Period 4 (1800-1848) Antebellum Period - AP US History
1/117
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
118 Terms
Federalists
Political party that formed in the 1790s led by Alexander Hamilton; Favored a stronger federal government and Hamilton's financial plan.
Democrat-Republicans
Political party formed in the 1790's; Led by Thomas Jefferson; Favored limited government and states rights.
Election of 1800
A.K.A. "Revolution of 1800"; Peaceful transfer of power from the Federalist party to the Democratic-Republican Party.
midnight judges
Federalist judges appointed by John Adams between the time he lost the election of 1800 and the time he left office in March 1801; Significantly included John Marshall
John Marshall
Appointed to the Supreme Court by John Adams in 1801; Served as a chief justice until 1835; Legal decisions gave the Supreme Court more power, strengthened the federal government, and protected private property.
Supreme Court Justices
Nine judges who serve lifetime appointments on the Supreme Court; Nominated by the president; Approved by the Senate.
Marbury v. Madison (1803)
Supreme Court decision that established the principle of judicial review
judicial review
Check-and-balance power of the Supreme Court to judge the constitutionality of laws passed by Congress and actions taken by the executive branch.
Louisiana Territory
Land from the Mississippi River to the Rocky Mountains
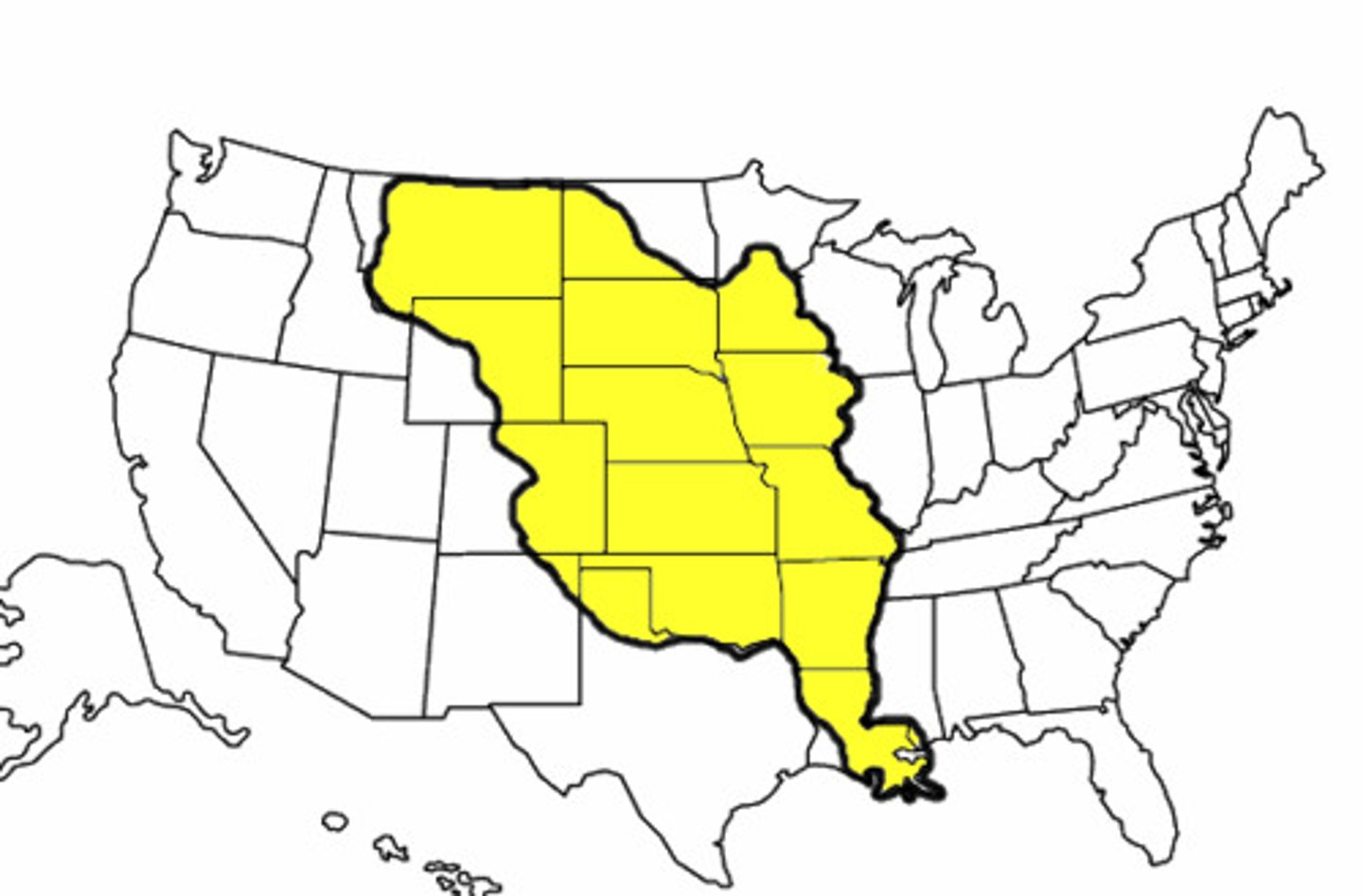
Louisiana Purchase (1803)
Territory in western United States purchased from France
Mississippi River
The most significant transportation route within the United States; Ends at the port of New Orleans.
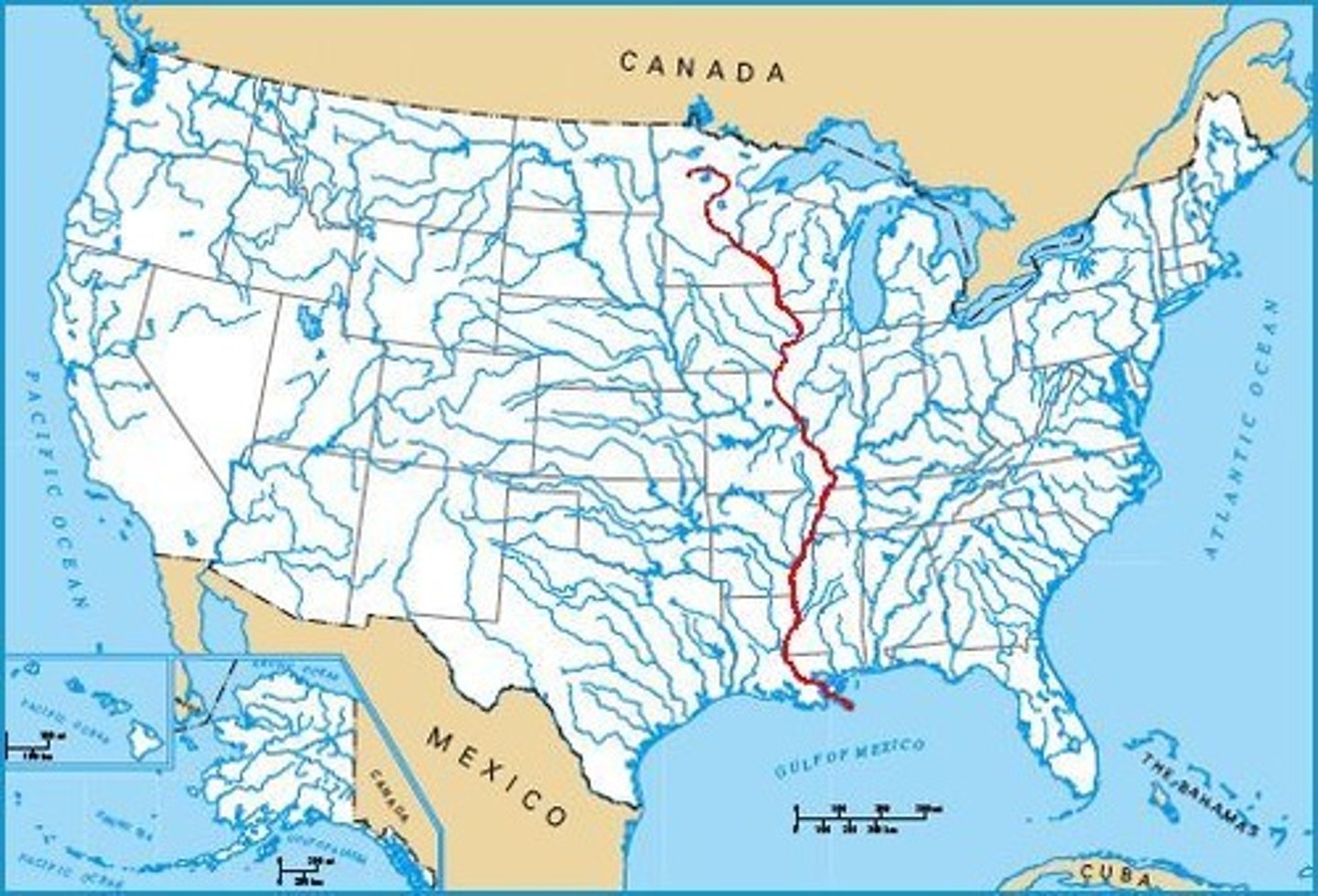
New Orleans
A strategic outpost on the mouth of the Mississippi River
Lewis and Clark
Two explorers sent by the president to explore the Louisiana territory
Corps of Discovery
The expedition led by Lewis and Clark in 1804-1806 that explored the Louisiana territory and the Oregon lands extending to the West Coast.
Impressment of sailors
British practice of taking American sailors and forcing them into military service

embargo
A ban on trade
Embargo Act (1807)
Jefferson issued a government-order ban on international trade in order to pressure Britain and France to respect neutral trading rights

