Proximal Femur and Pelvis
1/80
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
81 Terms
What kind of joint is the hip joint?
diarthrodial, synovial, ball and socket
What is the small indentation on the head of the femur?
fovea capitis
What ligament attaches in the fovea capitis?
ligament capitis femoris (teres)
Explain the direction that the head/neck of the femur projects
medially
superiorly
120-130o (more angle on a taller person) to the long axis of the shaft
anteriorly
15-20o (more angle on a taller person) from the shaft
Explain the location of the greater trochanter
on the lateral surface of the femur at the junction of body and base of neck
What other anatomical level does the greater trochanter coincide with?
level of the upper margin of the pubic symphysis
Explain the location of the lesser trochanter
on the posteromedial margin of the femur at the junction of the neck and shaft
How should the feet be positioned for a true AP of the pelvis?
internally rotated 15-20o
Where is the intertrochanteric crest located?
(prominent ridge) on the posterior surface of the femur between trochanters
Where is the intertrochanteric line located?
(less prominent ridge) on the anterior surface of the femur between trochanters
Where should you center for a hip x-ray?
femoral neck
How do you find the location of the femoral head?
draw a line between ASIS and pubic symphysis, 1½ inches perpendicularly distal to the middle of that line
How do you find the location of the femoral neck?
draw a line between ASIS and pubic symphysis, 2½ inches perpendicularly distal to the middle of that line
How do you find the location of the acetabulum?
draw a line between ASIS and pubic symphysis, acetabulum is at the middle of that line
Why do you need to rotate feet internally 15-20o for an AP hip?
to not foreshorten femoral neck and to superimpose the lesser trochanter
How is a patient positioned for a frog lateral hip?
hip flexed 90o and leg abducted 45o
What is a contraindication for doing a frog lateral hip?
hip fracture
What is the name for the “true lateral” hip view?
Daniellus Miller
Explain the Daniellus Miller view
shoot-thru lateral of the hip (trauma or post-op)
IR parallel to femoral neck
CR perpendicular to femoral neck
raise unaffected leg
What bones make up the pelvic girdle?
right hip bone and left hip bone
What bones make up the pelvis?
right hip bone, left hip bone, sacrum, and coccyx
What are 2 other names for the hip bone?
os coxae and innominate bone
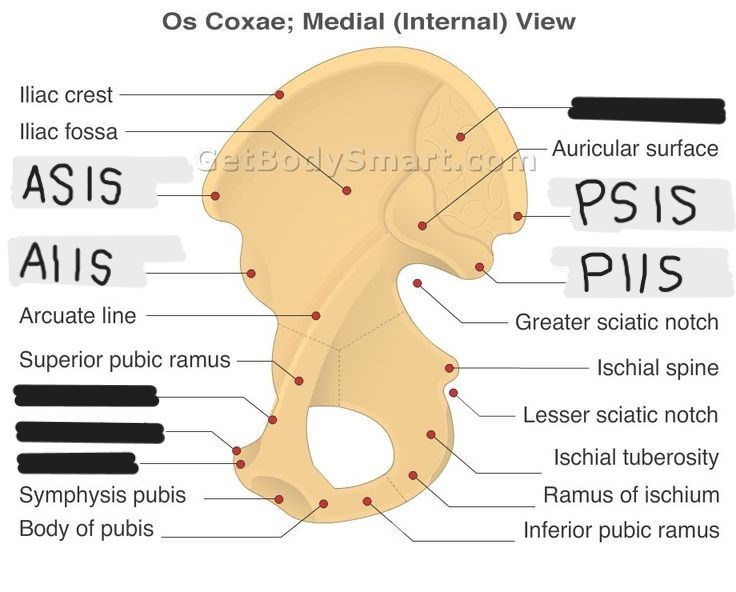
List and explain the location of the 3 bones that make up the hip bone
ilium - superior
ischium - posterior
pubis - anterior
Where do the 3 bones of the os coxae connect?
acetabulum
What fraction of the acetabulum is made up by the ilium? ischium? pubis?
ilium - 2/5
ischium - 2/5
pubis - 1/5
What is the body of the ilium?
the thick, inferior portion closest to the acetabulum
What is the ala of the ilium?
