5.2 Autoimmune Diseases
1/76
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
77 Terms
Define Autoimmunity.
Immune system mistakenly recognizes self tissue as foreign, and creates immune response
Self-tolerance is established by what 3 facts:
ability to identify and not react to self antigens
active regulation by T cells
a balance of T helper cell type 1 and 2
Which T helper cells are primary mediators of autoimmunity?
Th1 via cytokines
Inheritance of gene coding for a specific MHC molecule may make a person:
more susceptible to an autoimmune disease
MHC I complex will be on:
almost all nucleated cells
MHC II complex will be on:
APC
MHC III genes code for:
Complement
Define molecular mimicry:
Viral or bacterial antigens that resemble self antigens
What is an example of molecular mimicry?
Streptococcal infections causes Abs to develop that also recognize heart muscle Ags
What 2 types of cells are used for Antinuclear Antibodies (ANA) testing?
Mouse kidney or Human epithelial HEp-2 cells
What is an anti-nuclear antibody?
Ab formed to nuclear Ags that have been released into the blood (via apoptosis)
In Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) Where do the immune complexes commonly get trapped in the body?
Kidneys
Synovium
Blood cells, vessels, skin, lungs, liver, nervous system, heart
What are the most common symptoms you would see with SLE?
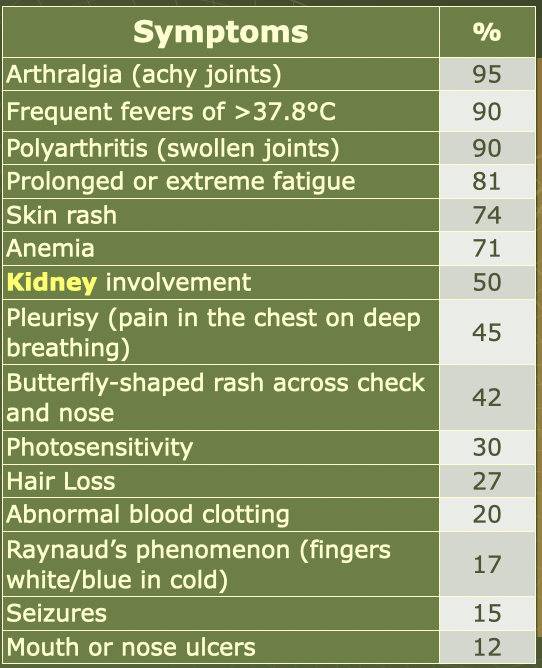
When screening with the ANA test what 2 patterns would you find for SLE?
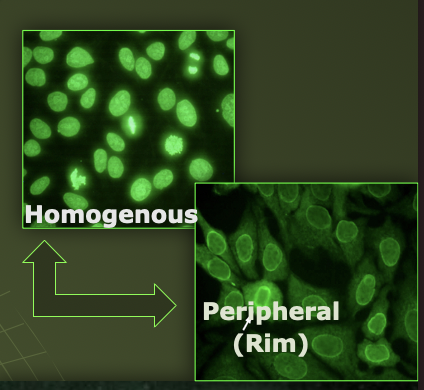
*For SLE, what are they specifically staining in the cell during ANA test?
Antinuclear antibodies
ds-DNA (most specific)
What happens to complement levels in SLE? Why?
Decreased Complement due to activation of complement by immune complexes (i.e. consumption)
What is the substrate of the confirmation test for SLE, that has ds-DNA in the kinetoplast?
Crithidia luciliae (hemoflagellate)
What type of antibody is seen in Drug induced SLE? What pattern?
anti-histone

What is a common but separate antibody seen with SLE?
Anti-phosholipid
What are the most common antibodies tested for Antiphospholipid syndrome?
Anti-cardiolipin, lupus anticoagulant, β2-glycoprotein-1
What does Antiphospholipid syndrome cause in the patient?
multiple miscarriages
clotting issues
migraines
thrombotic events
What are some common abnormal labs seen in Antiphospholipid Syndrome?
prolonged PTT
low platelets
In Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) Ig__ or Ig__ antibodies are formed against the ____ portion of ______.
IgM or IgG; Fc portion of IgG
What type of hypersensitivity is RA?
Type III
What are the 3 most common characteristic symptoms of RA:
Bilateral damage
Decreased joint space
Bony erosions
What is the screening test for RA called?It detects what type of Ab?
Screening Test: Rheumatoid Factor (RF)
detects serum IgM
What is the confirmatory test for RA called?
Confirmatory Test: Anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide assay (anti-CCP)
_________ titers of complement will happen with RA
Low
What are the 4 main organ specific AI diseases?

In Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis, autoAbs are produced against _______________ and ____________ cell components
Thyroglobulin and Thyroid
Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis: ____ TSH (________thyroidism)
High TSH; hypothyroidism
What type of hypersensitivity is Hashimoto’s
Type II
Main symptoms for these Hashimoto are:
Weight gain, lethargy, intolerance to cold
Goiter, enlarged thyroid, hypothyroidism, thyroid autoantibodies
Hashimoto’s:
__________ ____________ Antibody is seen in 90-95% of pts
Thyroid Peroxidase Ab (TPO Ab)
Hashimoto’s:
__________ antibody is seen in 80% of pts but may also be seen in_______cancer pts
Thyroglobulin Ab (TgAb); thyroid
Graves’s Disease:
____ TSH (_________thyroidism)
Low TSH; Hyperthyroidism
What type of hypersensitivity is Grave’s Disease?
Type II
Main symptoms for Graves’ Disease:
Thyrotoxicosis
diffusely enlarged soft goiter
Exophthalmos (35%)
Weight loss, tremors
Anxiety, difficulty sleeping, ↑ heart rate
Heat intolerance
Graves’:
__________ ____________ Antibody is seen in ~75% of pts
Thyroid Peroxidase Ab (TPOAb)
Graves’:
__________ ____________ ________________ are a better Ab to help diagnose
Thyroid-Stimulating Immunoglobulins (TSI)
Thyroid-Stimulating Immunoglobulins (TSI) will lead to continual production of _____ & _____
T3 & T4
Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus results from destruction of _______ ______ in the ____________.
beta cells; pancreatic islets
What are the 4 most common AutoAbs of βcell autoimmunity?
Abs to GAD (glutamic acid decarboxylase)
ICA = islet cell Abs
Insulin autoAbs, Insulin-associated Ag (IAA)
Abs to transmembrane protein, tyrosine phosphatase (IA-2A)
