Reproduction and Embryonic Development: Human Fertilization, Pregnancy, and Birth
1/85
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
86 Terms
What is the process called when sperm are released in the vagina?
Insemination.
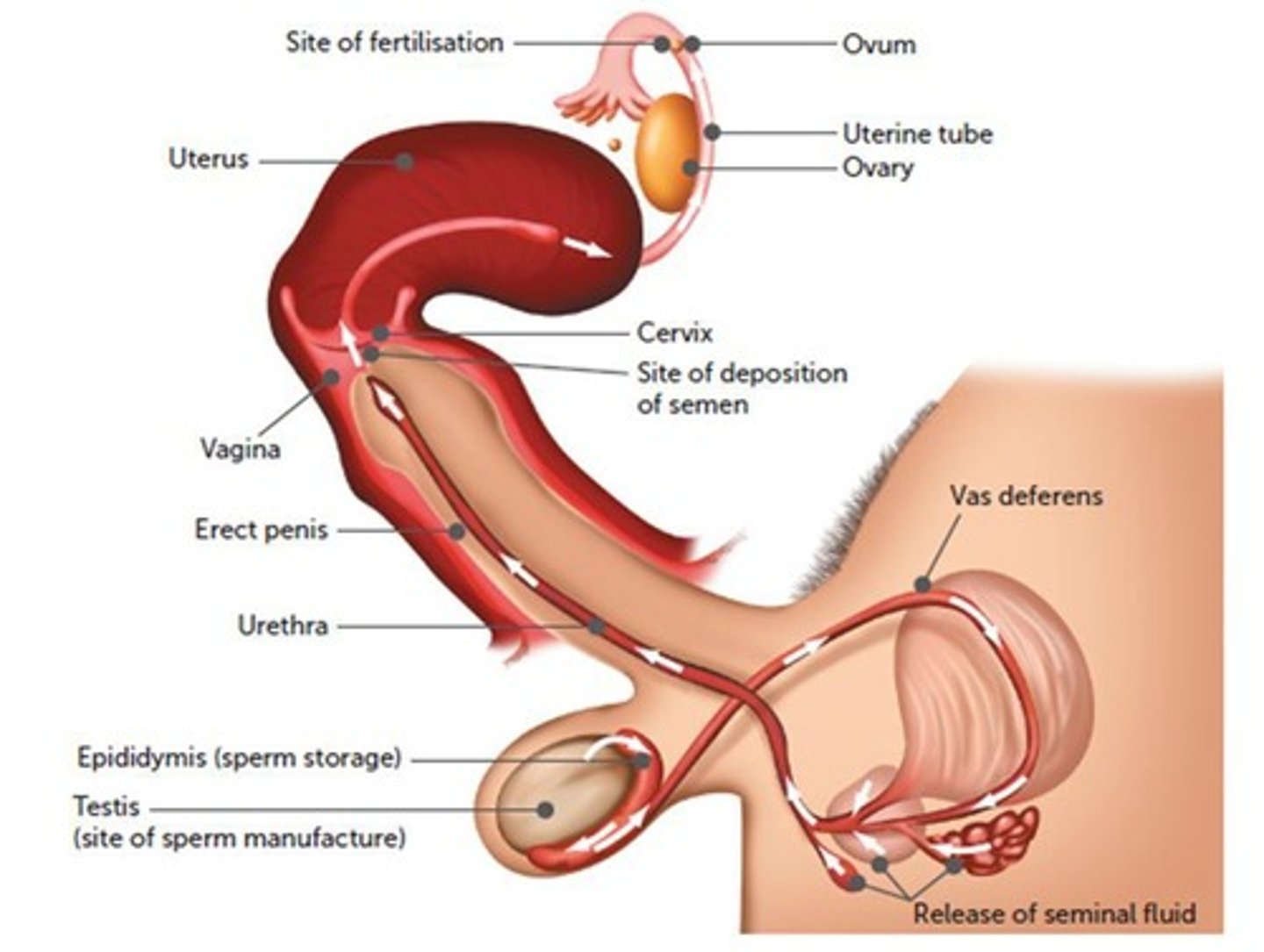
Where does fertilisation normally occur?
In the uterine tubes.
What is the secondary oocyte surrounded by?
Two layers: the outer corona radiata and the inner zona pellucida.
