Rubenstein - Chapter 12
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
Basic industry
A business that sells its products or services primarily to consumers outside the settlement. Ex: Cities with high levels of tourism that bring in outsiders. Hotels

non-basic industry
A business that primarily serves customers living in the same settlement. Ex: Grocery stores

Central place theory
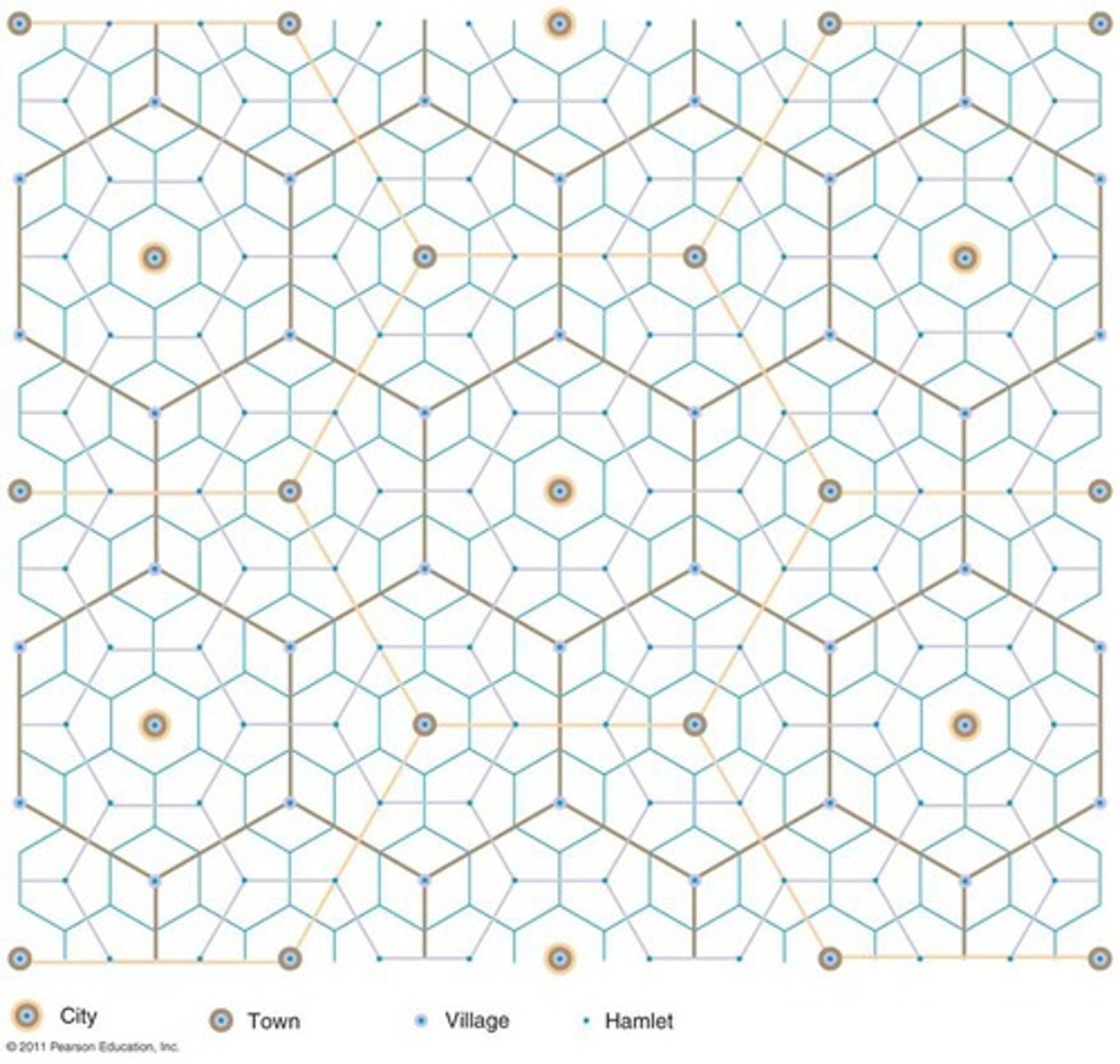
A theory that explains the distribution of services, based on the fact that settlements serve as centers of market areas for services; larger settlements are fewer and farther apart than smaller settlements and provide services for a larger number of people who are willing to travel farther.
Clustered rural settlement
A rural settlement in which the houses and farm buildings of each family are situated close to each other and fields surround the settlements.