declaration of war
The power of Congress to vote to go to war with another country; First declared in 1812 against Great Britain.
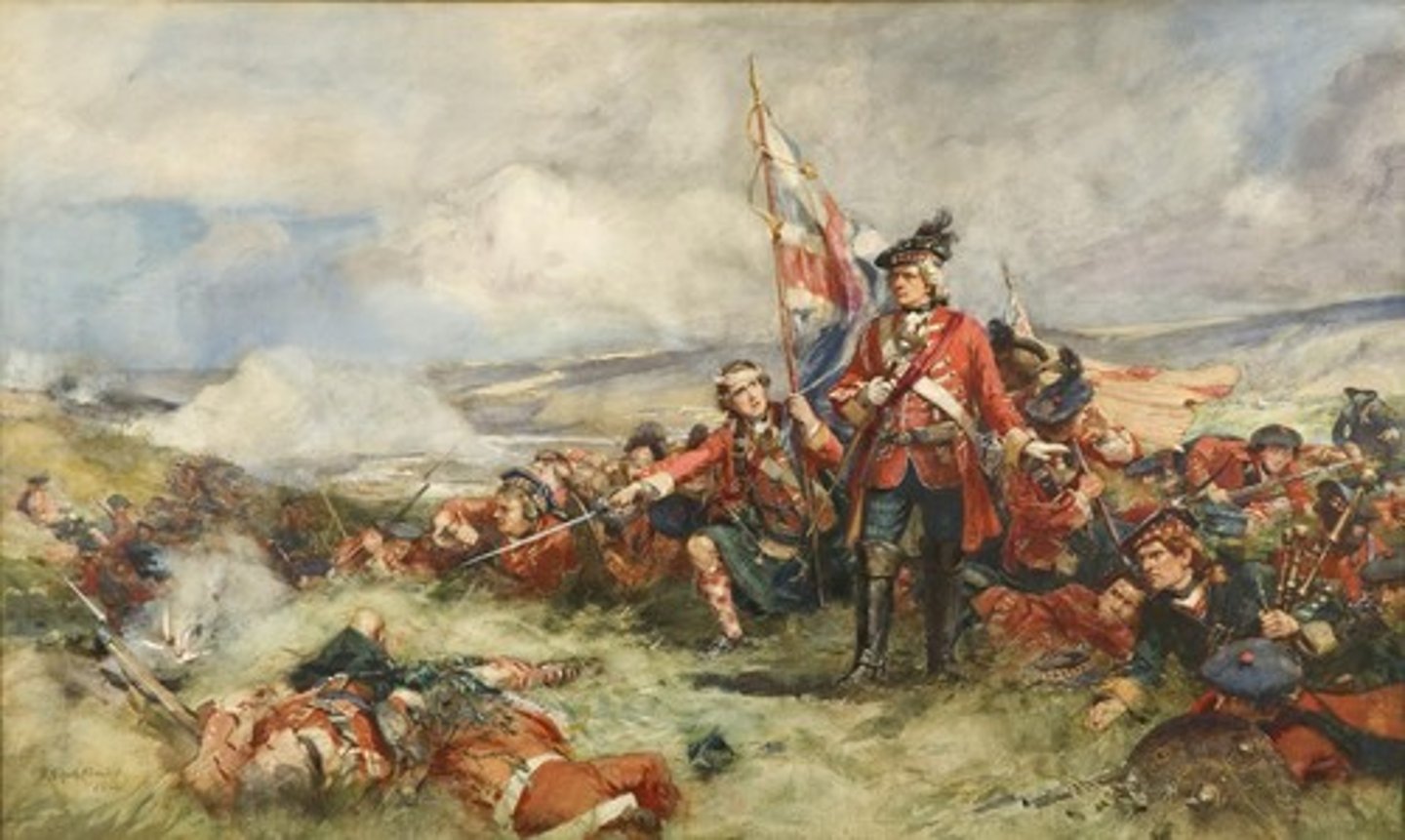
War of 1812
(1812-1815) Between the U.S. and Great Britain caused primarily by the British violation of American neutral rights on the high seas; Ended with an agreement of "status quo ante"; Facilitated American Nationalism; Sometimes called "Second American Revolution"

The Star-Spangled Banner
National anthem of the US; Written during the War of 1812.

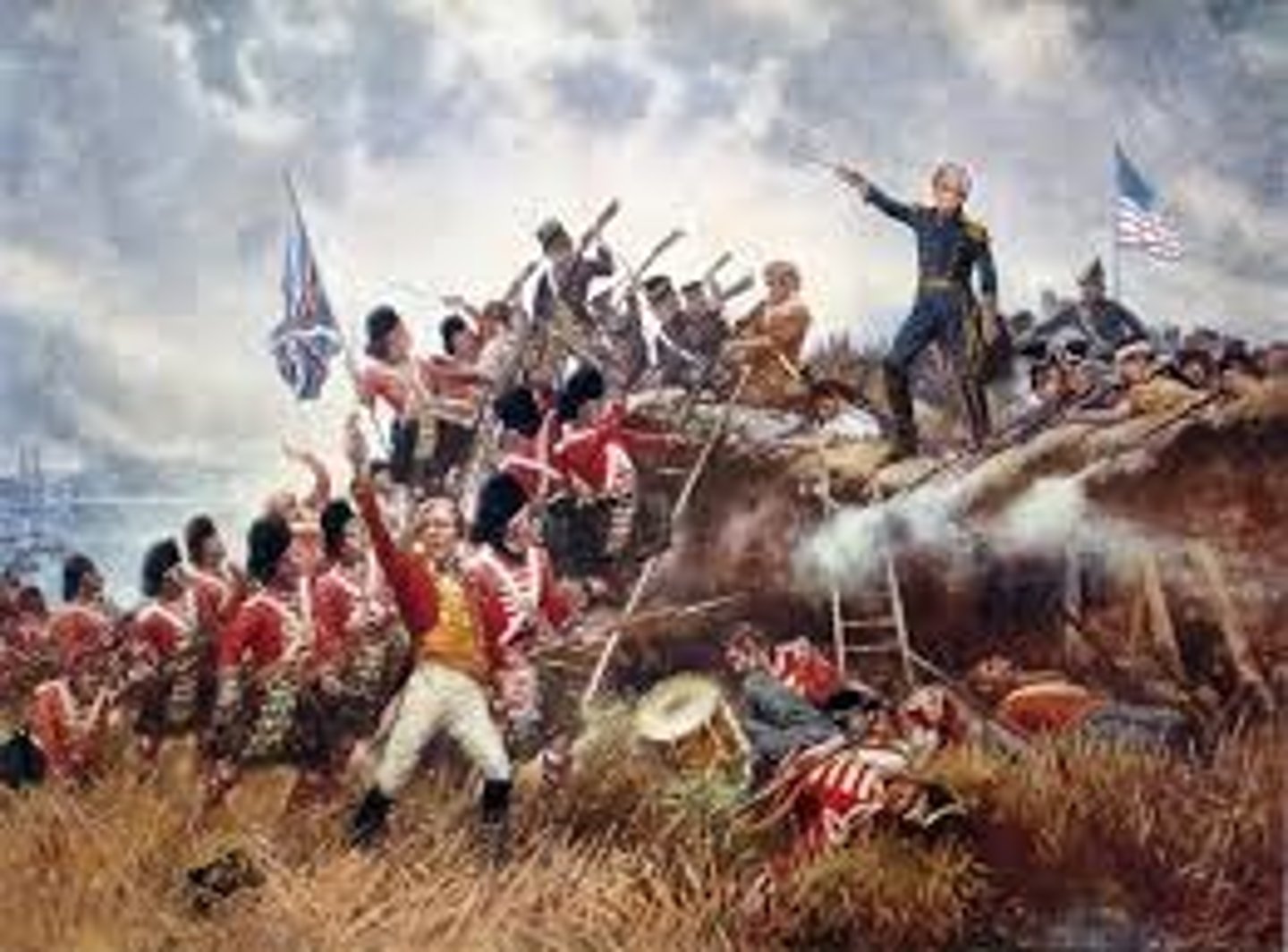
Battle of New Orleans (1815)
Last major battle of the War of 1812; Made General Andrew Jackson a national hero

Andrew Jackson
General who led American forces in Battle of New Orleans; Later Seventh President of the United States

Treaty of Ghent (1814)
Ended the War of 1812 and restored the status quo.
Hartford Convention (1814)
Meeting of Federalists during the War of 1812 in which anti-war Federalist threatened to secede from the Union; After Jackson's victory at New Orleans, Federalists were seen as treasonous.
nationalism
Identity with and devotion to the nation, inspiring unity
Henry Clay
Leader of the Whig Party who proposed an "American System" to make the United States economically self-sufficient; Worked to keep the Union together through political compromise.

