Overview of the Nervous System and Brain Functions
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
What is the primary function of the Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)?
To communicate between the body's organs, glands, and muscles to the Central Nervous System (CNS) and vice versa.
What are the two divisions of the Somatic Nervous System (SNS)?
Sensory neurons and Motor division.
What is the role of sensory neurons in the Somatic Nervous System?
They send messages from sensory receptors to the CNS for sensation.
What does the motor division of the Somatic Nervous System do?
It sends messages from the CNS to skeletal muscles to initiate movement.
What is the function of the Autonomic Nervous System (ANS)?
To transmit motor messages from the brain to the body's internal organs and glands, resulting in involuntary movements.
What are the two divisions of the Autonomic Nervous System?
Sympathetic Nervous System and Parasympathetic Nervous System.
What is the role of the Sympathetic Nervous System?
It prepares the body for increased activity, often referred to as 'fight or flight' responses.
What does the Parasympathetic Nervous System do?
It maintains energy levels appropriate for normal bodily functions and calms the body down.
What are the main structures of a neuron?
Soma, Dendrites, Axon, Axon Terminals, and Myelin Sheath.
What is the function of the soma in a neuron?
It contains DNA and determines the cell's functions.
What do dendrites do in a neuron?
They receive information from other neurons and carry it to the soma.
What is the role of the axon?
It carries information away from the soma.
What happens at the axon terminals?
They release neurotransmitters to communicate with other neurons.
What is the function of the Myelin Sheath?
It speeds up the transmission of electrical signals along the axon.
What is the process of neural transmission?
It involves passing a message along a neuron in the order: Dendrites → Soma → Axon → Axon Terminals → Synapse → Dendrites.
What is a synapse?
A very small gap between one neuron and the next.
What are neurotransmitters?
Chemicals that transmit information from one neuron to another across the synapse.
What is the function of the hypothalamus?
It regulates hormones and influences basic behaviors related to homeostasis, such as thirst and sleep.
What is the role of the thalamus in the brain?
It acts as a relay system for sensory messages on their way to the cerebral cortex, except for smell.
What does the cerebellum control?
Posture, balance, and fine motor coordination.
What is the function of the medulla?
It connects the brain and spinal cord and regulates vital organs like breathing and heart rate.