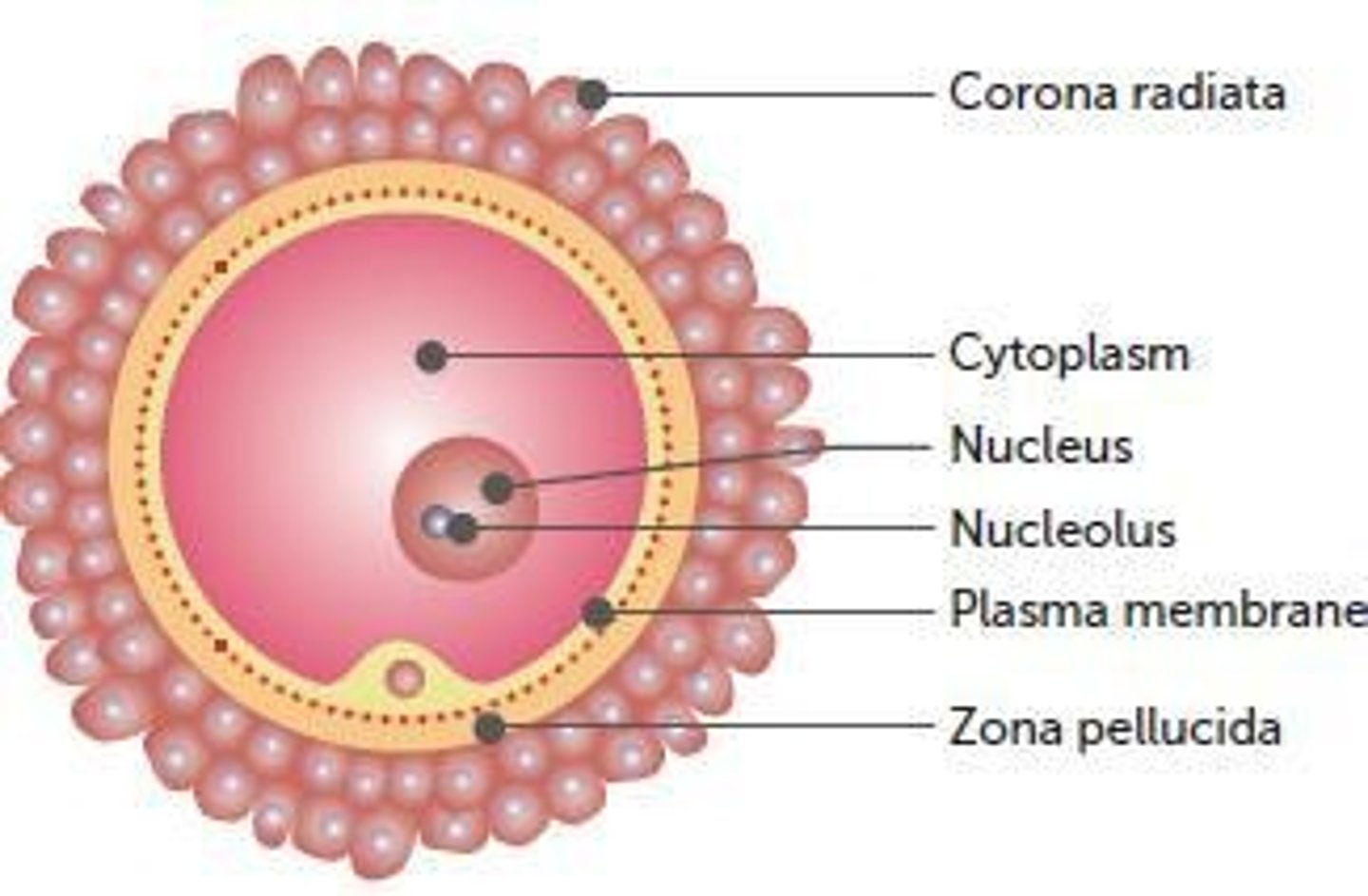
What is the function of the corona radiata?
It consists of follicle cells held together by cementing materials that contain acid.
What is the zona pellucida?
A glycoprotein matrix surrounding the plasma membrane of the oocyte.
Why is a large number of sperm required for fertilisation?
Due to high sperm mortality and the insufficient enzyme amount in one sperm to break down the acid in the corona radiata.
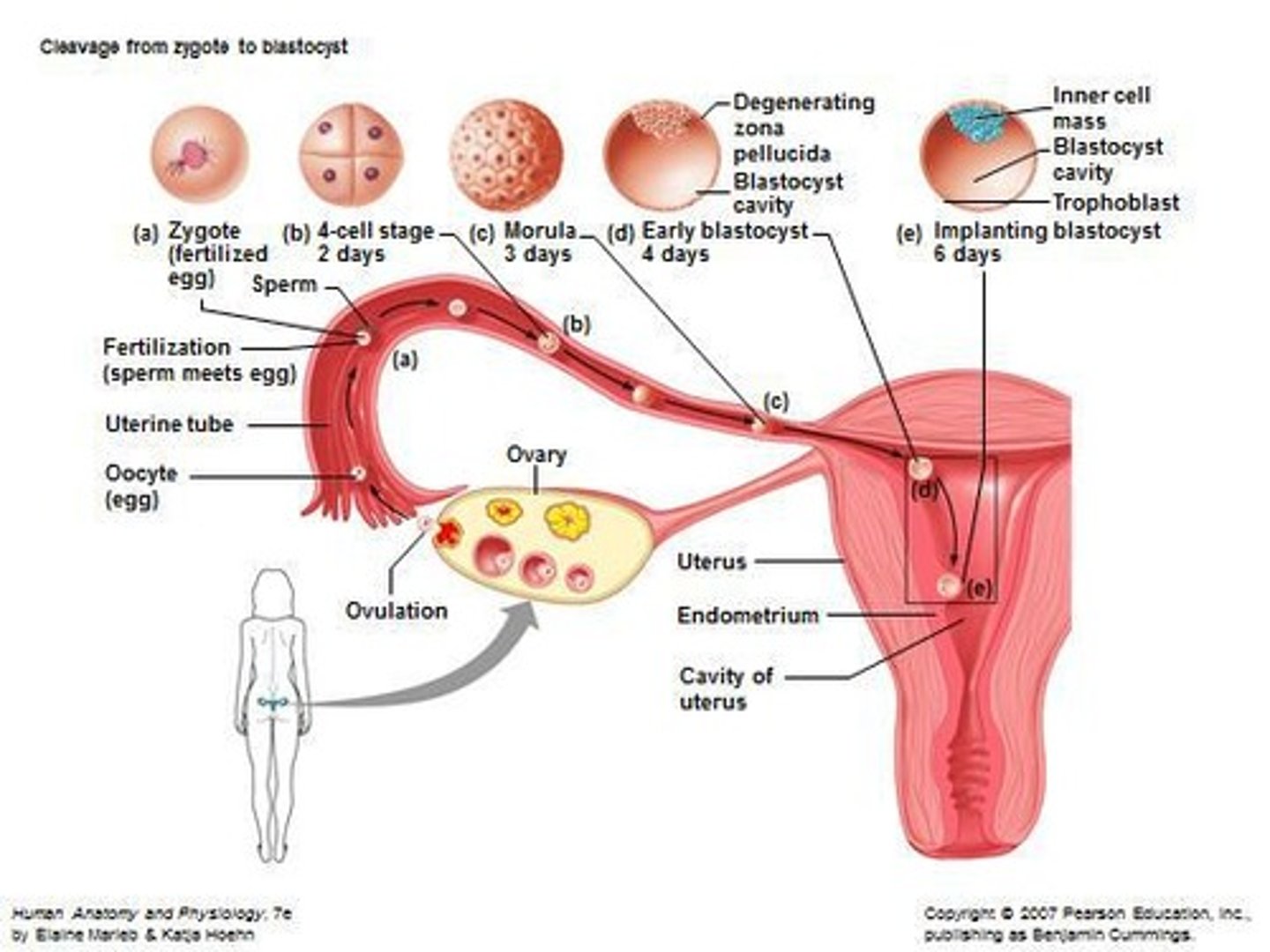
What is the first series of cell divisions after fertilisation called?
