PIPE | Thermodynamics
1/209
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
210 Terms
temperature
Enthalpy of an ideal gas is a function only of
A. enthalpy
B. entropy
C. pressure
D. temperature
Carnot
Which of the following is the most efficient thermodynamic cycle?
A. Brayton
B. Otto
C. Carnot
D. Diesel
Energy can neither be created nor destroyed
What is the first law of thermodynamics?
A. internal energy is due to molecular motions
B. entropy of the universe is increased by irreversible processes
C. energy can neither be created nor destroyed
D. heat energy cannot be completely transformed into work
zero
An ideal gas is compressed isothermally. What is the enthalpy change?
A. always negative
B. always positive
C. zero
D. undefined
adiabatic
Name the process that has no heat transfer
A. isothermal
B. isobaric
C. polytropic
D. adiabatic
increases
An ideal gas is compressed in a cylinder so well insulated that there is essentially no heat transfer. The temperature of the gas
A. decreases
B. increases
C. remain constant
D. is zero
pascal
What is the SI unit of pressure
ideal gas
The equation Cp = Cv + R applies to which of the following
A. enthalpy
B. ideal gas
C. two phase states
D. all pure substances
shaft work
In the flow process, neglecting kinetic and potential energies, the integral of Vdp represents what?
A. heat transfer
B. flow energy
C. enthalpy change
D. shaft work
enthalpy
Mechanical energy of pressure transformed into energy of heat
A. kinetic energy
B. enthalpy
C. heat exchanger
D. heat of compression
thermodynamics
The theory of changing heat into mechanical work
A. thermodynamics
B. kinematics
C. inertia
D. kinetics
mean effective pressure
Average pressure on a surface when a changing pressure condition exist.
A. back pressure
B. partial pressure
C. pressure drop
D. mean effective pressure
stirling cycle
Which of the following cycles consists of two isothermal and two constant volume processes?
A. diesel cycle
B. ericsson cycle
C. stirling cycle
D. otto cycle
a fixed region in space
A control volume refers to what?
A. a fixed region in space
B. a reversible process
C. an isolated system
A. a specified mass
isometric
In the polytropic process, PVn= constant, if the value of n is infinitely large, the process is
A. isobaric
B. isometric
C. isothermal
D. polytropic
compressed liquid
If the temperature is held constant and the pressure is increased beyond the saturation pressure, then the working medium must be:
A. compressed liquid
B. subcooled liquid
C. saturated vapor
D. saturated liquid
subcooled liquid
Is one whose temperature is below the saturation temperature corresponding to its pressure
A. superheated vapor
B. wet vapor
C. subcooled liquid
D. saturated liquid
Avogadro’s number
Number of molecules in a mole of any substance is a constant called
A. Rankine constant
B. Avogadro’s number
C. Otto constant
D. Thompson constant
Charles’ Law
If the pressure of a gas is constant the volume is directly proportional to the absolute temperature.
A. Boyle’s law
B. Joule’s law
C. Charles’ Law
D. Kelvin’s Law
atomic number
The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom of the number of electrons in the orbit of an atom
A. atomic volume
B. atomic number
C. atomic weight
D. atomic mass
fusion curve
In a P-T diagram of a pure substance, the curve separating the solid phase from the liquid phase is:
A. vaporization curve
B. fusion curve
C. boiling point
D. sublimation point
10
A water temperature of 18°F in the water cooled condenser is equivalent in °C to
A. 7.78
B. 10
C. 263.56
D. -9.44
22.6 × 105
The latent heat of vaporization in Joules per kg is equal to
A. 5.4 × 102
B. 4.13 × 103
C. 22.6 × 105
D. 3.35 × 105
heat
Form of energy associated with the kinetic energy of the random motion of large number of molecules
A. internal energy
B. kinetic energy
C. heat of fusion
D. heat
critical point
In the condition of pressure and temperature at which a liquid and its vapor are indistinguishable
A. critical point
B. dew point
C. absolute humidity
D. relative humidity
compressed liquid
If the temperature is held constant and the pressure is increased beyond the saturation pressure, then, the working medium must be:
A. saturated vapor
B. compressed liquid
C. saturated liquid
D. subcooled liquid
vapor
When a substance in gaseous state is below the critical temperature, it is called
A. vapor
B. cloud
C. moisture
D. steam
approximately as a gas
Superheated vapor behaves
A. just as gas
B. just as steam
C. just as ordinary vapor
D. approximately as a gas
zeroth law of thermodynamics
Which of the following provides the basis for measuring thermodynamics property of temperature
