IQ1 Reproduction
1/25
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Module 1
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
Two methods of reproduction
Sexual
Involves two parents
Mixing of genes
Offspring are unique
Asexual
Involves only one parent
Offspring genetically identical clones
bacteria, plants, some animals
two types of sexual reproduction in animals
Internal: union of gametes and development of offspring inside the female reproductive tract.
External: union of gametes and development of offspring outside the body. e.g ocean
Internal vs External fertilization (advantages and disadvantages
Types of Fertilization | Advantages
| Disadvantages
|
Internal
|
|
|
External
|
|
|
Gametes
Gametes are sex cells sperm and egg witch are haploid ( 23 half the number of chromosomes) because they combine with the other half to make diploid (full set) 46 called Zygote
what does fusion of gametes produce
zygote which is a diploid cell ( contains full 46
What happens during fertilization?
A haploid sperm fuses with a haploid egg to form a diploid zygote with 46 chromosomes. which then undergoes mitosis creating a new individual.
types of reproduction advantages and disadvantages
Type of Reproduction | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|
Asexual Reproduction | - Only one parent needed → no mate required | - No genetic variation → all offspring are identical, so less ability to adapt to environmental changes |
Sexual Reproduction | - Produces genetic variation, increasing adaptability | - Requires two parents → finding a mate can take time and energy |
Which type of reproduction increases genetic variation?
Sexual reproduction.
what are the Male parts of plant called and what do then consist of.
the male parts are called the Stamen and consist of the Anther- A fluffy structure that
produces pollen - which is the sperm of plant.
filament – stalk which supports the anther.
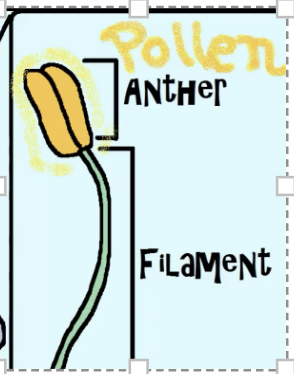
what is the anther
the anther is male and is a fluffy structure that produces pollen - the sperm of the plant

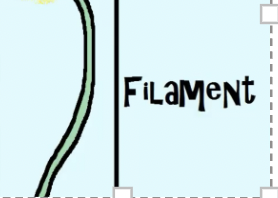
what is the filament
male stalk that supports anther
What are female parts of plants called
pistil and contain Stigma – called the sticky stigma so pollen can stick to it
Style – supports stigma
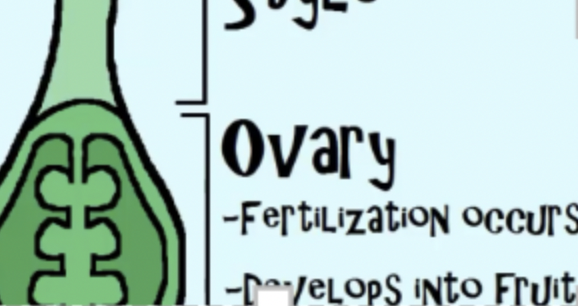
ovary - which is where fertilization occurs and where seeds are formed
it will ripen into a fruit
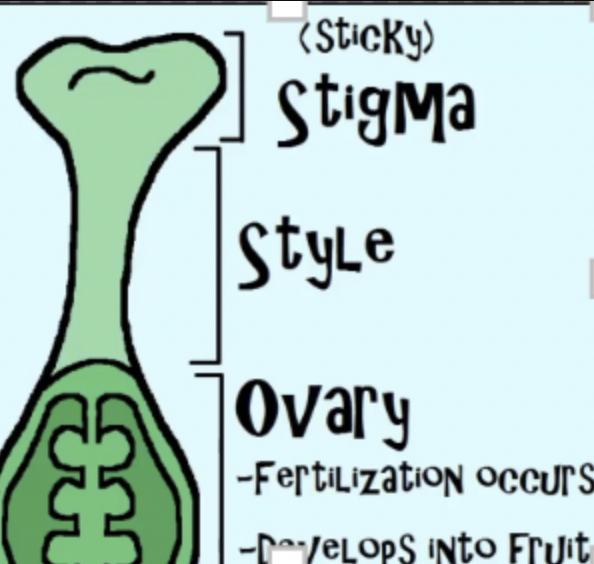
what is the stigma
the stigma is in the female section of plant and is sticky so that pollen can easily stick to it.
