Eukaryotic cells
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
What is a eukaryotic cell?
Cell with a nucleus and membrane bound organelles
In a eukaryotic cells how are chromosomes formed?
When the DNA is tightly wrapped around proteins called histones
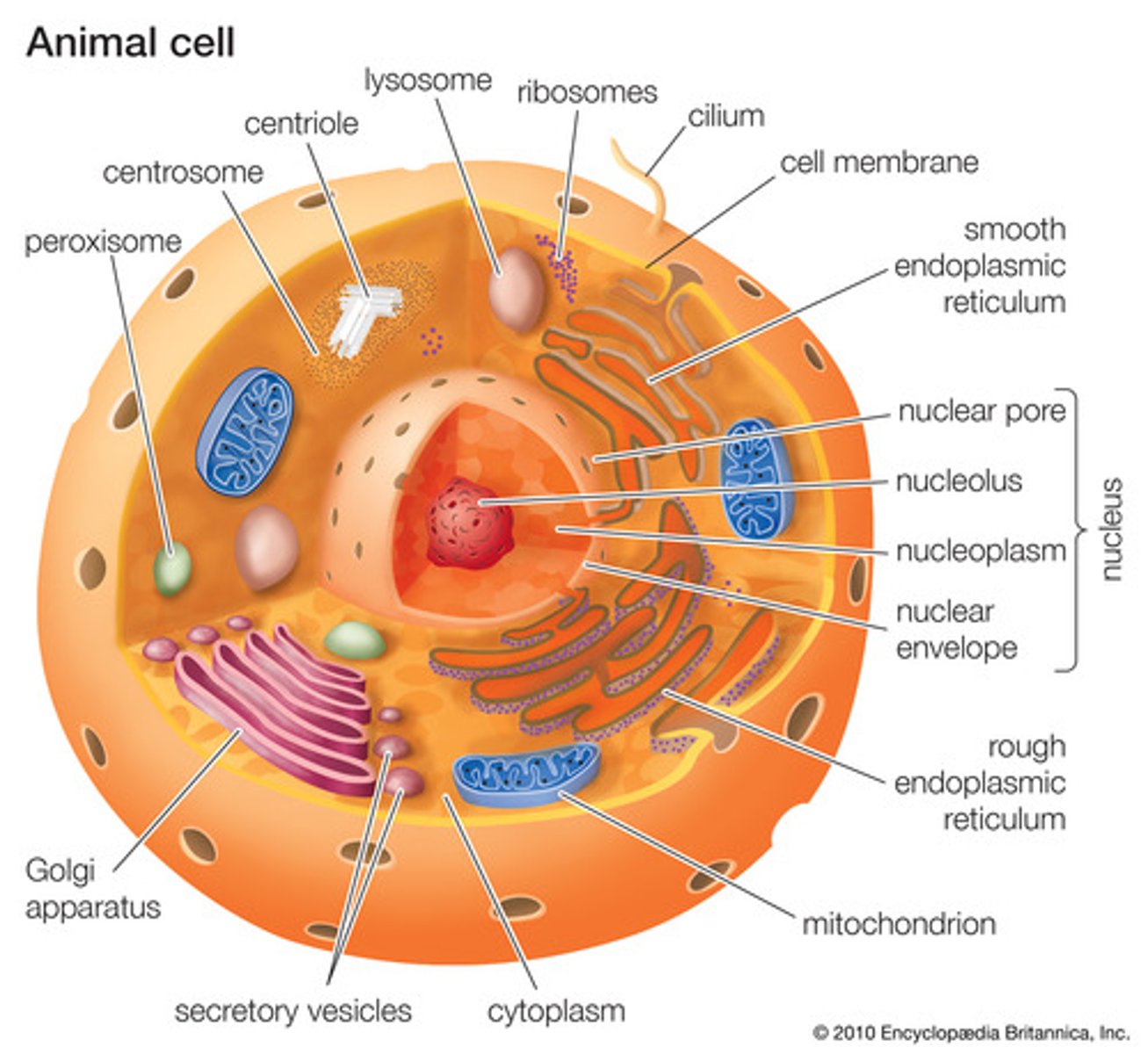
What are the parts of an animal cell
Ribosomes
Rough Endoplasmic reticulum (RER)
