Chapter 2: Neurons and Glia
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
Transcription
The process whereby the genes encoded by the genomic DNA are converted to messenger RNA (mRNA)
occurs in the cellular nucleus
Transcription is the process of converting the genetic template in DNA to messenger RNA.
True or False
True
Neurons are similar to other cells
Neuron cells also have
Organelles
Cell membranes
Cytoplasm
Genetic material
Basic functions like metabolism, protein synthesis
What do all cells including neurons derive from?
Stem Cells and Precursor cells
Stem cells
cells that are able to produce cells identical to themselves (self-renew) and may produce daughter cells that differentiate into a more mature cell type
During development
Each cell starts as an egg that has been fertilized
then divides and forms a group of identical embryonic stem cells
form an inner mass of cells in a developing zygote that are totipotent or capable of forming any type of cell in the human body
Neural Stem cells
cellular source of the central nervous system (CNS) and peripheral nervous system (PNS).
Neural Restricted Progenitors
NRP
can differentiate into a limited range of neuron types
Totipotent
Embryonic stem cells form an inner mass of cells in a developing zygote
capable of forming any type of cell in the human body
Early-stage embryo
How important are neurons for normal human functioning?
They control most of our major functions, including regulating systems that are integral to life like heart rate and respiration
also provide a means for us to experience our world through sensory systems (somatosensory and special senses) and allow us to move through and manipulate our environment through motor systems
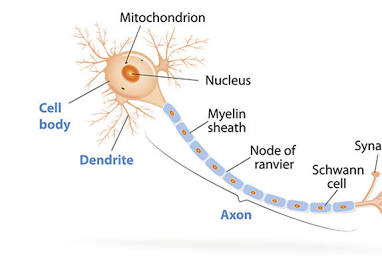
Neurons are polarized
meaning that the different ends of a neuron are specialized to perform certain functions. The functional poles of a neuron include the dendritic trees and axons.
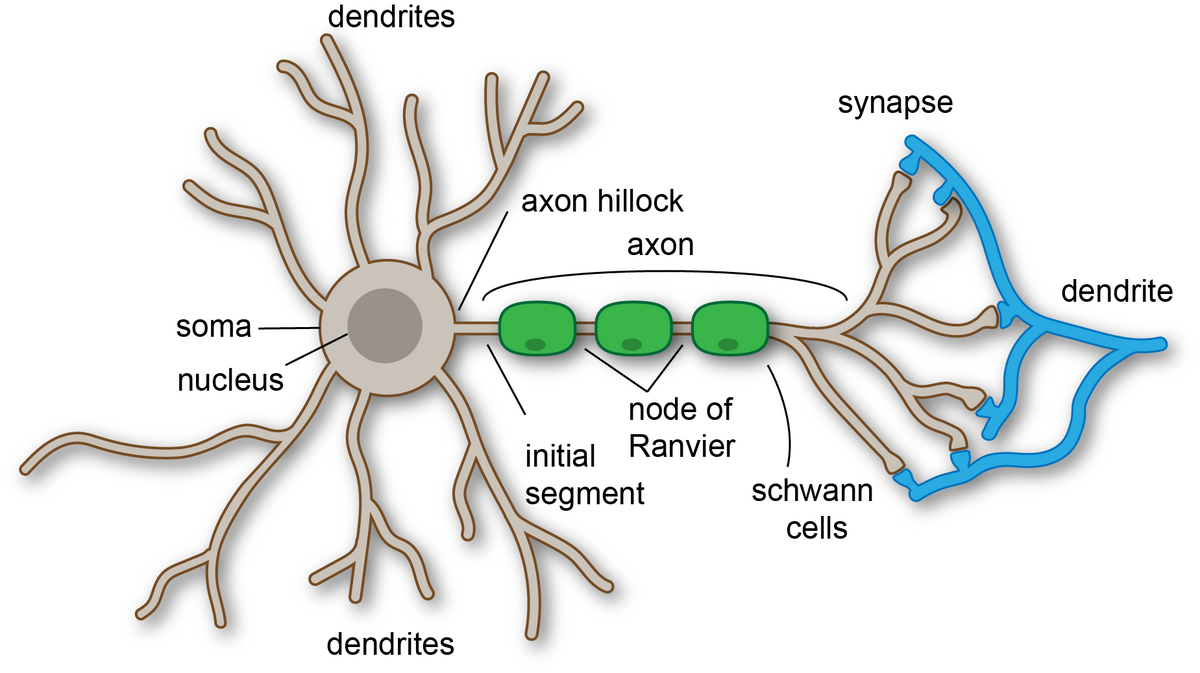
Soma
The cell body
generally lies between the dendrites and the axon and contains the nucleus and all the major cell organelles
functions as the organizing center for the neuron
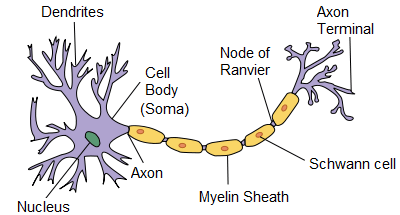
Dendrites
are the receiving end of a neuron
They receive messages from other neurons on specialized structures called dendritic spines.
Axon
Each neuron has one, and only one
the sending end of the neurons and the site of action potential propagation
may extend for long distances, making neurons the largest cells in the body
may be myelinated, which speeds up action potential propagation
Cytoskeleton
The unique shape of neurons is provided for by the neuronal..