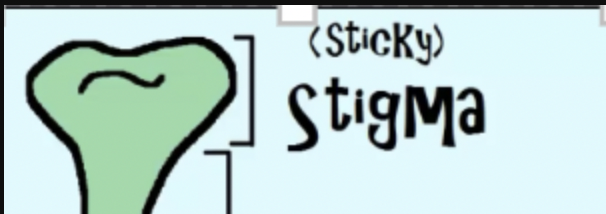
what is the style
Female part that supports stigma
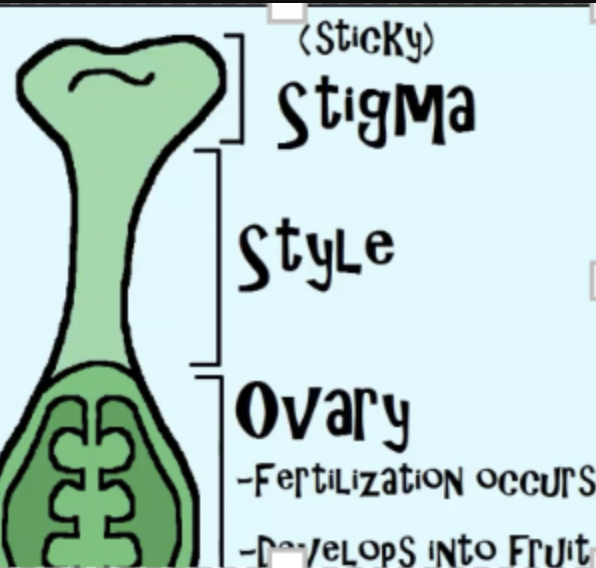
what are the ovaries of plant
which is where fertilization occurs and where seeds are formed
it will ripen into a fruit
What is pollination?
Pollination is the transfer of pollen from the male part of a plant to the female part, allowing fertilization to occur.
Where does pollination occur in flowering plants?
pollen is transferred from the anther (male) to the stigma (female) of a flower.
Where does pollination occur in conifers and what is conifers
conifers are none flowering pants and pollination occurs in their cone
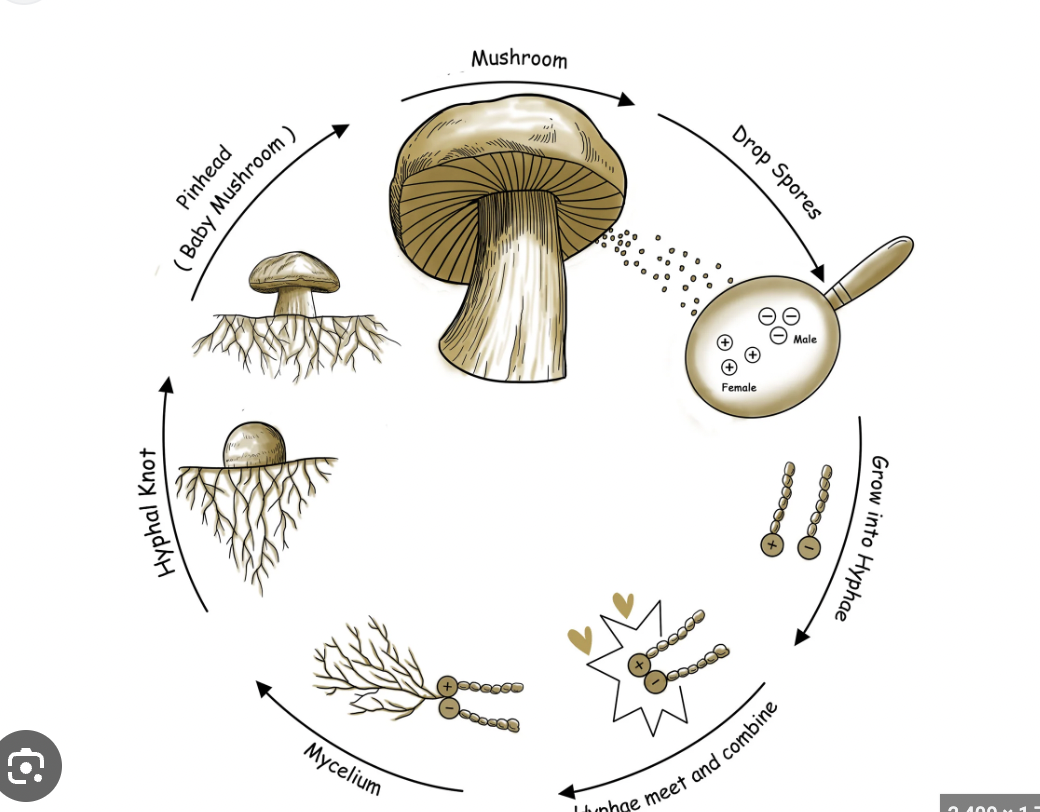
what is Spore formation
a form of asexual reproduction plant releases spores, which are reproductive cells that can develop into a new organism.
Spores are usually released into the air or water and can survive harsh conditions.