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (SER)
Nuclear pore
Nucleolus
Nuclear membrane
Chromatin
Mitochondria
Cytoplasm
Vesicle
Plasma membrane
Golgi apparatus
Cytoskeleton
Centrioles
Lysosome
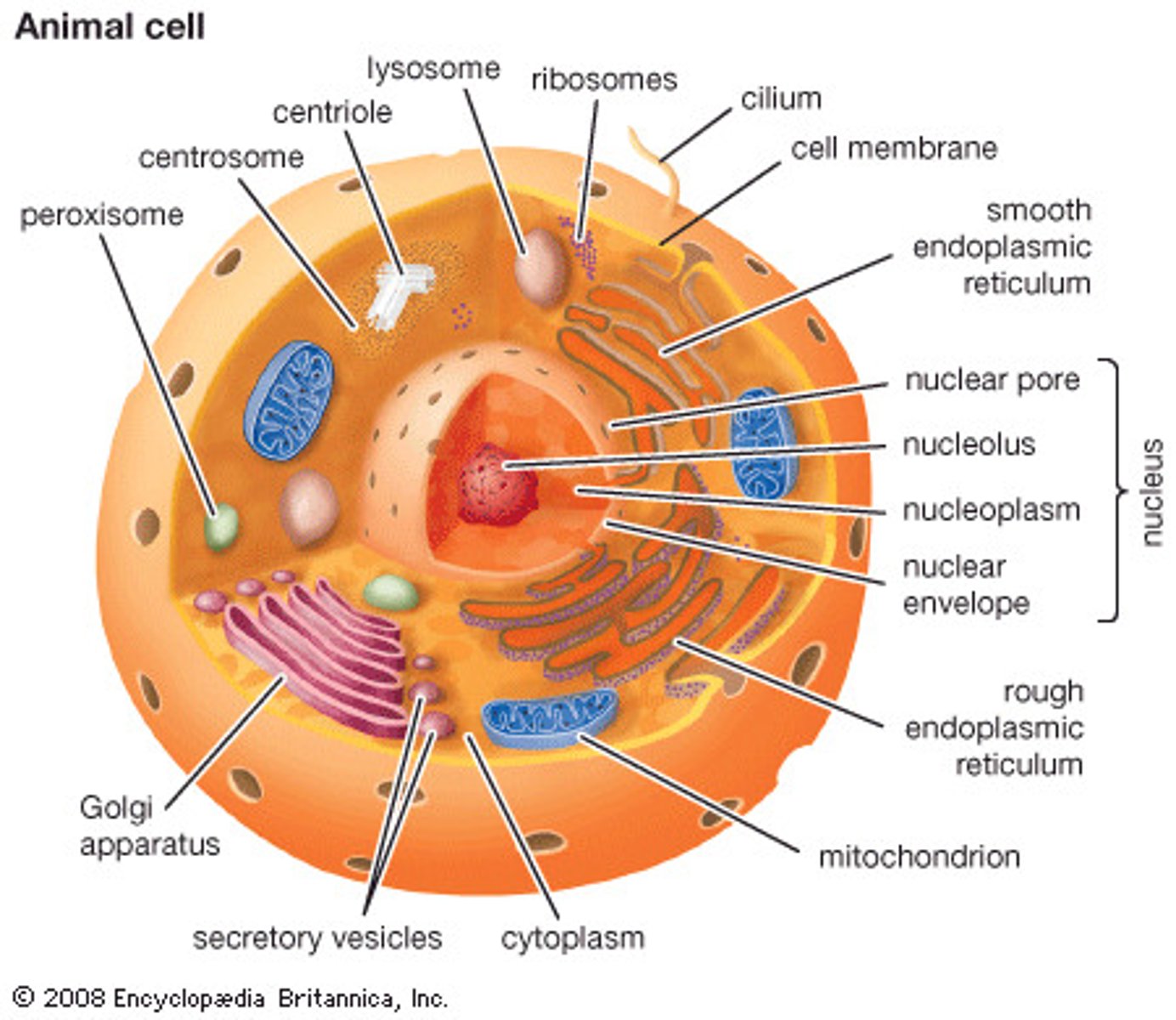
What is the function of ribosomes?
Ribosomes make proteins
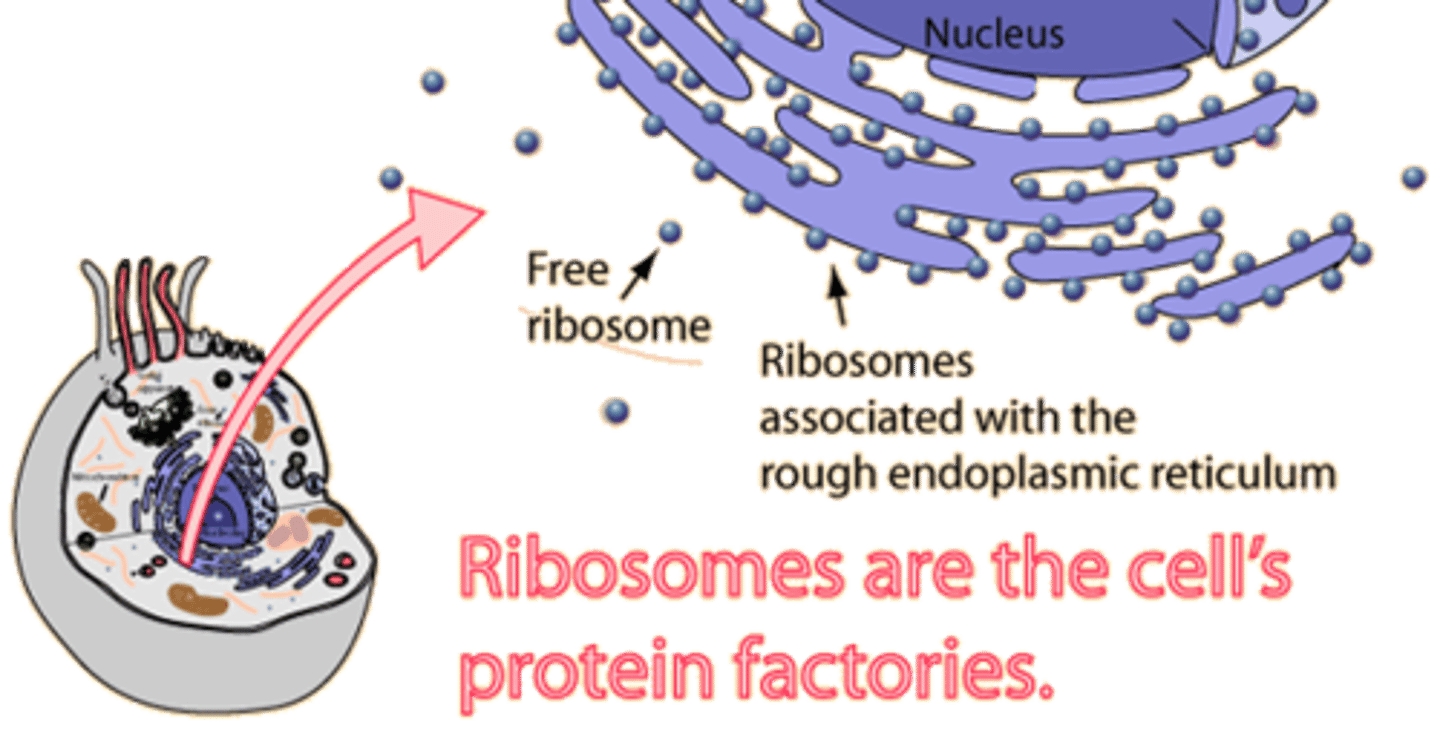
What is the structure of a ribosome?
