MOD 2 - The OR
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
Sterile HCP
direct patient contact throughout surgery
surgeon and their assistant
residents
students
Non-sterile HCP
not have direct contact with the patient
Anesthesiologist
circulating nurse
medical radiation technologists
students
sales/service representatives
technologists
Non-sterile members in the sterile field
they do not enter the sterile field but may operate equipment that is draped within the field
is the back considered sterile or non-steril
non-sterile, so we do not reach behind our backs
Pre-operative Care
peri-anesthesia nurse confirms the type of surgery, diagnostics are completed, vital signs and answers patient’s questions
surgeon will visit pt to review surgery procedure, get consent
Intra-operative Care
During the course of the surgical operation
Post-operative Care
pt moved to the post-anesthetic recovery unit to be monitored for several hours
who can terminate the surgery anytime
Anesthesiologist (and surgeon?)
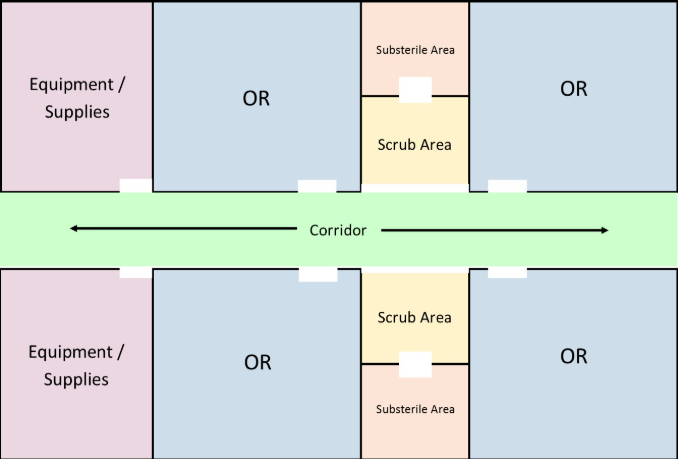
Central Corridor - OR Layout
resembles a hotel
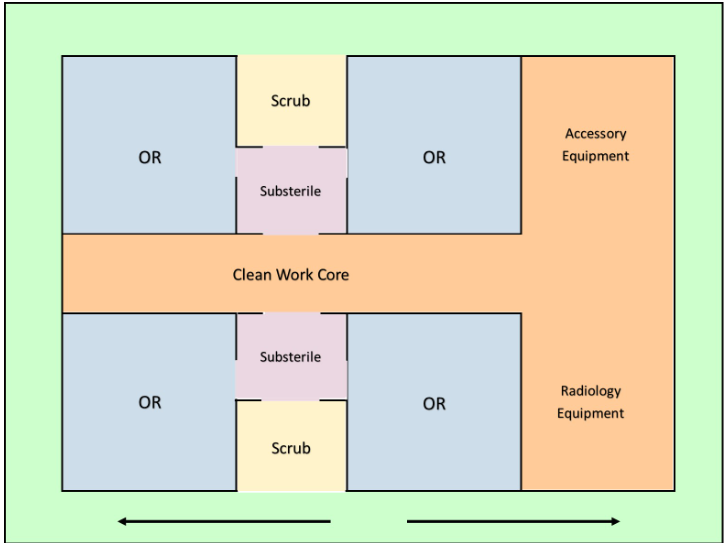
Central Core - OR Layout
a clean core with a peripheral corridor