Example: Mushrooms release spores from their gills.
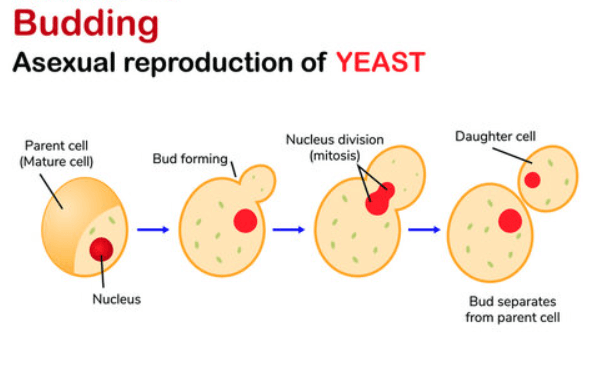
what is budding
a form of asexual reproduction A new organism develops as a small growth (bud) on the parent and eventually detaches.
Common in yeast.
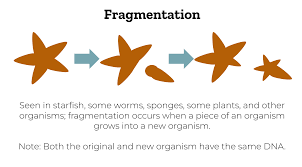
Fragmentation
a form of asexual reproduction Fragmentation in multicellular or colonial organisms is a form of asexual reproduction or cloning, where an organism is split into fragments upon maturation and the split part becomes the new individual e.g starfish
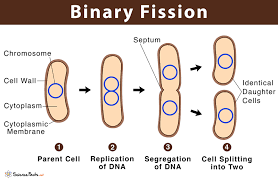
Binary fusion
the process of asexual reproduction in which a single cell divides into two identical daughter cells. This process is used by prokaryotic organisms like bacteria and is a much simpler and faster method than the mitosis seen in eukaryotes
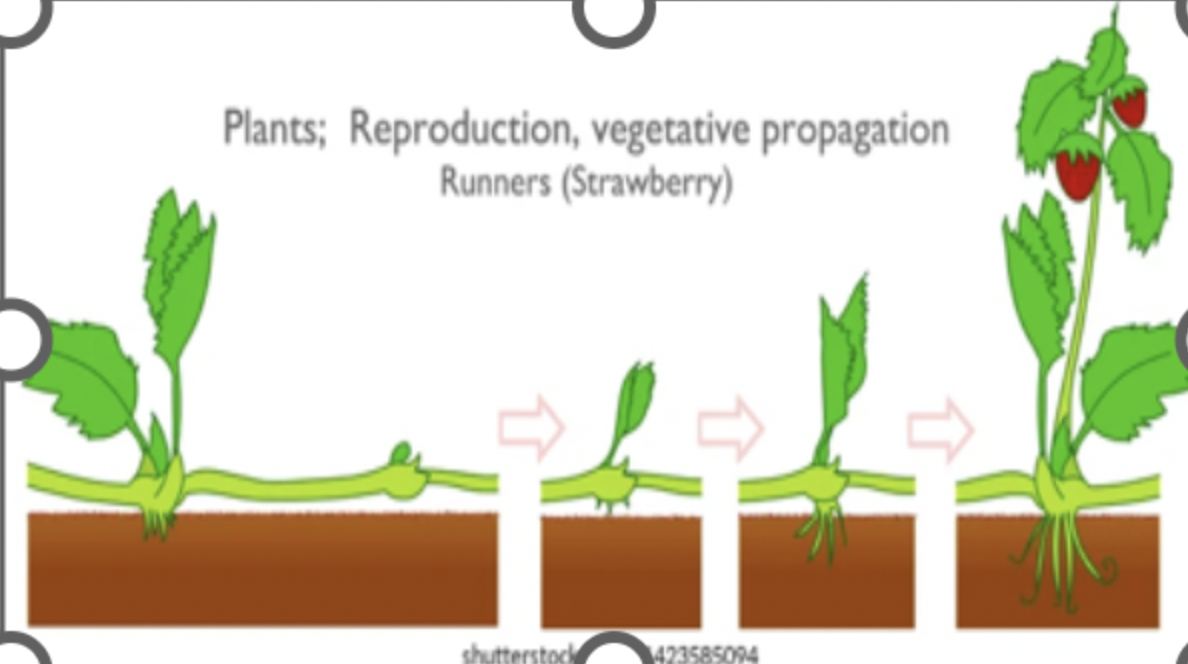
