Unit 2 Test
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
73 Terms
Patient Bill of Rights
15 guarantees for all patients seeking medical care and basic rights/responsibilities for effective patient care
HIPAA
Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act of 1996
OSHA
Occupational Safety and Health Act
-requires employers to provide a safe, healthful workplace
-achieved through standards, training, outreach, education, and assistance
CSA
Controlled Substances Act
-federal law regulating manufacture and distribution of controlled substances
-includes narcotics, depressants, stimulants
-classifies drugs based on abuse potential and medical use
CLIA
Clinical Laboratory Improvement Act
-regulates all labs for safety and specimen handling
-ensures accuracy and timelines of testing
-FDA authorizes and enforce CLIA
Title VII of Civil Rights Act of 1964
-applies to employers with 15+ employees
-prohibits discrimination by race, national origin, gender, religion
-Pregnancy Discrimination Act (1978)- protects against pregnancy-related discrimination
ADA
Americans with Disabilities Act of 1990
-prohibits discrimination against qualified applicants/employees with disabilities
-requires reasonable accommodations unless they cause undue burden to employer
Implied Consent
based on patient’s actions or conduct, not words
Expressed Consent
given orally or in writing
Informed Consent
ensures patient/guardian knows, understand, and accepts treatment
Malpractice
any treatment by a medical professional that does not follow the standards of care
Tort
“wrong” or a harmful act committed by one individual to another
Negligence
when a patient does not receive adequate and appropriate care, which leads to suffering and harm
Advanced Directive
written instructions for care if a patient is too sick or injured to speak for themselves meant to guide the provider, family and healthcare team
Living Will
legal paper that says what treatments a patient wants or does not want and when
Durable Power of Attorney
legal paper that names a healthcare agent (proxy) to make medical choices if the patient can’t speak or decide; allows more specific instructions than a living will
DNR
Do Not Resuscitate
-legal paper that says a patient does not want CPR or advanced life support if their heart or breathing stops
Anatomy
the study of body parts and their locations
Physiology
the study of how body parts work and what they do
Sagittal Plane
divides the body into left and right sides
Transverse Plane
divides the body into upper and lower sections, not necessarily equal
Frontal Plane
Also called coronal plane, divides the body into anterior and posterior sections
Cranial Cavity
within the skull, houses the brain
Spinal Cavity
within the spine, spinal cord, nerves
Thoracic Cavity
within the chest; heart, lungs, esophagus, trachea, thymus gland, large blood vessels
Abdominal Cavity
within the abdomen; stomach, small and large intestines (most of large), liver, gallbladder, pancreas, spleen, kidneys, adrenal glands
Pelvic Cavity
below abdominal cavity; bladder, reproductive organs, rectum, lower large intestine, appendix
Integumentary System
-largest organ
-hair, nails, and glands = accessory organs
Skeletal System
-gives the body structure and posture
-protects soft internal organs
-provides attachment points for muscles
Muscular System
-responsible for movement, voluntary and involuntary
-heart muscle made of specialized fibers that allow it to function as a pump
-muscles and skeleton work together to provide body with structure and movement
Skeletal Muscle
responsible for body movement; also called voluntary muscle or striated muscle
Smooth Muscle
found within the walls of hollow organs and blood vessels, and in the iris of the eye; also called the involuntary muscle
Cardiac Muscle
found only in the heart; cross-fibered to allow the heart to contract from the top and bottom to pump blood
Immune and Lymphatic System
-helps stop infections
-When a germ (pathogen) is found, defenses are activated
Cardiovascular System
-pumps blood through the body
-blood delivers oxygen and nutrients to cells
-blood removes cell waste
Urinary System
-filters blood to remove waste
-waste + water = urine
-kidneys make urine
-bladder stores urine until elimination
Gastrointestinal System
-starts with the mouth (oral cavity)
-digestion keeps the body in balance (homeostasis)