the “wing” that projects superiorly
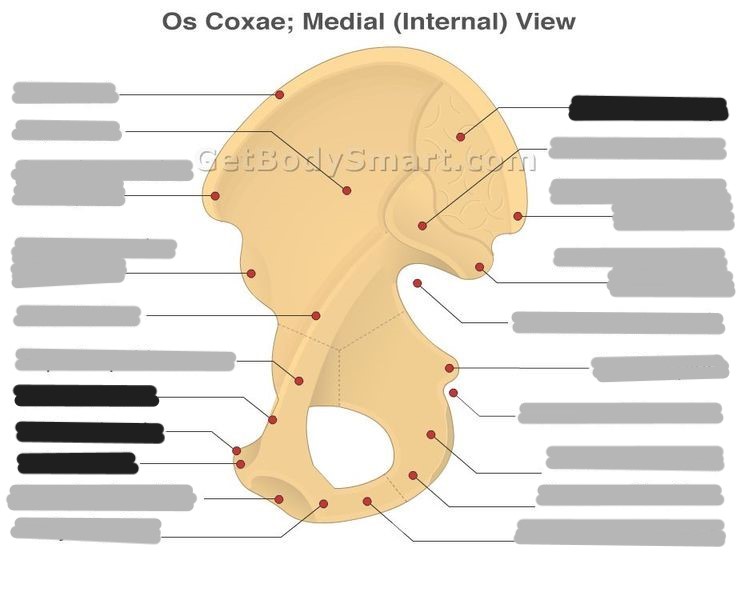
The auricular surface of the ilium articulates with the ___
sacrum
What is another name for the arcuate line?
medial line
What is the body of the ischium?
the thickened posterior portion that helps make up the acetabulum
What is the ramus of the ischium?
forms the inferior border of the obturator foramen; passes anteriorly from the ischial tuberosity
What is the ischial tuberosity?
a palpable landmark that supports weight when sitting; the most inferior structure of the pelvis
Where is the ischial tuberosity located relative to the pubic symphysis?
tuberosity is 1-2 inches inferior to symphysis
What is the ischial spine?
a pointed process on the ischium that extends medially and is situated between the greater and lesser sciatic notches
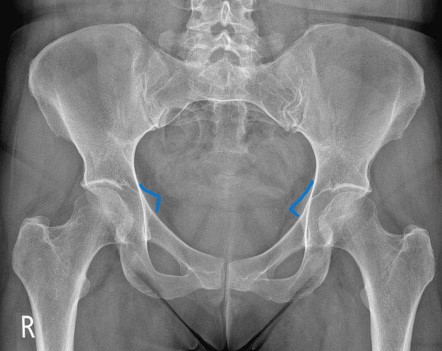
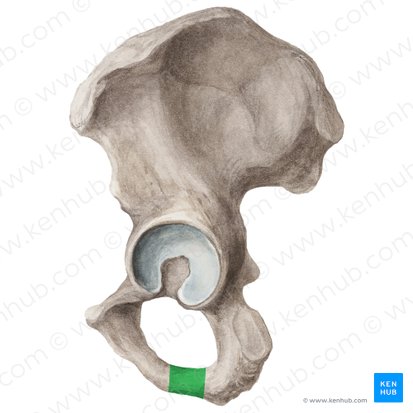
What anatomical structure is outlined in blue?
ischial spines
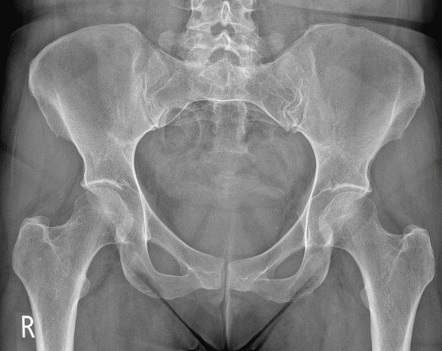
Is this a right or a left hip bone?
left
What is the body of the pubis?
the part that forms the anterior/inferior 1/5 of the acetabulum
Explain the superior and inferior pubic rami
superior: extends anterior from the body and forms the upper border of the pubic symphysis
inferior: extends down from superior ramus and joins the ischial ramus
What is the articular surface of the pubis?
the part that connects to the other pubis at the pubic symphysis
What anatomical structure is outlined in blue?
pubic arch
What makes up the obturator foramen?
pubis (body and rami) and ischium (body, ramus, and tuberosity)
What is the largest foramen in the human body?