Neurons need to generate significant amounts of cellular energy
so they have many mitochondria
Nucleus
Located in the soma, contains the cell’s DNA,
involved in gene expression
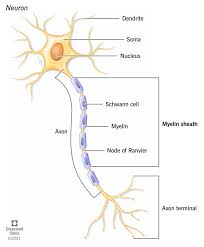
Myelin Sheath
A fatty, insulating layer that wraps around the
axon
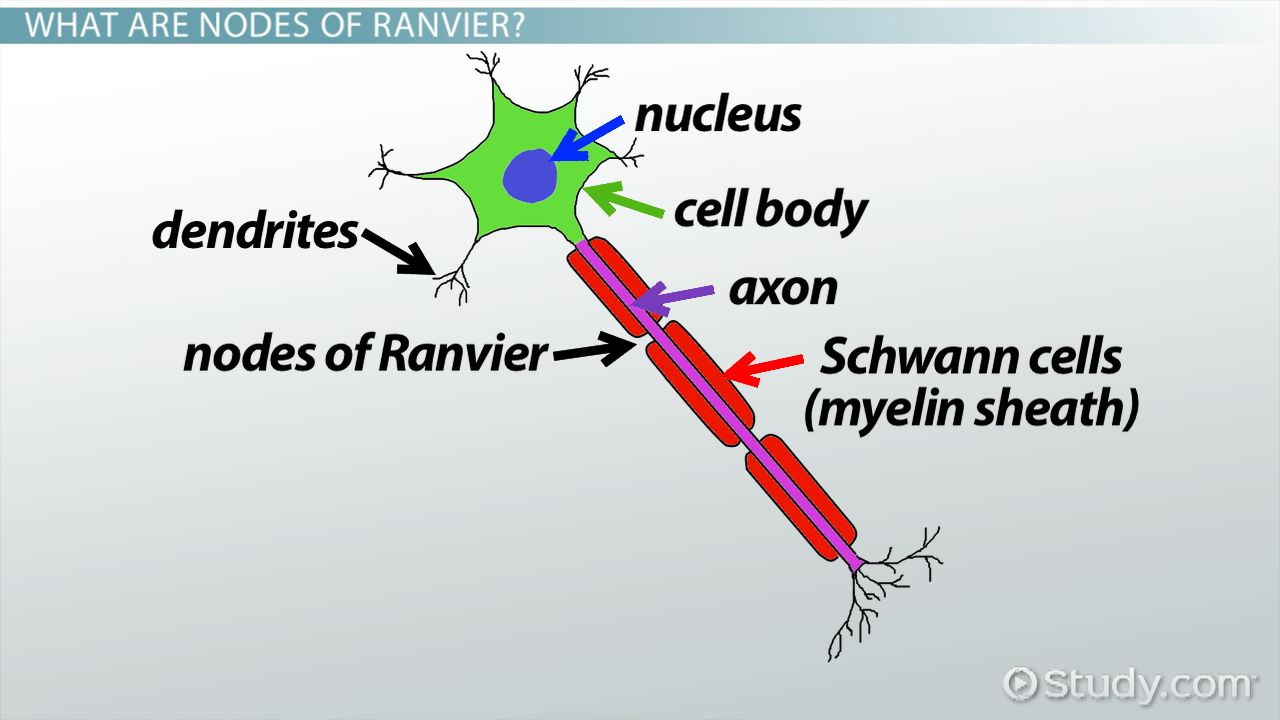
Node of Ranvier
Gaps in myelin sheath that allow for rapid,
saltatory conduction of action potentials
Axon terminal
Transmits signals to other neurons or the target
cells, contain synaptic vesicles that store
neurotransmitters
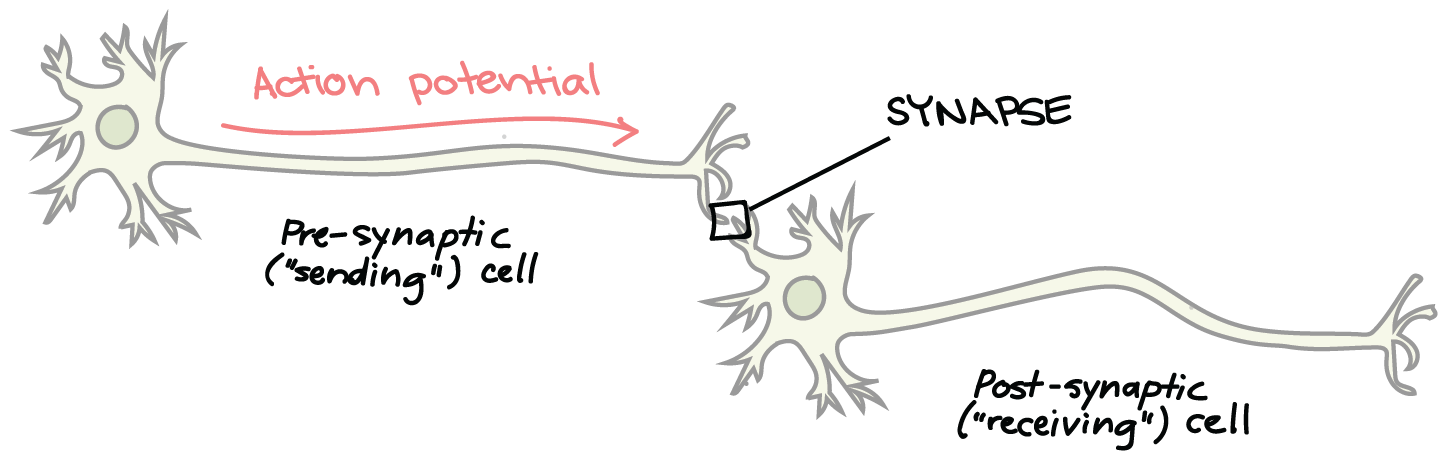
Synapses
Essential for the transmission of neuronal
impulses from one neuron to the next
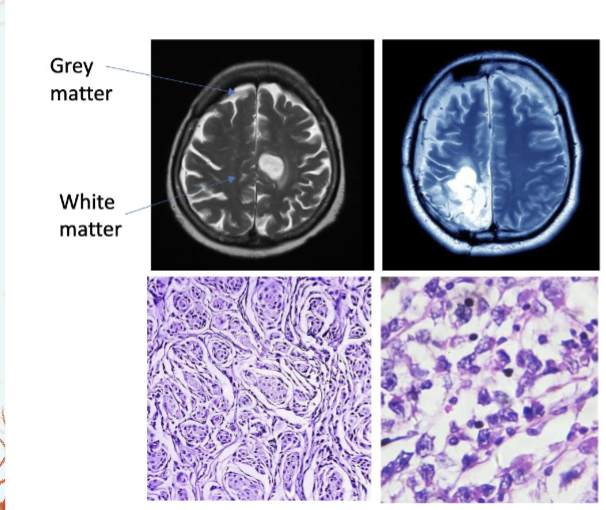
Difference between Grey matter and White Matter
Grey Matter→unmyelinated
White Matter→ myelinated
Specialized neuron functions
Detect environment
● Relay neural impulses
● Process neural
information
● Execute response
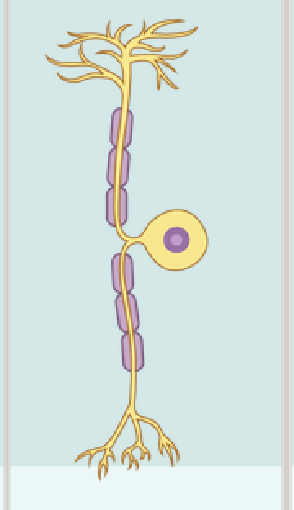
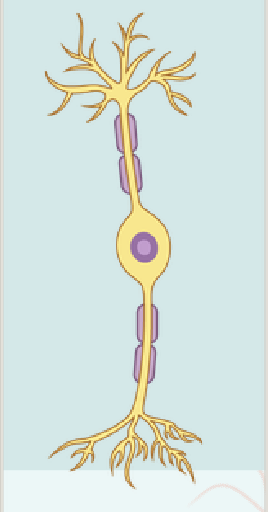
Unipolar Neuron
Single elongated process, with the cell body located off to the side
Bipolar Neuron
Two processes separated by the cell body
often situated within the special senses (seeing, hearing, balance, olfaction, taste), where a one-to-one correlation with incoming sensory stimuli is needed
ex: are located in the retina, where they transfer information coming from the light-sensing rods and cones to the neurons that make up the optic nerve
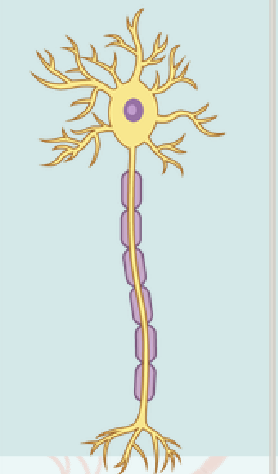
Multipolar Neuron
