L59: structure and function of oral cavity
1/113
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
114 Terms
what are the components of the ailementary canal?
esophagus
stomach
small intestine
large intestine
what are the accessory organs of the digestive tract?
salivary glands
teeth
gallbladder
pancreas
liver
what animals are considered hindgut fermenters?
horse and rabbit
what animals are considered foregut fermenters?
ruminants and deer
what is the alimentary tract/canal?
the transport, physical processing, and storage of the digestive system from mouth to anus
what is the process of food passage?
food chewed by mouth
food becomes bolus that will be swallowed
bolus reach stomach and becomes ingesta, when reaches small intestines called chyme
nutrients and water absorbed from ingesta, waste becomes feces that will exit via rectum
what will the feces of an animal living in a dry area appear as?
dry feces since most of the water is being reabsorbed into the body
what are the functions of the oral cavity?
ingestion
mastication
insalivation
oral fissure
opening of the mouth
palatale dorsal arch
located at the most caudal part of the oral cavity where both palatoglossal arches combine
mucosa of oropharynx
highly sensitive, can initiate swallowing reflex in animal
what is another name for lips?
oral fissure
angle of mouth/ oral comissure/ comissure of the lip
point where the upper and lower lip meet; used as a landmark in surgeries to gain entry into oral cavity
function of mouth
ensure proper closure of rima oris/oral fissure
sucking milk in young
prevent loss of saliva and food while chewing
what muscle provides support to the lips?
orbicularis oris muscle
what mucosa is present in the lips?
labial glands = minor salivary glands on the oral surface
what happens when the orbicularis oris muscle contract?
mouth will close but important to note DOES NOT have control over jaw movement
describe the surface of the outer skin of the lips
keratinization to protect against tough material
what is the composition of the lower lips?
stratified squamous epithelium
labial glands
which animals have prehensile upper lips?
horse
sheep
goat
what do we mean when we say an animal has prehensile upper lips?
animal uses upper lip to bring food to the mouth
what is seen in animals with flews?
lots of drooling will be seen because oral fissure not closed as well, animal cannot contain as much saliva in oral cavity
lip fold
present between the lips and the gum, exclusive to dogs
lip frenulum
located at rostral part of lip fold, exclusive to dogs
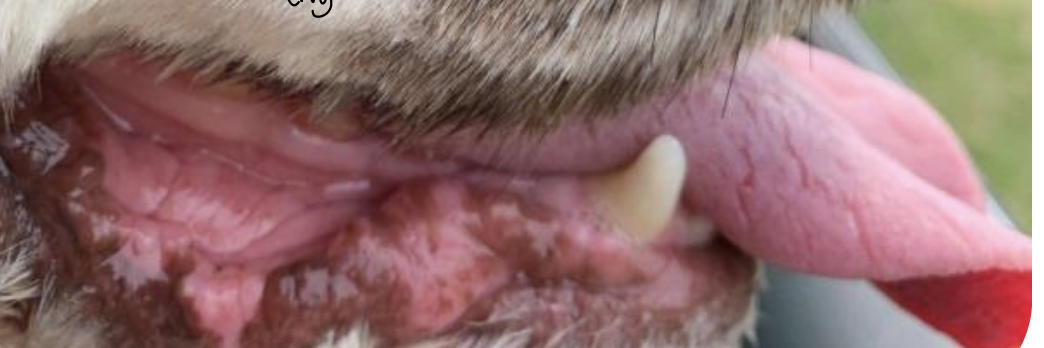
what is this image showing in the dog?
lip fold dermatitis
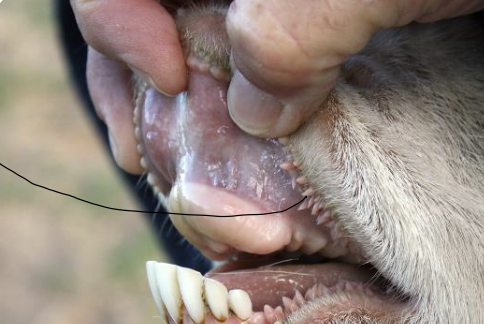
what is the black line pointing to in the goat?
conical papillae
what is the function of the conical papillae in ruminants?
reduce direct contact between mucous membrane and rough food material
prevent back flow of food outside of the oral cavity to be able to swallow
what direction do the conical papillae face?
backwards
where are conical papillae present?
labial and buccal mucosa
what structure forms the caudo-lateral boundary of the oral cavity?
