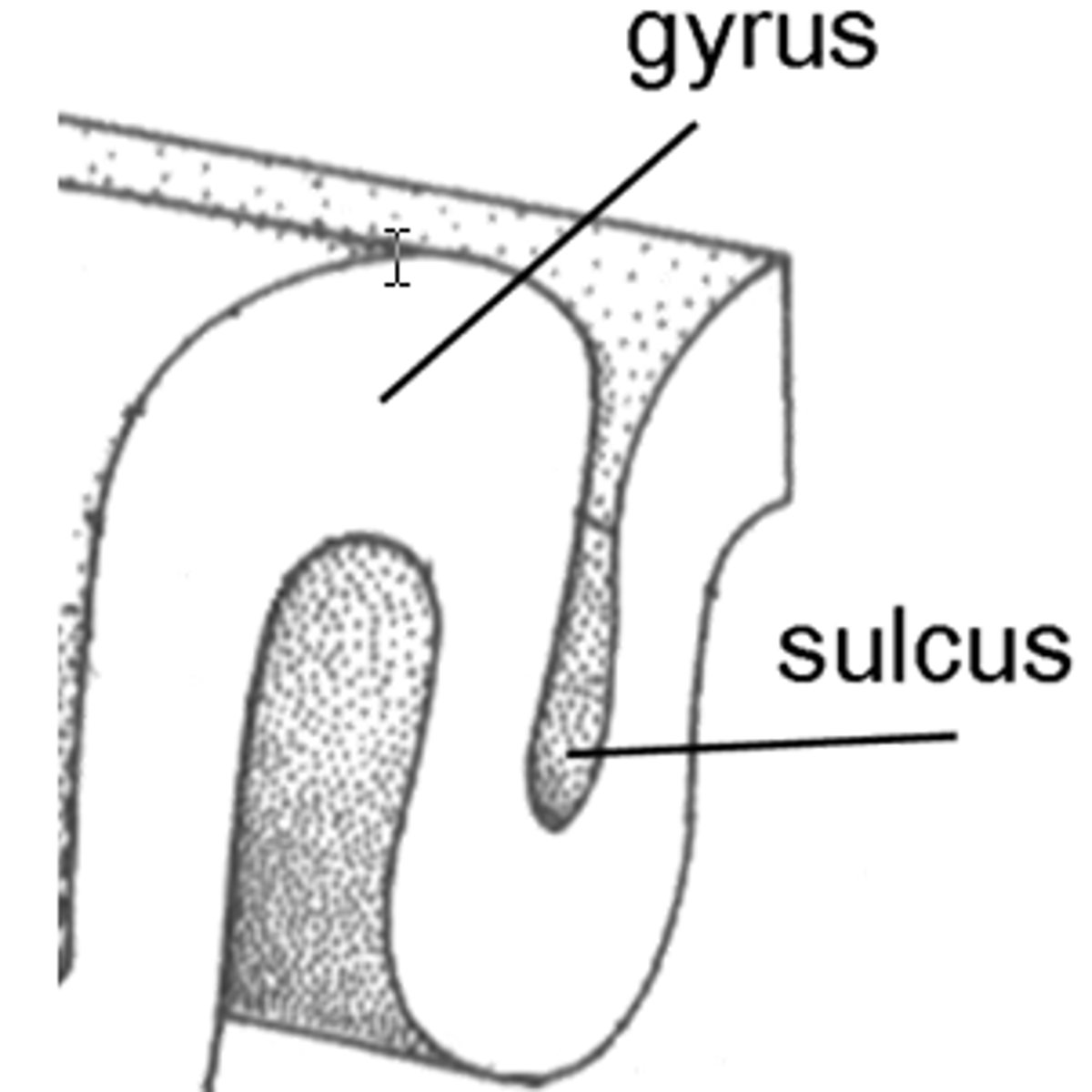
Gyrus (gyri plural)
Elevated ridges of cerebrum, increases surface area