Have more than two processes, a single axon, and multiple dendrites
They are the most numerous type of neuron shape and many neuron subtypes
There are three types of cytoskeleton scaffolds:
microfilaments, intermediate filaments, and microtubules
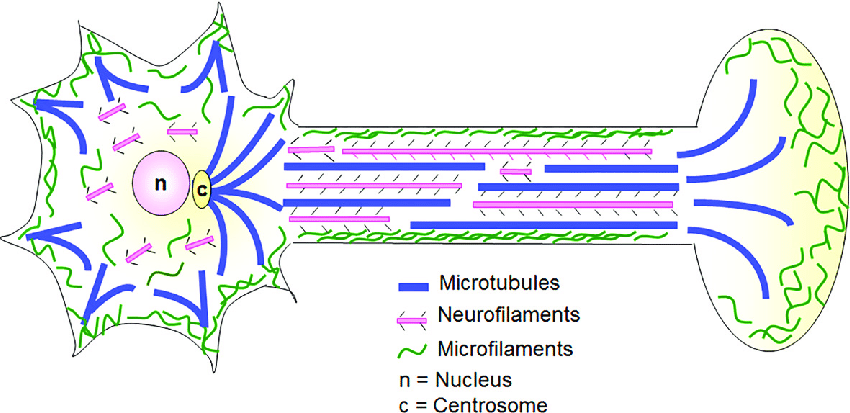
Microfilaments
the smallest type of cytoskeletal elements
6 nanometers (nm) in diameter
composed of polymerized filaments of the protein, actin
function both in maintaining structures and in transporting cellular components with the cooperation of myosins
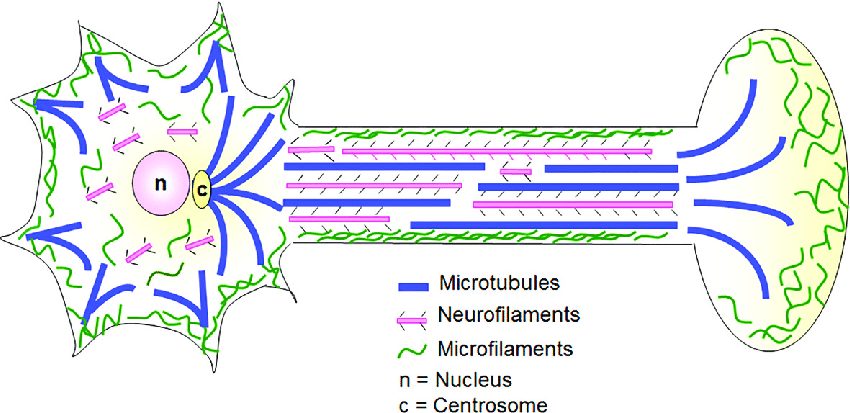
Intermediate Filaments
10 nm in diameter, but these filaments may be composed of different proteins.
referred to as neurofilaments, of which there are several types (e.g., neurofilament light, medium, and heavy chains, internexins, peripherin
proteins are specific for the type of cell where they are expressed
only known function is to maintain structure
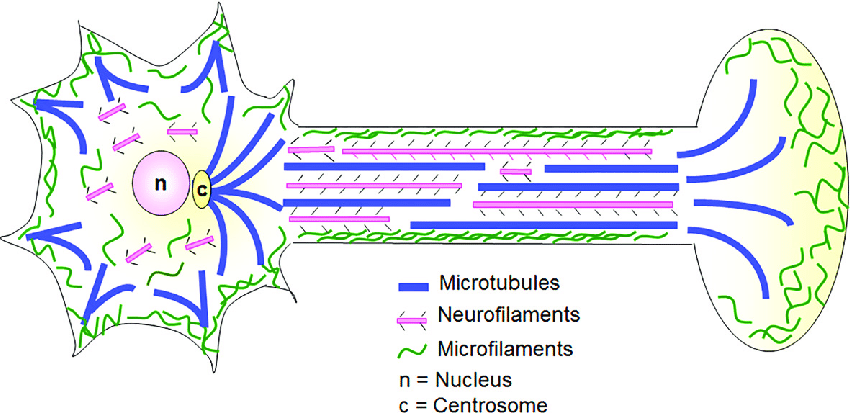
Microtubules
largest cytoskeletal element, having a diameter of about 25 nm
spiral-shaped polymers of the dimeric protein, tubulin
are found in the shafts of axons and dendrites, where they function both in maintaining structure and in the transport of cellular components
second function, it is important to note that microtubules are directional. They have a plus (+) end, where tubulin monomers are preferentially added during polymerization, and a minus (−) end, where tubulin monomers are preferentially removed during depolymerization.