2 subunits
1) protein subunit
2) RNA subunit (made in the nucleolus)
What is the function of the RER?
Folds and processes proteins that have been made at the ribosomes
Ribosomes are attached to it to make those proteins
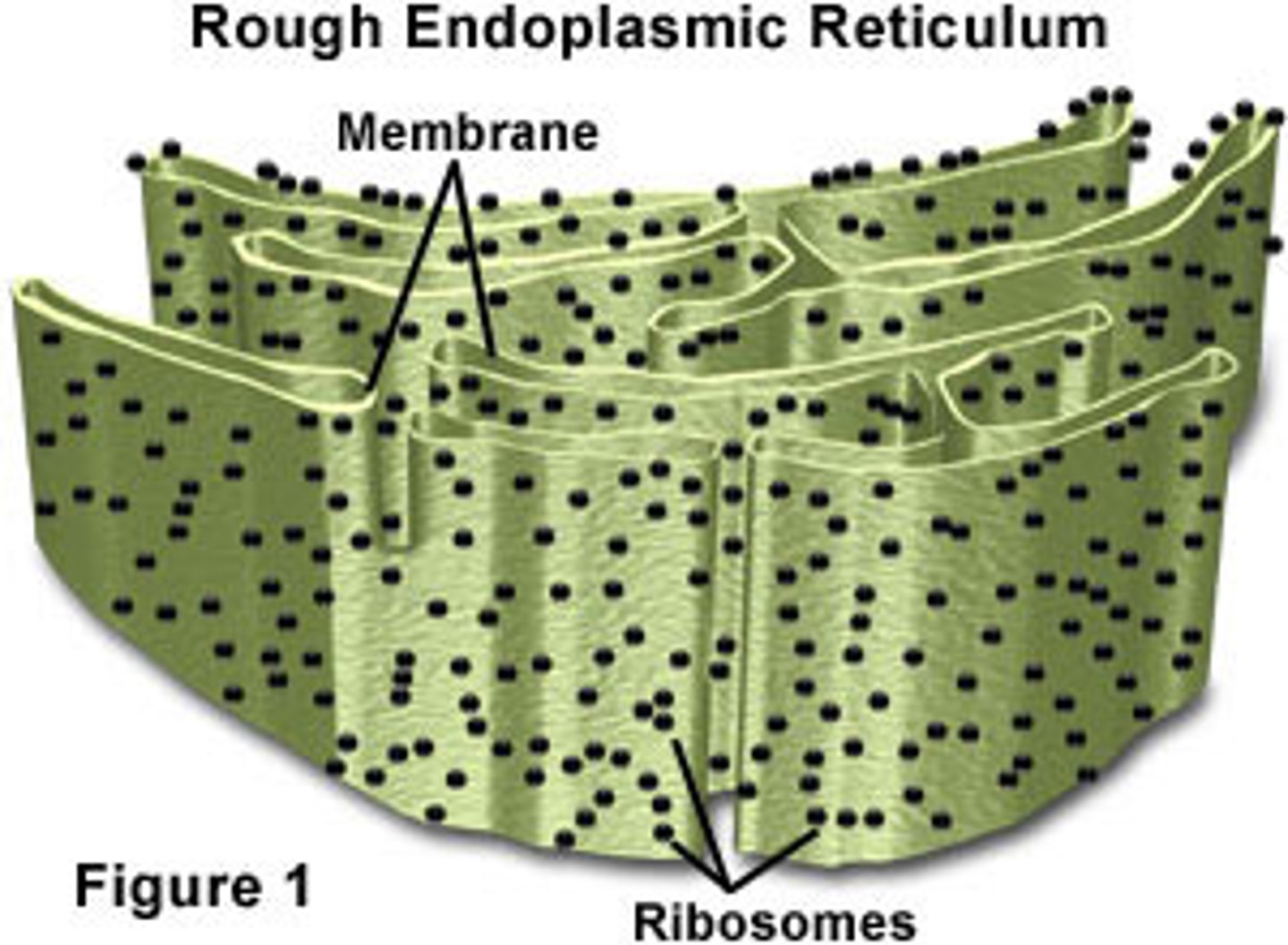
What is the structure of the RER?