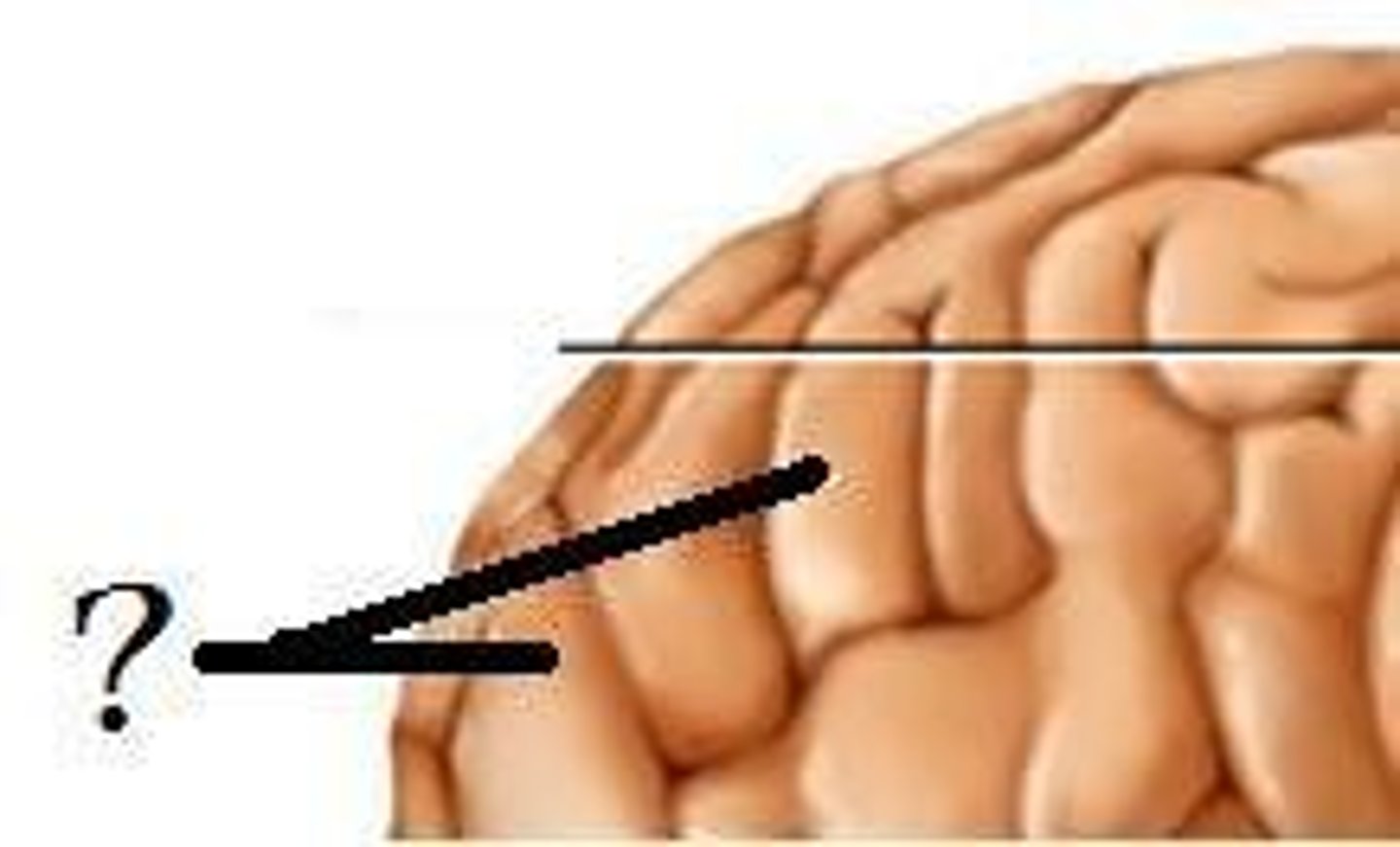
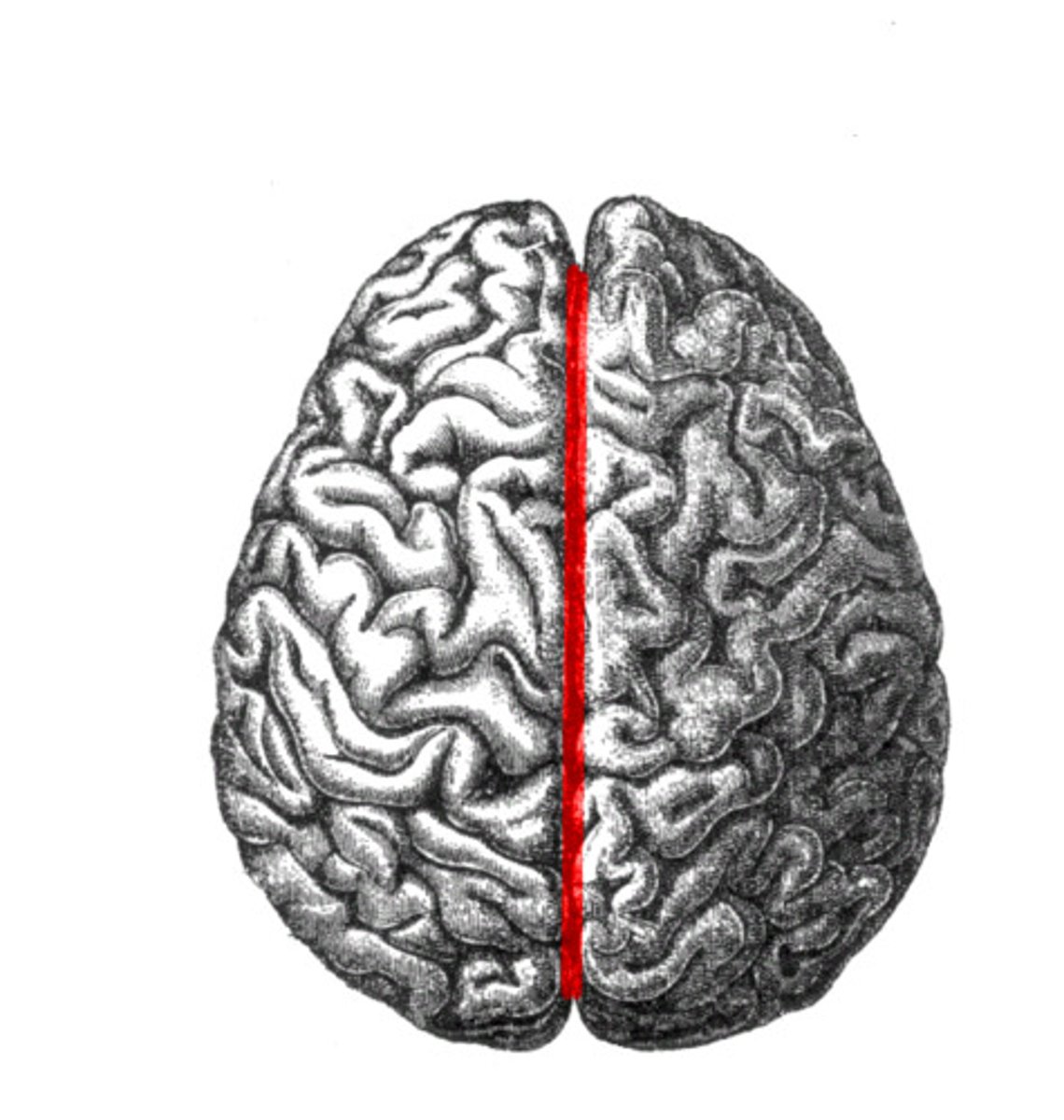
Longitudinal Fissure
Separates right and