the cheeks
what is another name for cheeks?
buccae
what muscle forms the major bulk of the cheeks?
buccinator muscle
what muscle is responsible for facial expression and closing of the jaw?
buccinator muscle
which species have narrow cheeks?
carnivores
which species have wider cheeks?
herbivores
what are the minor salivary glands of the cheeks?
buccal glands
what is different about the cheeks in cats and dogs?
zygomatic and molar salivary glands are major, normally they are minor glands in the cheeks
what provides sensory innervation to the lips and cheeks?
trigeminal nerve (CN 5)
what provides motor innervation to the lips and cheeks?
facial nerve (CN VII)
orbiculus muscle
skeletal muscle of the lips under voluntary control for facial expression
what is the muscle of the cheeks for facial expression?
velocinatory muscle
what does the facial artery branch from?
external carotid artery
what branches from the facial artery?
superior labial
angularis oris
what branches from the maxillary artery?
inferior alveolar then mental arteries
infraorbital then lateral nasal artery
what is the rostral limit of the oral cavity?
rima oris
what is the caudal limit of the oral cavity?
palatoglossal arch
what structure makes up the floor boundary of the oral cavity?
mylohyoideus muscles
what is the vestibule of the mouth?
Space outside the teeth
what is the oral cavity proper?
space inside the teeth
what are the organs of the oral cavity?
tongue
teeth
openings of salivary glands
what salivary glands are located in the vestibule of the oral cavity?
parotoid gland
zygomatic gland
MCQ: what animal has prehensile lips?
horse, sheep, and goat
what are the transverse ridges of the hard palate?
rugae
hard palate
rostral bony portion including incisive, maxillary, and palatine bones
incisive papilla
opening of the incisive ducts on both sides – ducts of the vomeronasal organ
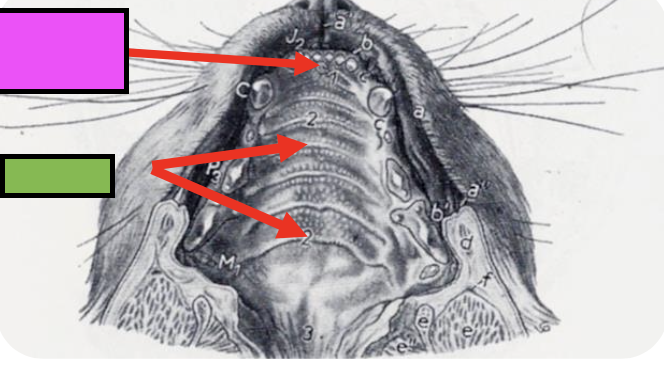
what is the pink box pointing to?
incisive papillae
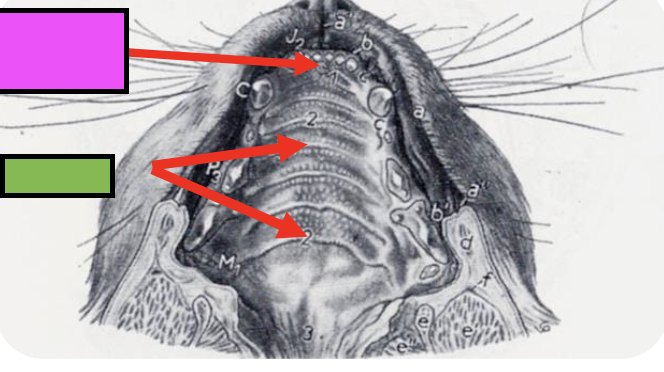
what is the green box pointing to?
rugae
what is the purpose of rugae on the hard palate?
makes surface uneven to help prevent loss of food and push it back into oral cavity
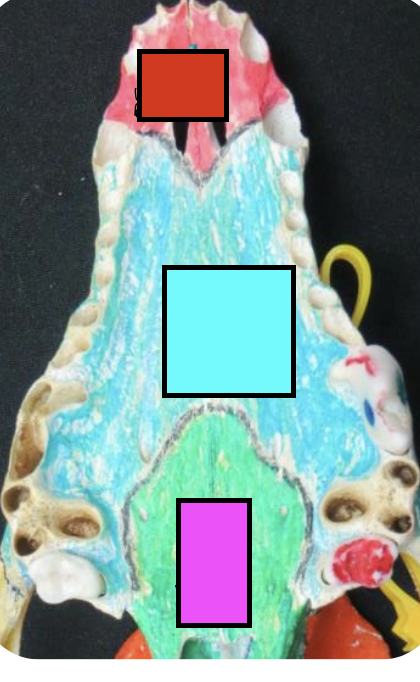
what is the red?