A. zeroth law of thermodynamics
B. first law of thermodynamics
C. second law of thermodynamics
D. third law of thermodynamics
ethylene glycol
Which of the following is commonly used as liquid absorbent
A. silica gel
B. activated alumina
C. ethylene glycol
D. none of these
air cooler
Mechanism designed to lower the temperature of air passing through it
A. air cooler
B. air defense
C. air spill over
D. air cycle
anemometer
A device for measuring the velocity of wind
A. aneroid barometer
B. anemometer
C. anemoscope
D. anemograph
second law of thermodynamics
Heat nromally flowing from a high temperature body to a low temperature body wherein it is impossible to convert heat without other effects
A. zeroth law of thermodynamics
B. first law of thermodynamics
C. second law of thermodynamics
D. third law of thermodynamics
boiling point
The temperature at which its vapor pressure is equal to the pressure exerted on the liquid
A. absolute humidity
B. calorimetry
C. boiling point
D. thermal point
increase velocity and decrease pressure
A nozzle is used to
A. increase velocity and decrease pressure
B. decrease velocity as well as pressure
C. increase velocity as well as pressure
D. decrease velocity and increase pressure
internal energy
The sum of the energies of all the molecules in a system where energies appear in several complex form
A. kinetic energy
B. potential energy
C. internal energy
D. frictional energy
flow energy, kinetic energy, height above datum, and internal energy
The total energy in a compressible or incompressible fluid flowing across any section in a pipeline is a function of
A. pressure and velocity
B. pressure, density, and velocity
C. pressure, density, velocity, and viscosity
D. flow energy, kinetic energy, height above datum, and internal energy
specific gravity
The ratio of the density of a substance to the density of some standard substance
A. relative density
B. specific gravity
C. specific density
D. relative gravity
compressed liquid
Is one whose pressure is higher than the saturation pressure corresponding to its temperature
A. compressed liquid
B. saturated liquid
C. saturated vapor
D. superheated vapor
sublimation
The changing of solid directly to vapor without passing through the liquid state is called
A. evaporation
B. vaporization
C. sublimation
D. condensation
weight density
Weight per unit volume is termed as
A. specific gravity
B. density
C. weight density
D. specific volume
newton
What is the SI unit of force?
A. pound
B. newton
C. kilogram
D. dyne
discharge
The volume of fluid passing a cross-section of steam in unit time
A. steady flow
B. uniform flow
C. discharge
D. continuous flow
B. Q + Vdp = H2 - H1
What equation applies in the first law of thermodynamics for an ideal gas in a reversible open steady-state system?
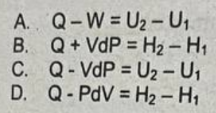
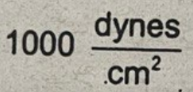
A pressure of 1 milibar is equivalent to
quasi-static process
When a system deviates infinitesimally from equilibrium at every instant of its state, it is undergoing:
A. isobaric process
B. quasi-static process
C. isometric process
D. cyclic process
centripetal force
What is the force which tends to draw a body towards the center about which it is rotating?
A. centrifugal force
B. centrifugal motion
C. centrifugal advance
D. centripetal force
adiabatic
What is the process that has no heat transfer?
A. reversible isometric
B. isothermal
C. polytropic
D. adiabatic
turbojet
Which of the engine is used for fighter bombers?
A. turbojet
B. pulsejet
C. rockets
D. ramjet
kinetic energy
Exhaust gases from an engine posses:
A. solar energy
B. kinetic energy
C. chemical energy
D. stored energy
zero
At critical point the latent enthalpy of vaporization is
A. temperature dependent
B. zero
C, minimum
D. maximum
centripetal force
What is the force which tends to draw a body towards the center about which it is rotating?
A. centrifugal force
B. centrifugal in motion
C. centrifugal advance
D. centripetal force
quasi-static process
When a system deviates infinitesimally from equilibrium at every instant of its state, it is undergoing
A. isobaric process
B. quasi-static process
C. isometric process
D. cyclic process
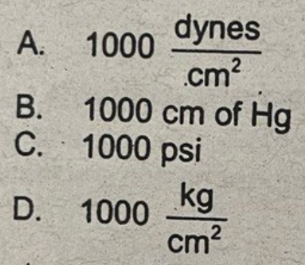
1000 dynes/cm2
A pressure of 1 millibar is equivalent to
A. 1000 dynes/cm2
B. 1000 cm of Hg
C. 1000 psi
D. 1000 kg/cm2
potential at a point
Work done per unit charge when charged is moved from one point to another
A. equipotential surface
B. potential at a point
C. electrostatic point
D. potential difference
2
How many independent properties are required to completely fix the equilibrium state of a pure gaseous compound?