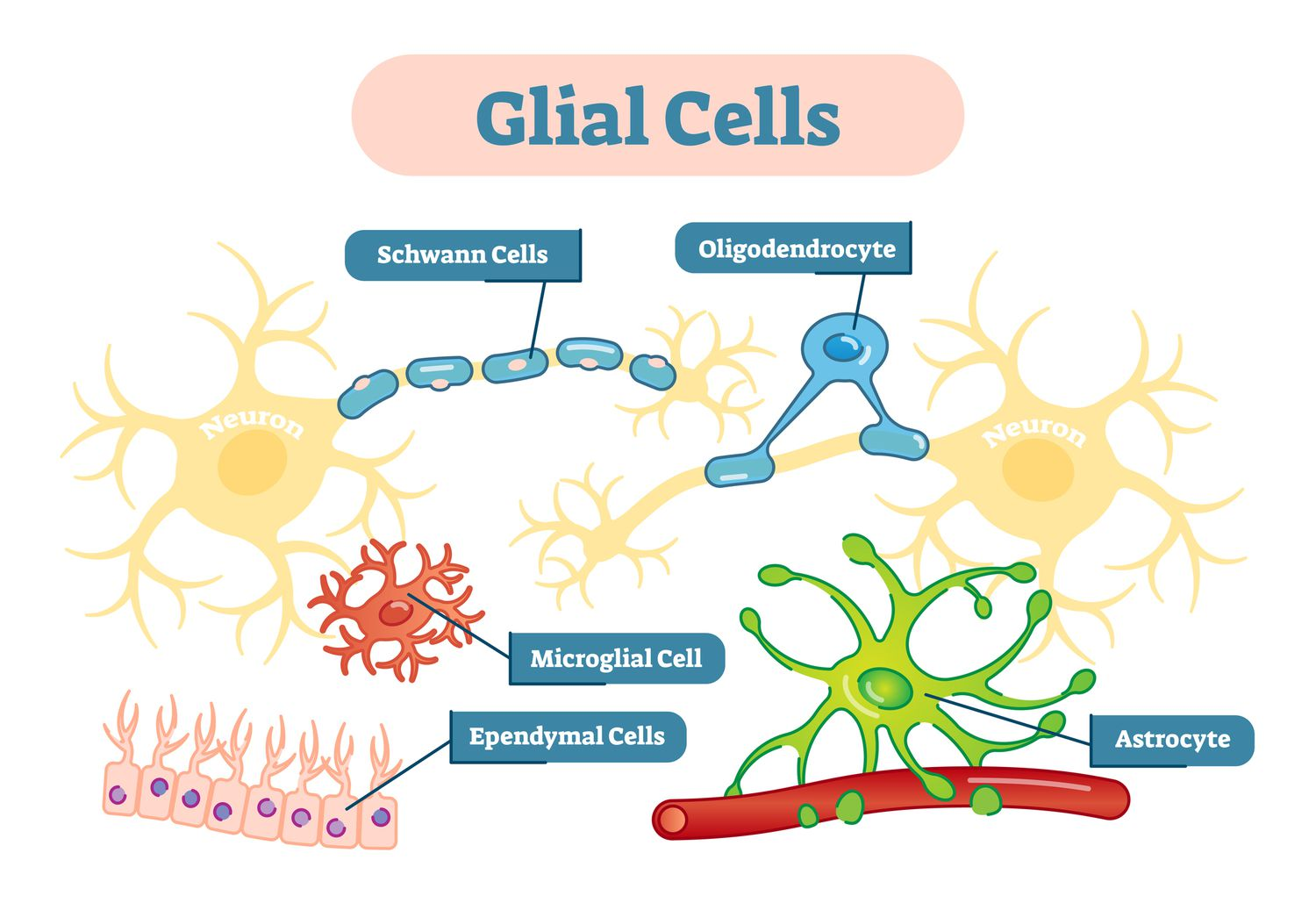
Glia
provide vital support, insulation, nourishment, and defense for neurons, ensuring the overall health and function of the nervous system. Their key roles include insulating nerve fibers with myelin, controlling ion and water balance, clearing debris, producing cerebrospinal fluid, and providing an immune response against pathogens
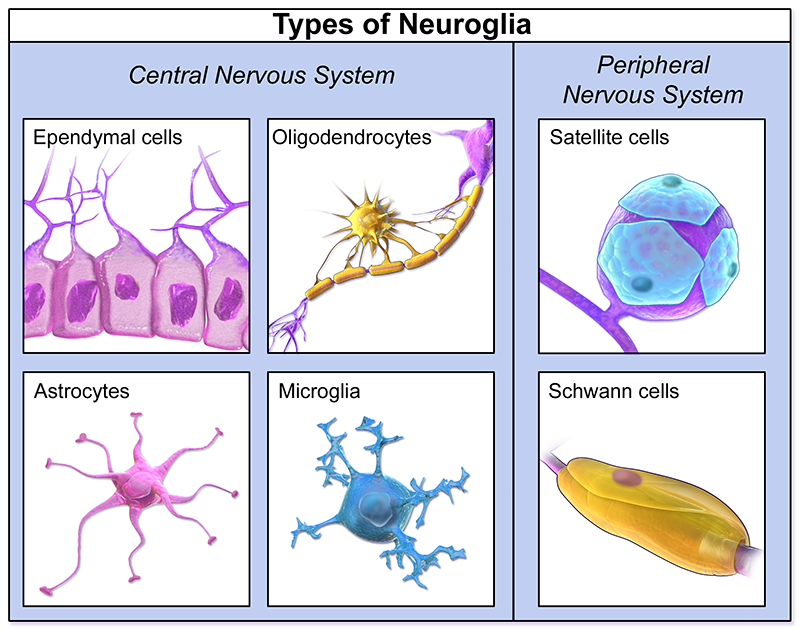
Glia of the CNS
Astrocytes
oligodendrocytes
microglia
ependymal
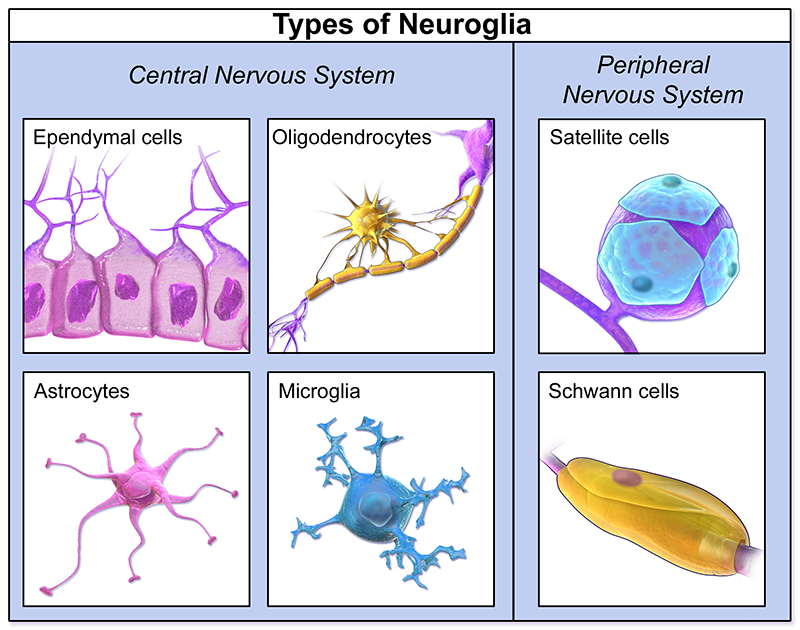
Glia of the PNS
Satellite cells
Schwann cells
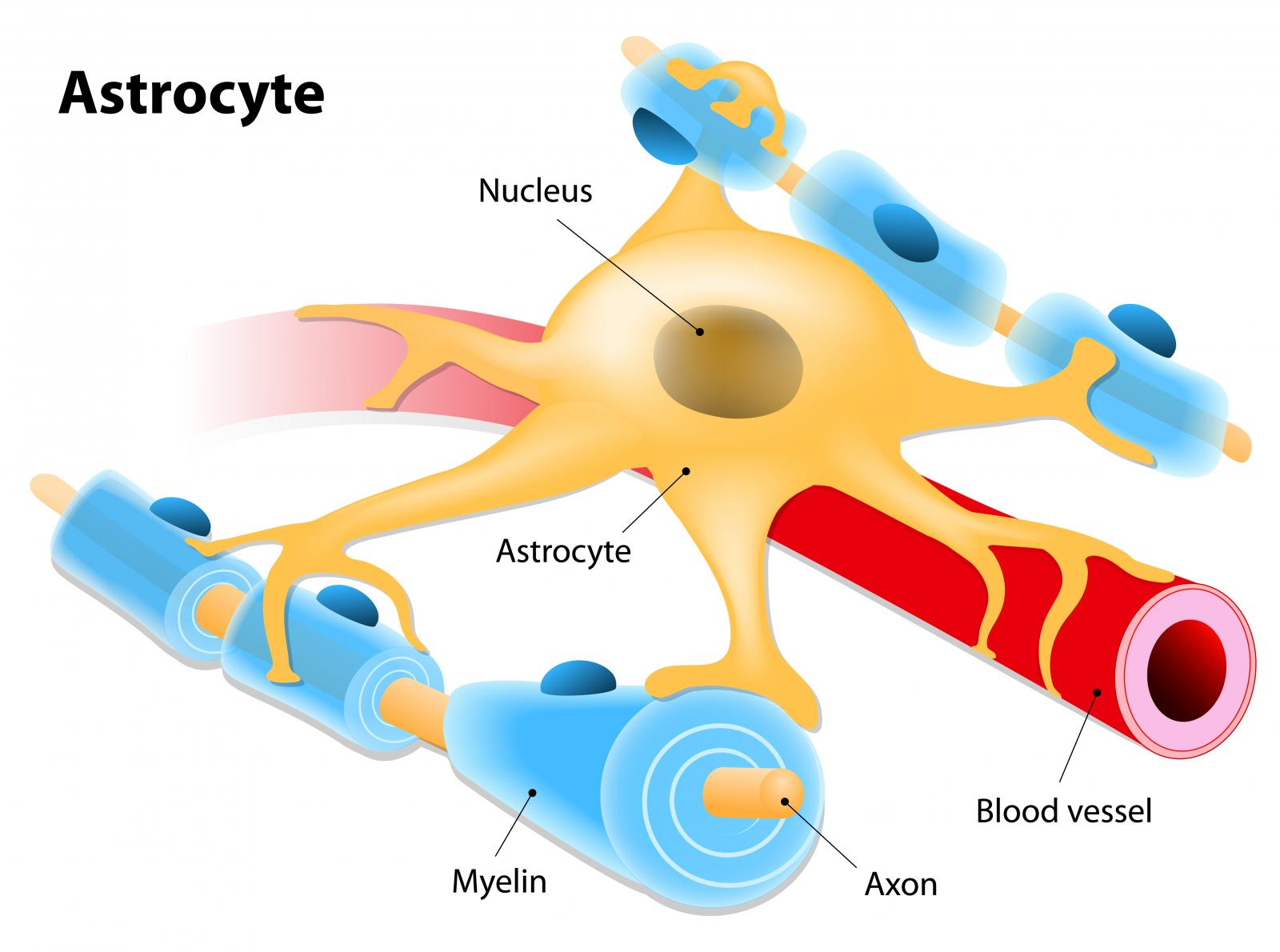
astrocytes