incisor bone
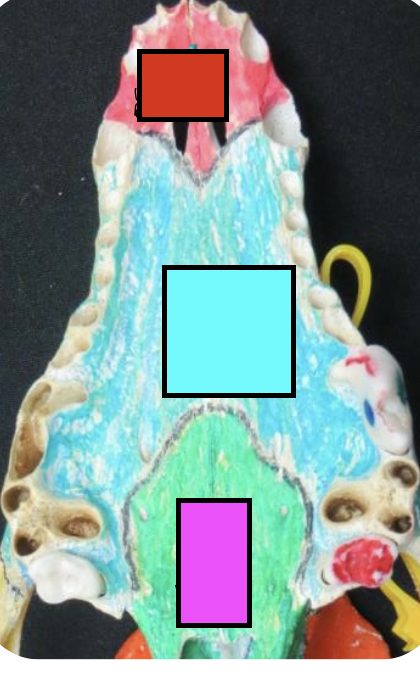
what is the blue?
maxillary bone
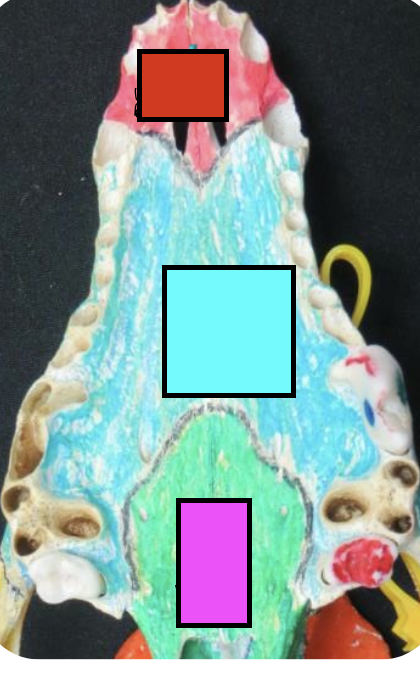
what is the green?
palatine bone
what is something to note of the papillae of the cat and cow?
backward pointing papillae on the hard palate help in grasping food
what are the sublingual / buccal drugs?
buprenorphine
detomidine
which species is buprenophine effective in?
cats
what do we prescribe buprenorphine for?
pain relief and sedation
what species is detomidine effective in?
horses and calves
what is detomidine prescribed for?
pain relief and sedation
MCQ: which nerve innervates the muscles of the hard palate?
vagus and glossopharyngeal
describe the oral mucosa of ruminants?
keratinixation of oral mucosa
less sensitive lips and oral mucosa= dont feel abnormal objects in food
which species have a keratinized soft palate?
ruminants and horses
which species do not have a keratinized soft palate?
dogs and cats
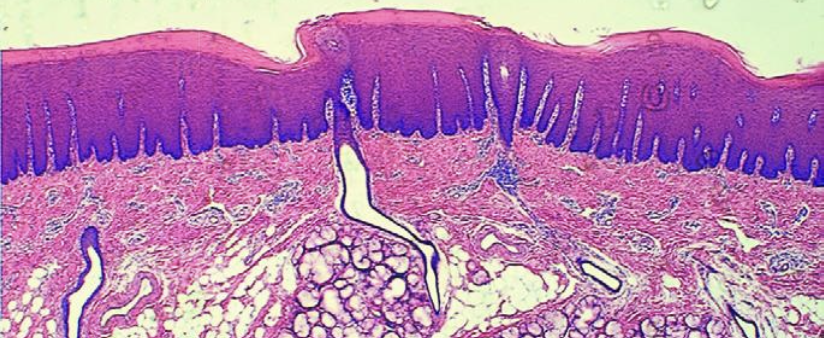
what does this image show?
soft palate of a cow
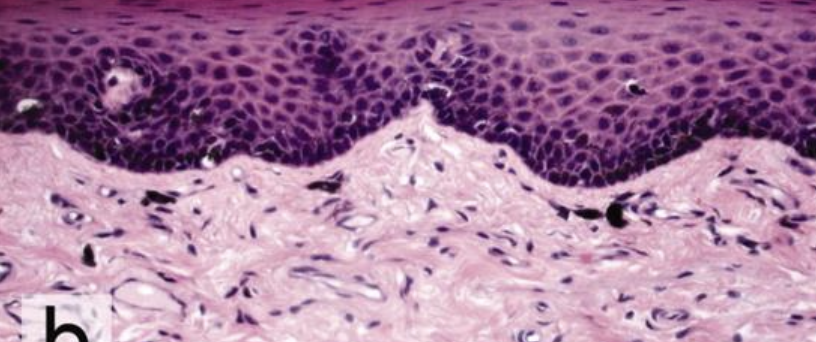
what does this image show?
soft palate of a dog
which animal does not have salivary glands in the hard palate?
pigs
what is the histology of the hard palate?