American System
Henry Clay's proposal to make the U.S. economically self-sufficient: (1) protective tariffs (2) internal improvements at federal expense (3) creation of a second Bank of the United States
Tariff of 1816
first protective tariff in US history designed primarily to help America's textile industry
Second Bank of the United States
Privately owned bank that operated as both a commercial and fiscal agent for the US government; Established in 1816 under a charter that was supposed to last 20 years
Era of Good Feelings
The decline of the Federalist Party and the end of the war of 1812 gave rise to a time of relative political unity.
"peculiar institution"
Slavery, unique to the south
Cotton Belt
Seep south area that stretched from South Carolina to Georgia to the new states in the southwest frontier; Had the highest concentration of slaves
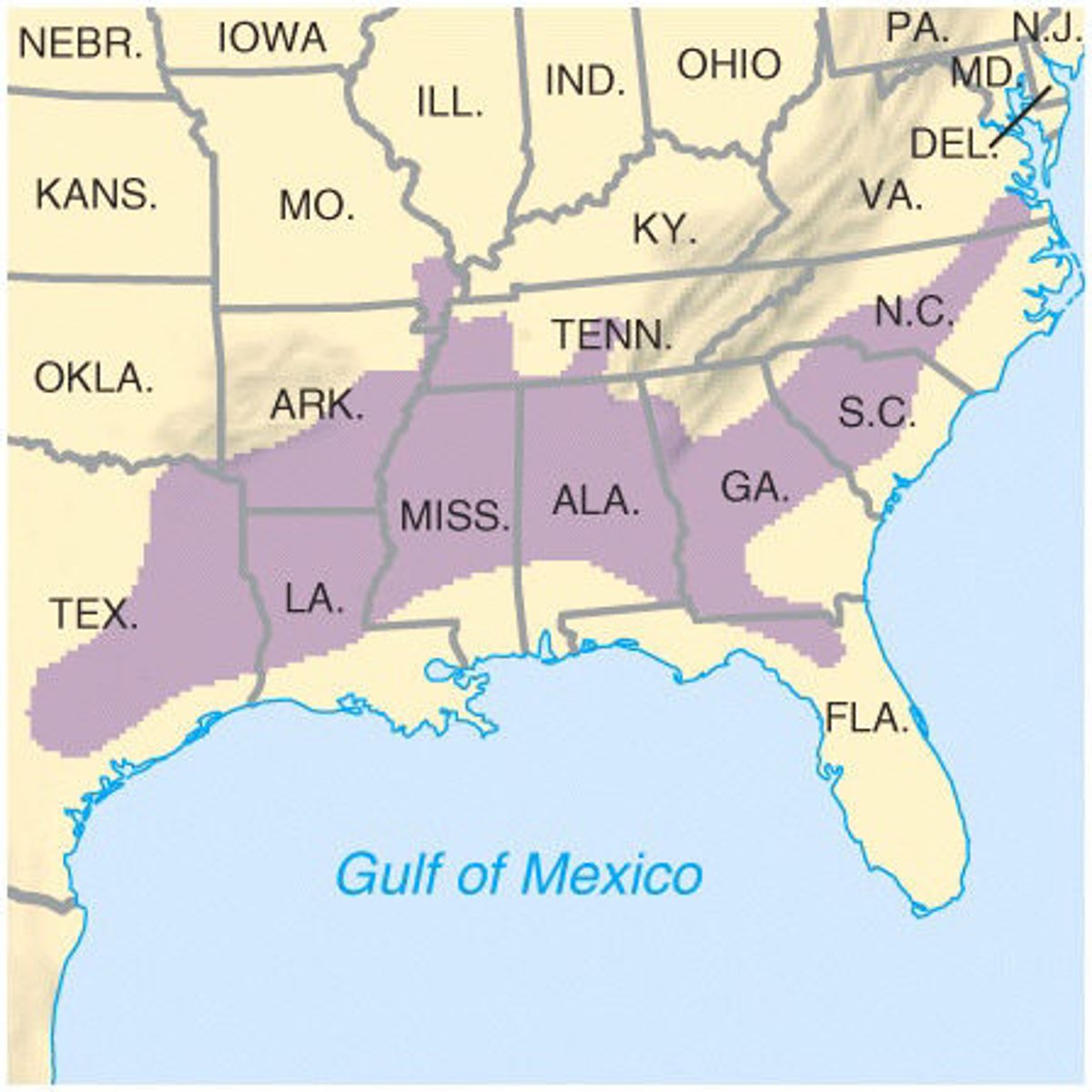
Missouri Compromise (1820)
Law proposed by Henry Clay admitting Missouri to the U.S. as a slave state and Maine as a free state
McCulloch v. Maryland (1819)
Supreme Court decision that upheld the constitutionality of the B.U.S.; Maryland did not have the right to tax the federal bank and John Marshall wrote, "The power to tax is the power to destroy."
loose construction
Of the Constitution Marshall said "intended to endure for ages to come and, consequently, to be adapted to the crises of human affairs."
Gibbons v. Ogden (1824)
Decided that Congress alone has the right to control interstate commerce
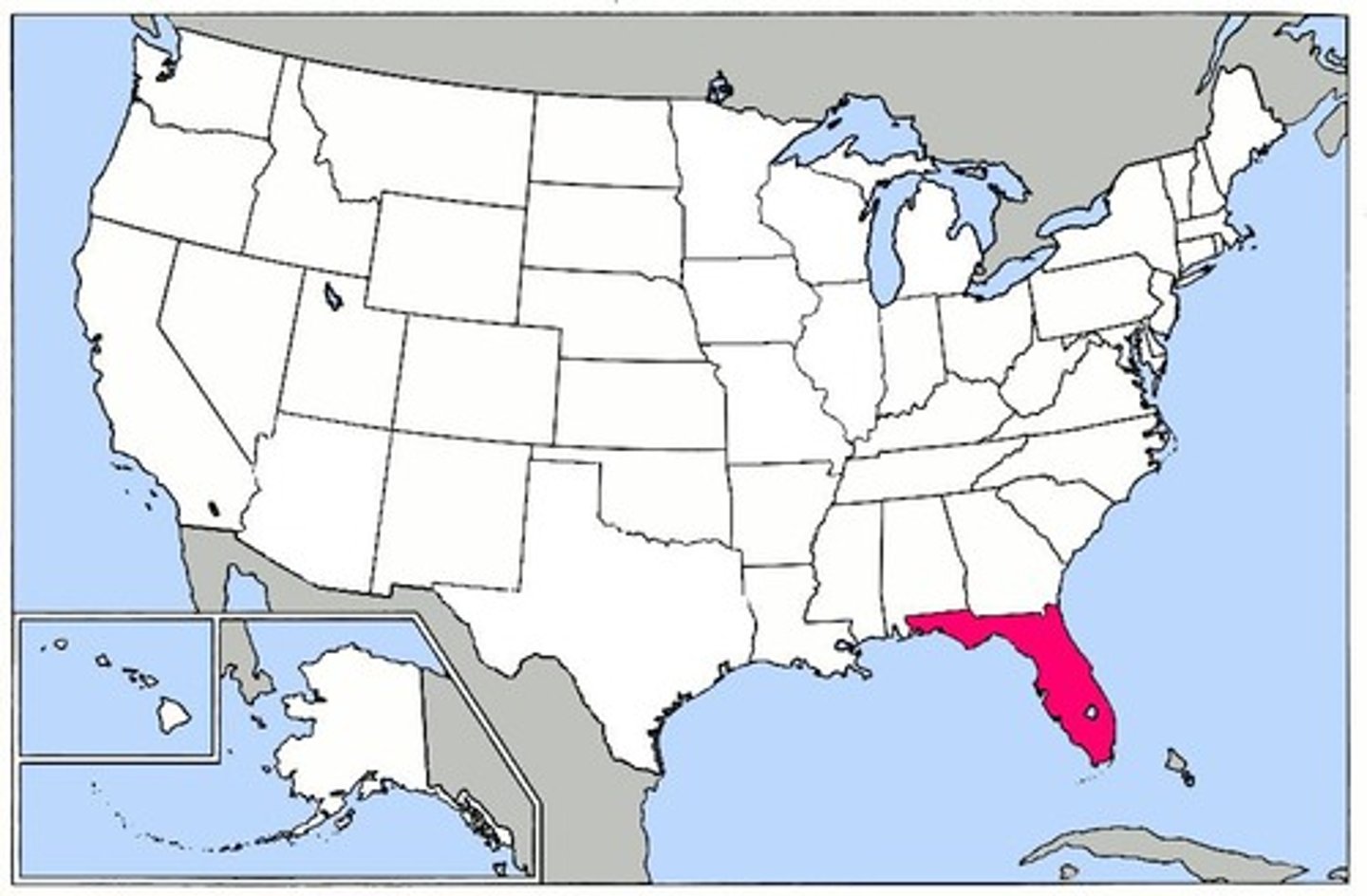
Florida
Sold to US at Adams-Onis Treaty (1819)
Monroe Doctrine
Unilateral declaration that the Americas would be closed to further European colonization stated the U.S. would not allow European interference in the affairs of the Western Hemisphere
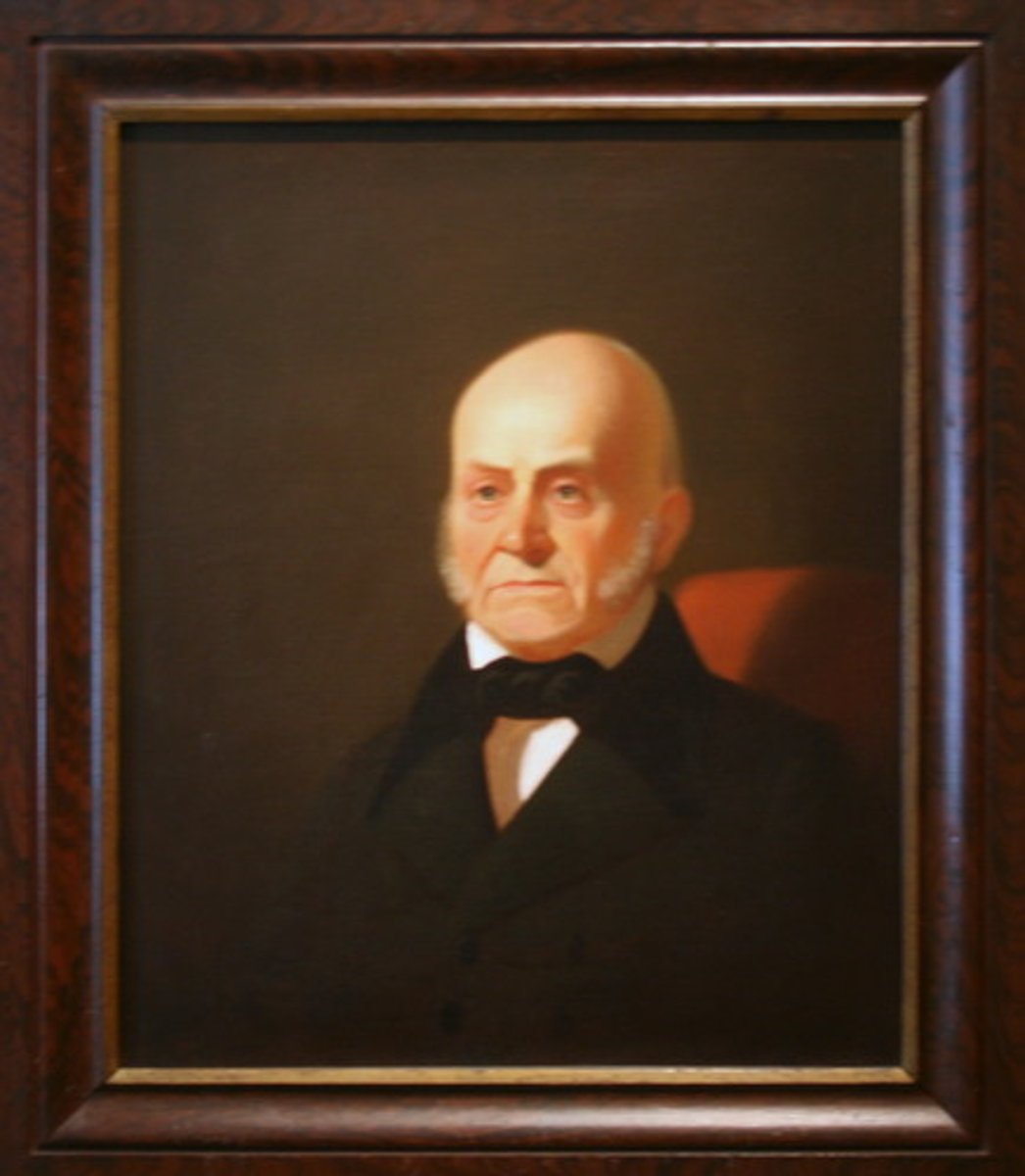
John Quincy Adams
As Secretary of State he was author of Adams-Onis Treaty (Florida Purchase) and Monroe Doctrine; Later 6th President of the United States and antislavery advocate.