obturator foramen
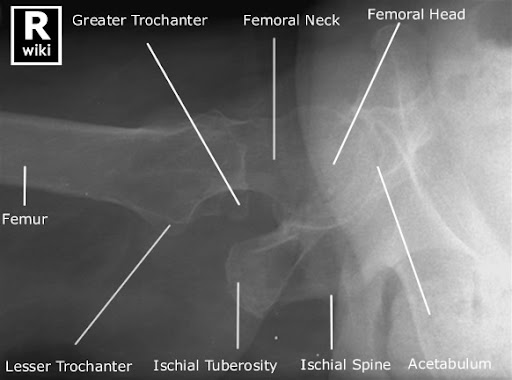
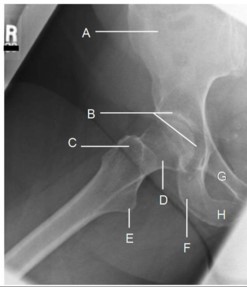
A. ala
B. acetabulum
C. greater trochanter
D. neck
E. lesser trochanter
F. ischial tuberosity
G. superior pubic rami
H. ischial rami
What kind of joint is at the acetabulum?
cartilaginous (triradiate cartilage), amphiarthrodial, synchondrosis
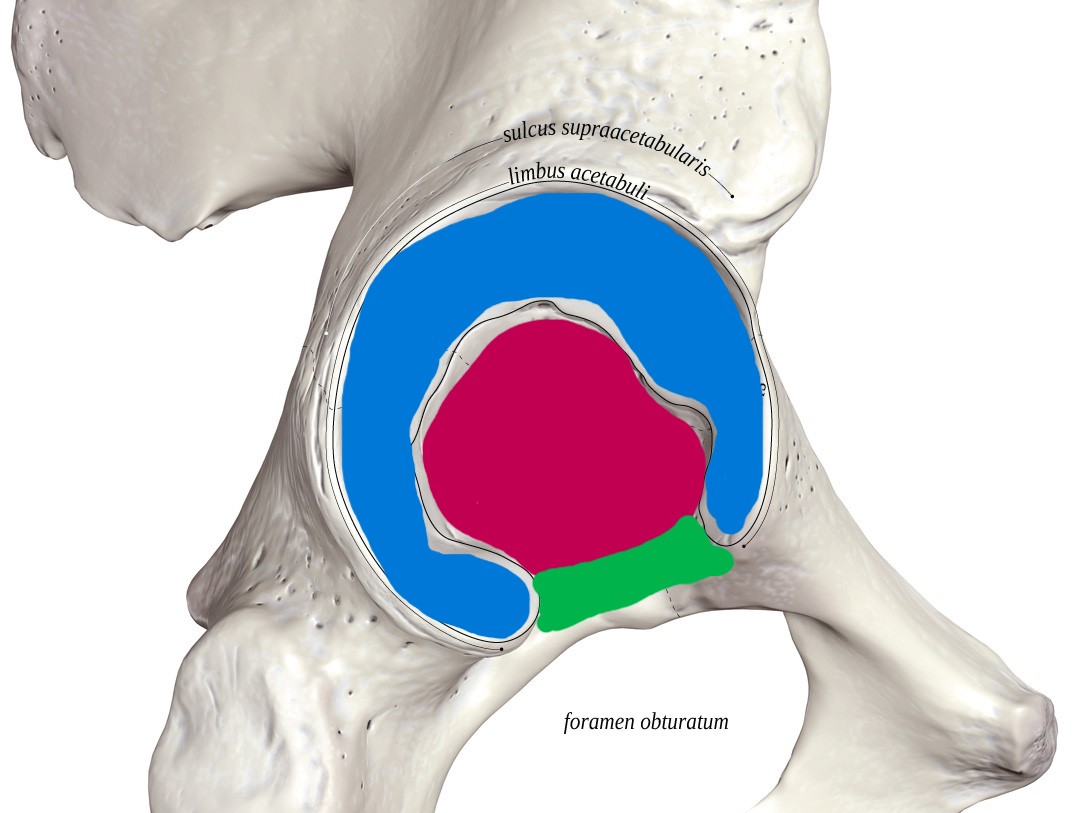
What anatomical structure of the acetabulum is at each color?
