Cytogenetics
1/91
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Prelim Mock Exam
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
92 Terms
More or less 100,000
Approximately, how many genes are there in humans?
Ribosomal RNA (rRNA)
Its primary transcript is a huge molecule of about 13,000 nucleotides.
Messenger RNA (mRNA)
Its production is catalyzed by RNA polymerase II:
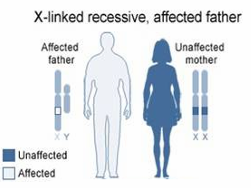
50% sons, 50% daughters
How will you counsel the following parents on the probability of producing abnormalities in their children?
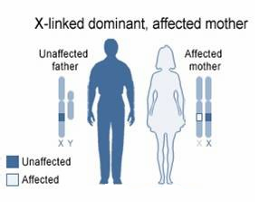
0% sons, 100% daughters
How will you counsel the following parents on the probability of producing abnormalities in their children?
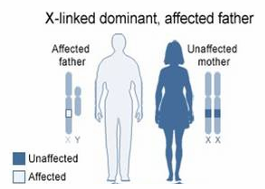
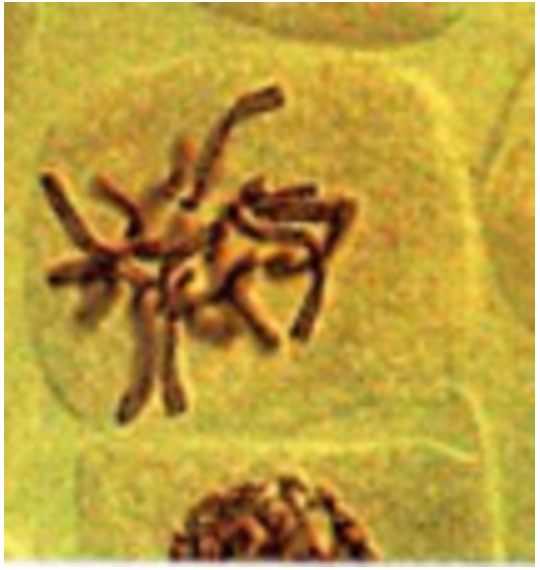
Prophase I
Identify the type of Cell Division & Phase

Autosomal Recessive Inheritance
genes for autosomal-recessive traits are also located on the autosomes
the presence of one normal allele is usually sufficient to prevent expression of disease.
S (synthetic) phase
At which phase in the Cell Cycle is the DNA duplicated?
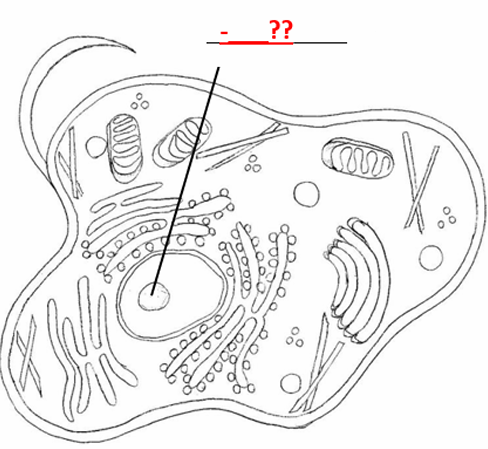
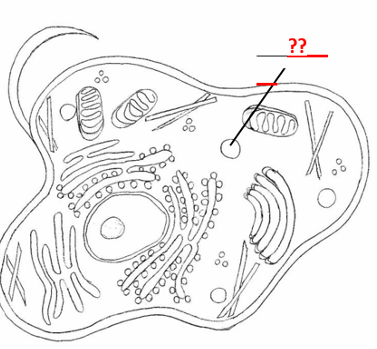
Center for ribosomal RNA
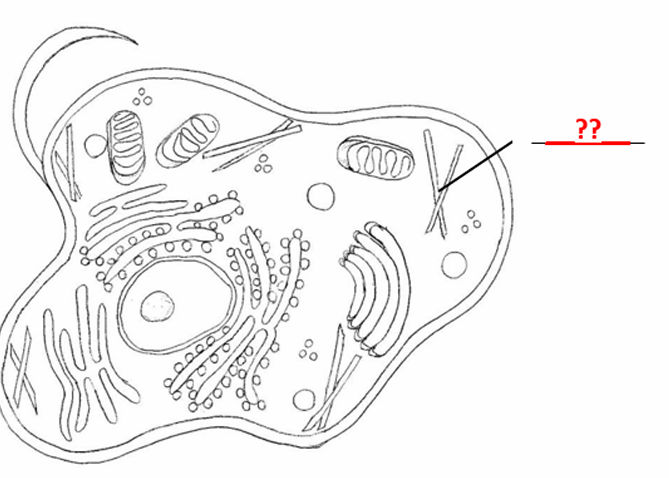
Identify the pointed cell part:
Anaphase II

Transfer RNA (tRNA)
Its production is catalyzed by RNA polymerase III
Messenger RNA (mRNA)
It carries the genetic code from the nucleus to the cytoplasm to act as a template for protein synthesis
6.7%
The concept that a couple have, to have 10 children before they would have 1 child identical to another, unless they are identical twins, is based on this percentage of heterososity
Gregor Johann Mendel
He established genetics as a new science
autosomal recessive inheritance
This type of Inheritance requires that the Individual have 2 copies of the trait to express the phenotype.