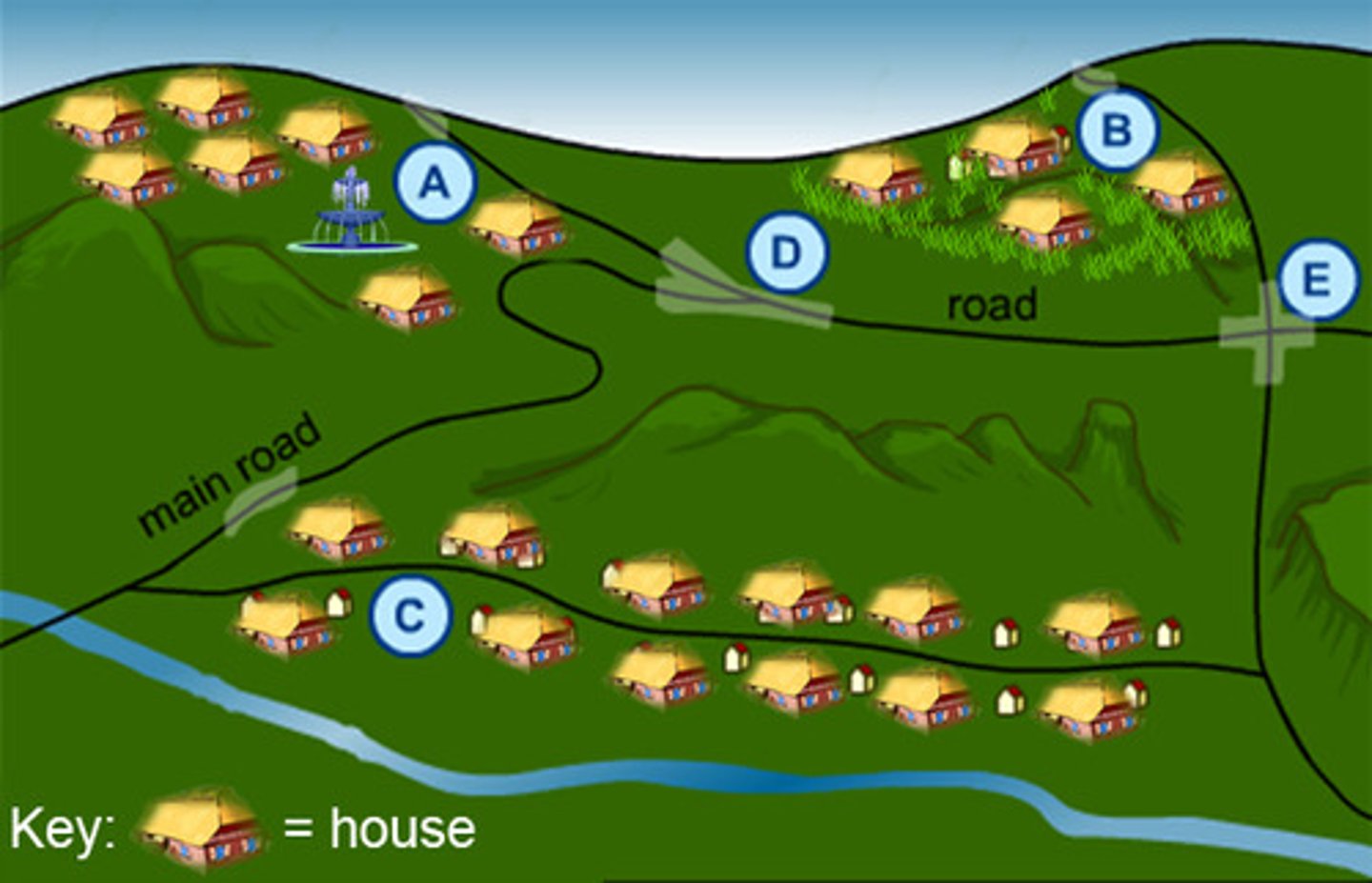
Dispersed rural settlement
A rural settlement pattern characterized by isolated farms rather than clustered villages.

Enclosure movement
The process of consolidating small landholdings into a smaller number of larger farms in England during the eighteenth century.