blue: rim
pink: fossa
green: notch
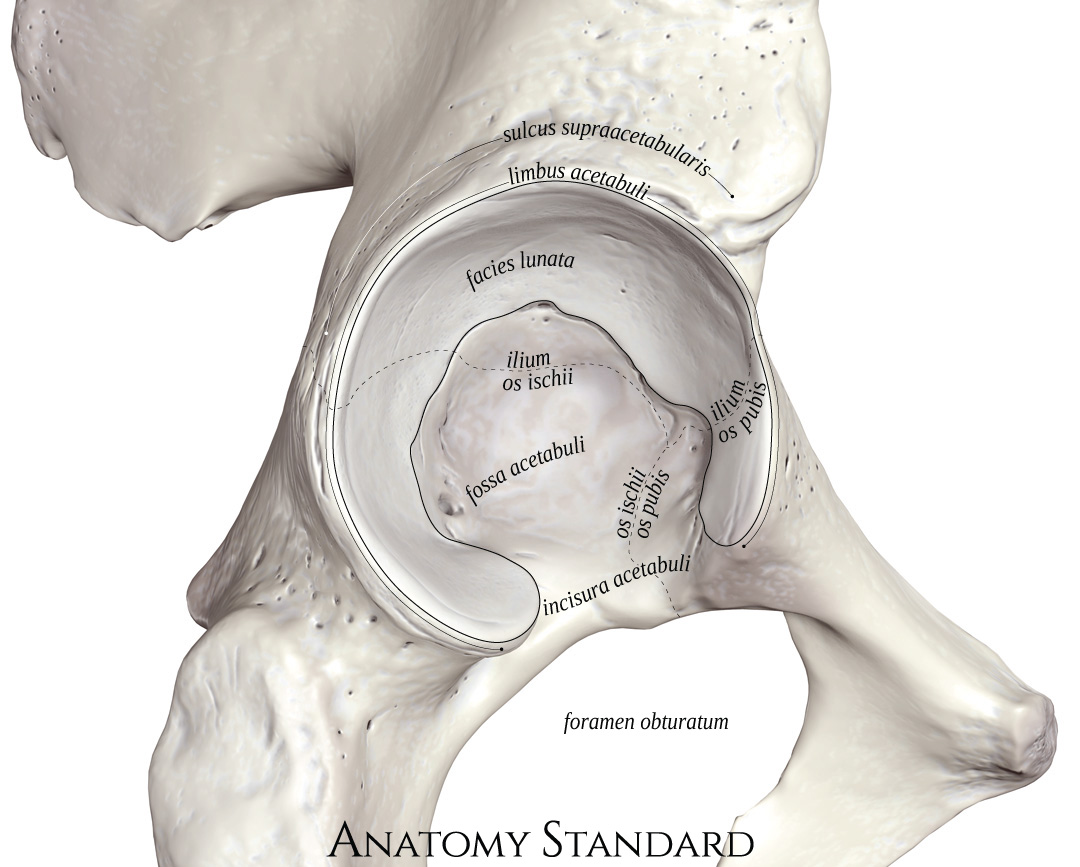
What part of the acetabulum is the articular surface?
rim
When does ossification of the acetabulum complete?
at 18 years old
The acetabular rim is made up of the ___ and ___
anterior and posterior walls
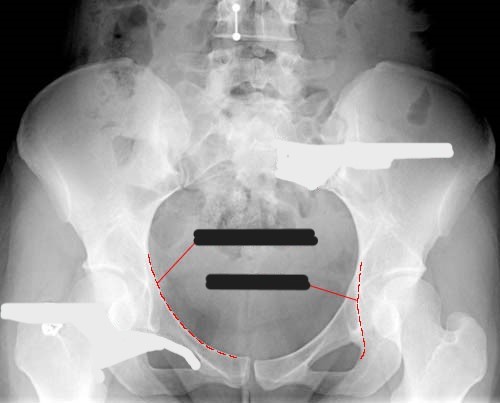
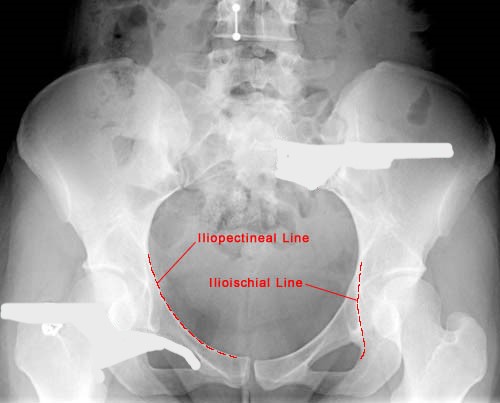
What is the pelvic brim?