Glia cell of the CNS
star-shaped cells that have several processes that extend from the cell bodies
found in gray matter and white matter
forms the blood-brain barrier to separate brain tissues from blood vessels
Maintains chemical concentrations; links neurons and blood vessels to help
with nutrient transfer and remove wastes
• Aids in the repair of damaged areas of the brain; glial scar formation
guides neurons during embryonic development
Cellular communication
• Neuronal survival
• Nutrient supply
• The formation of barriers
• Development of the brain
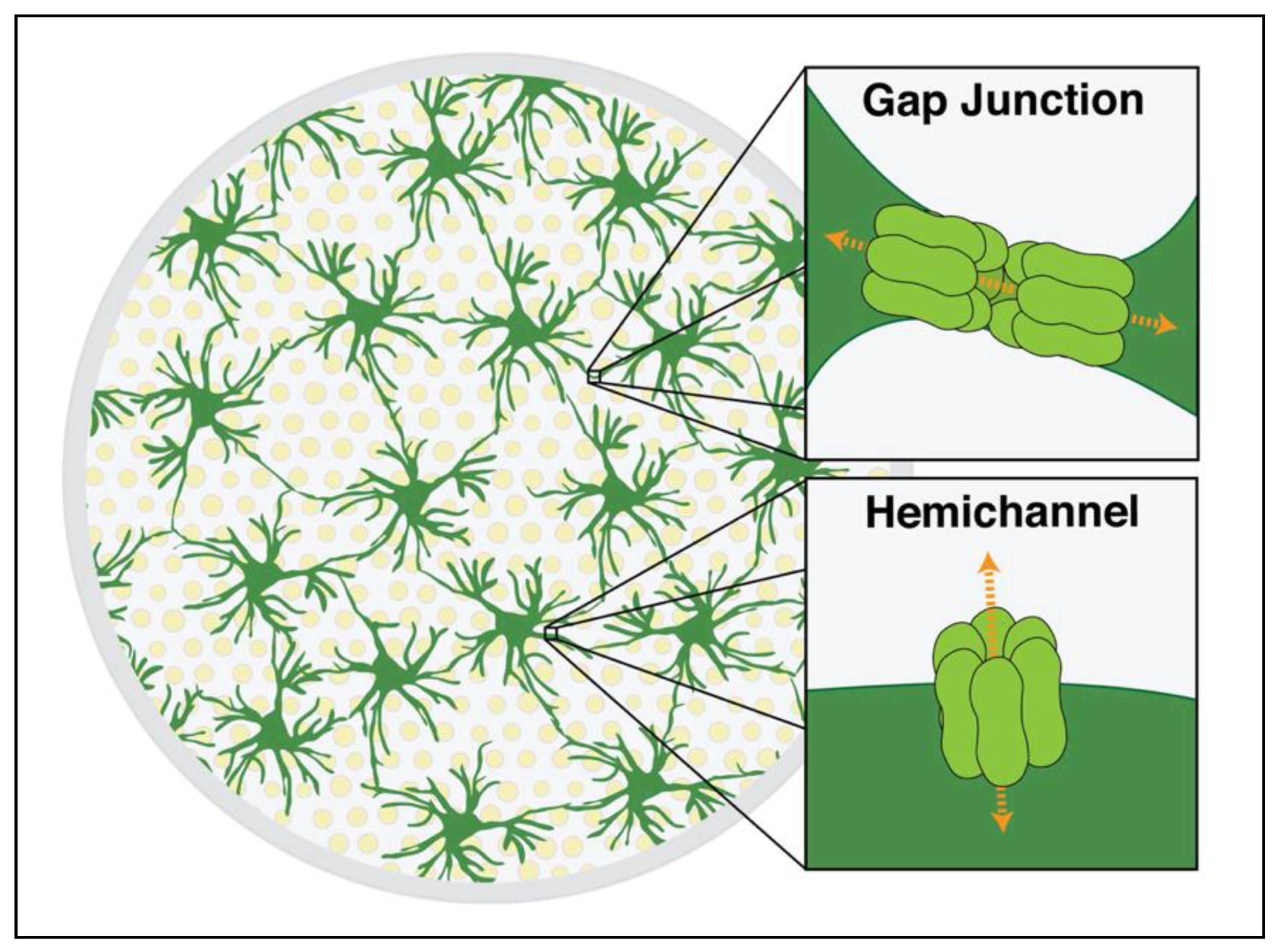
How do Astrocytes communicate?