What is the corpus callosum?
A thick band of nerve fibers that connects the left and right hemispheres of the brain.
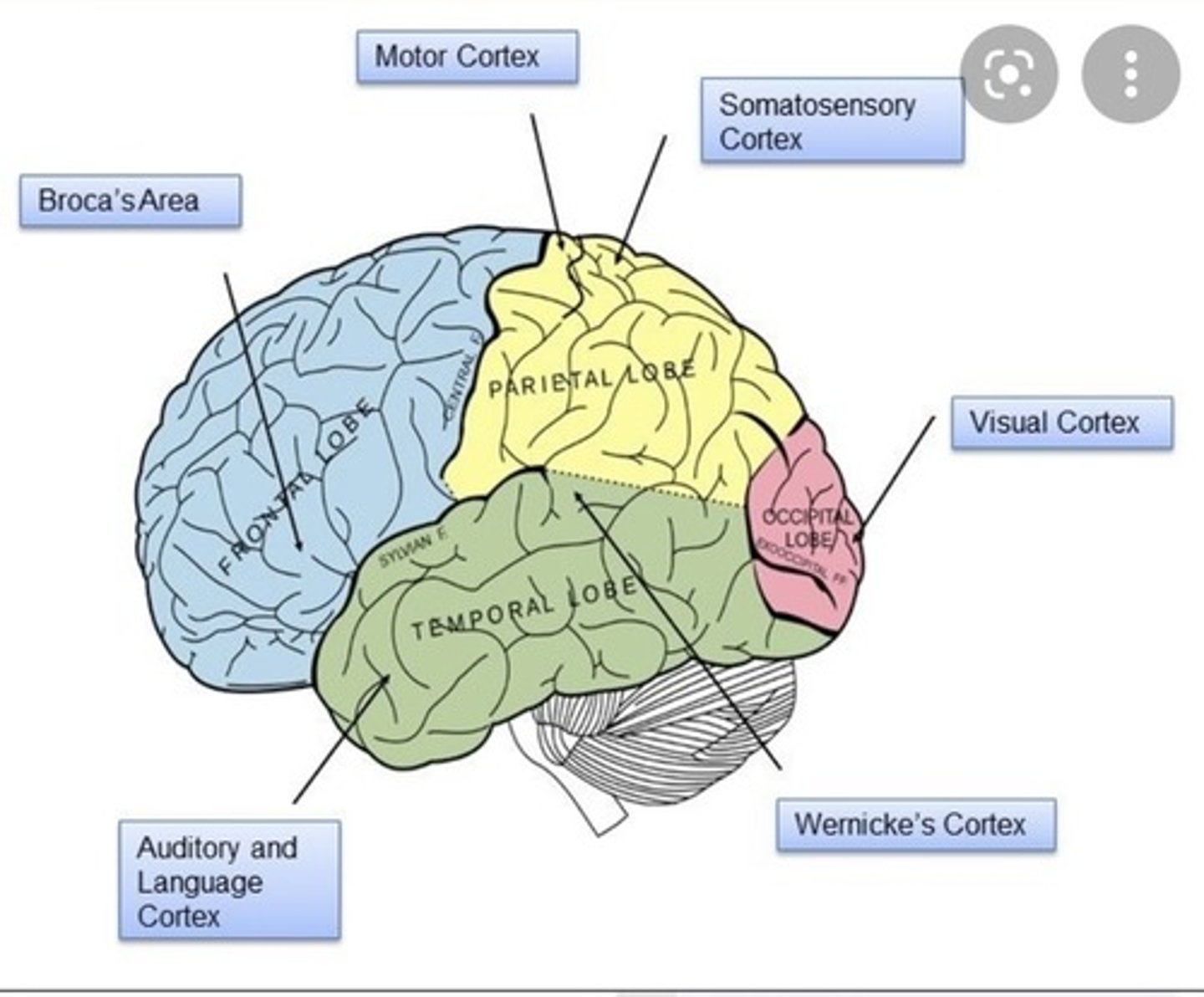
What is the primary role of the frontal lobe?
To initiate voluntary movement, produce speech, and engage in planning, judgment, and problem-solving.
What is Broca's area responsible for?
It controls the muscles involved in speech production and is located in the left frontal lobe.
What happens if Broca's area is damaged?
The individual may struggle to produce clear and fluent speech, often being aware of their communication difficulties.
What does the primary somatosensory cortex process?
It processes bodily sensations such as touch, temperature, and pressure.
What is the primary function of the occipital lobe?
It is the major visual area of the cortex, processing visual information.
What is Wernicke's area responsible for?
It is involved in the comprehension of speech and the formation of meaningful sentences.
What was the significance of Phineas Gage's accident?
It demonstrated that different parts of the brain control specific behaviors, particularly the role of the frontal lobe in personality and cognition.
What does an Electroencephalogram (EEG) measure?
It shows brain function by detecting general patterns of electrical activity.
What does a Computerized Tomographic (CT) scan show?
It provides structural images of the brain using X-rays taken from different angles.
What is the purpose of a Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI) scan?
It shows both the structure and function of the brain by detecting oxygen levels in the blood.
what are located in the frontal lobe?
pre frontal cortex (executive functions), Primary motor cortex (movement of the skeletal muscles), Broca's area (clear and fluent speech)
Whats located in the Parietal lobe?
Primary Somasensory cortex (sensations)
Whats located int he occipital lobe?
Primary visual cortex
Whats the occipital lobe used for
Registers + processes visual information.
Whats the parietal lobe used for?
process bodily functions, sensation (heat, touch, pressue), special orientation
Whats the frontal lobe used for
Initiates volunatry movement, PLANNING, MORAL COMPASS, ABSTRACT THOUGHT, SOCIAL SKILLS.
Whats the temporal lobe used for?
Language processing, hearing, visual recongition
Whats located int he temporal lobe?
Primary auditory cortex, wernickes area (comphrension of language).
Corpus callosum
connects the 2 hemisphers together
Whats located int he Hindbrain?
Medulla, cerebellum, spinal cord
Whats located in the forbrain?
thalmus, hypothalmus
Whats located in the mid brain?
come back to