Forms an extensive membrane system of flattened sacks called
cisternae which are continuous with the nuclear membrane. Has ribosomes attached.
What is the function of the SER?
Synthesises, stores and transports lipids and carbohydrates

What is the structure of the SER?
Forms extensive membrane system of flattened sacks called cisternae
What is the function of the nucleolus?
Makes ribosomes
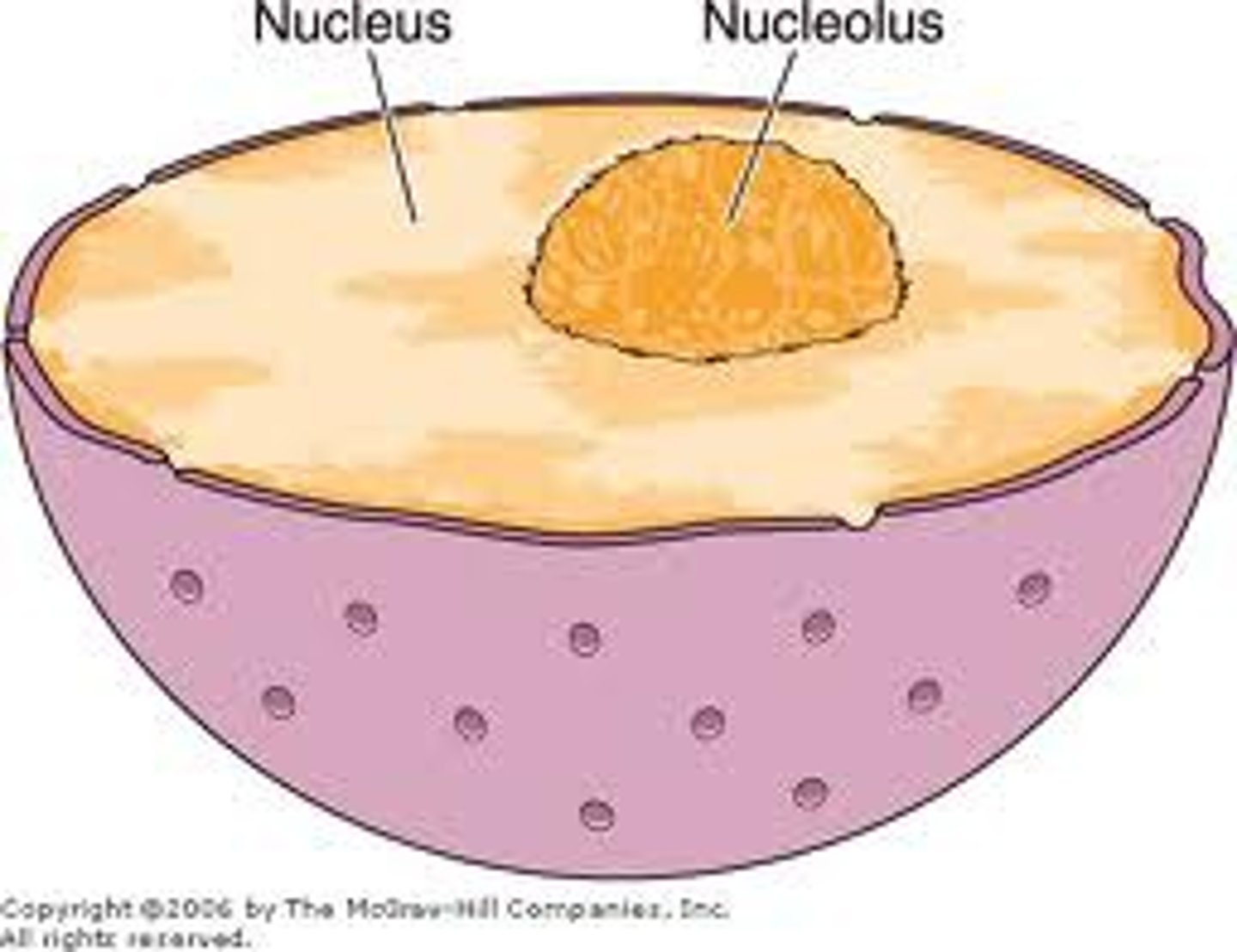
What is the structure of the nucleolus
dense, non-membranous body composed of protein and RNA molecules
What do mitochondria do?