Cleavage.
What happens to the size of cells during early embryonic development?
Cells decrease in size after each division due to rapid mitotic division without a G1 phase.
What is a zygote?
A single diploid cell formed by the union of egg and sperm.
What characterizes the morula stage?
It is a solid ball of cells formed by mitotic division of the zygote.
What is a blastocyst?
A fluid-filled spherical stage that becomes implanted in the endometrium, with an inner cell mass that forms the embryonic disc.
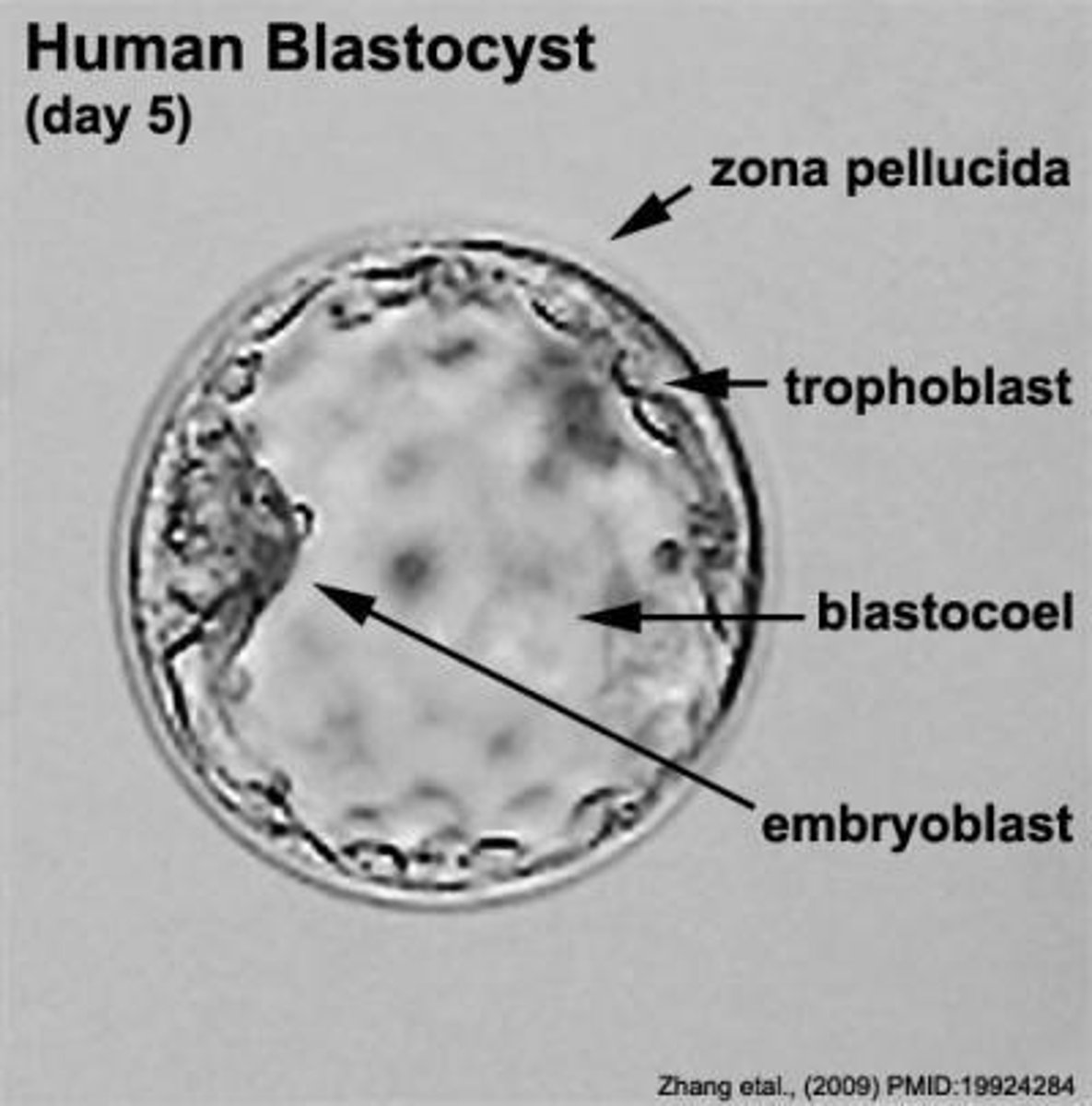
What are the two layers of the blastocyst?