Keratinized Stratified squamous epithelium
where are salivary glands located in the hard palate?
caudal portion only
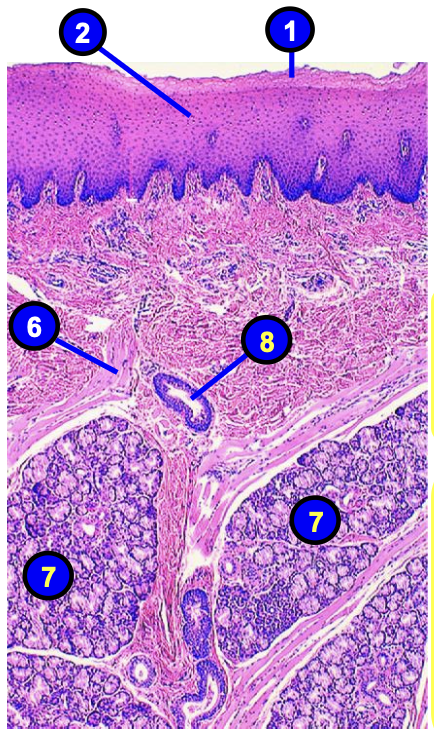
what is number 7?
seromucous labial glands in propria submucosa of the lip
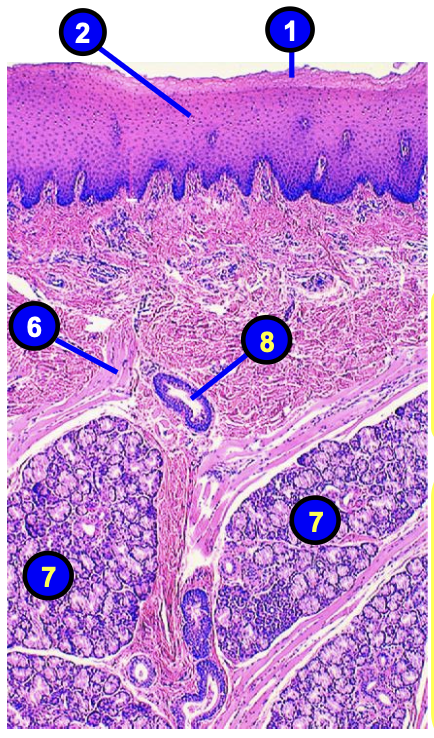
what is number 2?
keratinized stratified squamous epithelium of the lip
what does the tunica muscularis consist of in the lip?
skeletal muscle fibers of the orbicularis oris muscle
what is the outer layer of the lip?
cutaneous/skin
what is the middle layer of the lip?
Orbicularis oris muscle
what is the inner layer of the lip?
Stratified squamous epithelium
what structure is absent in the oral cavity but present in the cheek?
muscularis mucosae
what are signs of unilateral facial paralysis?
dullness of the face
drooped ears
loose lips
drooling
food and water loss with eating
which nerve is damaged in unilateral facial paralysis?
facial nerve (CN 7)
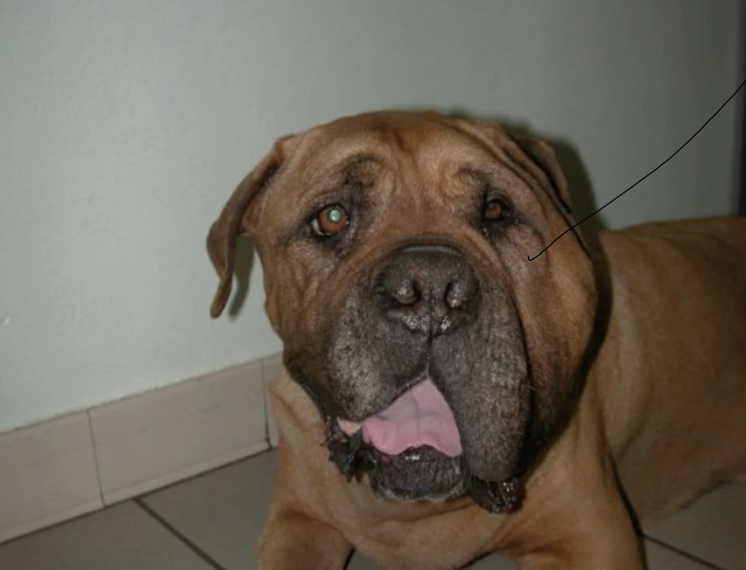

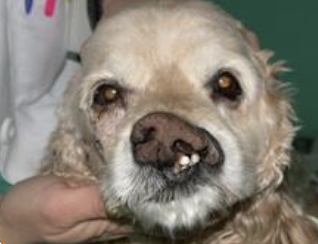
what is this dog suffering from?