left hemispheres
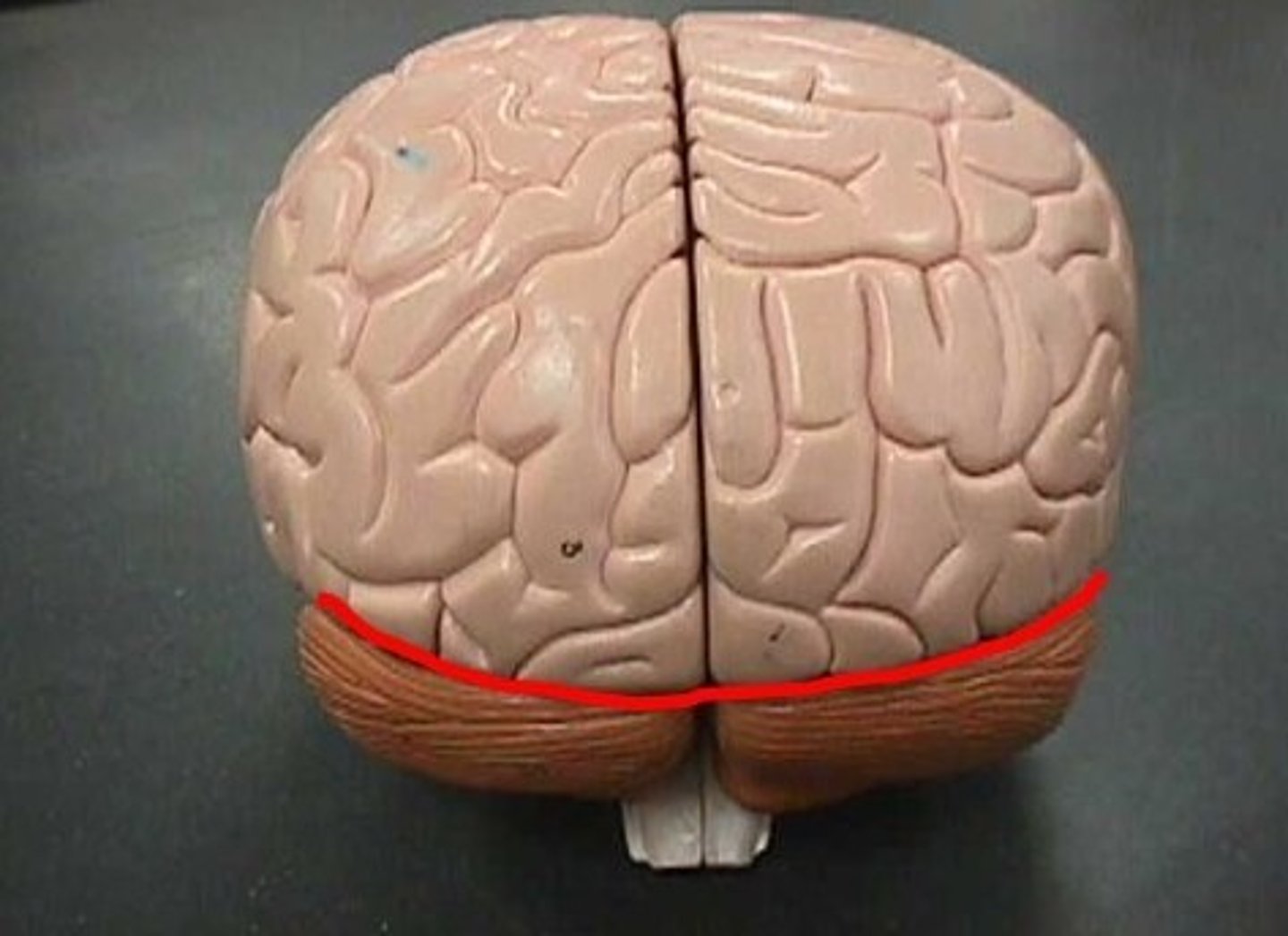
Transverse Fissure
Separates cerebrum from cerebellum