A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
h = u pV
Which of the following relations defines enthalpy?
A. h = u + p/T
B. h = u pV
C. h = u + p/V
D. h = pV + T
internal energy is negative
Which of the following is true for water at a reference temperature where enthalpy is zero?
A. internal energy is negative
B. entropy is non-zero
C. specific volume is zero
D. vapor pressure is zero
h-s
On what plane is the Mollier diagram plotted?
A. p-V
B. p-T
C. h-s
D. h-u
z = PV/RT
The compressibility factor z, is used for predicting the behavior of non-ideal gases. How is the compressibility factor defined relative to an ideal gas? (subscript c refers to critical value)
A. z = P/Pc
B. z = PV/RT
C. z = T/Tc
D. z = (T/Tc)(/Pc/P)
the fraction of the total mass that is saturated vapor
How is the quality x of a liquid-vapor mixture defined?
A. the fraction of the total volume that is saturated vapor
B. the fraction of the total volume that is saturated liquid
C. the fraction of the total mass that is saturated vapor
D. the fraction of the total mass that is saturation liquid
hg - hf
What is the expression for heat of vaporization?
A. hg
B. hf
C. hg - hf
D. hf - hg
zero
What is the value of the work done for a closed, reversible, isometric system?
A. zero
B. positive
C. negative
D. indeterminate
W = MRT ln(V2/V1)
What is the equation for the work done by a constant temperature system?
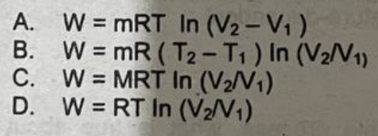
n = 0
What is true about the polytropic exponent n for a perfect gas undergoing an isobaric process?
A. n > 0
B. n < 0
C. n = ∞
D. n = 0
D. Both: heat transfer = 0, Isentropic = reversible
How does an adiabatic process compare to an isentropic process?
A. Adiabatic: heat transfer = 0, Isentropic: heat transfer = 0
B. Adiabatic: heat transfer = 0, Isentropic: heat transfer = 0
C. Adiabatic: reversible, Isentropic: not reversible
D. Both: heat transfer = 0, Isentropic = reversible
always zero
During an adiabatic, internally reversible process, what is true about the change in entropy?
A. always zero
B. always less than zero
C. always greater than zero
D. temperature-dependent
C. ds > 0
For an irreversible process, what is true about the change in entropy of the system and surroundings?
A. ds = dq/dt
B. ds = 0
C. ds > 0
D. ds < 0
reversible
For which type of process does the equation dQ = Tds hold?
A. irreversible
B. reversible
C. isobaric
D. isothermal
ΔS (surrounding) + ΔS (system) >= 0
Which of the following is true for any process?
A. ΔS (surrounding) + ΔS (system) > 0
B. ΔS (surrounding) + ΔS (system) < 0
C. ΔS (surrounding) + ΔS (system) <= 0
D. ΔS (surrounding) + ΔS (system) >= 0
two isothermal two isentropic
The ideal reversible Carnot cycle involves four basic processes. What type of processes are they?
A. all isothermal
B. all adiabatic
C. all isentropic
D. two isothermal two isentropic
W/ΔS
What is the temperature difference of the cycle if the entropy difference is ΔS, and teh work done is W?
A. W - ΔS
B. W/ΔS
C. ΔS/W
D. ΔS - W
increased boiler life
Which of the following is not an advantage of a superheated closed Rankine cycle over an open Rankine cycle?
A. lower equipment cost
B. increased efficiency
C. increased turbine life
D. increased boiler life
In practical terms, the susceptibility of the engine materials to corrosion is not a key limitation on the operating efficiency
Which of the following statements regarding Rankine cycle is not true?
A. Use of a condensable vapor in the cycle increases the efficiency of the cycle
A. The temperature at which energy is transferred to and from the working liquid are less separated than in a Carnot cycle
C. Superheating increases the efficiency of a Rankine cycle
D. In practical terms, the susceptibility of the engine materials to corrosion is not a key limitation on the operating efficiency
0°C and 1 atm pressure
Which of the following is standard temperature and pressure (STP)
A. 0K and 1 atm pressure
B. 0F and zero pressure
C. 32F and zero pressure
D. 0°C and 1 atm pressure
loses electrons
A substance is oxidized when which of the following occurs?