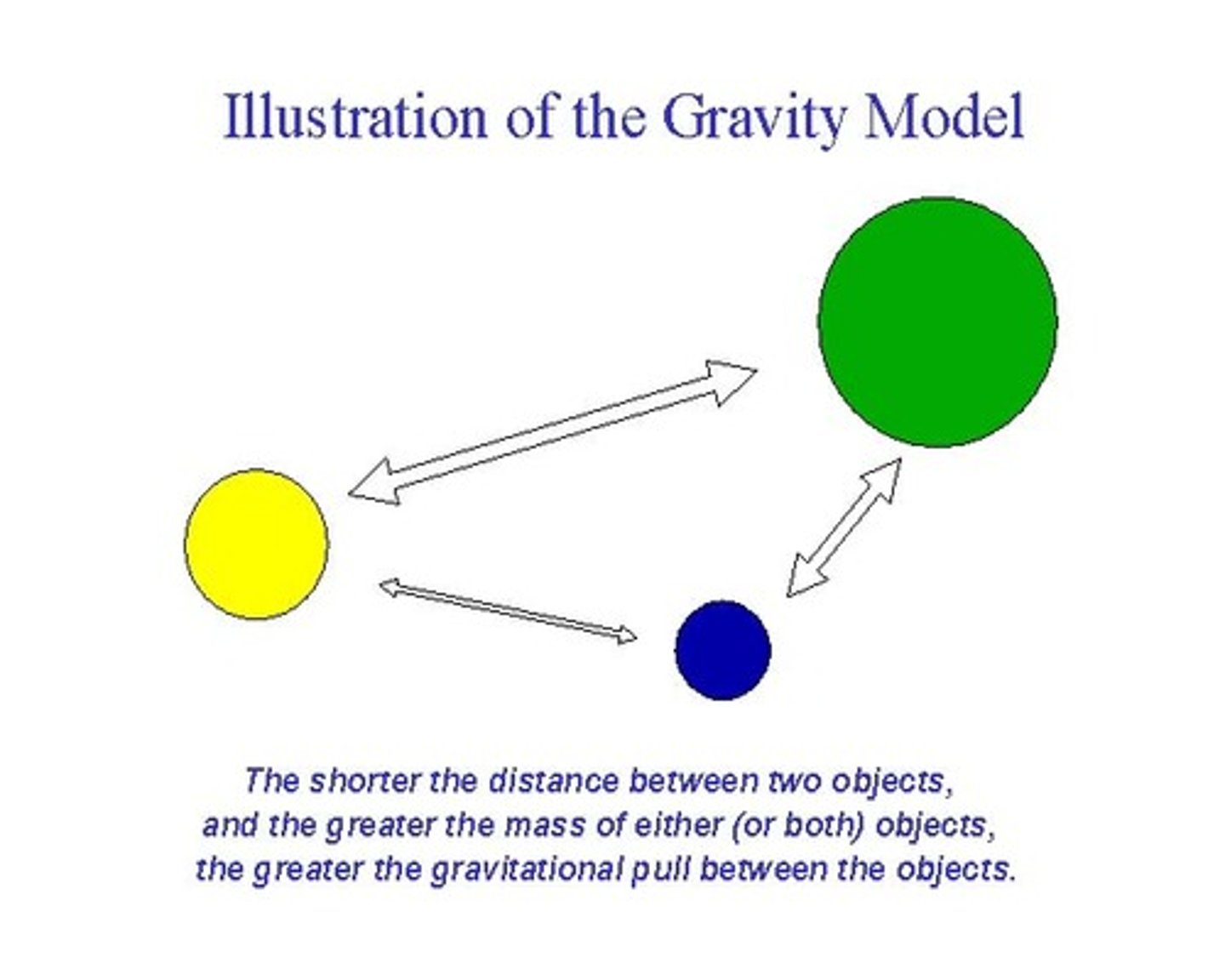
Gravity model
A model that holds that the potential use of a service at a particular location is directly related to the number of people in a location and inversely related to the distance people must travel to reach the service.