Diencephalon
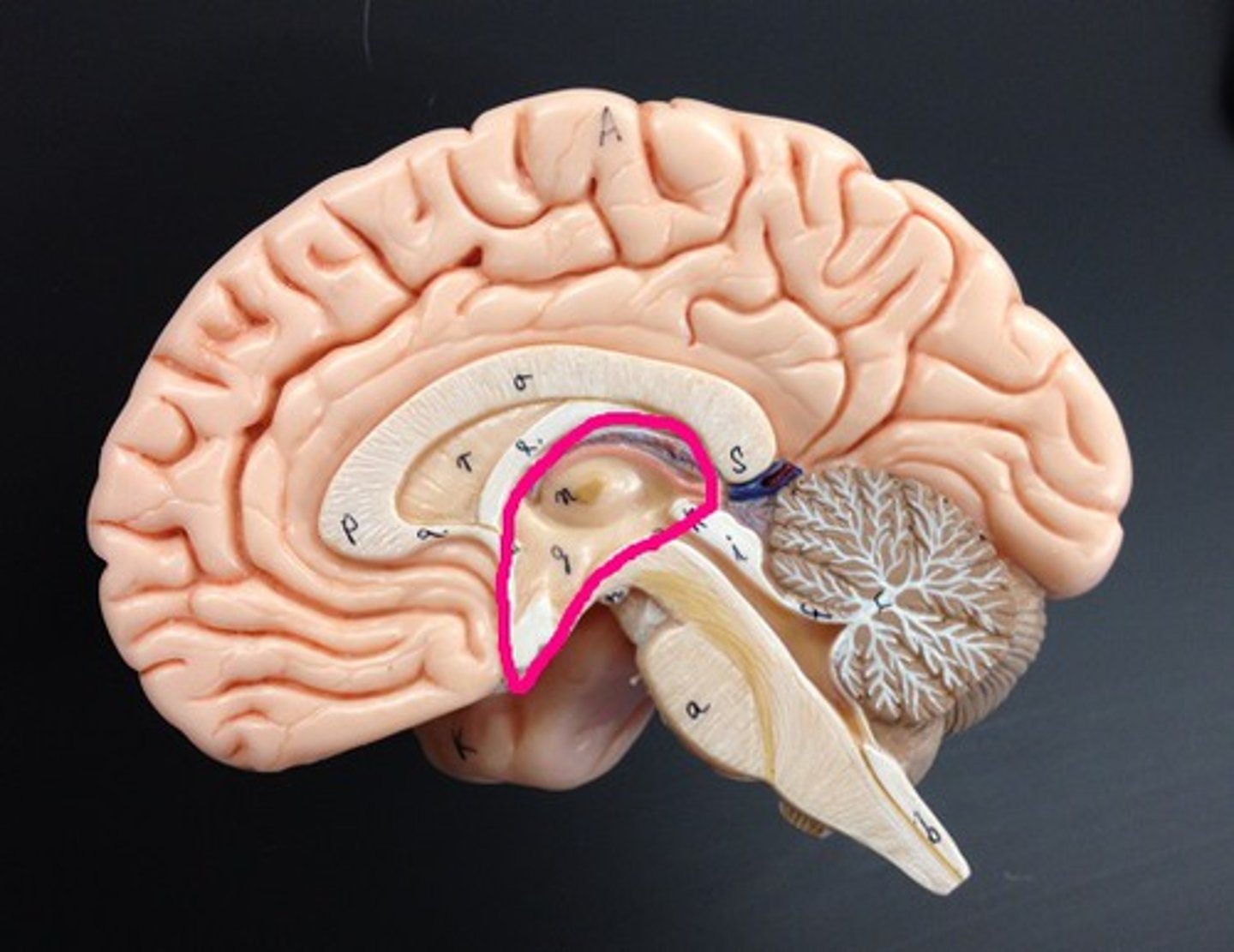
Thalamus
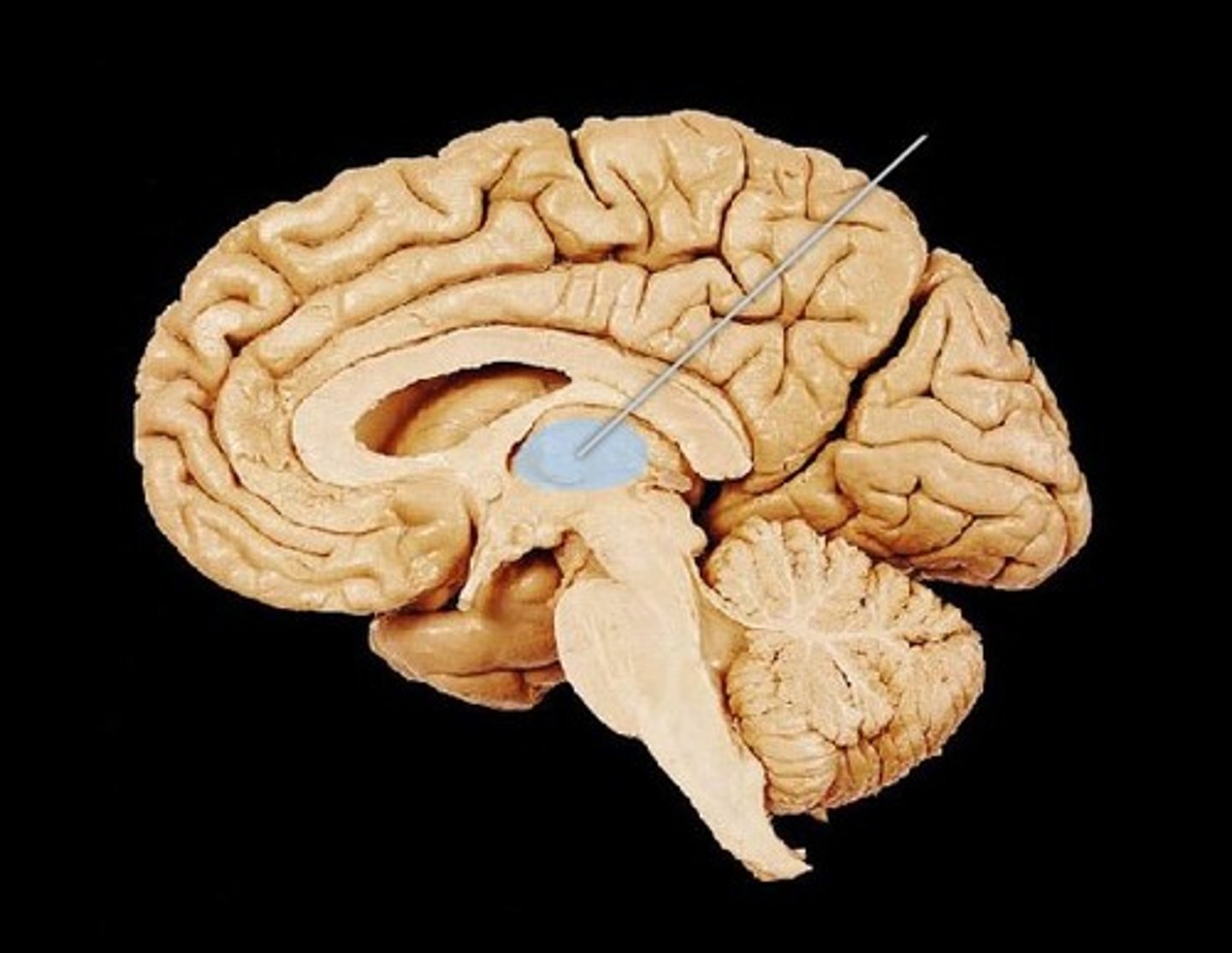
Hypothalamus
