ch 18 and half of 19
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
What pathogens are included in the DTaP vaccine? What type of vaccines are the components?
Diphtheria: Purified diphtheria toxoid, Pertussis: Acellular fragments of purified from Bordetella pertussis, Tetanus: purified tetanus toxoid.
What pathogens are included in the MMR vaccine? What type of vaccines are the components?
Measles, Mumps, Rubella (MMR) – Attenuated virus; Chickenpox, HPV: Ag fragments
What is meant by “attenuated”?
Pathogen is weakened so cannot cause disease but can still have immune response
What are the different vaccine types? What are the advantages/disadvantages of each?
DTap-protects, effective but requires multiple doses and boosters: no live bacteria
Toxoid-safe stable, long lasting, but only targets toxin not bacteria, requires booster: inactivated toxin
Meningitis, Haemophilus influenzae (Hib), Strep pneumonia vaccines-Effective for high risk but strain coverage
Viral vaccines- strong immune response, single dose but rare adverse events, preexisting immunity
Killed virus or antigen component-safe cannot cause disease, but weaker immunity needs boosters
mRNA vaccine- quick production strong response no live virus, but requires cold storage, short-term effects
What is gamma globulin? Where do we get it (example – where does immune plasma for COVID patients come from?
Gamma Globulin- antibodies from pooled serum (human or animal) can be from generalized (broad) or specialized preparations (Hep A)
You can get gamma globulin through plasma donations from other people
Immune plasma for COVID patients come from other individuals that have recovered from COVID-19. (donors)
What are the advantages of passive immunization?
Some advantages include protection for immunocompromised (weak immune), immediate protection, temporary protection while immunity develops
What are the disadvantages of passive immunization?
Some disadvantages is that there is serum sickness-reaction type 3 hypersensitivity formed by immune complexes(animal prep serums) and no lasting immunity.
Is there a natural way to get someone else’s Ab?
Yes, Placental transfer, breastfeeding, convalescent plasma transfusion (from recovered individual)
Describe the 4 types of immunity
Natural means it is from the body – active meaning self made, passive meaning from someone else
Artificial means made in the lab – active meaning stimulate to self make, passive means provided not by self
Active= Long-lived Passive= Short-lived
Naturally acquired ACTIVE immunity
(ex. Immunity after cold or flu)
Naturally Acquired PASSIVE immunity through placenta/breast milk
Artificially acquired ACTIVE immunity vaccine
Artificially acquired PASSIVE immunity –
(ex. Rabies immune globulin injection/hep B HBIG)
Naturally Acquired ACTIVE immunity
self made from the body; disease or normal exposure (Antigen own made /Long Lived memory cells)
(ex. Immunity after cold or flu)
Naturally Acquired PASSIVE immunity
from someone else’s body; through placenta/breast milk(Antibody NOT own/Short Lived no mem cells)
Artificially acquired ACTIVE immunity
stimulate to self make; vaccine (Antigen tells body to make it themselves/Long Lived memory cells)
Artificially acquired PASSIVE immunity
provided not by self ; gamma globulin injection (Antibody not own/ Short Lived no mem cells)
(ex. Rabies immune globulin injection/hep B HBIG)
Type I Hypersensitivity (Immediate): Anaphylactic Reaction
How does sensitization occur?
Immunization – sensitized to allergen, produces IgE antibody;
Cellular response – IgE binds to Fc receptor (mast cells and basophils);
Antigen binds to IgE
Cross-linking of IgE antibodies form
Degranulation-release of chemical mediators (histamine, prostaglandins, leukotrienes)
Type I Hypersensitivity (Immediate): Anaphylactic Reaction
What type of antibody is responsible for this hypersensitivity?
IgE binds to mast cells and basophils using Fc receptors
Type I Hypersensitivity (Immediate): Anaphylactic Reaction
What types of cells become sensitized?
Mast cells and Basophils
Type I Hypersensitivity (Immediate): Anaphylactic Reaction
What chemicals do they release? What effects do these chemicals have (what are the symptoms)?
Histamine, prostaglandins, and leukotrienes are released.
Symptoms include smooth muscle contraction (bronchia), vascular permeability, swelling/edema, respiratory distress, and death.
Type I Hypersensitivity (Immediate): Anaphylactic Reaction
What are eczema, hay fever, asthma, and anaphylaxis?
They are conditions that are associated with Type 1 hypersensitivity reactions.
Type II Hypersensitivity: Cytotoxic Reactions (Blue Baby)
Which types of antibodies are responsible?
Involves IgG or IgM antibodies
Type II Hypersensitivity: Cytotoxic Reactions (Blue Baby)
What second line of defense component is activated?
The complement system is activated (cell lysis or damage by macrophages)
Type II Hypersensitivity: Cytotoxic Reactions (Blue Baby)
ABO blood groups – for each type: what are the surface antigens, what antibodies are made, receive from?
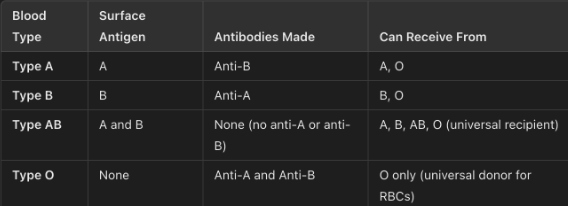
Hemolytic disease of the newborn: (blue baby)
What blood type do the mother and fetus have to be for this to occur?
Mother Rh- , Fetus Rh+.
Which pregnancies are affected and why?
Usually the subsequent pregnancies are affected because the preformed anti Rh antibodies cross placenta
Type II Hypersensitivity: Cytotoxic Reactions (Blue Baby)
What immunoglobulin is responsible for this disease?
IgG is responsible because it is the only class that can cross the placenta.
Type II Hypersensitivity: Cytotoxic Reactions (Blue Baby)
What fetal cell type is this Ig “cytotoxic” to?
Fetus’s red blood cells (erythrocytes)
Type II Hypersensitivity: Cytotoxic Reactions (Blue Baby)
What can be used to prevent this?
RhoGAM (Rh immunoglobulin) can be used to prevent it.