mass democracy
Expansion of voting rights; Universal white male suffrage
property qualifications for voting rights
States eliminated these in favor of a system of voting by all white men
spoils system
A system of public employment based on rewarding party loyalists and friends; A symbol of expanding democracy where common men can hold government jobs.
tariff
tax on imports
Tariff of Abominations (1828)
High rates exposed North-South tensions
Southern economy
Consumers of manufactured goods with little manufacturing industry; Hostile to tariff
Northern economy
Based on manufacturing; Favor strong national government and protective tariff
South Carolina Exposition and Protest (1828)
Written by Vice President Calhoun of South Carolina to protest the the "Tariff of Abominations", which favored Northern industry; Proposed states could nullify Federal laws like the tariff
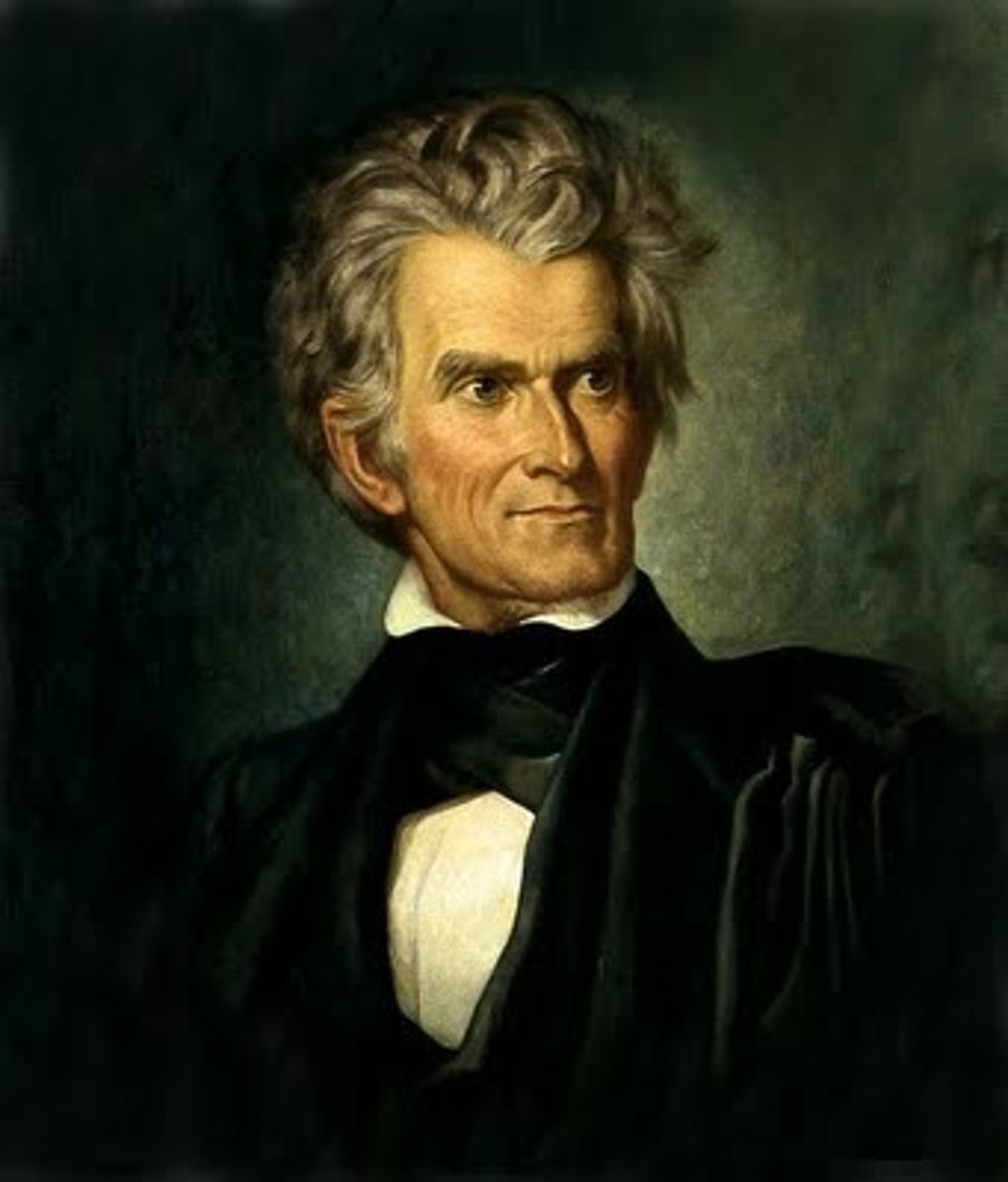
John C. Calhoun
South Carolina political leader who defended slavery as a positive good and advocated the doctrine of nullification, a policy in which state could nullify federal law.

Nullification Crisis (1832)
After South Carolina declared the federal tariff null and void, President Jackson obtained a Force Bill to use military actions against South Carolina - ended with a compromise to lower tariffs over an extended time
Indian Removal Act (1830)
Law that transplanted all Indian tribes to the west of the Mississippi River
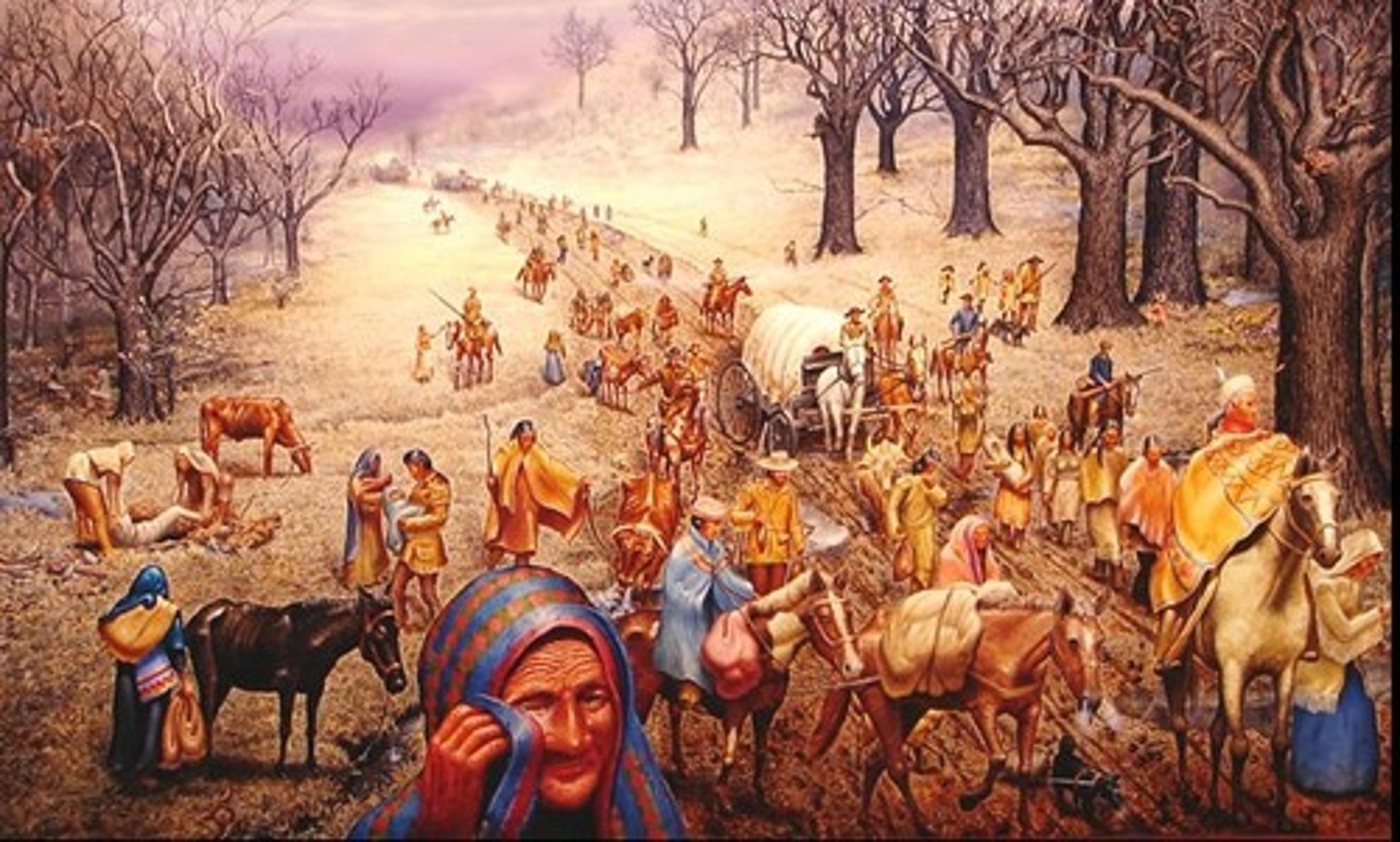
Trail of Tears
Forced migration of Native American nations from the Southeastern United States to Indian Reservations west of the Mississippi River; Following the passage of the Indian Removal Act of 1830