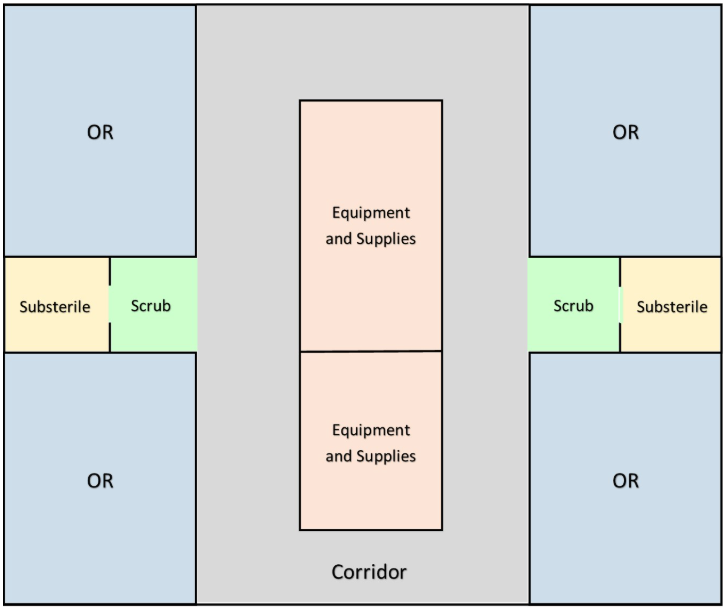
Central and Peripheral Cores - OR Layout
a racetrack design
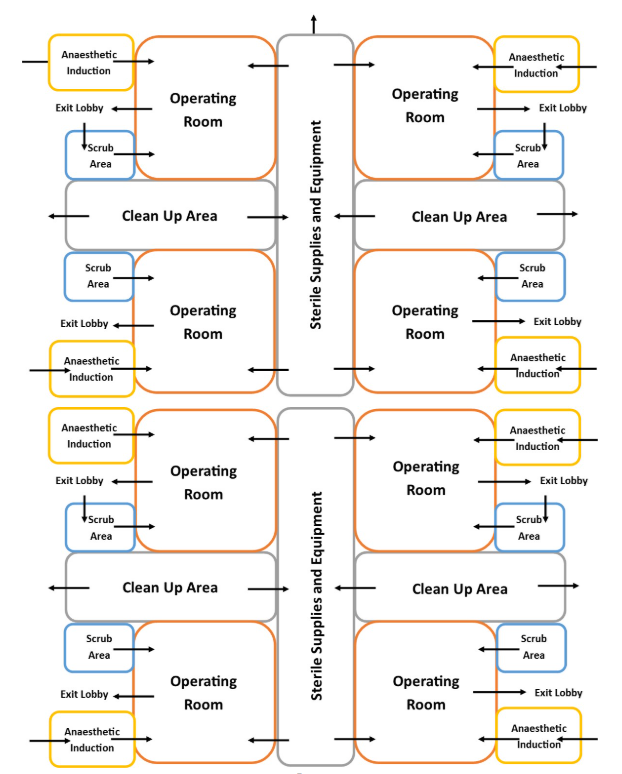
Grouping or Cluster Plans - OR Layout
with peripheral and central corridors
OR Zones
Zone 1: Unrestricted (& Transition)
Zone 2: Semi-restricted
Zone 3:Restricted
Zone 1: Unrestricted (& Transition)
attire
accessibility to whom
where
public
street clothing
pt bay
locker/change rooms
desk area
Zone 2: Semi-restricted - Zone 2
attire
accessibility to whom
where
authorized personnel
Scrub suits and head/hair/beard coverings
peripheral storage areas, corridors
Zone 3:Restricted
attire/sterilization
where
OR scrub suits, head cover, shoe covers (or dedicated OR shoes) and a new mask
hand wash prior to entry
OR suites
Preoperative Medications Purpose
Allay anxiety and fears.
Minimize the danger of aspirating secretions.
Produce some analgesia and amnesia.
Dull awareness of the physical environment.
Reduce the risk of nausea and vomiting.
Raise the pain threshold.
Anesthesia Purpose
Performing procedures/surgery without pain and discomfort.
In the case of a general anesthetic, providing temporary memory loss of the surgery.