Trophoblast (outer layer forming part of the placenta) and embryoblast (inner cell mass forming the embryo).
What is implantation?
The process where the developing embryo is implanted into the uterus, occurring naturally or through in vitro fertilisation (IVF).
What is cell differentiation?
The process of changing unspecialized embryonic cells into specialized cells, tissues, and organs.
What is embryogenesis?
The first two months of pregnancy, after which the developing individual is called a foetus.
What are the primary germ layers formed during embryonic development?
Ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm.
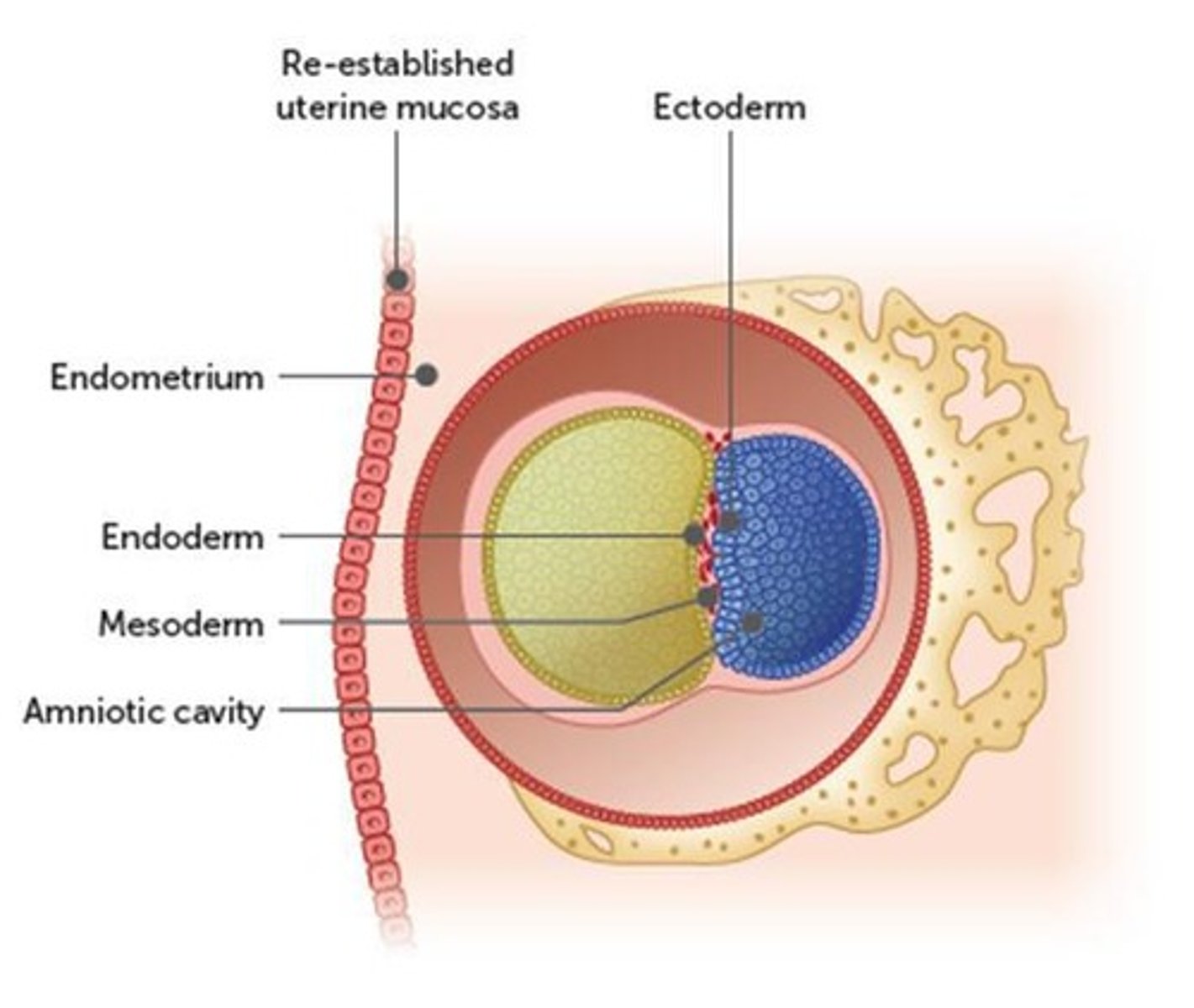
What occurs during the embryonic stage of development?
Primary germ layers differentiate into organs and organ systems.
What is the foetal stage?
The period from 8 to 38 weeks where organs grow and mature to support life independently.
What is the amniotic cavity?
The narrow space created between the embryoblast and trophoblast during embryonic development.
What happens to the embryoblast during embryogenesis?
It separates slightly from the trophoblast and flattens to form the primary germ layers.
What is the significance of the embryonic period?
It is the first two months of pregnancy during which the basic structures of the organism are formed.
What is the defining characteristic of the blastocyst stage?
It is a hollow sphere with an internal cavity called blastocoel.
What structures are formed by the ectoderm?
Nervous system (brain, spinal cord, nerves), lining of mouth and nostrils, epidermis of skin, lens and cornea of the eye, receptor cells of sense organs, enamel of teeth, anterior lobe of pituitary, adrenal medulla.
What structures are formed by the mesoderm?
Bones, cartilage, muscles, blood, lymphoid tissue, endothelium of blood vessels, epithelium of reproductive and excretory systems, epithelium of body and joint cavities, inner layer (dermis) of skin.