A. turns red
B. loses electrons
C. gives off heat
D. absorbs energy
kg/m-s
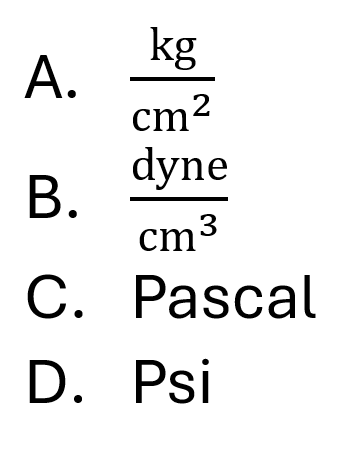
Which of the following is not a unit of pressure?
A. Pa
B. kg/m-s
C. bars
D. kg/m2
the principle conservation of energy
Which of the following is the basis for Bernoulli’s law for fluid flow?
A. the principle conservation of mass
B. the principle conservation of energy
C. continuity equation
D. fourier’s law
Newton meter
Which of the following is the definition of Joule?
A. Newton meter
B. kg-m/s2
C. unit of power
D. rate of change of energy
a mathematical expression defining a path between states
Equation of state for a single component can be any of the following except:
A. ideal gas law
B. any relationship interrelating 3 or more state functions
C. relationship mathematically interrelating thermodynamic properties of the material
D. a mathematical expression defining a path between states
properties
The state of a thermodynamic system is always defined by its:
A. absolute temperature
B. process
C. properties
D. temperature and pressure
increase only
In any non-quasi-static thermodynamic process, the overall entropy of an isolated system will
A. increase and then decrease
B. decrease and then increase
C, increase only
D. decrease only
randomness or disorder
Entropy is the measure of
A. the internal energy of a gas
B. the heat capacity of a substance
C. randomness or disorder
D. the change of enthalpy of a system
Entropy of a crystal at 0°F is zero
Which of the following statements about entropy is false?
A. Entropy of a mixture is greater than that of its components under the same condition
B. An irreversible process increases entropy of the universe
C. Net entropy change in any closed cycle is zero
D. Entropy of a crystal at 0°F is zero
force and time
Work or energy can be a function of all of the following except:
A. force and distance
B. power and time
C. force and time
D. temperature and entropy
dQ/T
Energy changes are represented by all except which one of the following:
A. mCpdt
B. -∫VdP
C. Tds - Pdv
D. dQ/T
enthalpy
U+ pV is a quantity called:
A shaft work
B. entropy
C. enthalpy
D. internal energy
shaft work
In flow process, neglecting KE and PE changes, ∫vdP represents which item below?
A. Heat transfer
B. Shaft work
C. Enthalpy change
D. Closed system work
Btu/hr
Power may be expressed in units of
A. ft-lb
B. Kw - hr
C.Btu
D. Btu/hr
In a steady state flow process
Equilibrium condition exist in all except which of the following?
A. In reversible processes
B. In processes infinitesimals where driving forces are infinitesimals
C. In a steady state flow process
D. Where nothing can occur without an effect on the system's surrounding
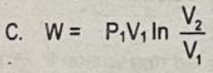
In a closed system (with a moving boundary) which of the following represents work done during an isothermal process?
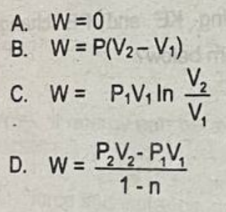
Fluid
A substance that exists, or is regarded as existing, as a continuum characterized by a low resistance to flow and the tendency to assume the shape of its container.
A. Fluid
B. Atom
C. Molecule
D. Vapor
pure substance
A substance that is homogeneous in composition and homogenous and invariable in chemical aggregation
A. Pure substance
8. Simple substance
C. Vapor
D. Water
simple substance
A substance whose state is defined by variable intensive thermodynamic properties
A. Pure substance
B. Simple substance
C. Vapor
D. Water
closed system
A system in which there is no exchange of matter with the surrounding or mass does not cross its boundaries
A. Open system
B. Closed system
C. Isolated system
D. Nonflow system
isolated system
A system that is completely impervious to its surrounding or neither mass nor energy cross its boundaries
A. Open system
B. Closed system
C. Isolated system
D. Nonflow system
open system
A system in which there is a flow of mass across its boundaries.
A. Open system
B. Closed system
C. Isolated system
D. Steady flow system
extensive properties
The properties that are dependent upon the mass of the system and are total values such as total volume and total internal energy.
A. Intensive properties
B. Extensive properties
C. Specific properties
D. State properties
intensive properties
The properties that are independent of the mass the system such as temperature, pressure, density, and voltage.
A. Intensive properties
B. Extensive properties
C. Specific properties
D. State properties
specific properties
The properties for a unit mass and are intensive by definition such as specific volume.
A. Intensive properties
B. Extensive properties
C. Specific properties
D. Thermodynamic properties