unilateral facial paralysis
what nerves do you have to consider during a cleft palate repair?
greater palantine foramen
greater palatine nerve
maxillary nerve (branch of CN 5)
what does the image show?
primary cleft palate or “harelip”; more rostral
secondary cleft palate
the soft palate and hard palate have not fused on both sides leading to a gap along the midline
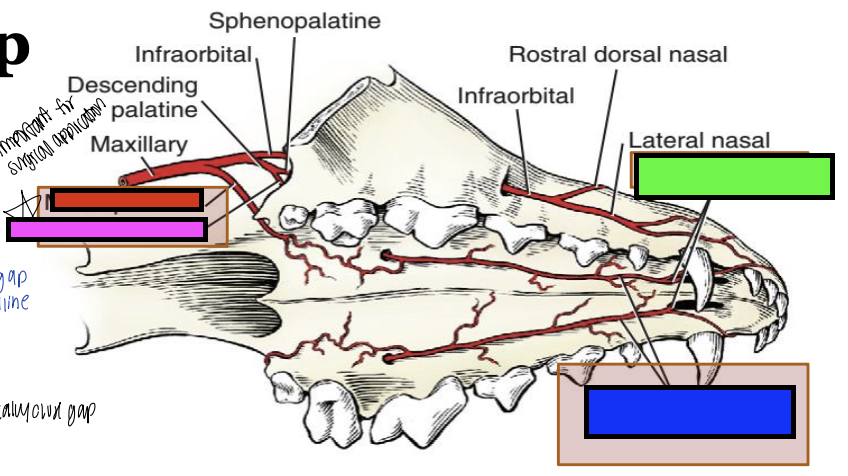
what is the green box?
rostral septal
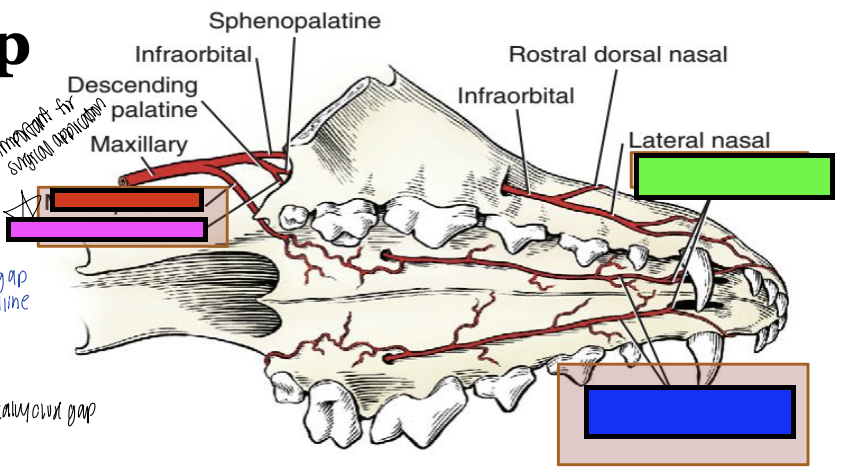
what is the blue box?