second party system
The new political arrangement caused by Andrew Jackson; Disagreed about the role and powers of the federal government and issues such as the national bank, tariffs, and federally funded internal improvements.
Bank War (1832)
Battle between President Andrew Jackson and Congressional supporters of the Bank of the United States over the bank's renewal in 1832. Jackson vetoed the Bank Bill, arguing that the bank favored moneyed interests at the expense of western farmers.
Panic of 1837
Economic collapse caused primarily by President Jackson's destruction of the Second Bank of the United States
Texas Revolution (1836)
Texans declare independence from Mexico with help from Americans; Form the independent Republic of Texas
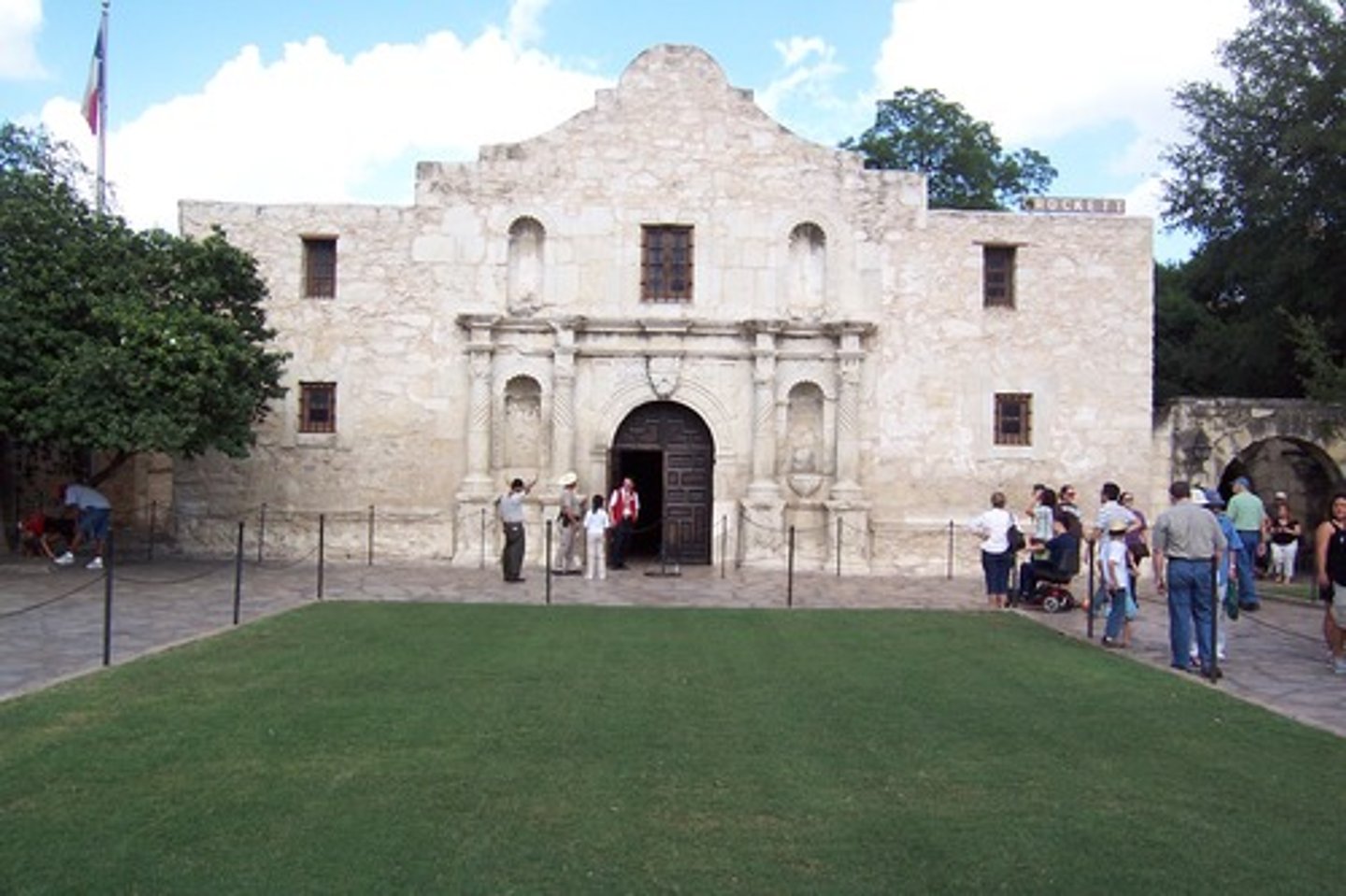
Alamo
A Spanish mission converted into a fort, it was besieged by Mexican troops in 1836. The Texas garrison held out for thirteen days, but in the final battle, all of the Texans were killed by the larger Mexican force.

Democrats
Succeeded the Jeffersonian Democrat-Republicans; Brought Andrew Jackson into office in 1828; Supported Jeffersonian ideas of limited government, drawing its support from the "common man".
Whigs
New party along Federalists vein; Anti-Jackson and dedicated to internal improvements funded by the national government; Led by Henry Clay.
Worcester v. Georgia (1832)
John Marshall ruled that the state of Georgia did not have the power to remove Indians
rugged individualism
Belief that success comes through individual strength of effort and private enterprise
Irish immigrants
Push factor: famine; Pull factor: American cities on the East coast
Tammany Hall
Political machine (corrupt) based in New York that capitalized on Irish immigrants for votes
German immigrants
Push factor: crop failures, autocratic government; Pull factor: democracy, interior midwest farmland
nativist movement
Those who opposed immigration; Fear that an influx of foreigners would undermine American culture, weaken the status of American workers, and destabilize American politics
Know-Nothing Party
A nativist movement formed in 1849 that opposed Irish and German immigration
Industrial Revolution
An event that results in the complete transformation of the economy, environment, and living conditions; Development of manufacturing; Fueled by technological improvements, capital, and immigrant labor.
industrialization
The process of becoming a developed manufacturing economy
mechanization
The application of machinery to manufacturing and other activities. Among the first processes to be mechanized were the production of textiles.
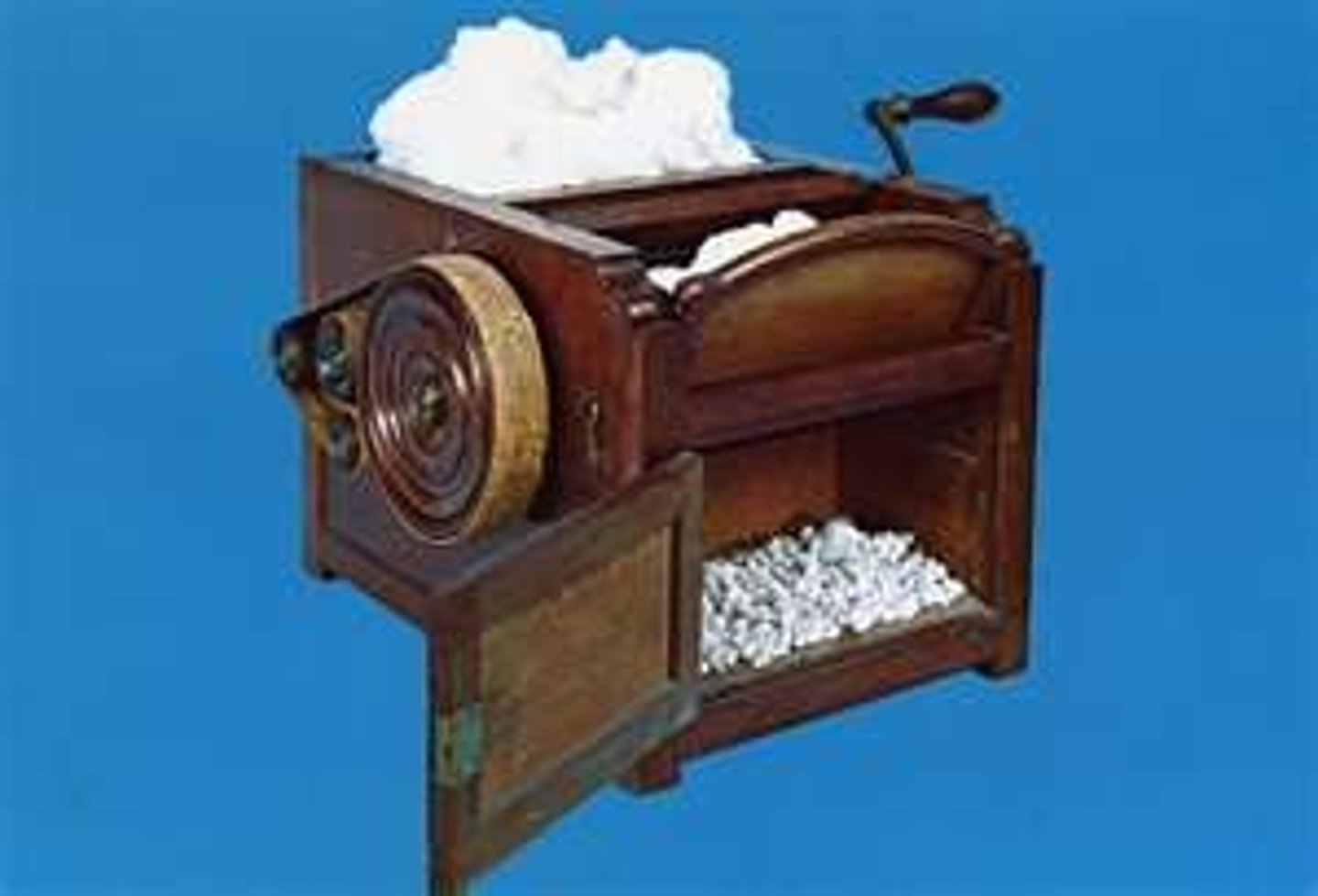
cotton gin
A machine for cleaning the seeds from cotton fibers; Invented by Eli Whitney in 1793; Led to increased reliance on slave labor in the South and a manufacturing resource for the North.

