Lecture 15: Hereditary, Genes, and DNA
1/77
Earn XP
Description and Tags
10/6/2025
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
78 Terms
What is the main idea of Darwin and Wallace’s theory of evolution?
The theory of natural selection
What 3 points does the theory of natural selection state?
Traits vary within a population of individuals that make up a species
Those traits are heritable
Certain traits allow better survival of individuals
Putting the three points of natural selection together, natural selection is where….
traits vary within a population, are heritable, and some traits allow for better survival
What did Darwin not known about his theory?
He didn’t known why there was stability or variation and how inheritance worked
What is the role of “nature” in natural selection?
Nature selects on inheritable variation
What is the relationship between traits and survival?
Certain traits allow individuals to survive better
What is the definition of heritable traits?
Traits that can be passed down from parents to offspring
During which time period did the study of genetics primarily occur?
Late 19th to early 20th century
What is one way we can study patterns of inheritance?
Through using mutations
What did Gregor Mendel do?
Discovered the fundamental laws of inheritance by deducing the existence of "heritable factors," which were later named genes
What organism did Gregor Mendel use to show that traits are passed from parents to offspring in discrete units, which come in pairs, and that some are dominant over others?
Pea plants
What are genes?
“Units” that control traits, and each gene can have different versions
What did genes prove?
Proved that “blended inheritance” wasn’t really a thing
What is a mutant gene?
A mutant gene is a version of a gene that can change a triat
How many versions of each gene do most cells carry?
Most cells carry 2 versions of each gene
How many versions of each gene are passed to sperm or egg?
Only 1 of the two versions is passed to sperm or egg
What did Mendel’s rules describe?
Mendel’s rules described sexual inheritance in eukaryotes
What two laws did Mendel come up with?
Law of Segregation
Law of Independent Assortment
What are different versions of a gene called?
Alleles
If an individual has the genotype Aa, what alleles can their sperm or egg cells carry?
Either A or a, but not both
What does the law of segregation state?
During the formation of gametes (sperm and egg cells), the two alleles (copies of a gene) for each trait separate, or "segregate," so that each gamete contains only one allele for that gene
What happens during fertilization in the context of the law of segregation?
The sperm and egg fuse, combining their alleles to form the offspring’s genotype
If a sperm with allele A fertilizes an egg with allele a, what will be the genotype of the offspring?
Aa
Where are genes located?
Genes are located on structures within the cell
What happens to the structure with genes during the production of sperm and eggs?
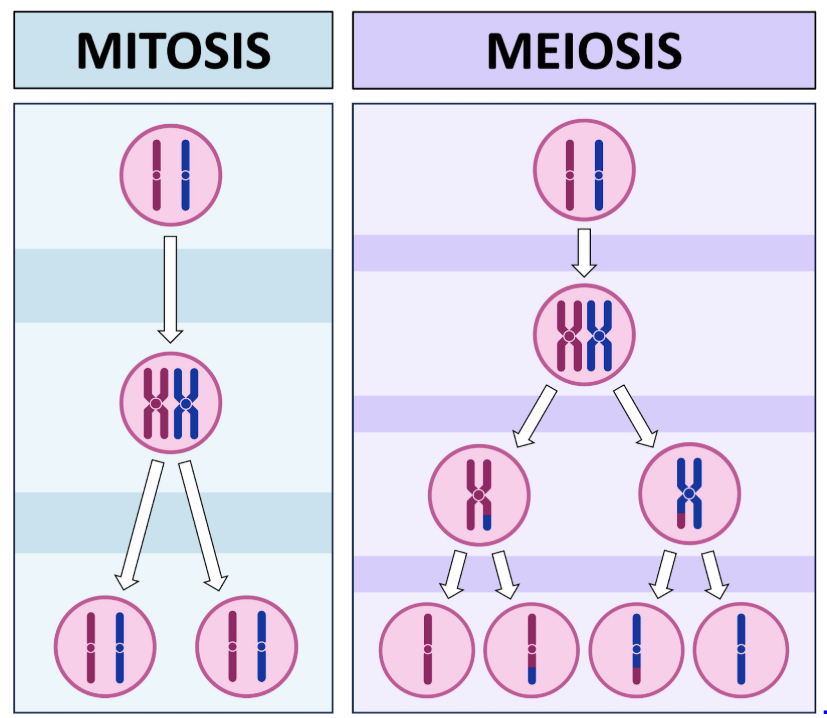
The structure with genes must behave differently during the production of sperm and eggs compared to mitosis
What cell structure follows Mendel’s rules?