Anesthesia definition
“a loss of sensation resulting from pharmacological depression of nerve function”
3 main categories of anaesthetic agents
General
Regional
Local
Local Anaesthesia causes
loss of sensation without the loss of consciousness (lidocaine [trade name Xylocaine])
pros
Minimum equipment required
Minimizes the recovery period
Avoids the undesirable effects of general anaesthesia
Reduced costs
cons
Lack of patient acceptance because of awareness during the procedure
Lack of feasibility of localizing some anatomical sites
Pain at the injection site
Individual variations in response to anaesthetic drugs
Unanticipated rapid absorption into the bloodstream
Methods of Local Anaesthesia
Topical (placed on the skin)
Local infiltration (injection into tissues)
local anaesthesia side effects
Light-headedness
Dizziness
Ringing in the ears
Loss of consciousness
Seizures
as techs we must recognize when there are problems related to anaesthesia, thus its important that
Decrease patient anxiety, noise and conversations
Assess patient for allergies and have antihistamines, epinephrine and corticosteroids available
Have resuscitative equipment, drugs, oxygen and suction equipment available
Monitor BP, pulse, breathing and appearance
Assess for burning, itching, swelling and tissue irritation
Remind patient who had a topical spray to the throat area not to eat or drink for at least one hour after the test — to prevent aspiration
Regional Anaesthesia
loss of sensation to a region of the body without loss of consciousness
Three common types of regional anaesthesia
Spinal
Epidural
Nerve blocks
Our concerns and precautions for pts under Regional (Spinal) Anaesthesia
some doc require pts to remain flat for at least 8 hours to decrease chance of headache SO know when the anaesthetic was administered
patient may be prone to hypotension, so take precautions when moving the patient
General Anaesthesia
loss of sensation with a loss of consciousness and reflexes
Major Disadvantages to General Anaesthesia
CNS depression
Nausea and vomiting
Aspiration
Amnesia effects
Hallucinogenic effects and flashbacks with certain agents
Taking six months for the effects to be totally removed from the body
Four Stages of General Anaesthesia
Stage 1 - Altered consciousness
Stage 2 - Excitement
Stage 3 - Surgical Anaethesia
Stage 4 - Stage of Danger
Stage 1 - Altered consciousness
pt is drowsy
everyone in room should remain quiet
Stage 2 - Excitement
pt is susceptible to external stimuli
pt has irregular breathing and moves around
remain quiet and be prepared to restrain pt
Stage 3 - Surgical Anaethesia
surgery now can be performed
pt has reg breathing and loss of sensation and consciousness
Stage 4 - Stage of Danger
pt is not breathing, has little to no HR
everyone should prepare for CPR
our role for pt under general anaesthesia
prevent air way obstruction from the tongue; turn head to side
be alert to hypotension
be alert of anesthesia wearing off
pts have low body temp so keep them warm
for pts recovering, explain what you are doing as the hearing is the first sense to return
Conscious Sedation
alter a patient's perception during a procedure as well as manage pain
Administration of Conscious Sedation Medications
must always be equipped with:
An oxygen source
Airway management equipment
Drugs to treat both anaphylaxis and other forms of hypotension
Appropriate monitors
when is the MRT most involved
in the OR when patients are usually already under anesthesia
types of mobile fluoroscopy
mini c-arm
Conventional C-arm
Biplanar C-arm
Dedicated Fluoroscopy Units
Angiography
mini c-arm
used by surgeons for surgeries of the upper extremities and the ankles and feet
techs are only required to set up and take it away and clean, ensure that req is properly filled
Conventional C-arm
commonly used in the OR for a variety of cases from cardiac studies, orthopedics to abdominal surgery
tech stays from start to finsih
Biplanar C-arm
permits the surgeon to see the AP and Lateral projections at the same time to ensure accuracy and improve efficiency
For cervical spine surgery
Dedicated Fluoroscopy Units
some ORs include specialized tables which have fluoroscopy units built in
dedicated urology and cardiac suites
Angiography
Most c-arms are built with angiography capabilities
when assessment and evaluation of blood flow is required
CT
known to be used for lung nodule excision, neuro and spine surgeries
MRI
No metallic objects can be in the vicinity of the MRI unit, therefore several safety precautions must be taken into consideration
Tech’s Resposibility
ensuring all equipment is clean and ready to go for any situation
Appropriate Attires
hospital attire: arms bare, no jewelry, faces cleanly shaven
OR area attire: OR scrubs, bouffant, booties
OR suite attire: mask, medical hand wash
ways to identify pt
confirming with the circulating nurse
confirm monitor is on right pt
if possible, checking the patient’s wrist band
our responsibility before surgery begins
ensure everyone is wearing lead (if a c-arm is being used)
extra lead is available outside the room incase more pple come in
Doning Attire in each Zone
Zone 1: Bouffant, booties, OR scrubs
Zone 2: new mask
Zone 2/3: lead protection (depends where it is)
when is hand hygiene done
start of donning
prior to entering zone 3
end of doffing
after removing drape
after cleaning C-arm
how to prepare equipment before imaging
must ask the Scrub nurse to help you place the sterile C-Arm drape
Do NOT touch the outside of the drape
can only touch the inside of the drape and lower 3-4 inches to pull it down, and the third/lowest strap
tasks after imaging
remove drape
clean equipment
fill out req
send images to PACS
Doffing Attire in each Zone
Zone 3/2": lead protection
Zone 2/1: mask
Zone 1: Bouffant and booties