These are where most of the reactions for aerobic respiration occur. Respiration transfers energy that the cell needs to work
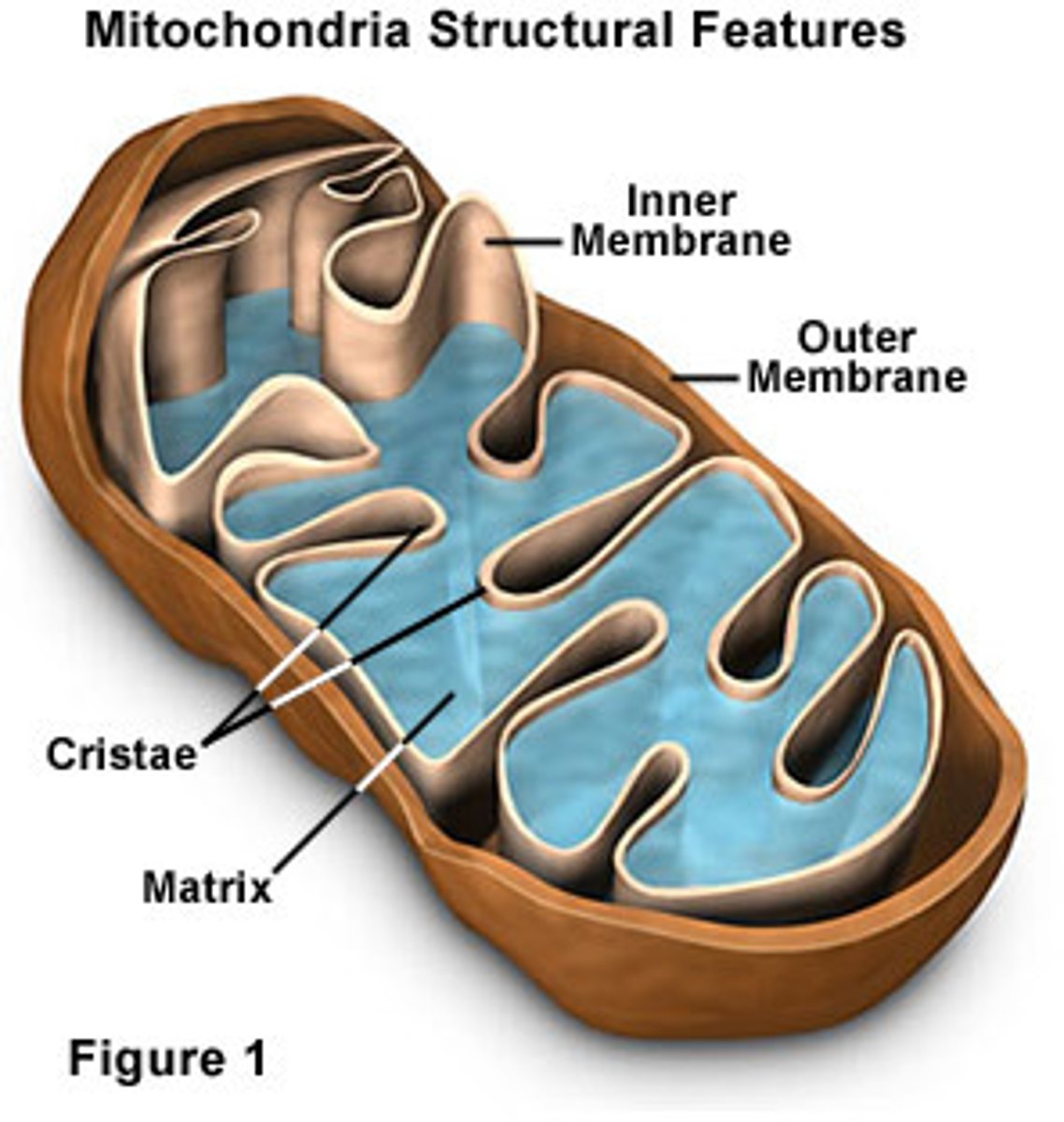
What is the structure of mitochondria?
Consists of an outer and an inner membrane, with an inter membrane space between them. The inner membrane, which is folded into cristae, surrounds the matrix
What is the function of the plasma membrane?