Runners
a form of asexual reproduction where Horizontal stems that grow above ground and produce new plants at their node (a point where buds and roots can form) They allow plants like strawberries and spider plants to spread
Bulbs
a form of asexual reproduction A form of vegetative propagation where a new, genetically identical plant grows from a bud at the base of a parent bulb. It consists of a short stem and a cluster of fleshy leaves that store food for the new plant. e.g onion
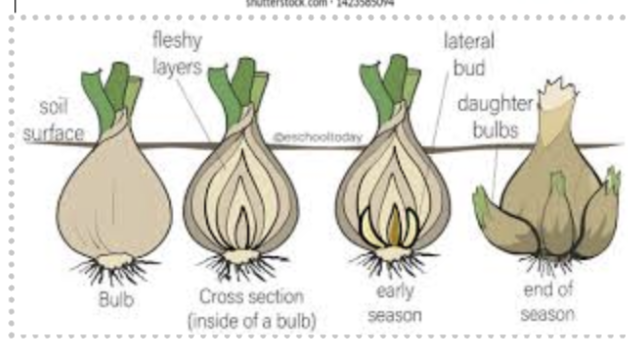
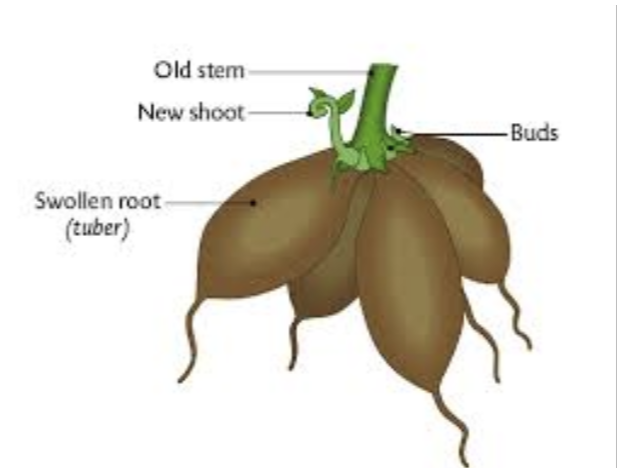
Stem tubers
a form of asexual reproduction Modified stems that store nutrients, allowing a plant to reproduce asexually through vegetative propagation. New plants can be grown by planting the entire stem tuber, which has buds that will sprout into a new shoot (leaves and stems) and roots. E.g potatoes and yams