What structures are formed by the endoderm?
Epithelium of digestive tract and associated glands (liver, pancreas), trachea, bronchi, lungs, urinary bladder, urethra, gall bladder, tonsils, thyroid, parathyroid, thymus glands, vagina and associated glands.
What are the four embryonic membranes?
Amnion, yolk sac, allantois, chorion.
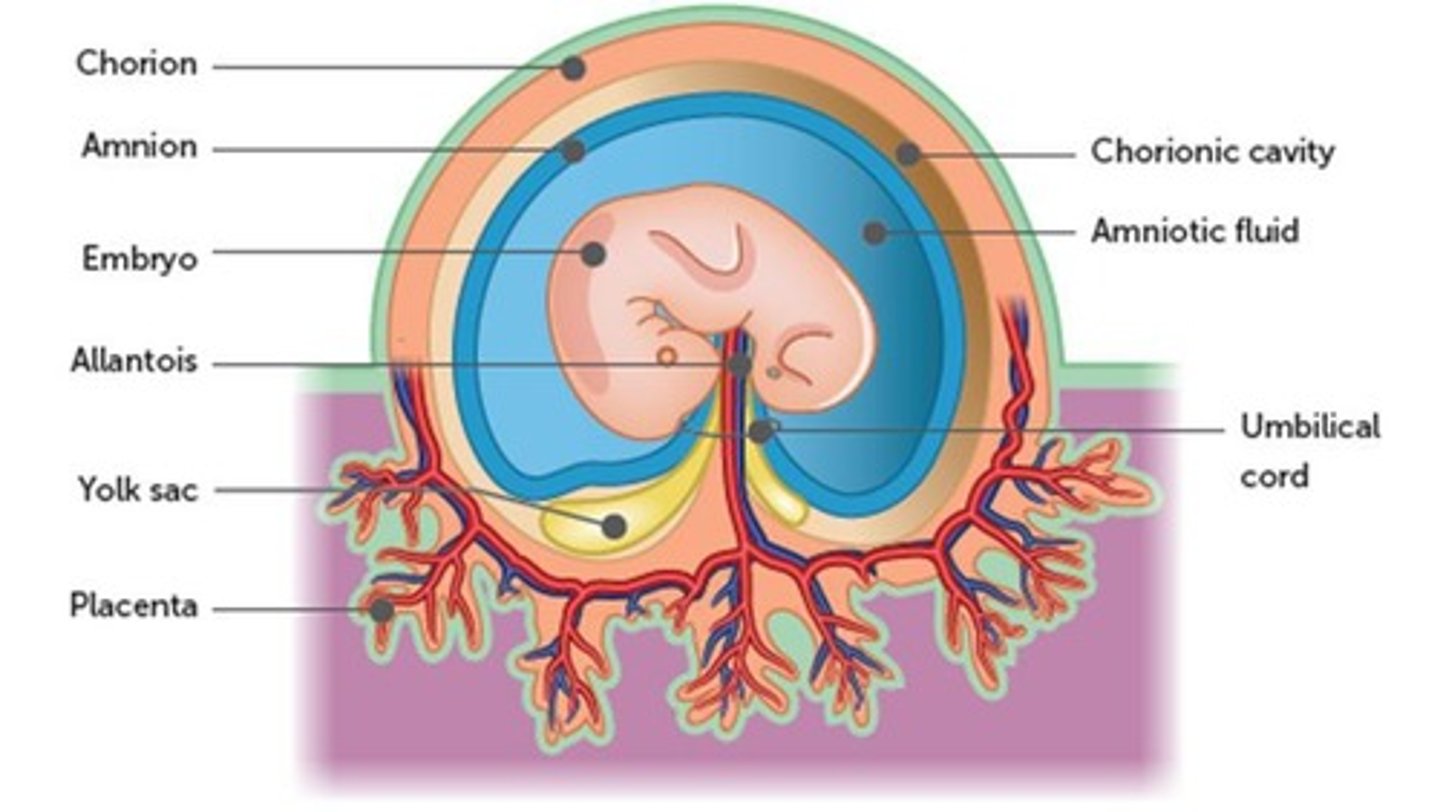
What is the function of the amnion?
Surrounds the embryo, secretes amniotic fluid for protection, temperature regulation, and allows movement.
What is the chorion and its role in embryonic development?
Formed from outer cells of the blastocyst and mesodermal cells, it surrounds the embryo and fuses with the amnion, becoming part of the placenta.