Meiosis
What is meiosis?
The special form of cell division that produces sperm and egg cells (four daughter cells) that have half the number of chromosomes as did the parent cell
How many chromosomes do sperm and egg cells have compared to the parent cell?
Half the number of chromosomes
How many of each kind of chromosome are typically found in a parent cell?
Two
How many of each kind of chromosome are typically found in a sperm or egg cell?
One
What can be mapped along linear chromosomes?
Mutant genes
What happens to chromosomes during meiosis?
Chromosomes replicate, and then the cell divides twice
Where do the chromosomes come from?
One set of chromosomes comes from the sperm, and the other set comes from the egg
What are sister chromatids?
Two identical copies of a single chromosome that are connected to each other at a centromere
What type of cell does Meiosis produce?
Sperm or egg cells
What is the main function of genes?
Genes contain instructions to make one kind of protein
What is the “one gene one enzyme (or protein) hypothesis”?
It suggests that each gene is responsible for producing a specific enzyme or protein
What two main components make up a chromosome?
DNA and proteins
Why were proteins initially thought to be the genetic material?
Because proteins were known to perform many functions in the cell, while DNA appeared to be less complex
What was the initial perception of DNA that led to the belief that it was not the genetic material?
DNA was thought to be boring because it had about equal concentrations of four nucleotides (A, C, G, T), and scientists didn’t know what it looked like
What was the “tetra-nucleotide” model of DNA?
It was an early, incorrect model of DNA structure
What are the 3 components of a nucleotide?
Phosphate group
Pentose sugar
Nitrogenous base
What did experiments in the 1940s-1950s suggest about DNA?
That DNA was the basis of stable inheritance
What is the main concept Griffith’s experiment demonstrated?
Bacteria can be transformed by DNA
What type of bacteria, Smooth (S) or Rough (R), kills mice?
Smooth (S) bacteria
Why did the Smooth (S) bacteria kill mice? Think structure
The Smooth (S) bacteria have a cell wall that protects the bacteria from the mouse’s immune system.
Why didn’t the Rough (R) bacteria kill mice?
The Rough (R) bacteria does not have a cell wall, therefore the mouse’s immune system can attack the bacteria
What happens when Rough (R) cells are mixed with heat-killed Smooth (S) cells?
The Rough (R) cells are transformed into Smooth (S) cells
What is stably inherited after the transformation of R to S?
The S trait
Through the transformation of R—>S, what did Griffith prove?
That there must be a “transformation principle”
What was the goal of Avery’s 1944 experiment?
To identify the molecule responsible for transforming R cells into S cells
What were the four different types of molecules tested in Avery’s experiment?
Proteins
RNA
Lipids
Carbohydrates
How did Avery test for the transforming molecule?
By destroying different types of molecules in the S cell extract using enzymes (proteinase and RNase) and observing if the extract could still transform R cells
What happened when proteinase was added to the S cell extract?
The sample still transformed R cells, indicating that proteins were not the transforming molecule
What happened when RNase was added to the S cell extract?
The sample still transformed R cells, indicating that RNA was not the transforming molecule
What happened when DNase was added to the S cell extract?
The sample did not transform (transformation was blocked), indicating DNA contains genetic information
What are the 3 rules of the game in scientific inquiry?
The hypothesis has to be testable
Occam’s razor
Reproducibility
What is Occam’s razor?
A principle that encourages using the simplest explanation that fits the facts
What is reproducibility?
Using reproducible, natural laws that don’t change and make the world go
What is a virus?