Through Gap Junctions that facilitate rapid signaling between astrocytes
Composed of channel proteins called connexins
Hemichannels function to secrete molecules into the environment
(e.g. ATP, glutamate)
Gap Junctions
What Astrocytes are connected to each other by
protein-based channels that adhere adjacent astrocytes to each other and produce small pores where the cytoplasm and small molecules can easily pass from one astrocyte to another
ions can easily pass through gap junctions, which allows signals to move rapidly across whole fields of astrocytes
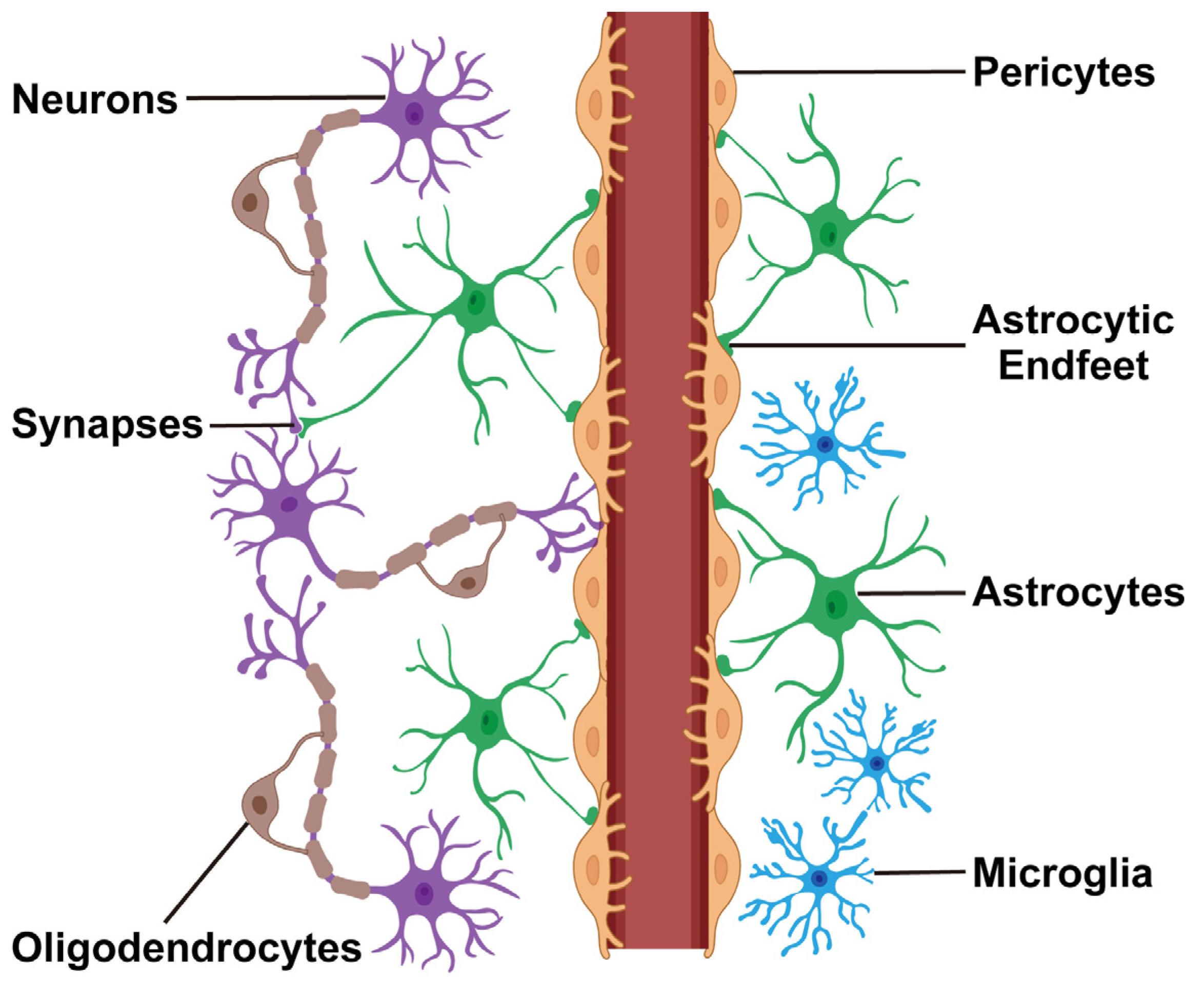
End feet
How Astrocytes can also deliver nutrients to neurons
specialized structures that form at the ends of the astrocytic cellular extensions
can connect to blood vessels and to neuron cell bodies
can shuttle nutrients from blood by absorbing these substances through end feet on the blood vessels and then transferring these nutrients to neurons through the astrocyte end feet on the neurons
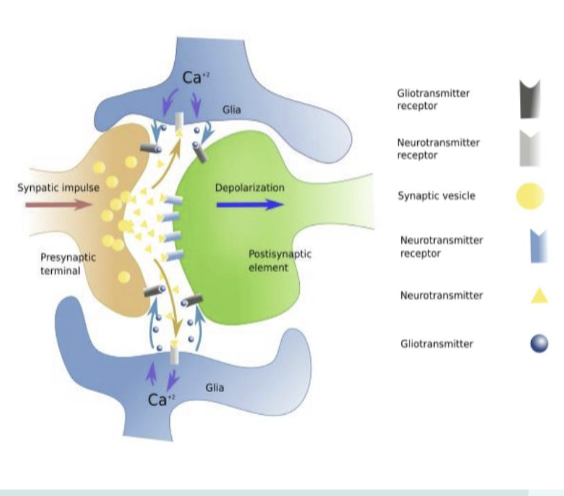
How do Astrocytes regulate transmission?
Tripartite Synapse
a synapse where astrocyte processes surround pre- and
postsynaptic neurons, actively sensing and
influencing communication
Gliotransmission
he process by which astrocytes release signaling molecules (ATP,
glutamate, D-serine) that modulate neuronal activity.
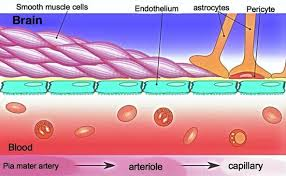
blood–brain barrier
keeps blood contained within vessels to both regulate the transfer of blood nutrients and to keep white blood cells that mediate immunity separated from brain tissue, which they may react against
The first layer consists of the endothelial cells that make up the blood vessel wall. connected by tight junctions, making the endothelial cells resistant to diffusion of blood components
basement membrane that is secreted by the endothelial cells. This is composed mainly of interconnected extracellular matrix proteins like laminin and fibronectin
Finally, blood vessels in the CNS are lined by astrocyte end feet
Glia limitans
is the superficial layer of the cortex
composed of astrocyte endfeet.