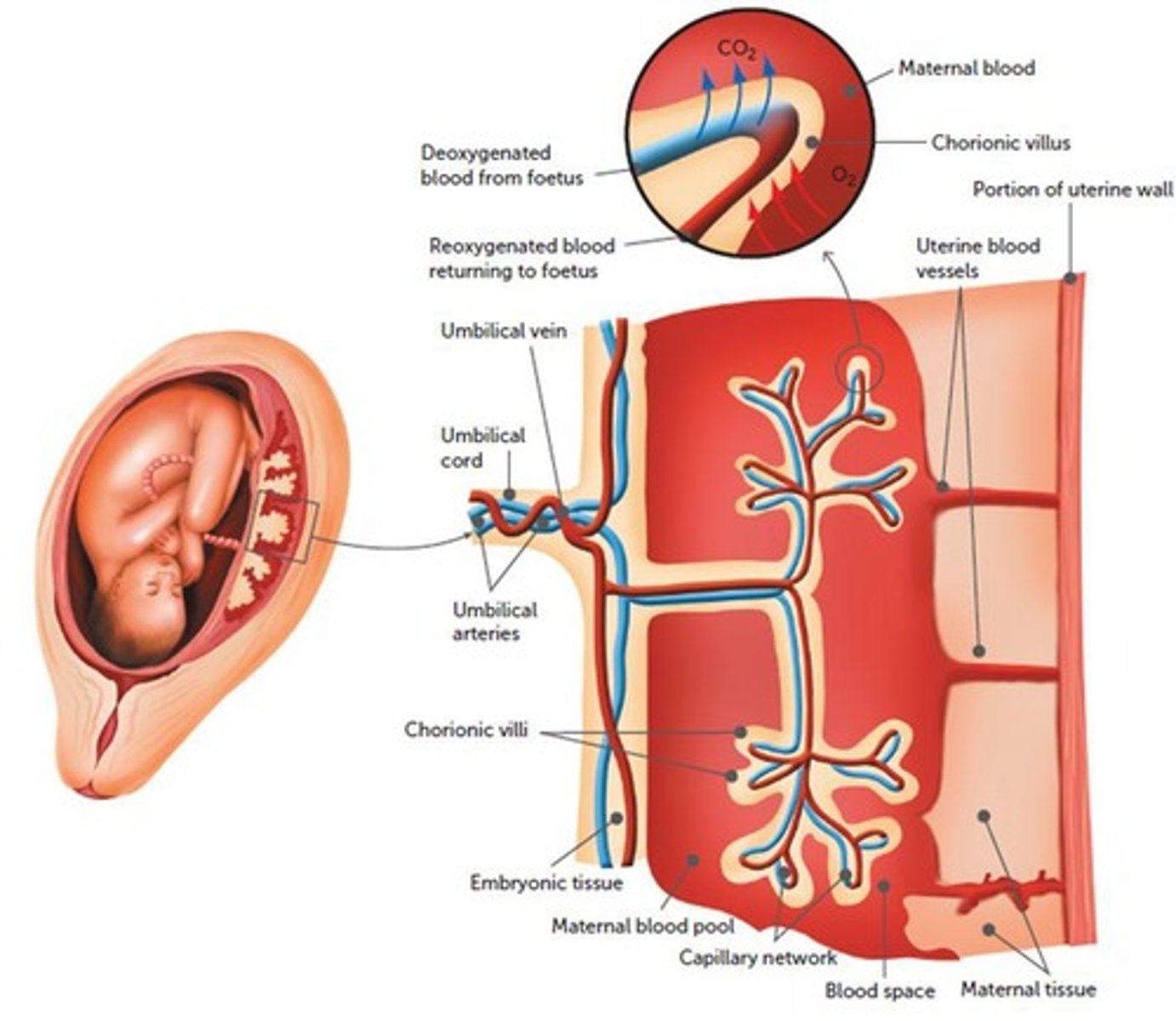
What is the placenta and its significance?
A combination of foetal and maternal tissues, it develops from the chorion, consists of chorionic villi for nutrient exchange, and becomes the main source of nutrition by week 12.

How does the umbilical cord function?
Connects the placenta to the fetus, containing two umbilical arteries carrying blood to the chorionic villi and one umbilical vein carrying blood back to the fetus.
What is gestation?
The time the embryo or fetus is carried in the uterus, typically 280 days.
What is parturition?
The process by which the fetus is expelled from the mother's body.
What changes occur before labor?
Ligaments of the pelvis soften, cervix softens and begins to open, and the fetus positions itself for birth.
What happens during the first stage of labor?
Contractions become regular, and the cervix begins to dilate.
What is the role of chorionic villi in the placenta?
They grow into the endometrium and are bathed in maternal blood for nutrient exchange.
When does the placenta begin to develop?
About 11 days after conception.
What is the dominant mode of nutrition for the fetus around 9 weeks?
The placenta becomes the dominant mode of nutrition.
What is the typical position of the fetus before labor?
Facing the woman's right or left hip bone, with knees drawn up and legs crossed.
What is the significance of the umbilical arteries and vein?
They facilitate the exchange of blood between the fetus and the placenta.
What is the primary function of the yolk sac and allantois?
They form the outer structure of the umbilical cord.
What happens to the mother's blood during the exchange at the placenta?
It enters through uterine arteries, flows through blood spaces for exchange, and exits through uterine veins.
What is the expected duration of the first stage of labor?
8-9 hours.
What is the role of the amniotic fluid?
It protects the embryo, maintains temperature, and allows movement.
What is the duration of contractions during labor?
Contractions last about 30-45 seconds with 5-30 minutes of rest in between.
How do contractions typically feel during labor?
They may feel like aching in the lower back, menstrual cramps, and pressure on the pelvis.
When does the first stage of labor end?
The first stage ends when the cervix is about 10 cm dilated.
What forms the birth canal during labor?
The uterus, cervix, and vagina form a single curved passage.
What happens during the second stage of labor?
The amniotic sac ruptures, and the cervix is fully dilated, allowing the baby to descend through the birth canal.
How long can the second stage of labor last?
It can last from 20 minutes to 2 hours.
What is the duration of contractions during the second stage of labor?
Contractions last 45-90 seconds with a 3-5 minute rest period.
What position does the baby's head turn to during delivery?
The head turns to face the mother's back initially, then turns sideways to face the mother's hips.
What occurs during the third stage of labor?
The umbilical cord is clamped, tied, and cut, and the placenta is expelled.
What happens to the umbilical cord after birth?
The umbilical cord is clamped, tied in two places, and cut between the ties.
What is the role of the placenta before birth?