major palatine
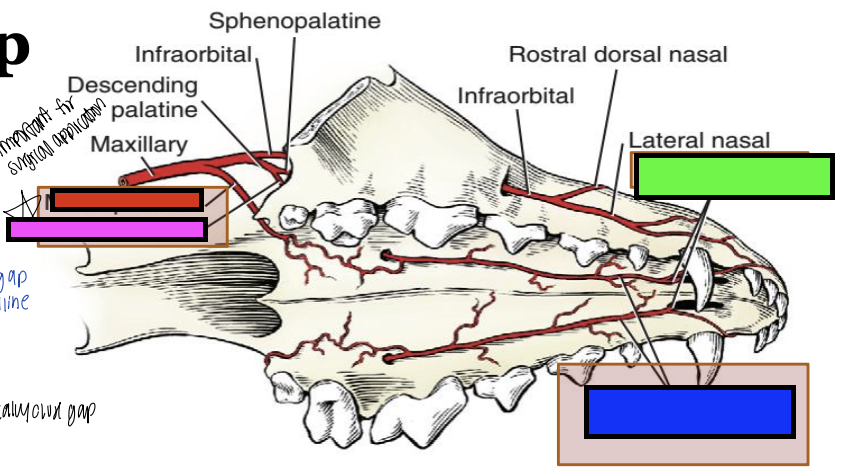
what is the pink box?
major palatine
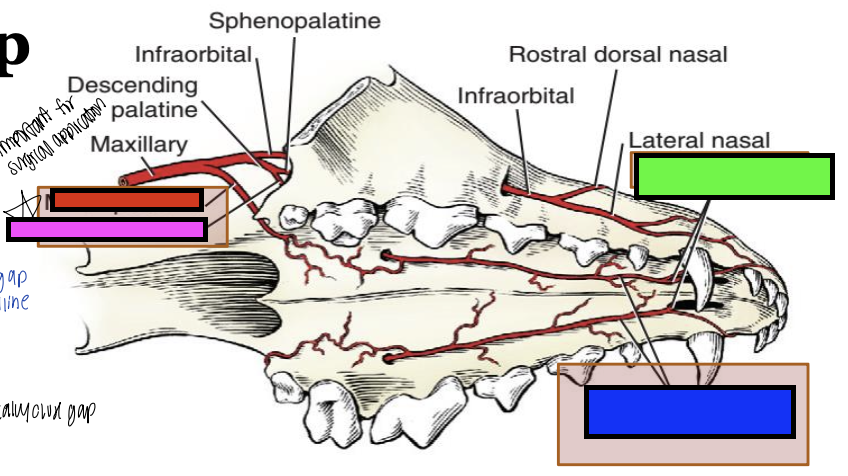
what is the red box?
minor palatine
what blood vessels do you have to consider during a cleft palate repair?
major palatine
minor palatine
rostral septal
what action are the soft palate muscles important for?
swallowing
what are the palatine muscles?
palatinus muscle
tensor veli palatini muscle
levator veli palatini muscle
palatopharyngeus muscles
what innervates the soft palate?
vagus nerve and glossopharygneal nerve
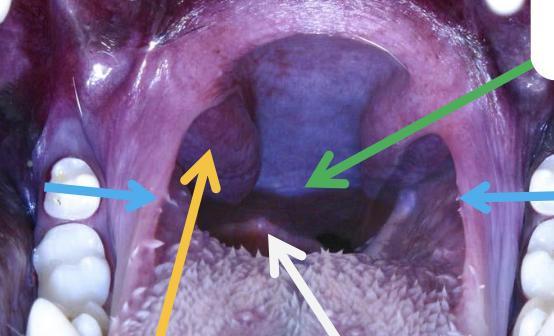
what is the green arrow pointing to?
soft palate
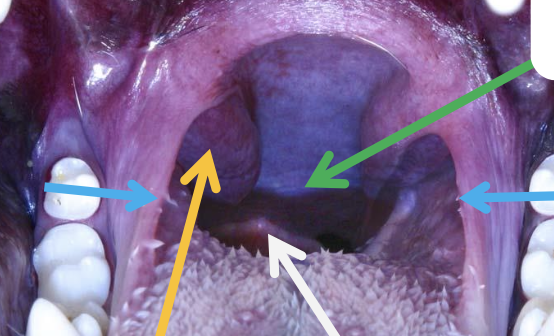
what are the blue arrows pointing to?
palatoglossal arch/fold
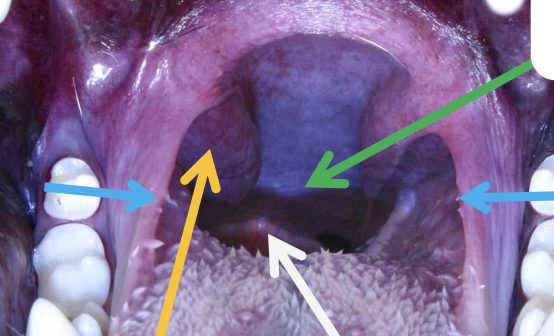
what is the yellow arrow pointing to?
palatine tonsils