Diseases of the Astrocyte
Astrocytoma- a tumor originating from an astrocyte
Glioblastoma multiforme is the most aggressive form, grade IV
glioblastoma
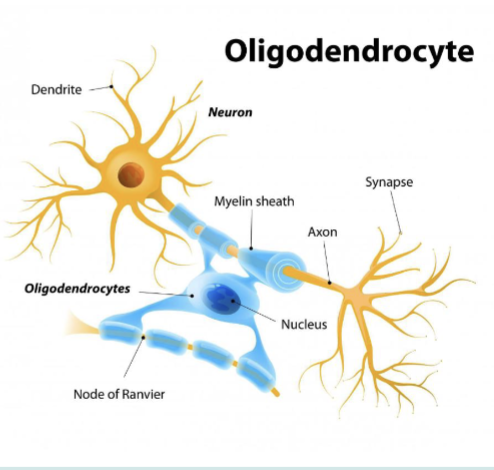
Oligodendrocytes
Which are the myelinating cells for the CNS
wrap axons creating the myelin sheath
Supports CNS and extends processes that form myelin sheath around axons, which increases the speed of nerve impulses.
•
Propagating neural
impulsesIncrease speed of action
potentialsCan interact with multiple
neurons
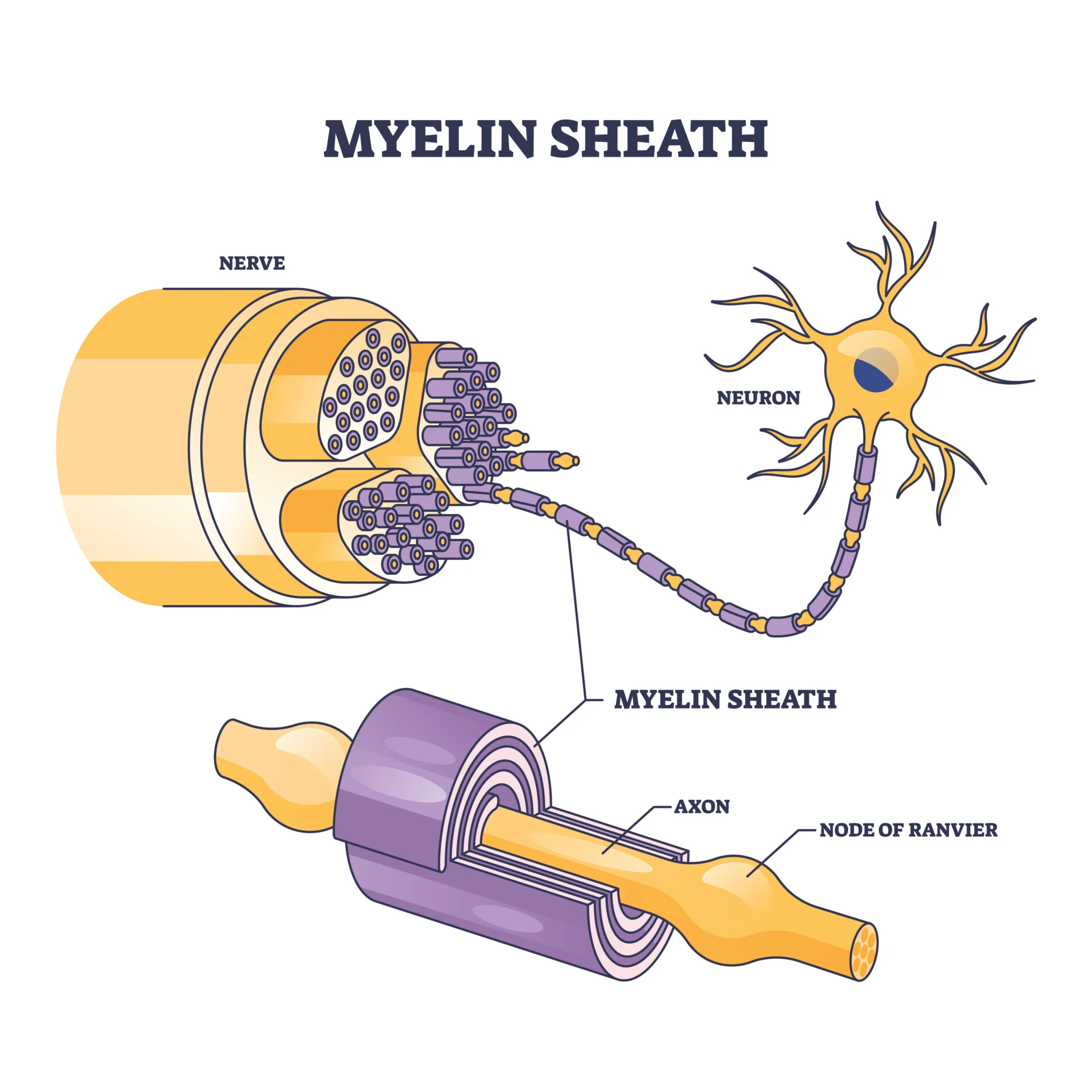
Myelin Sheath
formed from cellular extensions from myelinating cells that wrap around segments of axons to provide a layer of insulating material
Myelin speeds up action potential propagation, and the thicker the myelin sheath, the faster the action potential is propagated. In general, thicker axons are more heavily myelinated
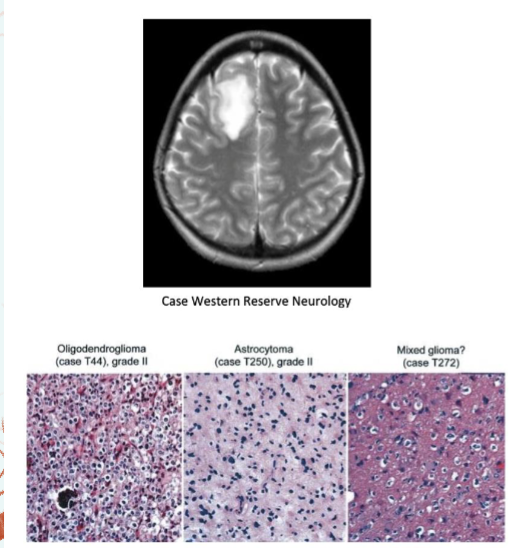
Diseases of the oligodendrocytes
Oligodendrogliomas are tumors that arise from oligodendrocytes
are tumors that arise from oligodendrocytes
Multiple Sclerosis - degeneration of the myelin sheath
caused by the immune system targeting myelin protein, women diagnosed more, motor/vision impairment,
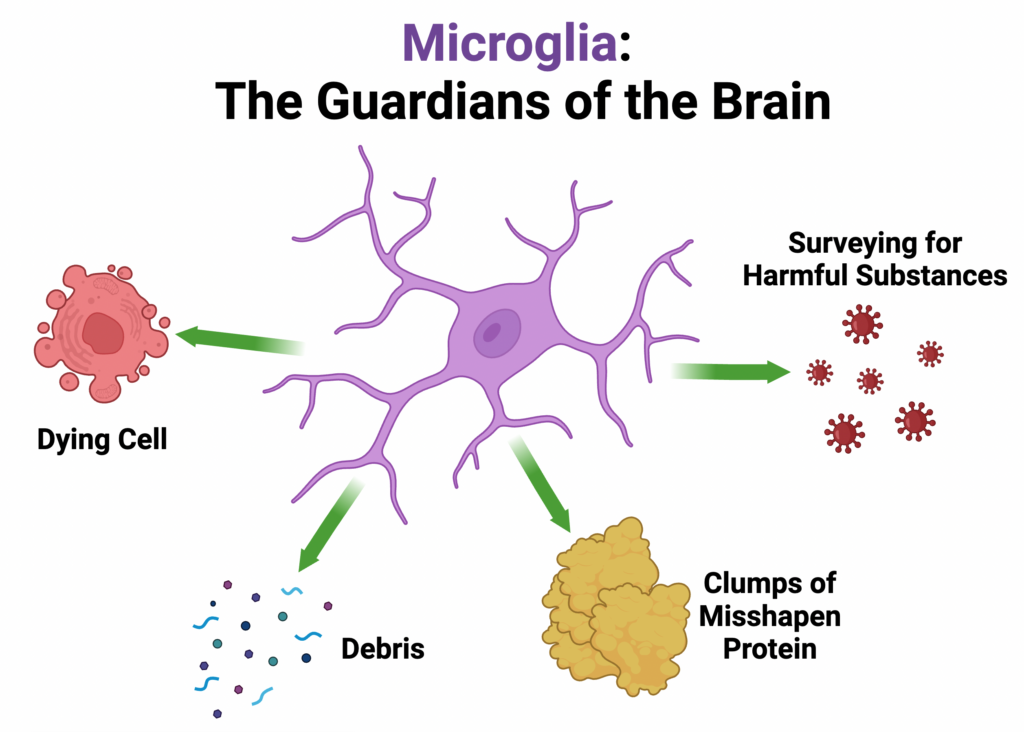
Microglia
Small cells are the resident immune cells for the CNS
do not originate from the common neural stem cell
Closely related to macrophages that are part of the innate immune system that operates in the periphery
cells act as macrophages to engulf necrotic tissue and pathogens;
proliferate during infection.