The placenta disposes of CO2 and other wastes and reoxygenates the blood.
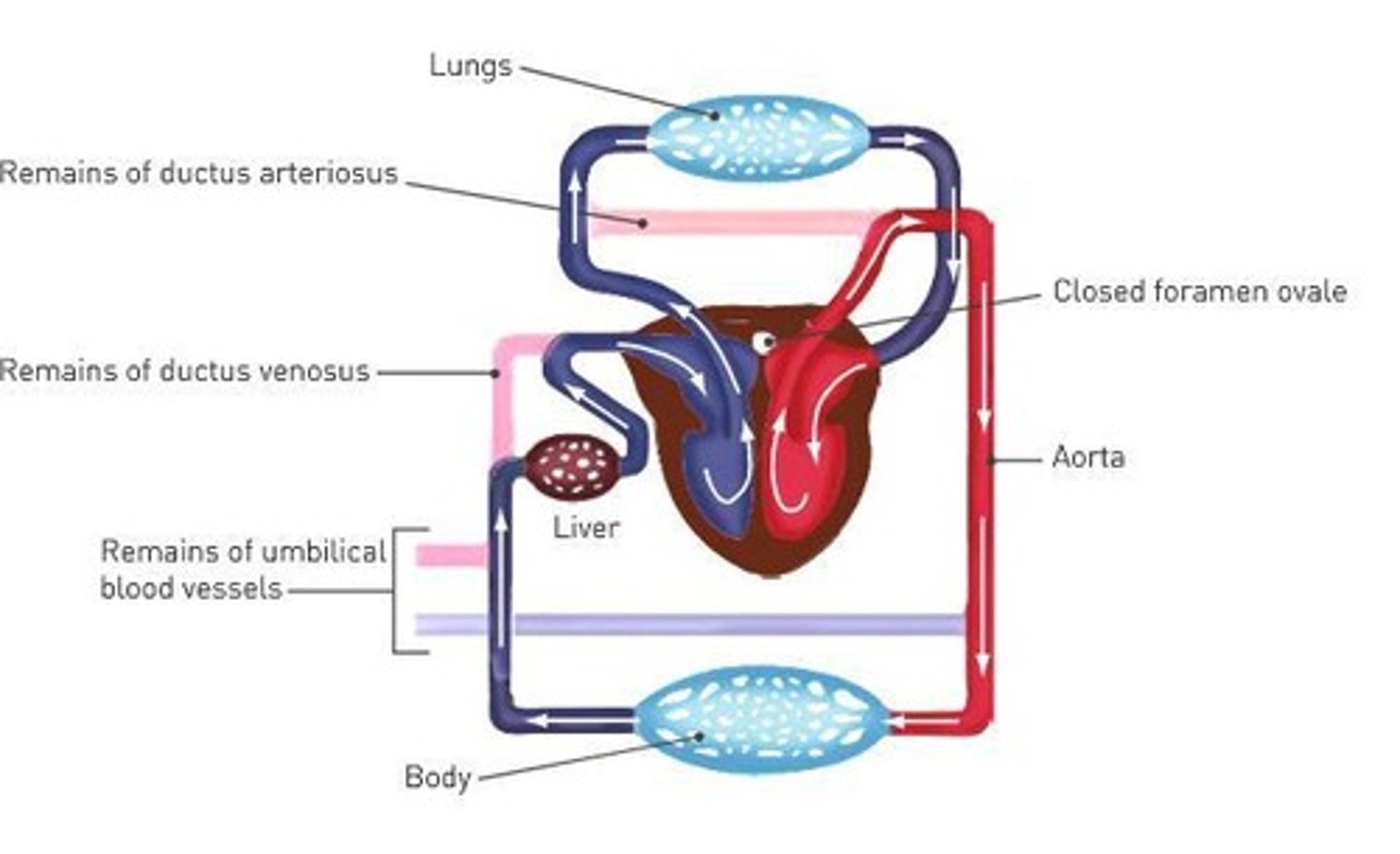
What happens to the foramen ovale after birth?
The foramen ovale closes.