-Pituitary Gland
-Mamillary bodies
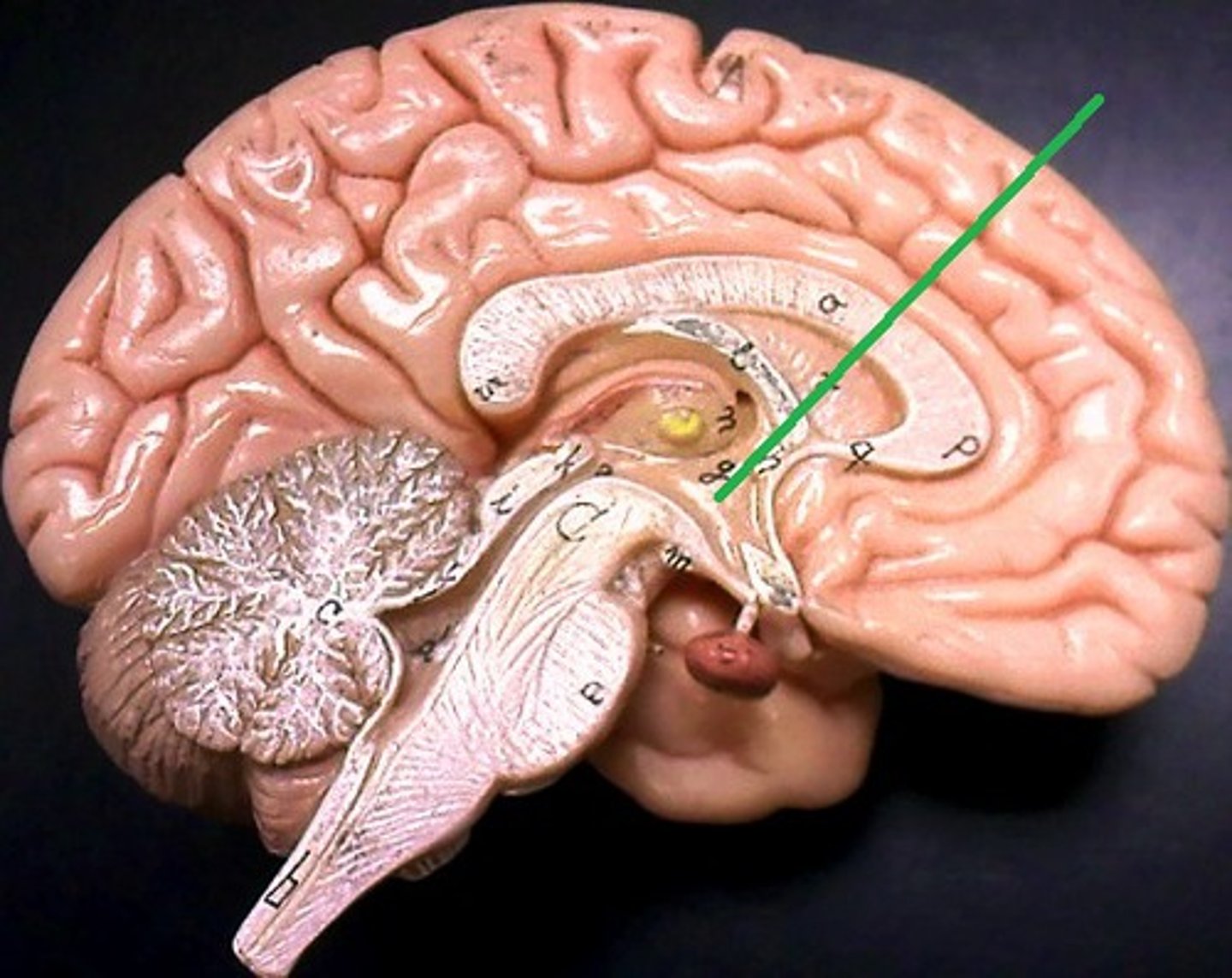
Epithalamus
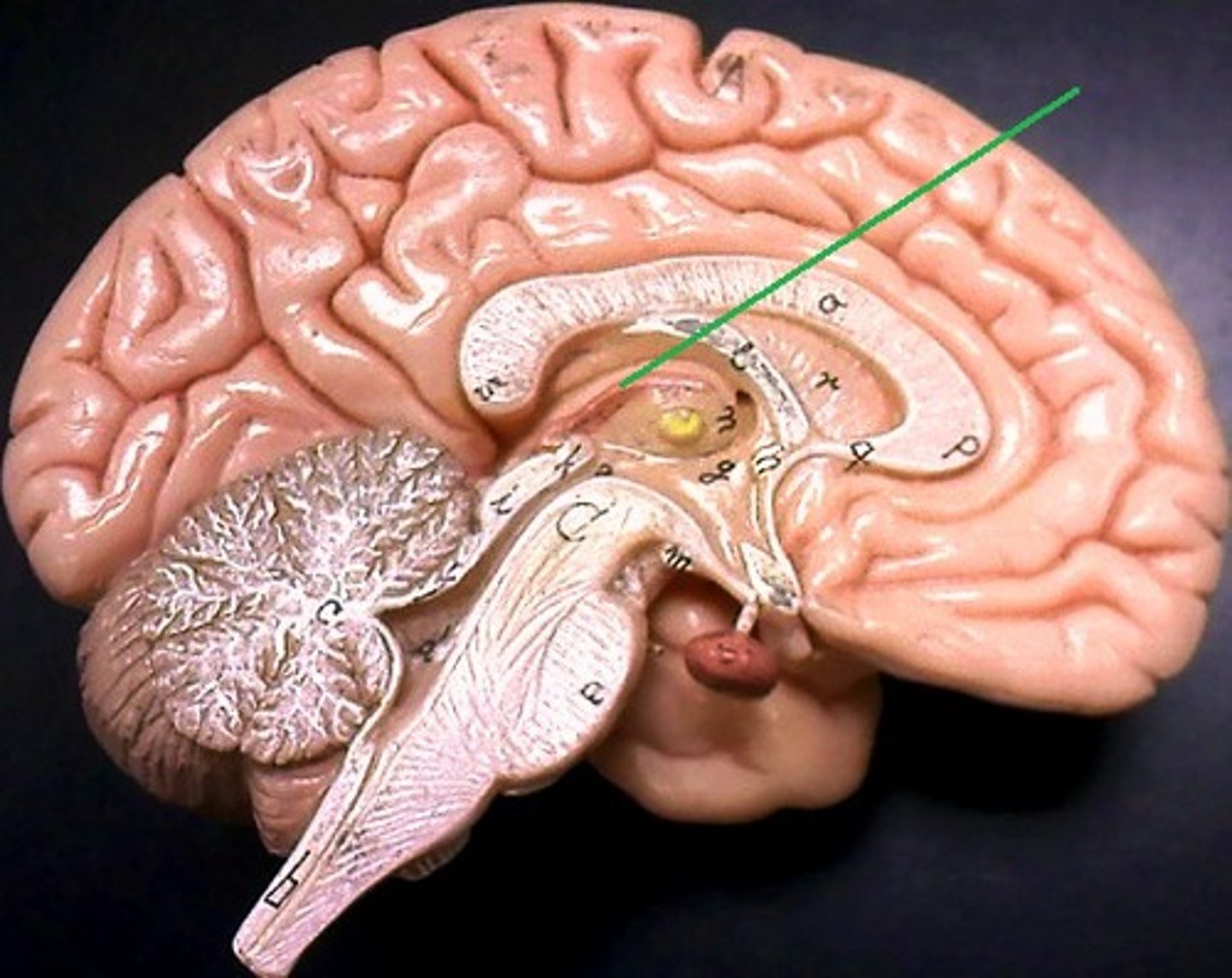