It protects the cell and regulates what can enter and what can exit the cell
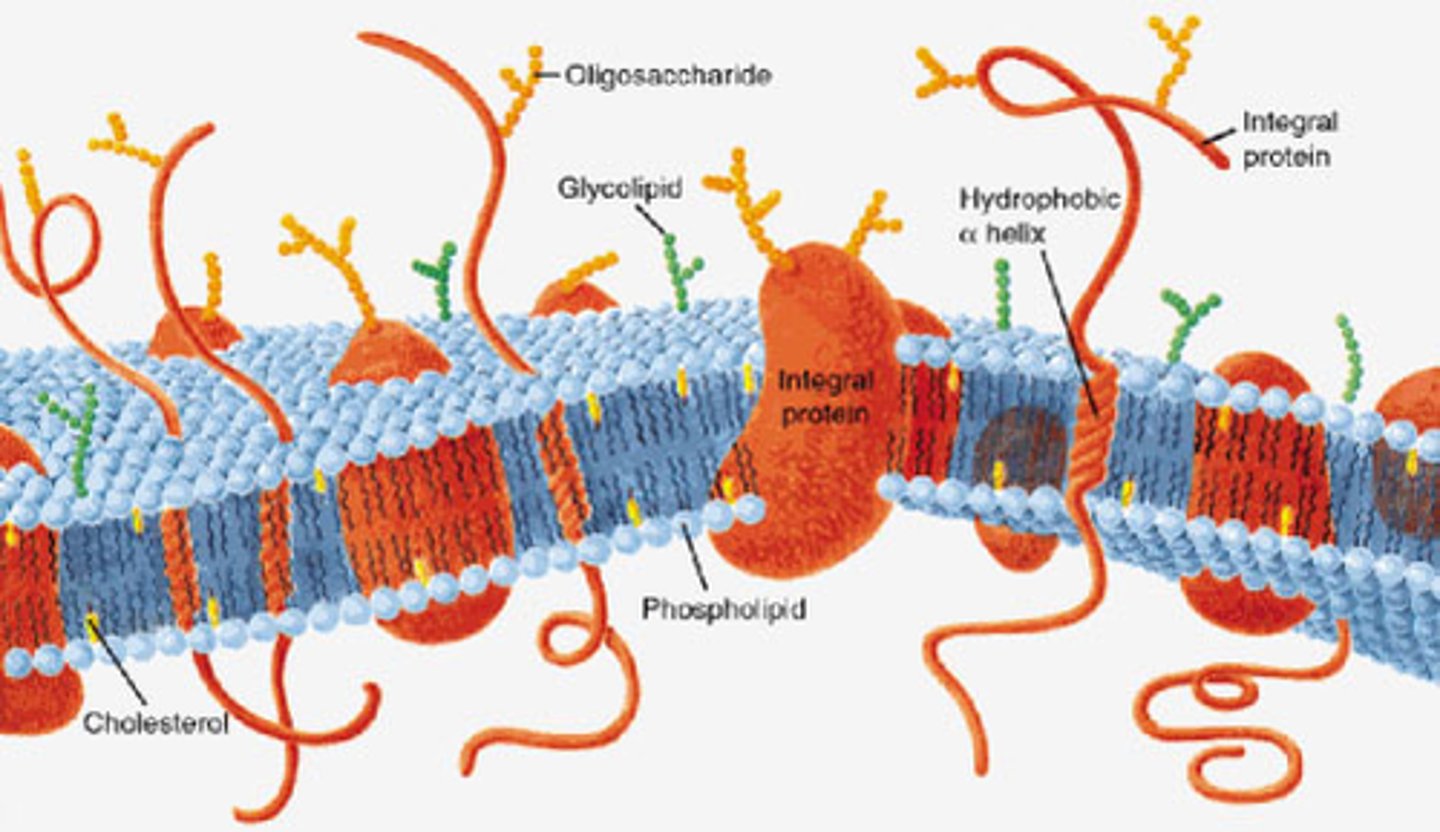
What is the structure of the plasma membrane?
Consists of phospholipid bilayer with proteins and glycoproteins embedded in it
What is the function of the Golgi apparatus?
Proteins which are received from the ER are further processed and sorted for transport to their eventual destinations: lysosomes, the plasma membrane or secretion
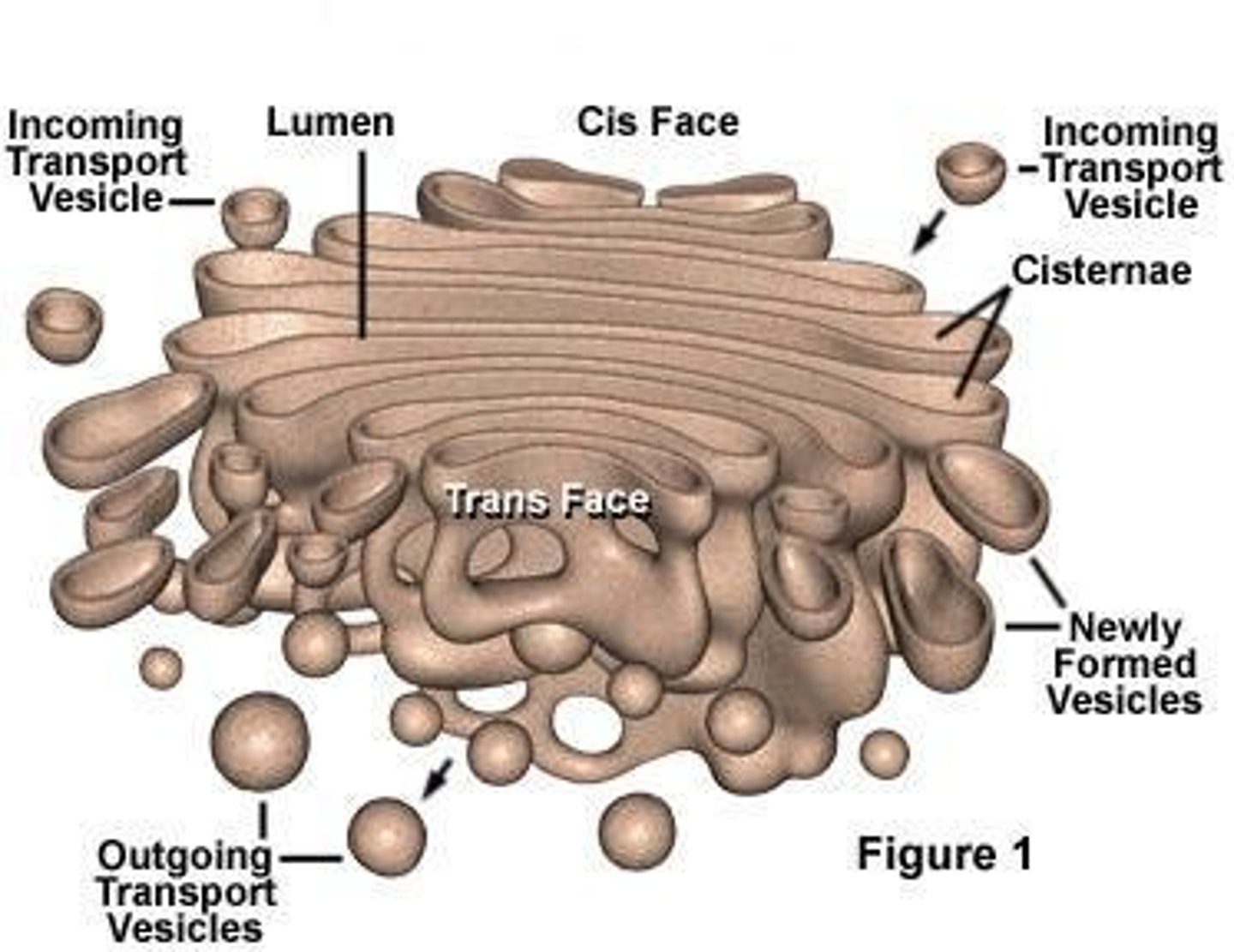
What is the structure of the golgi apparatus?