textile
A fabric made by weaving, used in making clothing
Samuel Slater
Known as the "Father of the American Industrial Revolution"; brought British textile technology to the United States
steam engines
A way to more efficiently generate power; Drove early industrialization
interchangeable parts
Identical components that can be used in place of one another in manufacturing; Invented by Eli Whitney and first applied to firearms; Basis of modern, mass-production assembly-line methods of manufacturing.
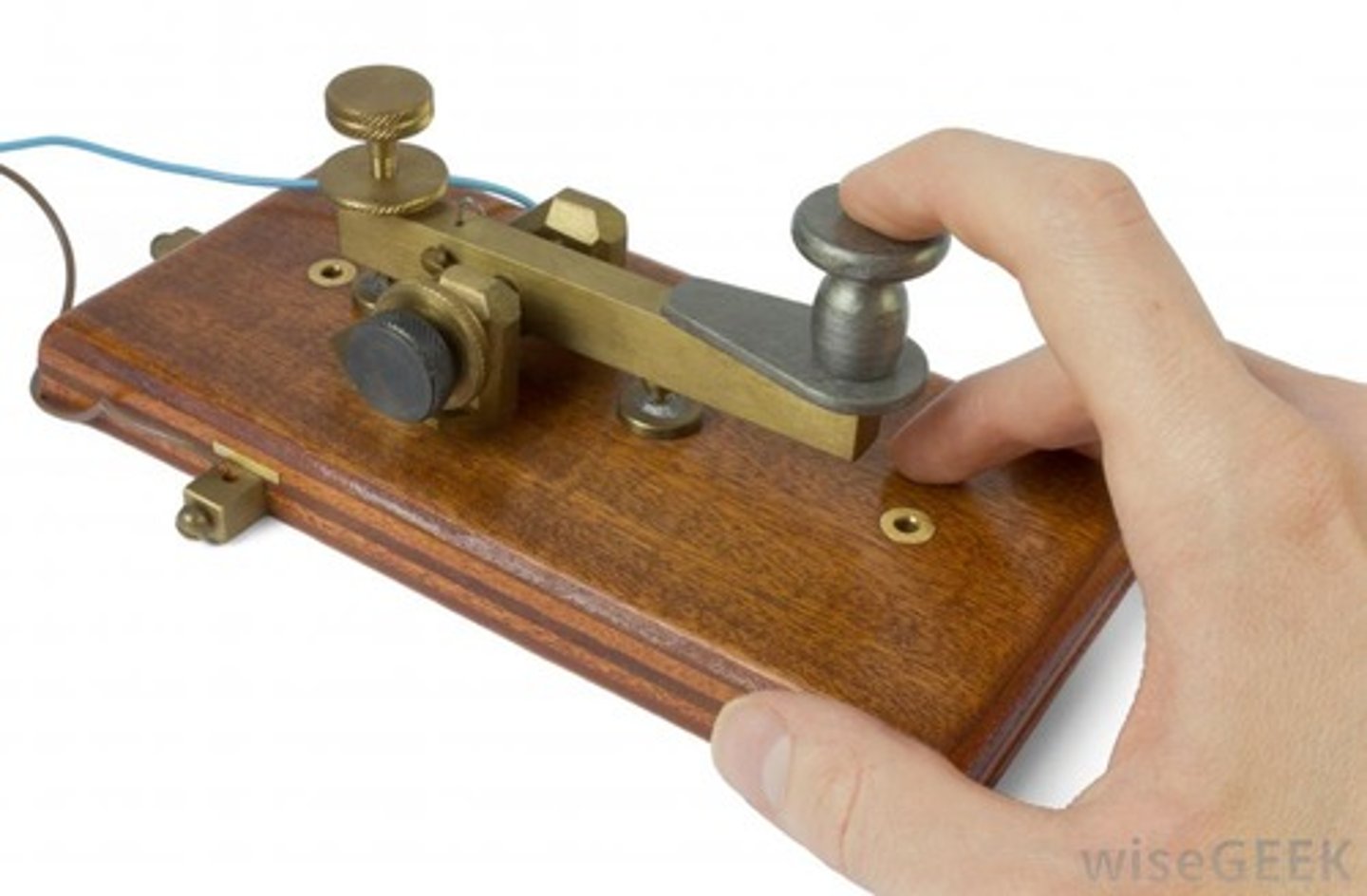
telegraph
Invented by Samuel Morse; Revolutionized communication

factory girls
They labored long hours in difficult conditions, living in socially new conditions away from farms and families; Employed in Lowell and other manufacturing centers.
Lowell system
Method of factory management that evolved in the textile mills of Massachusetts; First example of a planned automated factory
cult of domesticity
Women's role in the home (raising children, taking care of the house); The centrality and increasing importance of women in decisions made at home.

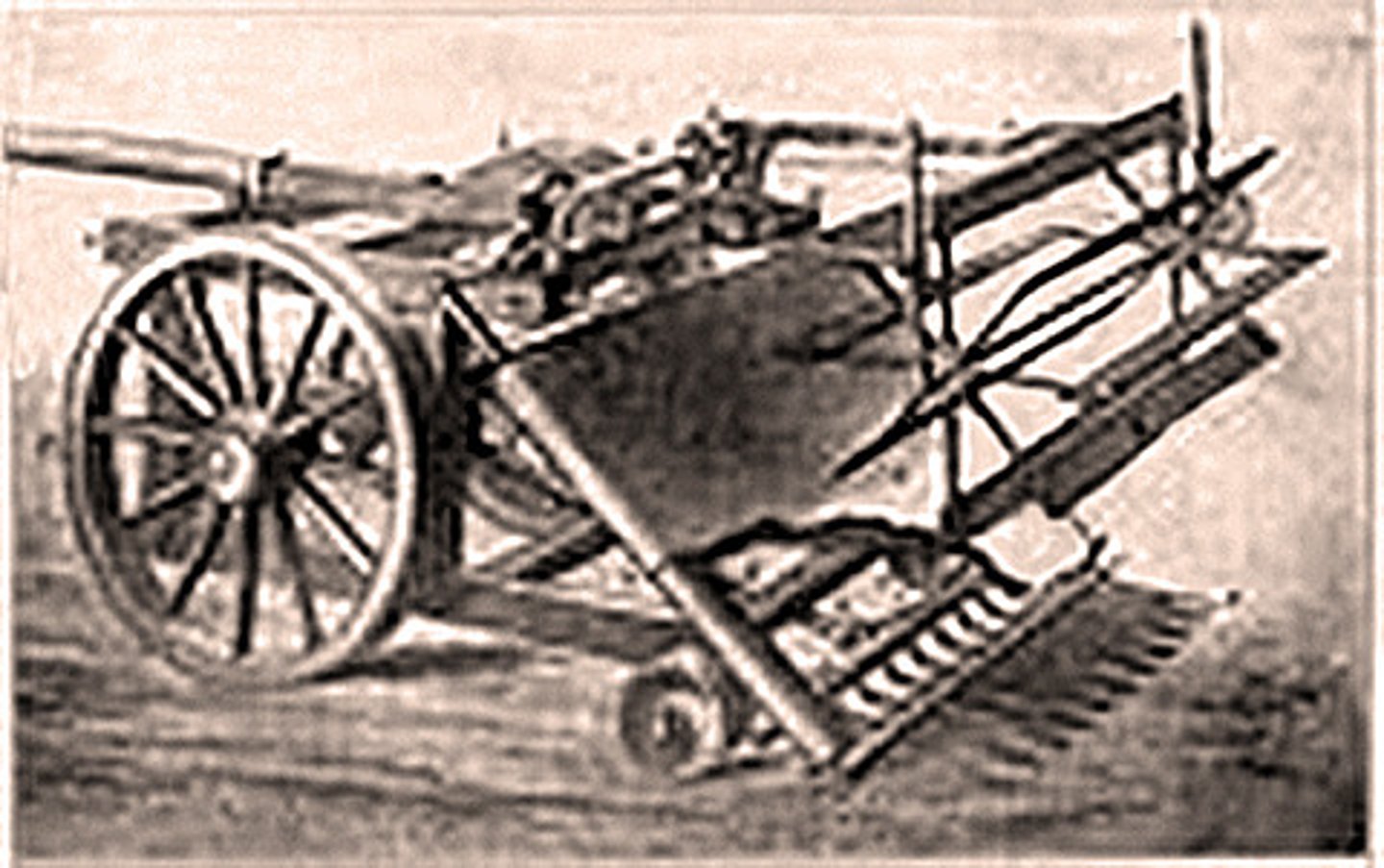
mechanical reaper
Machine invented by Cyrus McCormick that could harvest grain quickly; An agricultural invention that increased the efficiency of production.