Hinterland
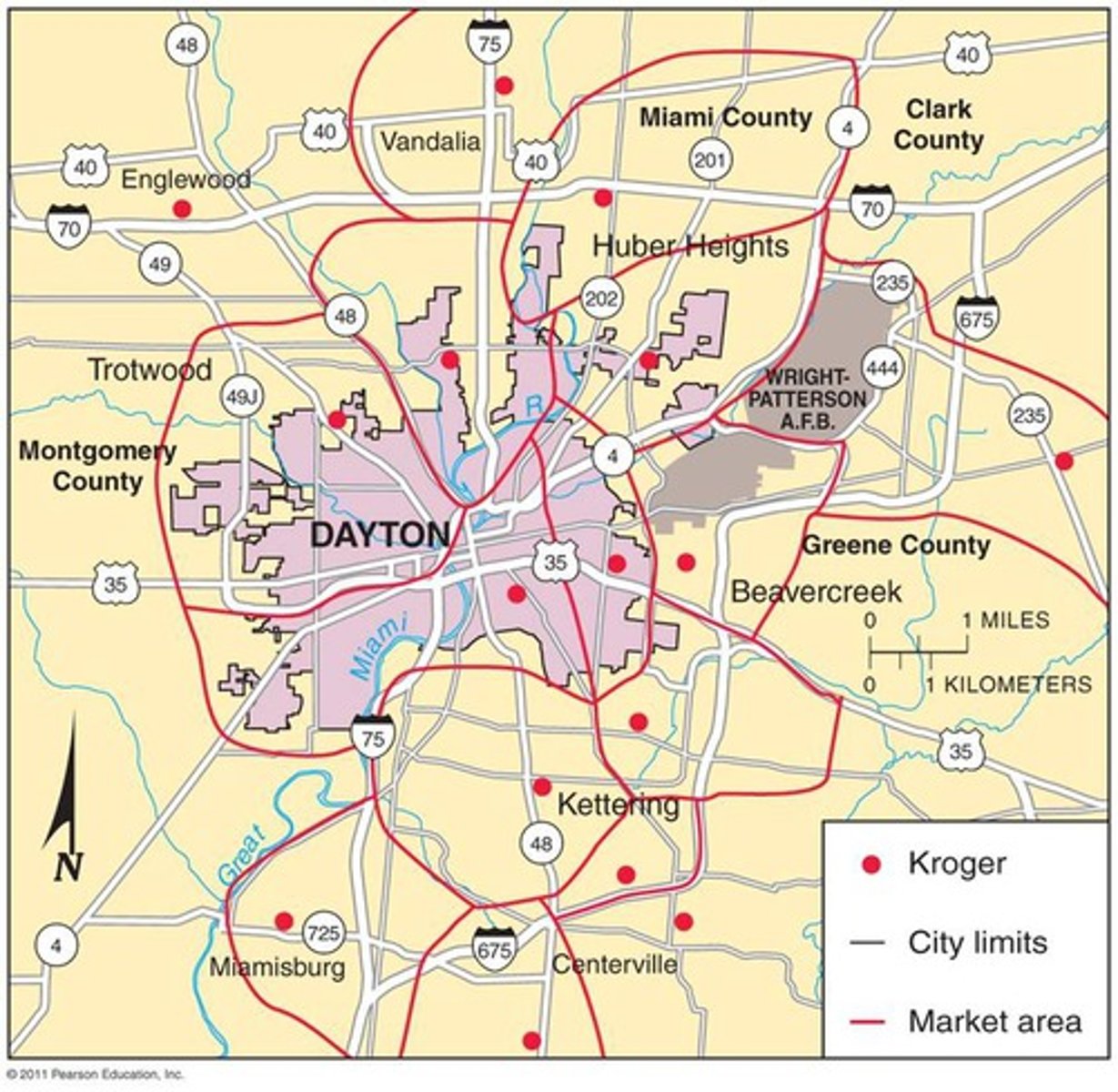
The area surrounding a central place, from which people are attracted to use the place's goods and services. (Also known as a market area.)