A stack of flattened membrane bound sacs called cisternae, with vesicles fusing into the sacks on one side.
What is the function of the cytoskeleton?
Supports cells organelles and keeps them in position. To strengthen the cell and help maintain its shape. To transport materials around the cell. To cause cells such as phagocytes to move around.
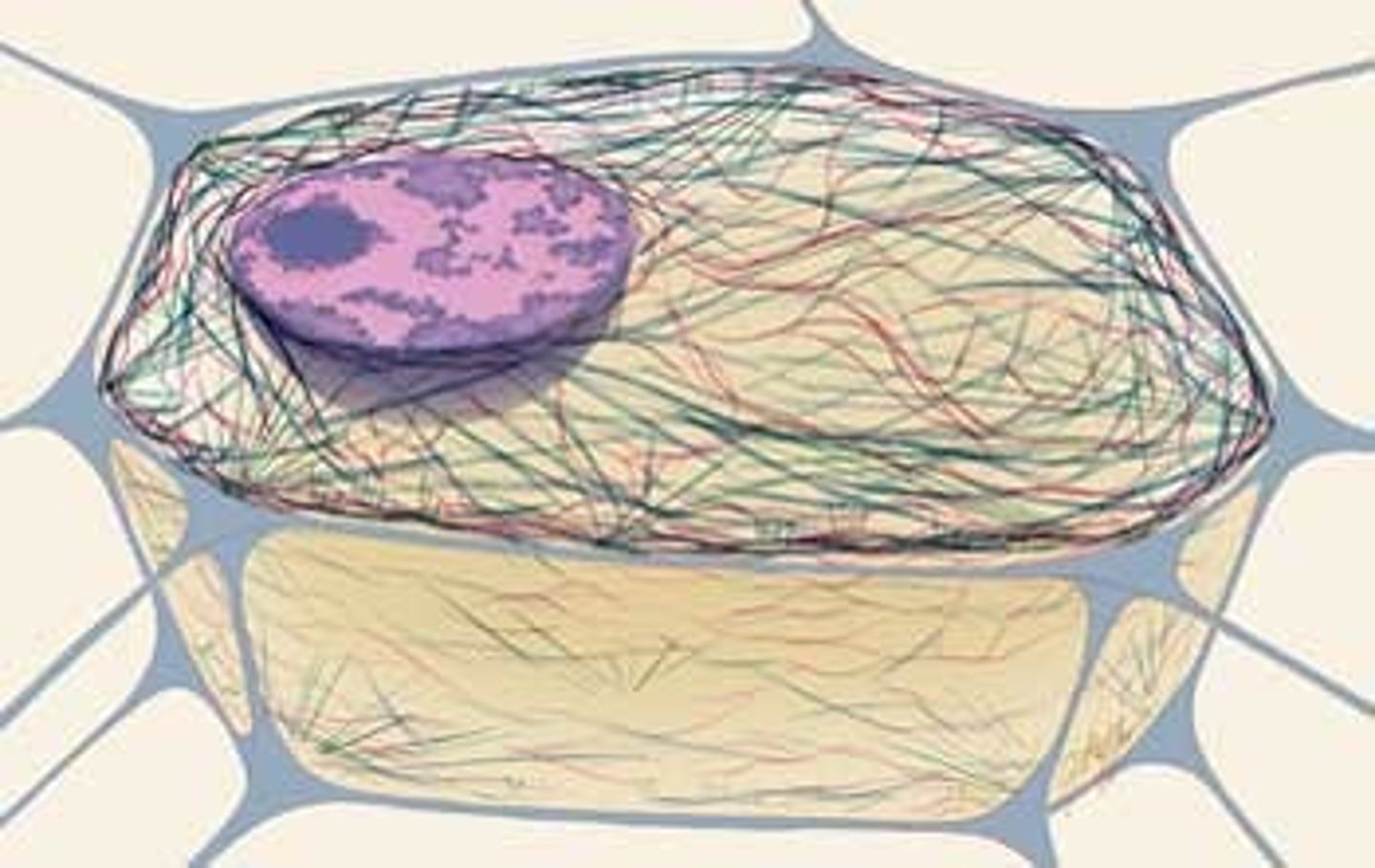
What is the structure of the cytoskeleton?