-water and nutrients are needed for body, organs, tissue, and cell function
Respiratory System
-moves air in and out of lungs
-works with cardiovascular to bring oxygen throughout the body through blood and removes CO2
Nervous System
-controls all other body systems
-central nervous system (CNS) - brain and spinal cord
-peripheral nervous system (PNS) - nerves throughout the body
Endocrine System
-made of organs and glands that make, store, and release hormones
-hormones control growth, metabolism, mood, reproduction, and body functions
-main glands/organs: pituitary, thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal glands, pancreas, ovaries, testes, pineal gland, hypothalamus
Reproductive System
male and female systems work together for fertilization and producing offspring
Varicella (chickenpox)
direct/indirect contact with droplets or airborne secretions
Viral Meningitis
direct contact, respiratory secretions, oral-fecal route
Bacterial Meningitis
direct contact, respiratory drops
Conjunctivitis (pink eye)
direct/indirect contact with eye discharge or respiratory secretions
Rhinovirus (common cold)
direct/indirect contact with airborne or respiratory drops
Strep Throat
direct contact, respiratory drops
Pertussis (whooping cough)
direct contact, respiratory drops Influ
Influenza (flu)
direct contact, respiratory drops
Viruses
rhinorvirus, chicken pox, HIV/AIDs, hepatitis, covid
Bacteria
E. coli (urinary tract infections), cholera, whooping cough
Fungi
histoplasmosis (lung infection from bird/bat droppings), athlete’s foot, yeast infection
Parasites
toxoplasmosis, pinworm, tapeworm, scabies, lice, lyme disease
Infection Cycle
transmission of a pathogen
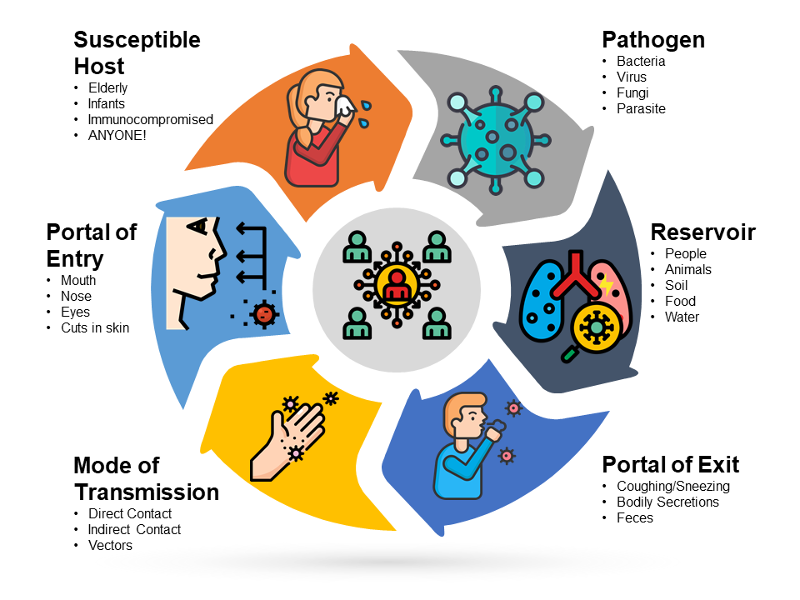
Infectious agents
bacteria, viruses, fungi, parasites, protozoa, metazoa, ectoparasites, Rickettsia
Reservoir/Source
-place where conditions are ripe for replication
-can be a person or an object
Portal of Exit
-how the pathogen departs the reservoir to another by way of body openings
-microorganisms leave the reservoir through the discharge of body secretions, excretions, respiratory drops, and body fluids
-make either direct or indirect contact with another host
Means of Transmission
-how the infectious agent travels through the portal of exit to a susceptible individual
-can occur through direct or indirect contact
Portals of Entry
-mouth, nose, throat, ears, and eyes
-intestinal, urinary, and reproductive tract
-open wounds and breaks in the skin
Susceptible Host
-a person who the pathogen can infect
-has low ability to fight disease
-causes may include poor health, nutrition, or hygiene
-higher risk: elderly, frail, immunosuppressed, chronic illness, or recent trauma
Incubation stage
interval time between exposure: time between exposure to flu virus and first symptoms (about 1-4 days)
Prodromal stage
initial stage: early signs like mild fatigue, sore throat, or low fever
Acute stage
peak stage: peak illness, high fever, body aches, cough, chills
Declining stage
Symptoms begin to subside: fever lowers, cough lessens, energy slowly returns
Convalescent stage
recover and recuperation: recovery phase, body repairs and regains full stage
Signs
what we can see
Symptoms
What the patient tells us
Universal Precautions
applying precautions if there is possible contact with: blood products, human tissue, body fluids, and fluid visibly contaminated with blood, and vaginal secretions/semen
Medical Asepsis
reduces microorganisms by: handwashing before/after patient care, wipe down workplaces between patients, use PPE for bodily fluids, clean supplies properly, separate clean and dirty areas in lab, cover coughs/sneezes and wash hands
Surgical Asepsis
eliminates microorganisms from entering the body
Sanitization
-clean equipment instruments to reduce microbes
-prepare items for disinfection or sterilization
-remove debris
-always wear gloves
-sanitization lowers the number of microorganisms to a safe level, but may not eliminate them all
Disinfection
-destroys or inactivates pathogens on surfaces and instruments
-does not kill all spores or certain viruses
-reduces infection spread by limiting microbial activity
-disinfection destroys most of the harmful microorganisms and pathogens on surfaces
SDS
-Safety Data Sheets required by OSHA to be accessible to all employees
-New chemicals must include SDS info
-Standard format for quick reference in emergencies
-Keep binder in central location/digital access