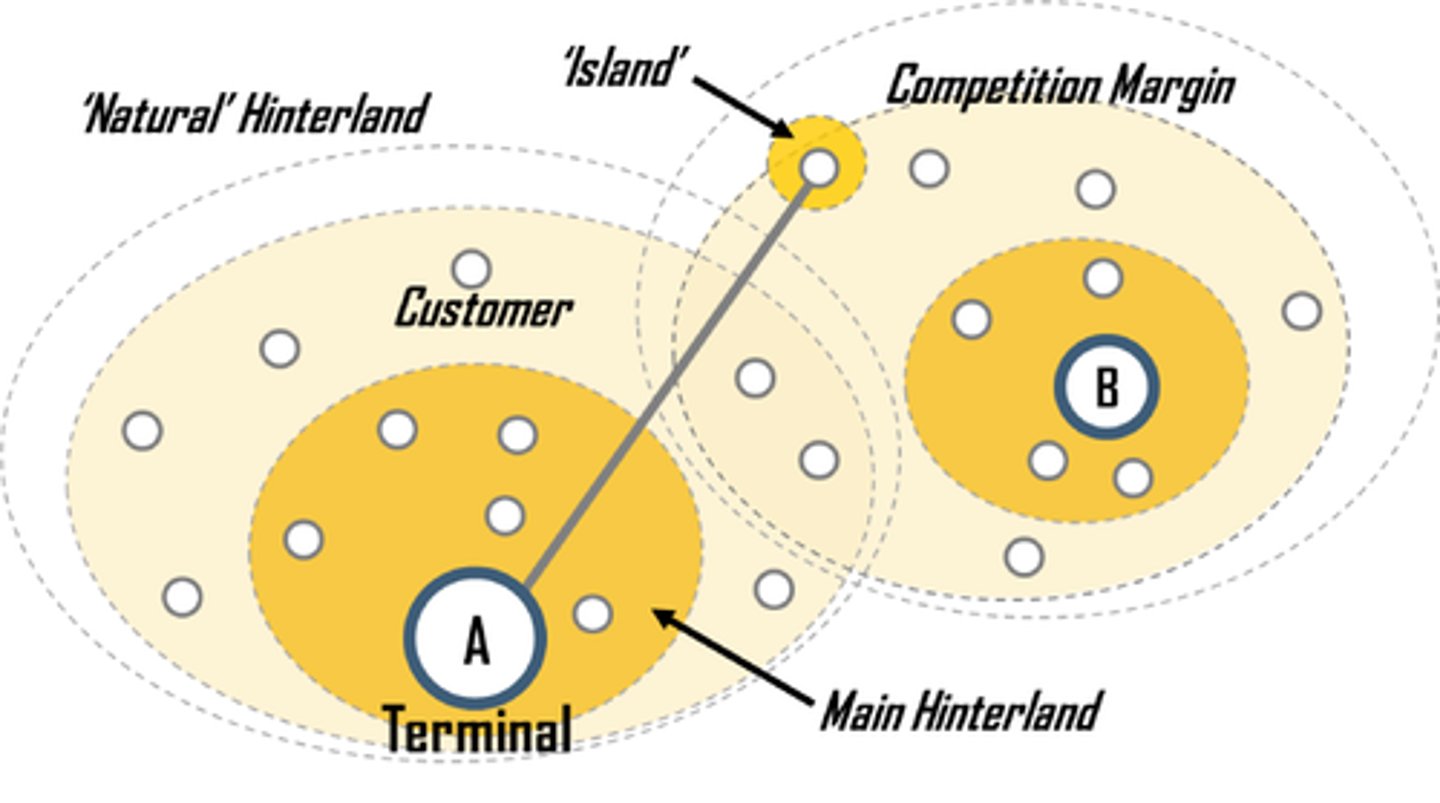
Market area
The area surrounding a central place, from which people are attracted to use the place's goods and services. (Also known as hinterland.)
Primate City
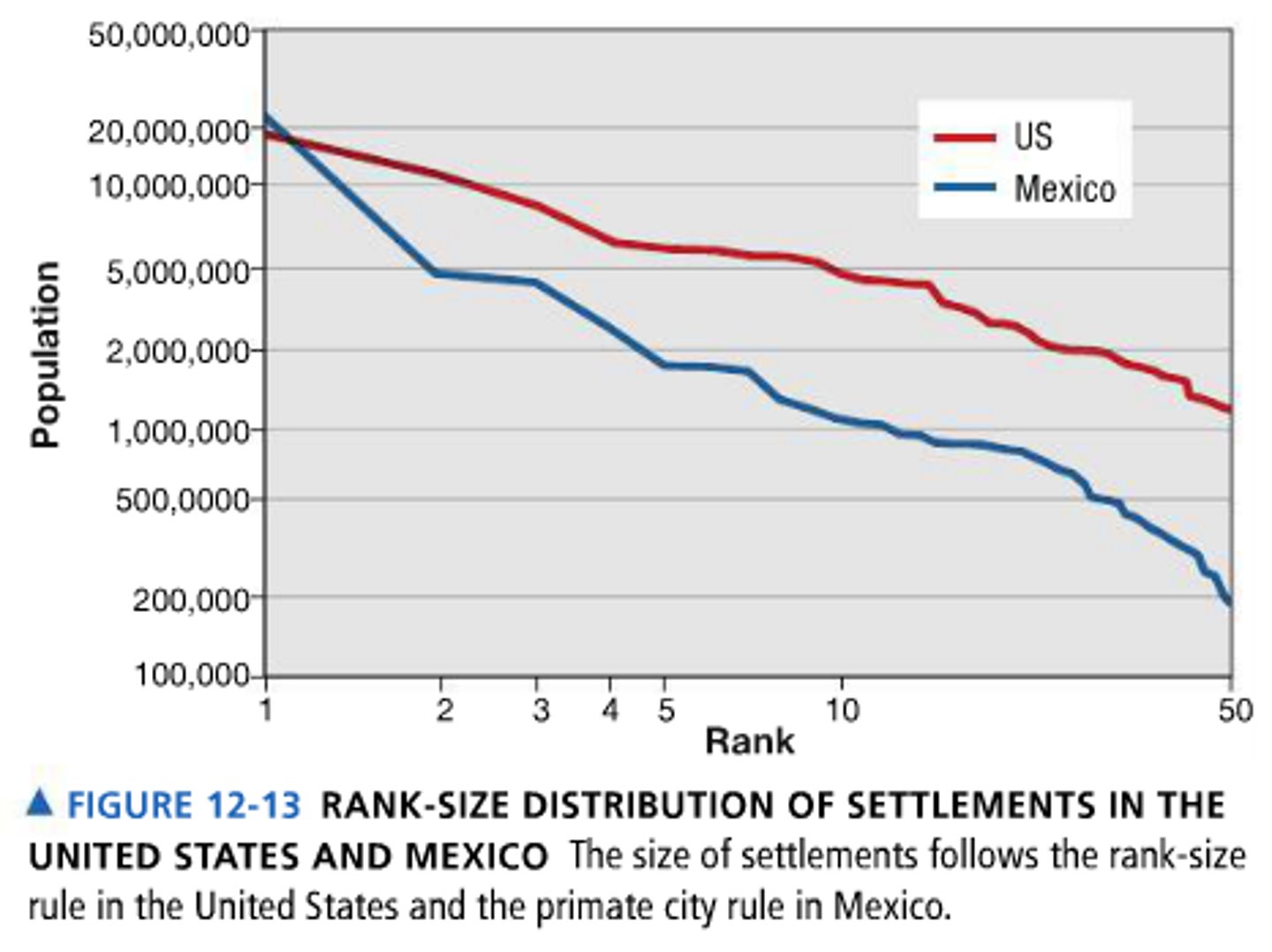
A city that is the largest settlement in a county, if it has more than twice as many people as the second-raking settlement.

Range
The maximum distance people are willing to travel to use a service.
Rank-size rule
A pattern of settlements in a country, such that the nth largest settlement is 1/n the population of the largest settlement.
Settlement/city
A permanent collection of buildings where inhabitants work and obtain services.
Threshold
The minimum number of people needed to support the service.
Business services
Their purpose is to facilitate other businesses
city-state
a city that with its surrounding territory forms an independent state.
consumer services
A business that provides services to individual customers who desire them and can afford to pay for them
public services
service offered by the government to provide security and protection for citizens/businesses
world cities
A group of cities that form an interconnected, internationally, dominant system of global control of finance and commerce. London, NYC, Tokyo
back office
Its function is to provide support for front office services
Offices of a company handling high-volume communications by telephone, electronic transaction or letter. Location can be flexible, increasingly in places like LDCs where space, English-speaking labor, low wages, and other costs are relatively low. Outside the CBD, Most back office workers work at night when American consumers are awake.
specialized producer-service center
More narrow and unique service centers, often related to specific industries. R&D and government could be specific examples of specialties. DO ONE THING WELL
dependent centers
Provide relatively unskilled jobs and depend for their economic health on decisions made in the world cities, regional command and control centers, and specialized producer-service centers. Four subtypes of dependent centers in the US: Resort, Retirement, and Residential Centers; Manufacturing Centers; Military Centers; Mining Centers
Periodic markets
When small vendors from all around meet up at a certain location to sell goods sometimes weekly and sometimes annually (Farmers Market)
a collection of individual vendors who offer goods/services on specialized market days. Used in LDCs and rural MDCs. Variations in the cycle of periodic markets can depend on ethnic differences.
Hierarchy of settlements
This is when settlements are placed in order according to size or the number of goods and services supplied by them. It has a pyramid shape as because there are more small settlements than large ones.
a way of arranging settlements into a hierarchy based upon their population or some other criteria
personal services
Services that provide for the well-being and personal improvement of individual consumers.
producer services
Provides services primarily to help people conduct other business.
transportation and information services
Businesses that diffuse and distribute services.