A particle that contains proteins and nucleic acid (and sometimes lipids)
Are viruses cells?
No, viruses are not cells, but they are produced by cells
What do viruses do to infected cells?
Make infected cells produce more virus proteins and nucleic acids
What is a bacteriophage?
A virus that infects and “eats” bacteria
True or False: Viruses are alive
False, viruses are not really alive
Explain why the behavior of chromosomes during meiosis suggested that chromosomes were the physical location of Mendelian genes
The parallel behavior between chromosomes during meiosis and Mendel’s hypothetical genes provided strong evidence for the chromosomal theory of inheritance, which states that genes are located on chromosomes
Mitosis produces 2 identical daughter cells, each with 46 chromosomes, from one parent cell with 46 chromosomes
Meiosis produces four haploid daughter cells (gametes) that each have half the number of chromosomes as the original diploid cell (23 chromosomes)
Describe Oswald Avery Experiment
Oswald Avery Experiment in 1944:
Destroyed different types of molecules the S cell extracted: Proteins, RNA, Lipids, or Carbohydrates
With an addition of Proteinases, the R cell transformed to an S cell
With addition of RNase, the R cell transformed to an S cell
1949: With addition of deoxyribonuclease, the R cell did not transform to an S cell
Showed that DNA, but not protein or RNA, could transform harmless bacteria into harmful ones, with this transformation being prevented only by enzymes that degrade DNA
DNA must contain genetic information
Describe the Hershey Chase Experiment
Hershey Chase Experiment in 1952:
Used bacteriophages (viruses that infect bacteria) labeled with radioactive isotopes
Radioactive phosphorus (32P) for DNA
Radioactive sulfur (35S) for protein
Found that 32P entered the bacteria, while 35S remained outside, demonstrating that DNA, not protein, is injected into the host cell and serves as the genetic material for viral reproduction
Define the theory of natural selection
Explains evolution as a process where organisms with advantageous, heritable traits for their environment are more likely to survive and reproduce, leading to those traits becoming more common over generations
Define protein primary sequence
the specific linear sequence of amino acids that are linked together by peptide bonds to form a polypeptide chain (order of amino acids determines the proteins 3-D folded structure and function)
Define nucleic acid sequence
the specific order of nucleobases (A, T, C, G for DNA; A, U, C, G for RNA) along a strand of DNA or RNA
Define transcription (of RNA from info in DNA)
the process of copying a segment of DNA into a complementary RNA molecule, most commonly messenger RNA (mRNA(
Uses the DNA as a template and is performed by the enzyme RNA polymerase, creating an RNA copy of the genetic information to be used for protein synthesis
Define translation (of protein from info in RNA)
the process where the genetic information encoded in messenger RNA (mRNA) is used to synthesize a protein
Process takes place in the cell’s ribosomes, where transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules bring amino acids to the ribosome, which links them together in the sequence specified by the mRNA codons to form a polypeptide chain
Define gene
the fundamental physical and functional unit of heredity, composed of a specific sequence of DNA that provides instructions for making proteins or regulating other genes
Organized on chromosomes and determine hereditary traits
Define meiosis
a specialized type of cell division that reduces the chromosome number by half, creating gametes (sperm or egg cells) for sexual reproduction
Involves 2 rounds of cell division (Meiosis I and Meiosis II), resulting in 4 genetically unique haploid cells from a single diploid parent cell
Define virus
an infection particle consisting of genetic material (DNA or RNA) enclosed in a protein coat, or capsid, and sometimes an outer membrane (envelope)
Not considered alive because they can’t reproduce on their own (need a host)
Define bacteriophage
a type of virus that infects and replicates only in bacterial cells
Define transformation of bacteira
the process where a bacterium takes up foreign DNA from its environment, incorporating it into its own genetic material, resulting in new traits
Define Chargaff’s rule
states that in any sample of double-stranded DNA, the amount of adenine (A) is equal to the amount of thymine (T), and the amount of guanine (G), is equal to the amount of cytosine (C).
Established the specific pairing pattern of bases in DNA and were crucial for understanding DNA’s structure and function