Glucose/A1C values that indicate DM
Fasting Plasma Glucose ≥ 126 mg/dL
Random Plasma Glucose ≥ 200 mg/dL
Hemoglobin A1c ≥ 6.5%
Failing Oral Glucose Tolerance Test
T1DM:
Why would AutoAb testing be done for patients?
To screen for Type 1 DM before beta-cell destruction
only for family members of T1DM
Addison’s Disease results from destruction or dysfunction of the _________ __________.
adrenal glands
For Addision’s Disease, List which classes of adrenal steroids will be deficient:

Main symptoms for Addisons pts are:
Fatigue, weakness, loss of appetite/weight, salt cravings, ab pain, nausea/vomiting, muscle pain
Low BP, dehydration, low blood sugar
May progress to shock and or death
Addison’s Disease:
____ glucose, cortisol, aldosterone, Na, Cl
decreased
Addison’s Disease:
____ K and renin levels
Increased
Addison’s Disease pts can also have Abs against ______________________
21-hydroxylase
Myasthenia Gravis results from Abs against ______________ ______________ at _______ _____
Acetylcholine Receptors at Neuromuscular Junctions
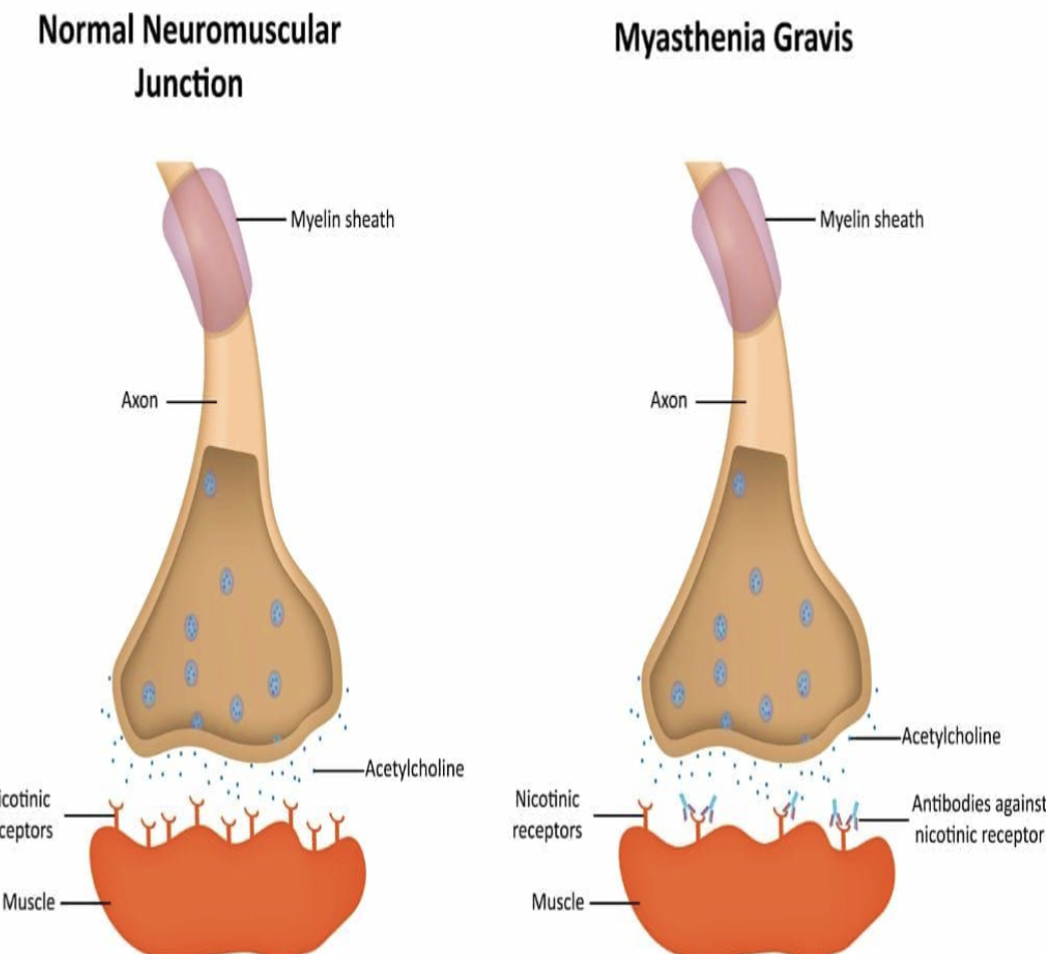
Myasthenia Gravis clinical signs
Drooping eyelids
Inability to retract the corners of the mouth
Inability to maintain support of the trunk, the neck, or the head
Multiple Sclerosis is an inflammatory AI disorder of the __________.
CNS
In Multiple Sclerosis, what important component is destroyed by AutoAbs?
myelin sheath
Another important characteristic of MS is: _____________ formation in the white matter of the _____
plaque; brain
MS Main symptoms
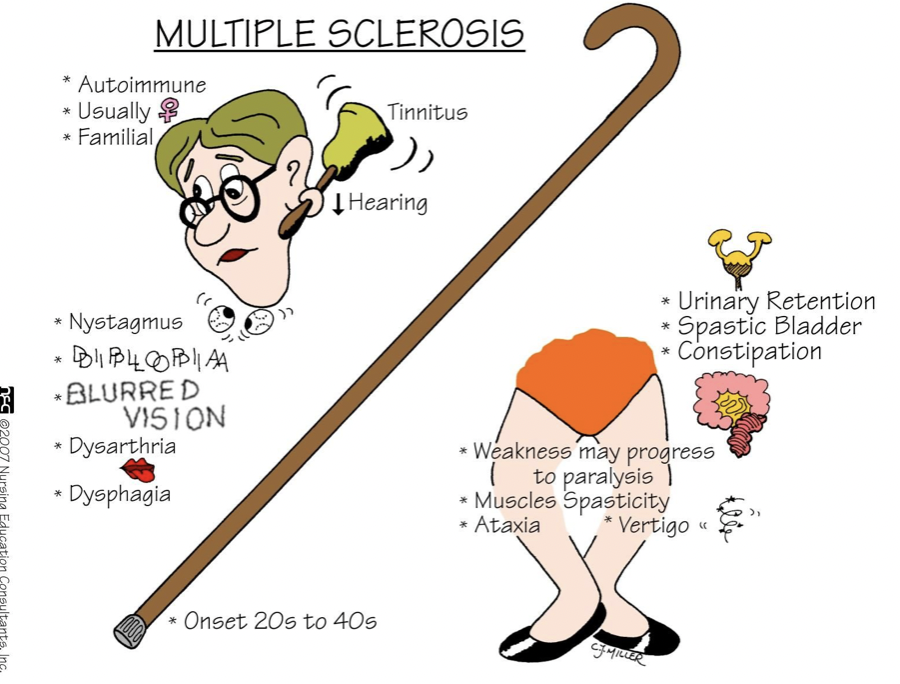
In MS, what key characteristic is seen with CSF electrophoresis?
Oligoclonal Bands
How is MS confirmed? What are they looking for?