group of different protein strands
-Microtubules (solid strands and are made of the protein actin)
-Microfilaments (solid strands and are made of the protein tubulin and are cylinders made up of many subunits of tubulin joined together)
Intermediate filaments
What is the function of centrioles?
centrioles are involved in spindle formation during cell replication they are found only in animal cells
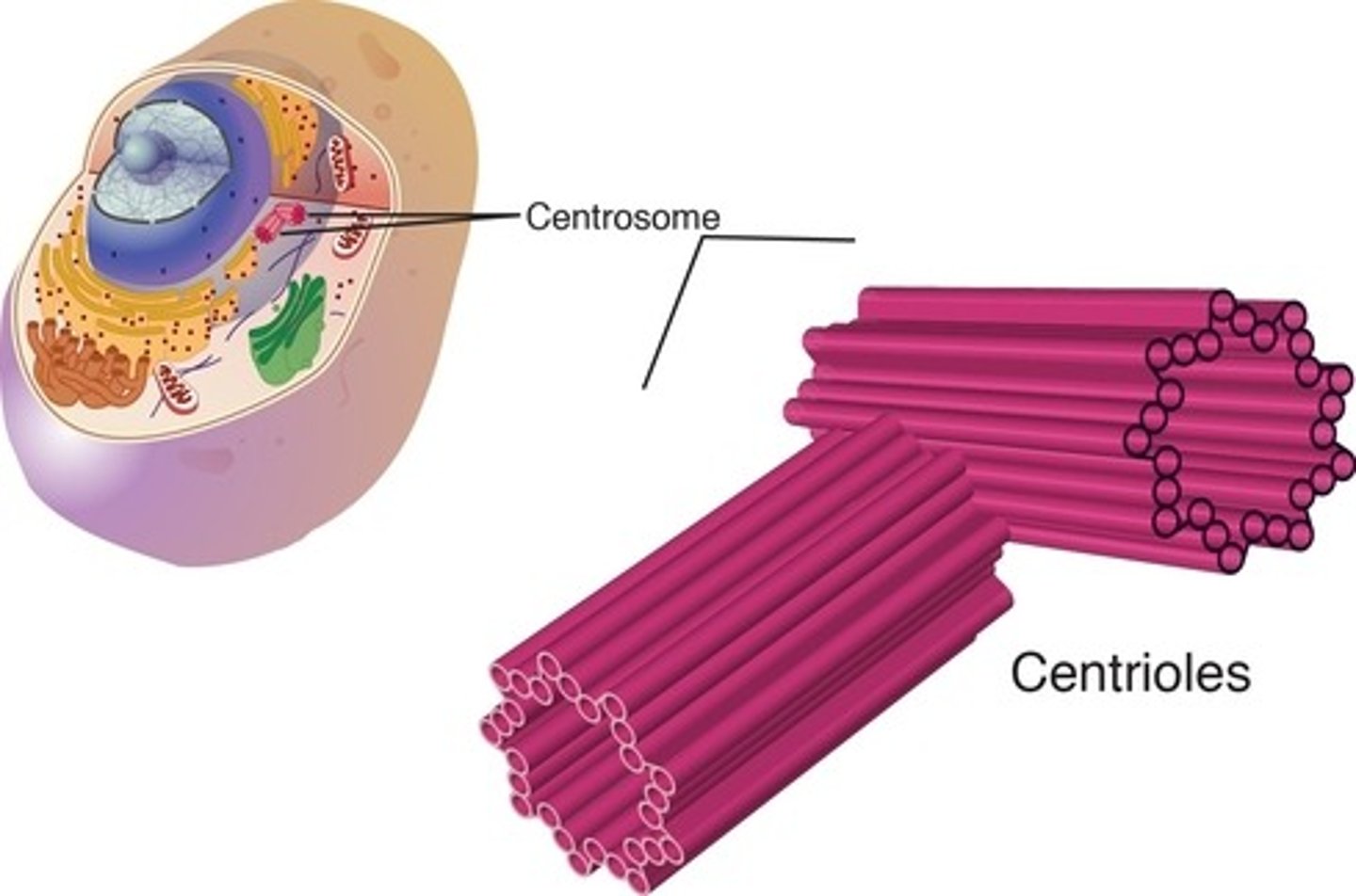
What is the structure of centrioles?
Hair-like structure found on the surface of cells. In cross section they have an outer membrane, a ring of 9 pairs of microtube.
What is the function of the nuclear pore?
The door between the cytoplasm and the nuclear membrane
What is the function of the nuclear membrane
controls movement of materials in and out of the nucleus
What is chromatin?
DNA molecules that are tightly coiled around proteins call histones.
What is the function of cytoplasm?
Site of chemical reactions and holds the components of the cell together
What is the function of a vesicle?
Transports substances in and out of the cell and between organelles