oblique plane that divides the pelvis into a superior and inferior part
What makes up the pelvic brim?
iliopectineal line, arcuate line, and anterior sacrum
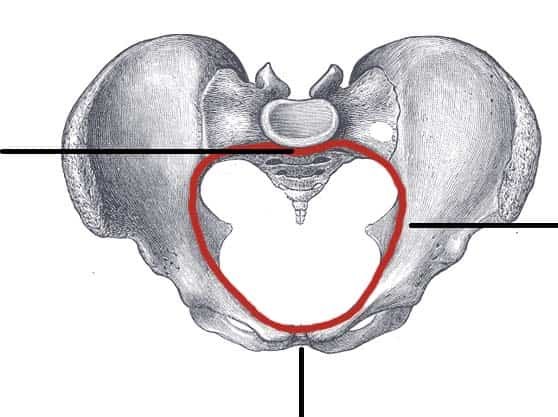
What does the red circle represent?
the pelvic inlet
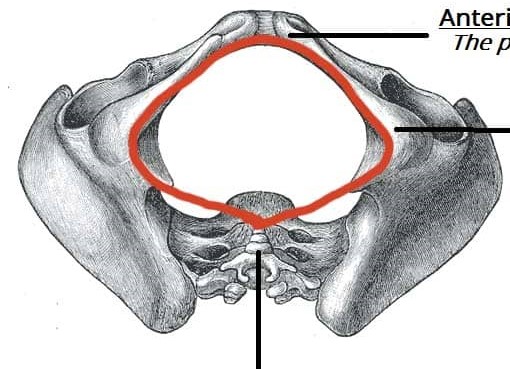
What does the red circle represent?
the pelvic outlet
What is another name for the pelvic brim?
linea terminalis (terminal line)
Explain the location of the greater pelvis
superior to the pelvic brim
lateral and posterior limits are formed by the ala
anterior limit is formed by abdomen
What is the “false pelvis”?
the greater pelvis
What is the “true pelvis”?
the lesser pelvis
What is the function of the greater pelvis?
support lower abdomen organs
What is the function of the lesser pelvis?
forms the birth canal
Explain the location of the lesser pelvis
inferior to the pelvic brim
“pelvic cavity” - the area between the inlet and outlet
contains reproductive organs, urinary bladder, pelvic colon, and rectum
Explain the pelvic inlet
superior aperture of the true pelvis
formed by the brim of pelvis (top of sacrum to symphysis)
Explain the pelvic outlet
inferior aperture of the true pelvis
triangular shape (end of coccyx to the right and left ischial tuberosities)
What is measured to find the longitudinal diameter of the pelvic outlet?
tip of coccyx to right and left ischial tuberosities
What is measured to find the transverse diameter of the pelvic outlet?
space between the ischial spines
How was the birth canal measured in the past?
pelvimetry
How is the birth canal measured now?
ultrasound
What tube angle is used for pelvic inlet views?
What tube angle is used for pelvic outlet views?
inlet: caudal
outlet: cephalic
Where are the sacroiliac (SI) joints located?
at the articulation of the articular surfaces of the sacrum and ilium
What type of joint are the SI joints?
synovial, diarthrodial, gliding
How do you demonstrate the SI joints?
25-30o oblique
if AP, side up is demonstrated
if PA, side down is demonstrated
The pubic bones are separated by ___
a pad of fibrocartilage
What type of joint is the pubic symphysis?
cartilaginous, amphiarthrodial, symphysis
What makes up the hip joint?
head of femur and the acetabulum of the os coxae bone
What type of joint is the hip joint?
synovial, diarthrodial, ball and socket
What is another name for the hip joint?
coxal joint
Explain the 3 main differences between a male and female pelvis
shape
female is broader, wider, and flared
male is narrow and less flared
pubic arch
female is >90o
male is <90o
inlet
female is larger and oval
male is smaller and round
What needs to be included on an AP pelvis image?
from greater trochanter to greater trochanter and from top of crest to ischial tuberosities
What are some causes for congenital hip dislocation?
abnormal formation
low amniotic fluid
confinement in utero
breech position
loose ligaments
Explain osteoarthritis
the most common type of arthritis leading to hip replacements
break down of the cartilage that cushions the joint
aging
prior trauma
congenital abnormalities