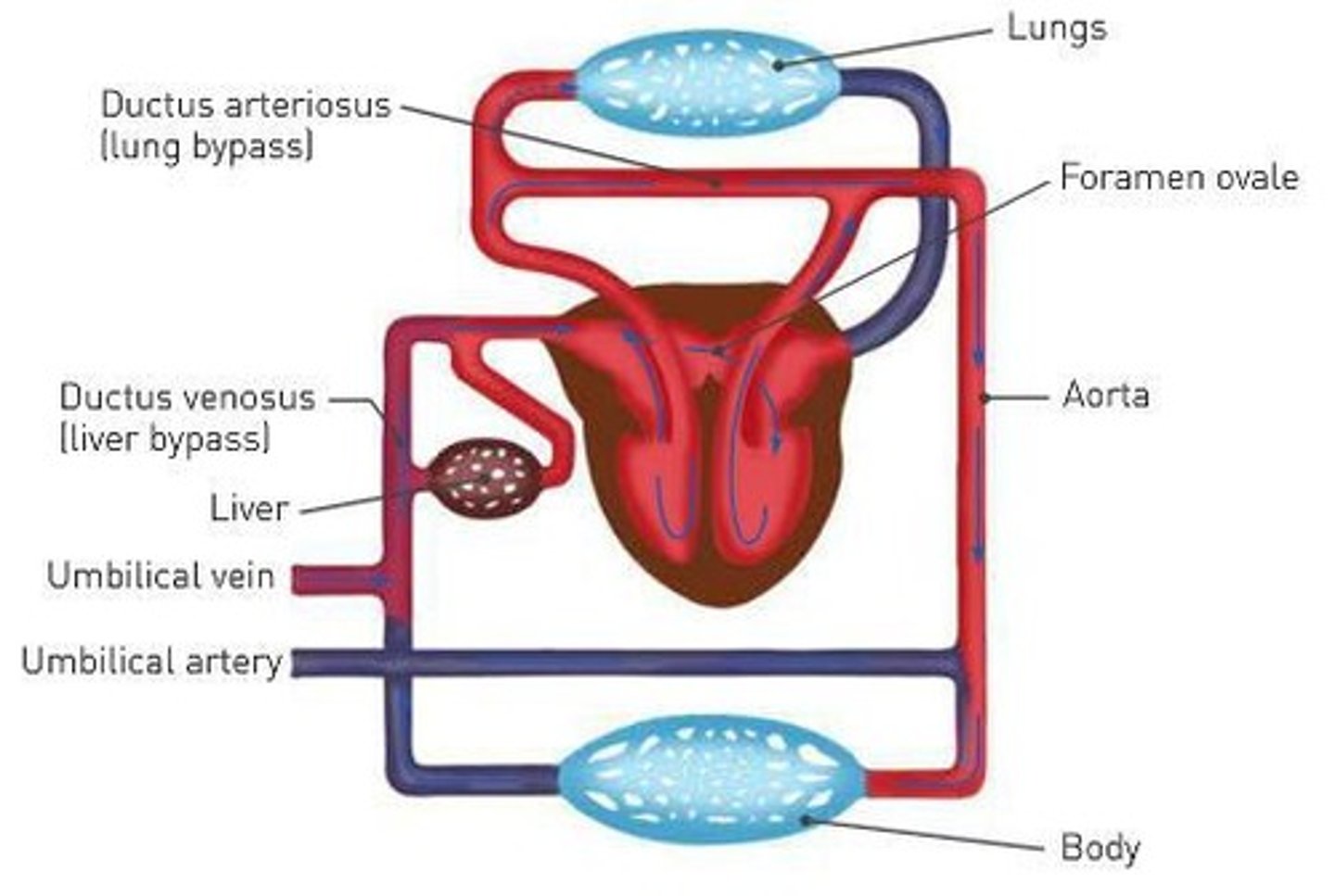
How does blood bypass the lungs in foetal circulation?
Blood flows directly from the right atrium through the foramen ovale into the left atrium.
What happens to the ductus arteriosus after birth?
The ductus arteriosus constricts.
What is the function of the umbilical arteries before birth?
They carry oxygen-poor, waste-laden blood to the placenta.
What happens to the umbilical vein after birth?
The umbilical vein degenerates.
What is the dietary requirement for an average pregnant woman?
An average pregnant woman needs about 300 additional calories per day and 65 grams of protein.
What nutrients should be increased during pregnancy?
Calcium, iron, and folic acid intake should be increased.
What is recommended for dental health during pregnancy?
Fluoride tablets after the twentieth week of pregnancy are recommended if fluoride is not added to drinking water.
What is the significance of the ductus venosus in foetal circulation?
It allows placental blood to bypass the liver by flowing into the inferior vena cava.
What changes occur in the baby at birth?
The baby undergoes significant physiological changes, including the closure of the foramen ovale and ductus arteriosus.
What is the recommended weight gain during pregnancy?
About 0.5 kg a week, totaling 13.4 kg.
What substances should be avoided to reduce chemical exposure during pregnancy?
No smoking, alcohol, and drugs.
What is the advice regarding exercise during pregnancy?
Maintain a regular exercise program but do not start any new program.
What type of medical checkups are recommended during pregnancy?
Regular medical checkups and oral supplements for deficiencies or hormonal imbalances.
What is the function of Folic Acid (Folate) during pregnancy?
Normal cell division and manufacture of protein.
What are the effects of Folic Acid deficiency during pregnancy?
Spina bifida and other neural tube defects.
What foods are rich in Folic Acid?
Wholegrain breads, cereals, green leafy vegetables, and legumes.
What is the function of Calcium during pregnancy?
Normal bone growth, teeth, heart, nerve, and muscle development.
What are the effects of Calcium deficiency during pregnancy?
Bone deformities.
What foods are good sources of Calcium?
Milk, cheese, and red meat.
What is the function of Vitamin A during pregnancy?
Normal growth of cells.
What are the effects of Vitamin A deficiency during pregnancy?
Bone deformities.
What foods are high in Vitamin A?
Green and yellow vegetables.
What is the role of Fluoride during pregnancy?
Important for teeth development.
What are the potential future problems associated with Fluoride deficiency?
Future dental problems.
What are teratogens?
Substances that may harm the developing fetus and result in physical defects.
What are the three major classes of teratogens?
Drugs and other chemicals, infectious diseases, and radiations such as X-rays.
What is the impact of Rubella exposure during pregnancy?
Can cause the child to be born deaf, blind, or with heart malformations.
What is Listeriosis and its risk during pregnancy?
Caused by eating food contaminated by Listeria monocytogenes, can cause miscarriages or stillbirth.
What is Foetal Alcohol Syndrome (FAS)?
A condition resulting from alcohol exposure during pregnancy, leading to lower birth weight, growth issues, facial irregularities, and mental retardation.
What are the effects of smoking during pregnancy?
Lower birth weight, increased risk of miscarriage, gastrointestinal problems, and higher risk of respiratory issues.
What is Thalidomide and its effects on pregnancy?
A chemical in sedatives that affects the embryo between the 28th and 42nd days of development, leading to limb deformities.