• Considered to be the immune system of CNS; clean the neural environment.
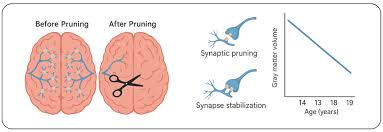
Synaptic Pruning
facilitated by Microglia
a natural process that occurs during brain development, where unnecessary or weak connections between neurons are eliminated
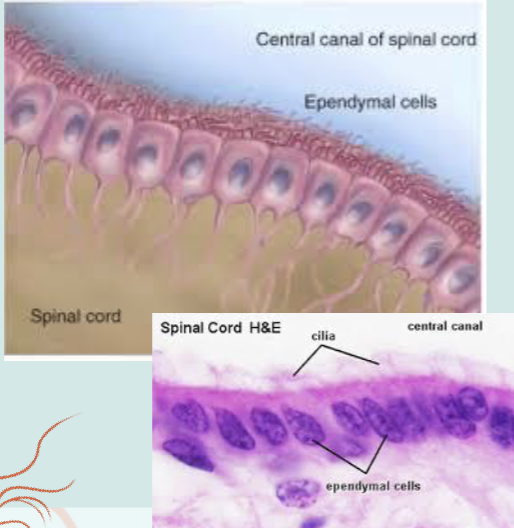
Ependymal Cells
Specialized glial cells that form the lining of the brain’s
ventricles and the central canal of the spinal cord
Play crucial roles in:
- propelling the circulation of
cerebral spinal fluid (CSF)
- regulating the migration of
neurblasts
Types of Ependymal Cells
E1 Cells
E2 Cells
E3 Cells
Tanycytes
Glia cells of the PNS
Satellite cells
Schwann cells
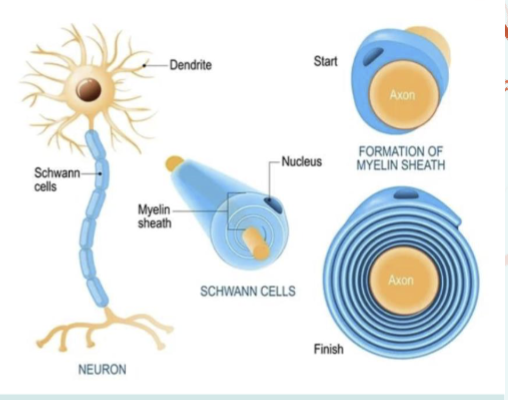
Schwann Cells
myelinating cells for the PNS
extend cellular processes to wrap layers around axon segments, the way in which they myelinate axons differs from the way oligodendrocytes wrap myelin in the CNS. Each Schwann cell wraps myelin around one segment of an axon
Myelination helps insulation, increase speed of action potentials, and can help with regeneration of a damaged axon
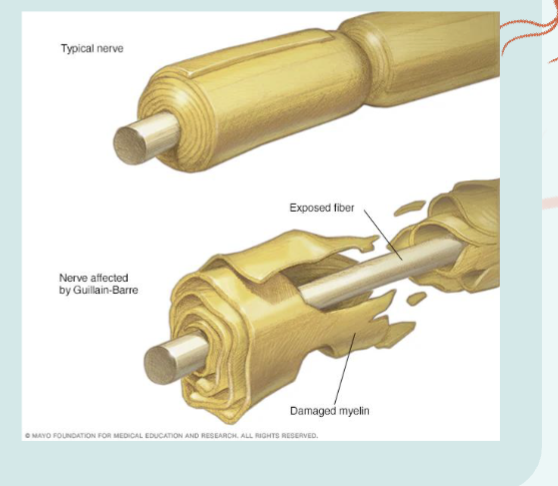
Guillain- Barre Syndrome
ccurs after a viral infection and occurs in one episode, from which the patient either recovers or does not. There is no gender preference in the incidence of Guillain-Barré syndrome, which is treated with plasmapheresis and/or immune suppression therapies including high doses of steroids.
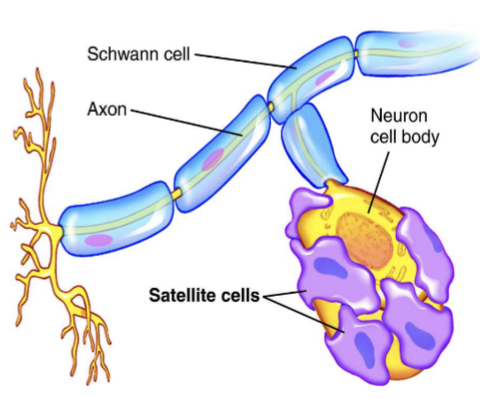
Satellite Cells
glial cell of the PNS
usually found in ganglia, groups of neuronal cell bodies
is to protect and regulate the environment around the dorsal root
ganglia (cell bodies) including ion balance and homeostasis
• Research continues into their role in neuron injury and pain modulation
responds to injury, forms gap junction, synthesize glutamate, express NT receptors