Heterozygous
Autosomal Dominant Traits are expressed in:
Adenine
Which of these is a Purine?
Cytogenetics
The science that involves the investigation of heredity at the cellular level:
Prophase

OO
Type O
Homozygous B
Type B
Homozygous A
Type A
Type AB & Type O Type AB & Type
0%
Type O & Heterozygous A Type O & Heterozygous
50%
Type O & Homozygous B Type O & Homozygous
0%
Made of phospholipid bilayer
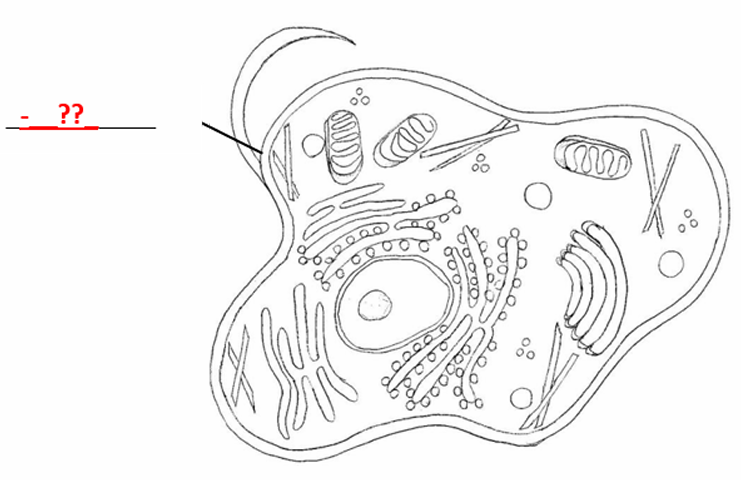
Heterochromatin
It is the condensed inactive form of chromosome at the periphery of the nucleus
Microtubules
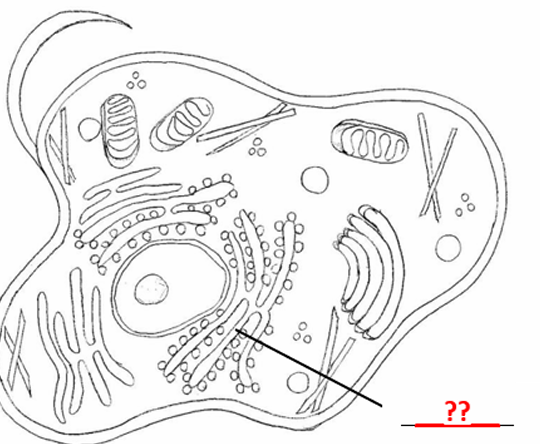
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
Type AB
This blood type group provides a good example of co-dominant alleles.
Metaphase

Cytosol
the fluid suspension or undisolved portion in the cytoplasm
Golgi apparatus
Packaging Machinery of the cell
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
detoxification of toxic materials
astral rays
assist in orienting the MTOC at the pole
Nucleus
contains the genetic material of the cell
Microtubules
act as intracellular pathways
x-linked inheritance
There is lack of male-to-male transmission in this inheritance
To replace dead or dying cells,
To produce more cells to enlarge the organism (growth and development)
For Reproduction, i.e. to increase the number of unicellular organisms.