internal improvements
Roads, turnpikes, bridges, canals, railroads; Built by states and the federal government.
turnpikes
Toll roads that first began to be constructed in the 1790s; The first infrastructure of the Transportation Revolution; E.g. Lancaster Turnpike, Cumberland Road (National Road).
National Road (1811)
A.K.A. Cumberland Road; First significant road built in the US at the expense of the federal government; stretched from the Potomac River to the Ohio River.
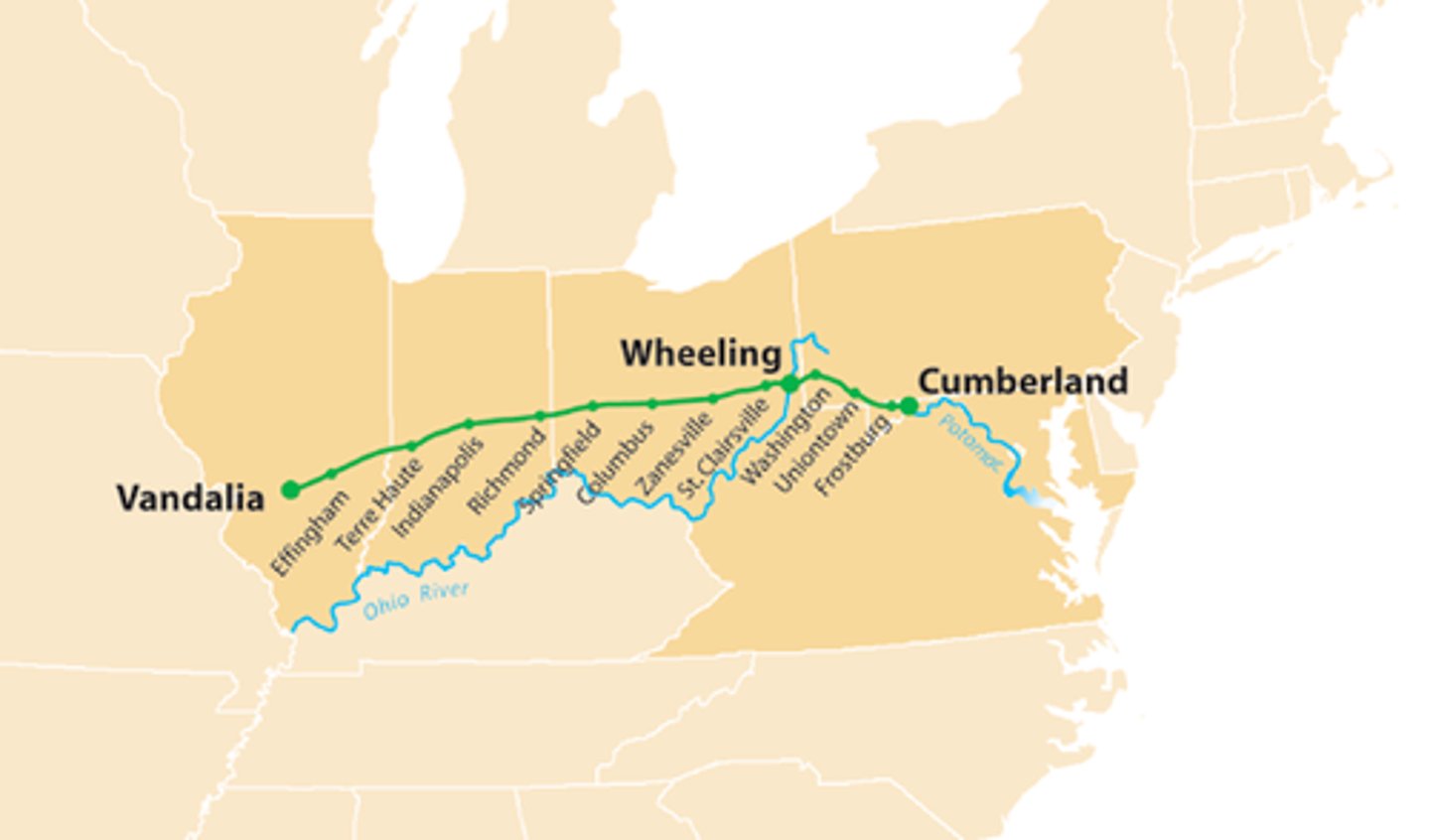
canals
an artificial waterway constructed to allow the passage of boats or ships inland or to convey water for irrigation; E.g. Erie Canal
Erie Canal
Built by the state of New York (without Federal assistance); Stretched from Buffalo to Albany.
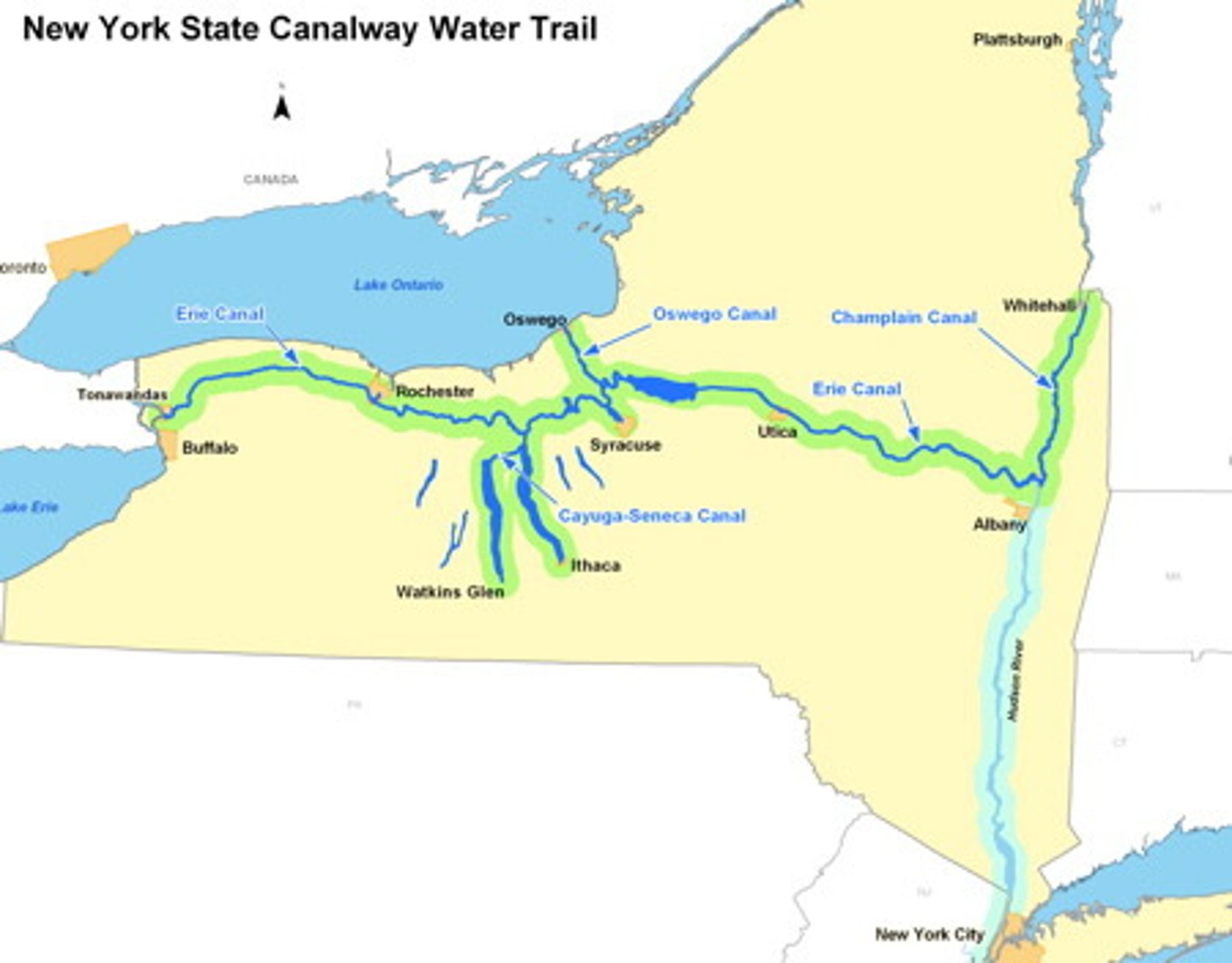
transportation revolution
1790s-1850s; Roads (turnpikes), steamships, canals, and railroads facilitated Western settlement and the market revolution.
Pony Express
A system of messengers on horseback established in 1860 to carry mail across the United States.
market revolution
Changes in the economic structure wherein people begin to buy, sell, and mass manufacture goods rather than barter or make them at home.
Deism
Liberal, rational religious philosophy of Washington, Jefferson, Franklin, and other founders.
Second Great Awakening
An upsurge in religious activity that began around 1800 and was characterized by emotional revival meetings; Led to several reform movements (abolitionism, temperance, women's rights) designed to implement the idea of human perfectibility and equality.