Confirmed with MRI
looking for white matter plaques in brain and spinal cord
Celiac Disease results from an intolerance to dietary ___________ causing poor______________ of nutrients
gluten; absorption
What are some key clinical signs of Celiac pts
Adults
Anemia (Fe def), diarrhea, bloating, fatigue, weight loss
Kids
Irritability, abdominal distention, diarrhea, failure to thrive, weight loss
What are the 3 most common AutoAbs found in Celliac’s:
Anti-Tissue Transglutaminase (TTG)
Anti-Gliadin
Anti-Endomysial (component of lining within intestine)
Goodpasture’s Syndrome is due to an AutoAb towards the ______________, ______________, and _______
glomerular
renal tubular
alveolar basement membrane
In Goodpasture’s Syndrome, damage to the glomerulus rapidly progresses to _________ __________
renal failure
Goodpasture’s Syndrome:
Glomerular damage is done by ______________ antibody making it a type ___hypersensitivity
cytotoxic; Type II
Goodpasture’s clinical signs

Goodpasture’s Treatment:
________________ can help remove circulating antibodies
Plasmapheresis
Scleroderma is a disorder that results in normal tissue/skin being replaced with:
Thick Tissue ( extra collagen produced)
Scleroderma will eventually lead to ____ when organs are changed (heart, lung, kidneys)
death
What does CREST (Scleroderma symptoms) stand for ?

Scleroderma ANA will show ____________ or _____________ pattern
speckled or nucleolar (95%)
___________ antibody is specific for Scleroderma but only seen in 15-20%
Scl-70
In Scleroderma___________ antibody is a marker for ________ .
Centromere; CREST
Sjögren’s Syndrome, an AI that affects the __________ glands, causing mostly dry ________and____
exocrine; dry eyes and mouth
Sjögren’s Syndrome has a____________ pattern
speckled
What are the 2 Sjögren’s Syndrome AutoAbs
Anti- SS-A/ Ro
Anti- SS B/ La
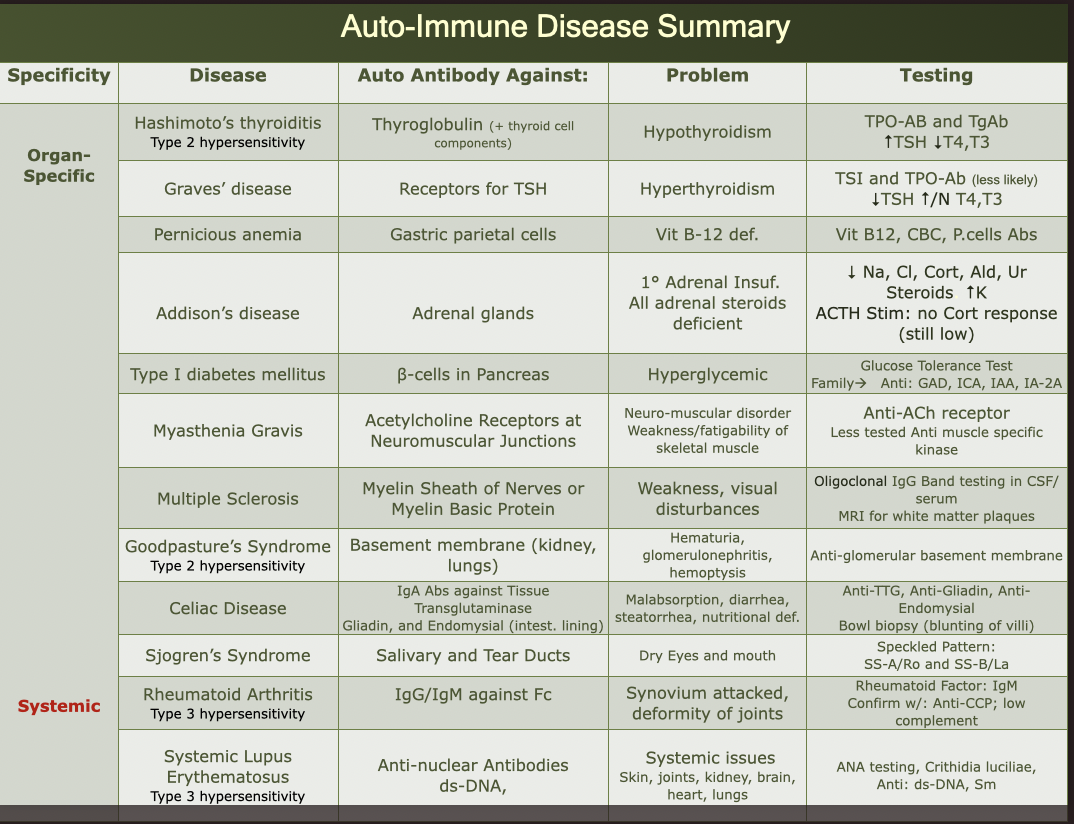
AI Diseases Summary Chart