Medulla Oblongata
Pyramids-Anterior
Olive-Posterior
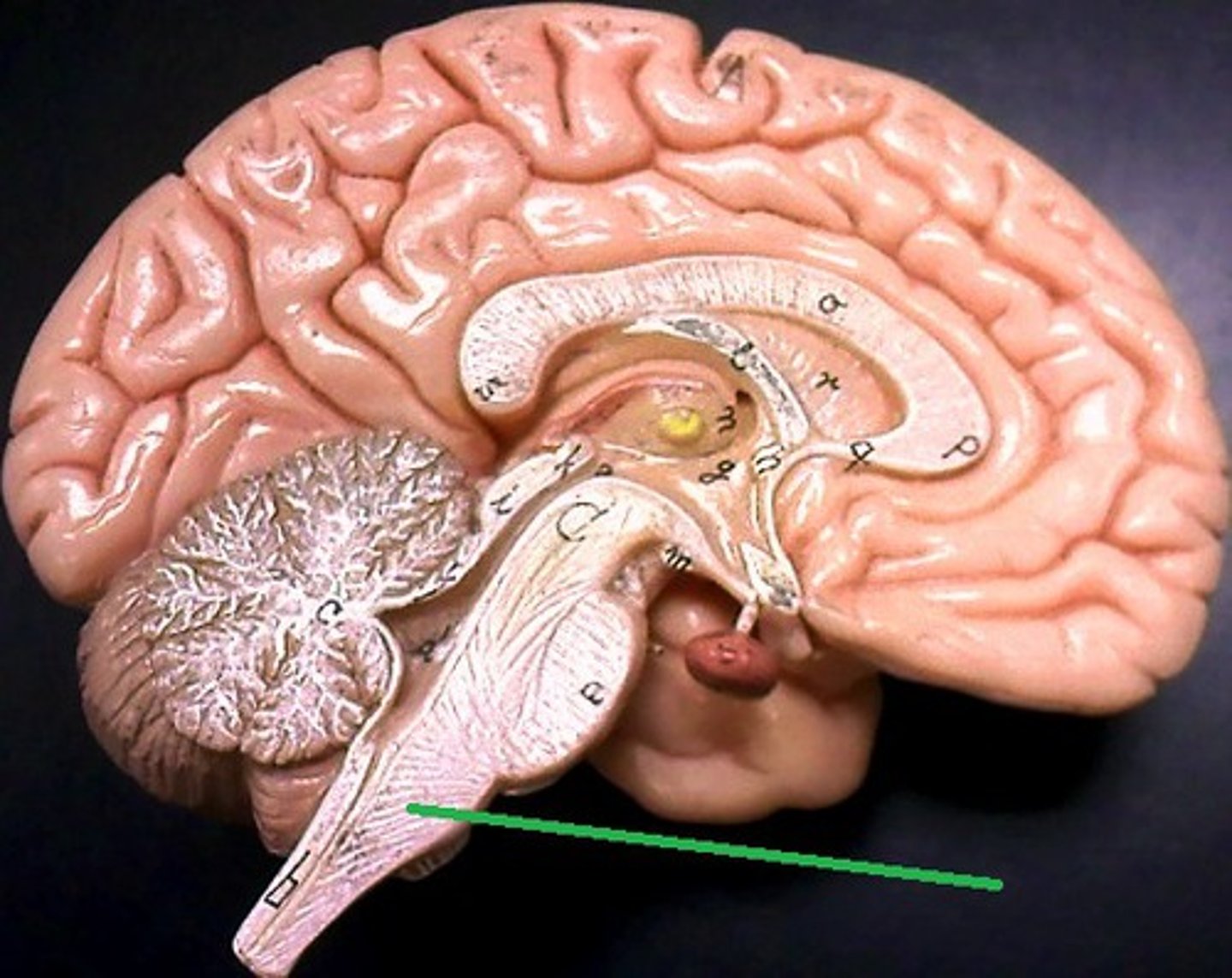
Pons