To increase the number of gametocytes (ova & spermatocytes)
These trigger the cell to begin a cell division event:
Law of Segregation
This law says, "The two alleles of a gene are never transmitted together from one parent to an offspring."
4
At the completion of Meiosis II, how many polar bodies are produced in total during Oogenesis?
nullizygous
if both alleles are missing.
Alleles
different forms of a trait; different forms of a trait
Phenotype
the external appearance of an organism caused by genotype.
homozygous
having two identical alleles of a particular gene or genes. having two identical alleles of a particular gene or genes.
Trait
Physical attributes expressed by genes and influenced by the environment, such as hair color, etc.
3
Each codon is composed of this number of consecutive nucleotides:
AA
Homozygous A
BO
Heterozygous B
AB
AB Group
100% sons, 100% daughters
How will you counsel the following parents on the probability of producing abnormalities in their children?
Anaphase
4n
In gametogenesis, when the germ cells are in the S phase of the cell cycle preceding meiosis, the amount of DNA is doubled to:
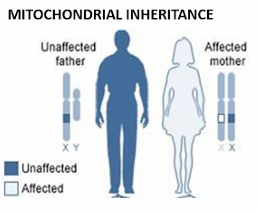
mitochondria are almost exclusively passed in the egg
A hallmark of mitochondrial inheritance is transmission from an affected woman to all of her children. Why?
UAA
UAG
UGA
These stop codons
Contain hydrolytic enzymes
Creationary Origin
Similarities or identical structures indicative of Creator’s prerogative.
Creationary Origin
Complete Genetic Information but has steadily declined over time via mutational degradation.
Evolutionary Origin
Residual evidence that multiple different organisms descended from common ancestors.
Evolutionary Origin
Human is Ape-Like Creature.
Evolutionary Origin
Genetic Information increased over time via DNA copying errors over millions of years.
50%
Heterozygous A & Homozygous B
50%
Heterozygous A & Heterozygous B
25%
Type AB & Heterozygous B
Mitosis = 2 daughter cells; Meiosis = 4 daughter cells
These are the correct numbers of daughter cells produced after each cell division:
0% sons, all carrier daughters
kinetochore
Spindle fibers attach to this region of the chromatid in preparation for migration.
Cytogenetics
The only clinical laboratory test to be able to survey the genetic cellular constitution of an individual:
2nd Day
firmament
3rd Day
water, dry land, grass, herb-yielding seed, fruit tree
4th Day
Sun, moon, & Stars
5th Day
marine creatures; sky creature
6th Day
earth living creatures; man & woman
7th Day
Creator rested & blessed the day
Uracil
It replaces thymine in RNA:
Pachytene
The phase when chiasmata are formed as random exchange of genetic material occurs between homologous Chromosomes
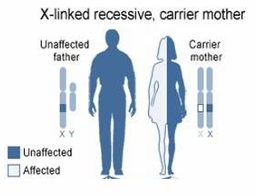
50% sons, half carrier daughters
starts from evening (sunset)
Originally, the correct accounting of one DAY is:
Zygotene
The phase wherein the homologous pairs of chromosomes approximate each other and make synapses via synaptonemal complex, forming a tetrad.
Karyokinesis
It refers to nuclear division.
Alfred Sturtevant
He showed that genes are arranged linearly on the chromosome
Blood Bank
deals with blood transfusion deals with blood transfusion
Hematology
counts the different blood cells counts the different blood cells
Serology / Immunology
deals with antigen antibody testing in Infectious diseases deals with antigen antibody testing in Infectious diseases
Type AB
This blood type group system provides a good example of co-dominant alleles.
Phosphodiester bonds
Nucleotides are linked to one another by these bonds formed between the sugar molecules:
Gregor Johann Mendel
He observed that organisms inherit traits via discrete units of inheritance
fathers cannot pass X-link traits to their sons
A son of a father with an X-linked dominant trait is worried of inheriting the same condition. Which is the best scientific explanation to give?
the last & most accurate test to be done
“Gold Standard” test means:
Euchromatin
Under the electron microscope, it looks like “beads on a string”
fibrillar region of the nucleolu
pars fibrosa
rRNA are synthesized in:
Law of Independent assortment
In this Law, “Alleles of different genes are passed randomly to offspring.”