Evangelical Christianity
An active and emotional trans-denominational Christian movement that emphasizes the authority of the Bible, salvation through belief in Christ, and conversion ("born again" experience); Came to prominence after the First and Second Great Awakenings and continued to be influential in social and political affairs into the 20th century.

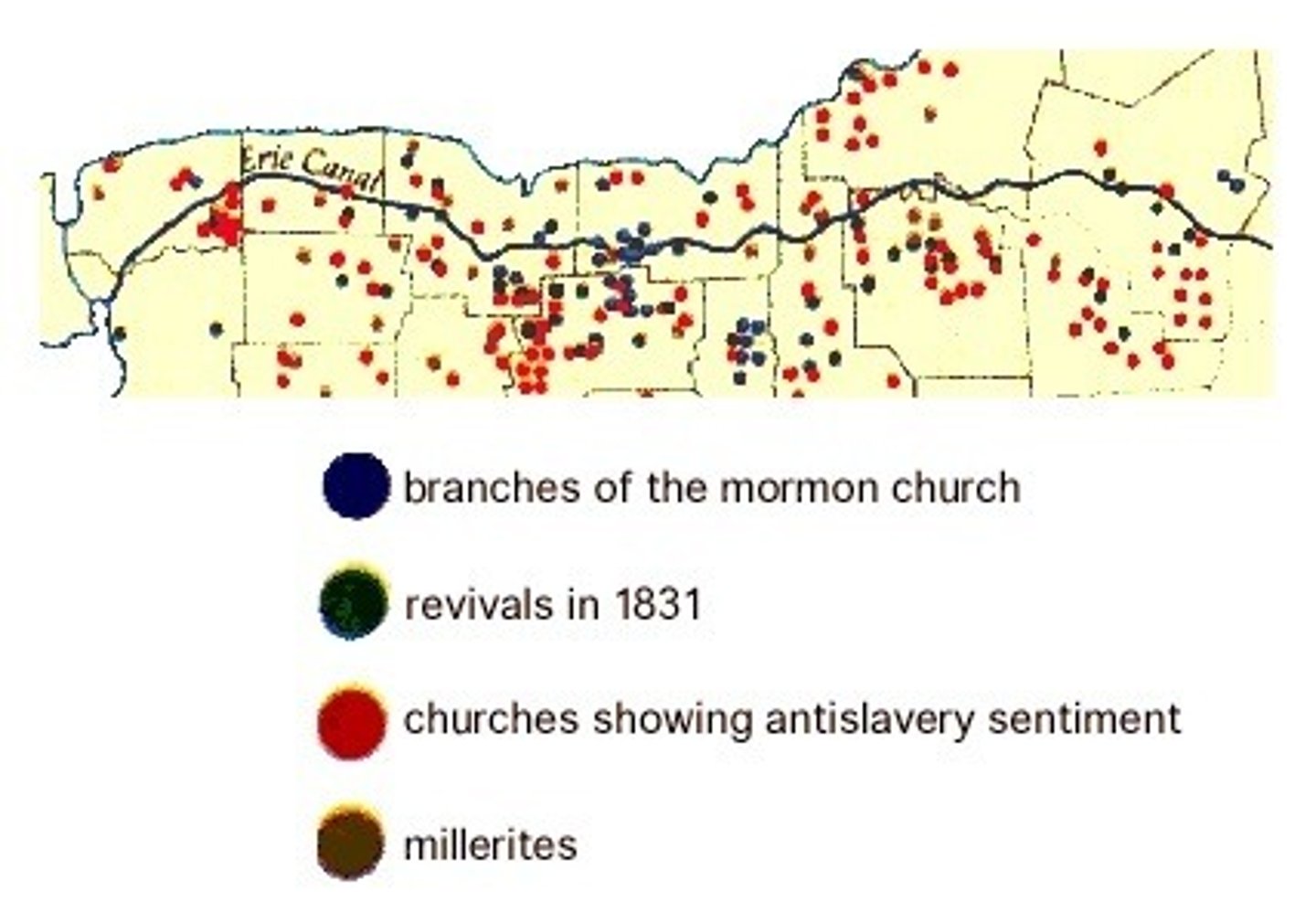
Burned-Over District
Area of New York State along the Erie Canal that was constantly aflame with revivalism and reform; As wave after wave to fervor broke over the region, groups such as the Mormons, Shakers, and Millerites found support among the residents.
Charles Grandison Finney
Revivalist minister who is known as the "Father of modern Revivalism"; advocated for temperance, the abolition of slavery, and equal education for women and African Americans.

Mormons
A.K.A. Latter-Day Saints; Church founded by Joseph Smith in 1830 (Second Great Awakening) with headquarters in Salt Lake City, Utah; Western pioneers.
education reform
Horace Mann was a major proponent
Reform Movements of the 1830s
Abolitionism, Women's Rights, Temperance, education reform, prison reform
social movement
A group of people who aim to improve their social situation by reforming government and changing people's thinking and actions
temperance
Restraint or moderation, especially in regards to alcohol or food
Seneca Falls Convention (1848)
The first convention in America for women right's held in NY; Issued "Declaration of Sentiments and Resolutions"
"Declaration of Sentiments and Resolutions" (1848)
Drafted at the Seneca Falls Convention; Outlines the case for the right to vote for women, as well as other rights denied to women at the time.
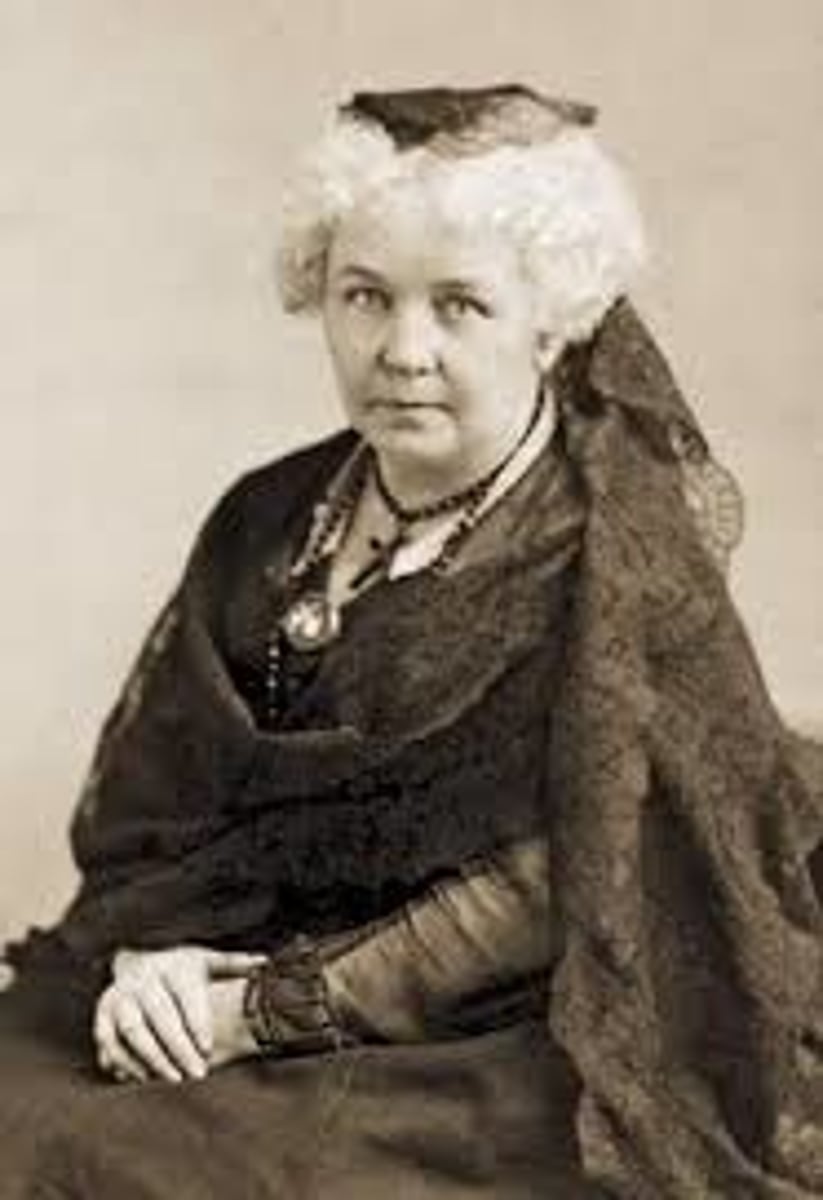
Elizabeth Cady Stanton
Advocate of women right's, including the right to vote; organized (with Lucretia Mott) the first women's rights convention at Seneca Falls, NY in 1848.

Utopian communities
Idealistic societies in the reform era; Based on the belief that a perfect society could be created on Earth; E.g. Book Farm in Massachusetts, Oneida Community in New York