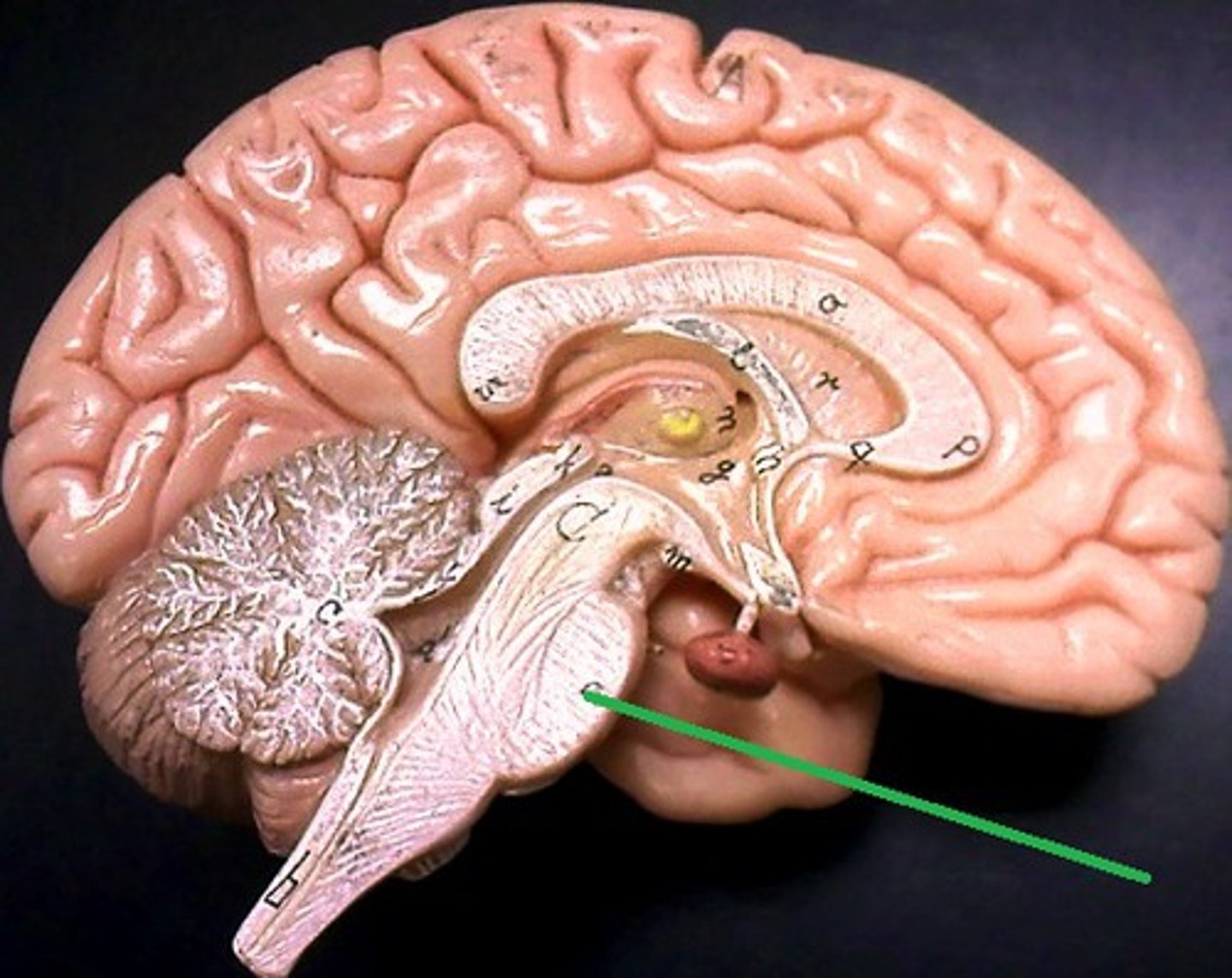
Midbrain
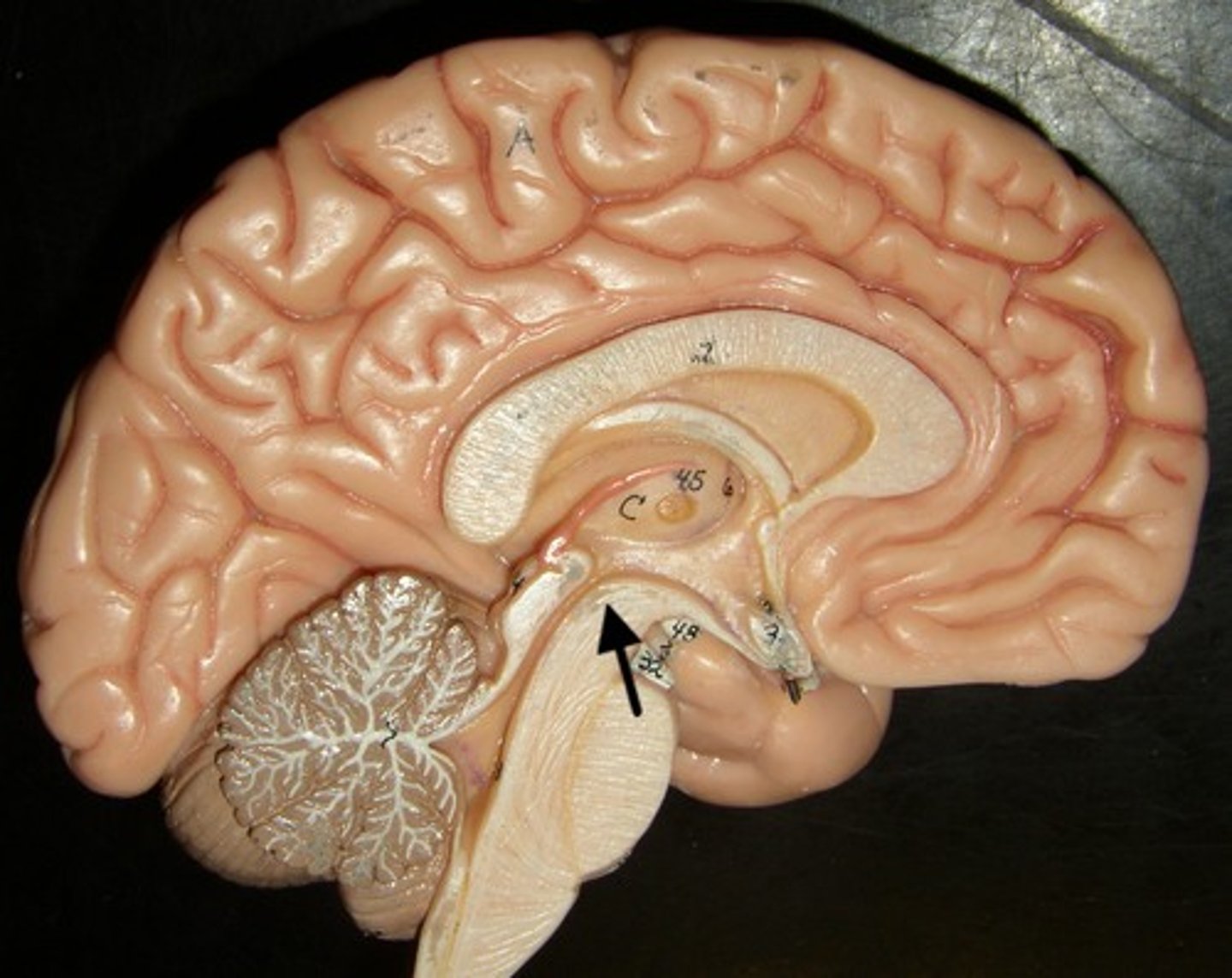
Cerebellum
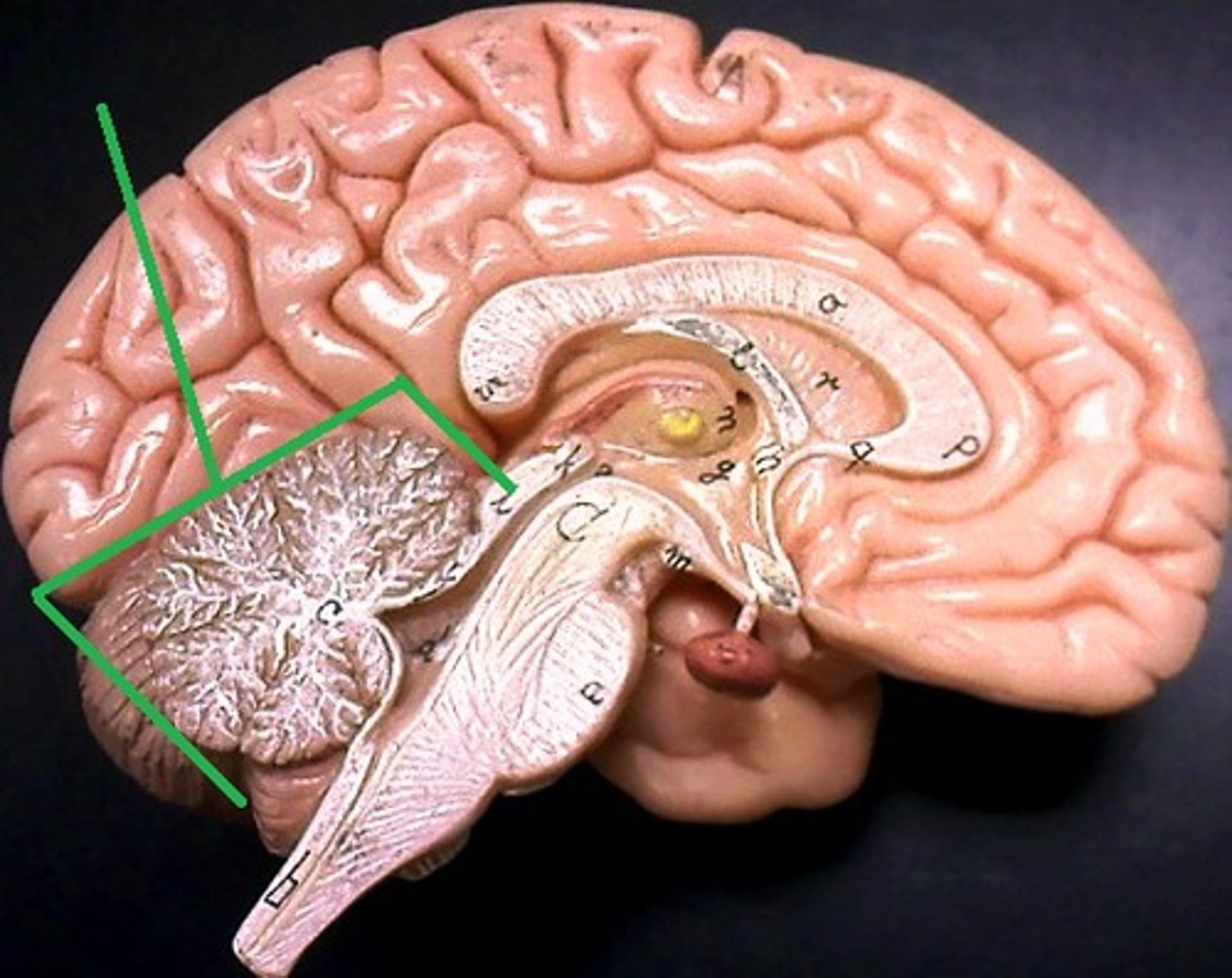
Function of Epithalamus
Contains pineal gland that secretes hormone Melatonin (regulates circadian cycles)